Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SMS Procces For Element 10
Uploaded by
Syed AmjadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SMS Procces For Element 10
Uploaded by
Syed AmjadCopyright:
Available Formats
The inspection and maintenance of all tools shall be carried out at least once in every working week
by a competent electrician.
All tools shall be stored in a clean, dry place, and a record of issue and receipt shall be maintained
by the storekeeper.
19. Monitoring and Auditing
Job Site Safety Inspection Program
Outline:
Why safety inspection?
Planning & scheduling
Scope
Safety Inspection Checklist
Corrective Action Reports
Records, tracking & follow-up
Communicating results
Conducting Safety Inspections.
Why Safety Inspection?
Why do we need safety inspections?
Can we trust people to inspect inspections?
What do we look for during safety inspections?
Do we just note the deficiencies during safety inspections?
Planning & Scheduling of Safety Inspection:
Develop annual plan for 'announced '& 'unannounced' safety inspections.
Include physical & behavioral safety items
Unannounced safety inspection routinely conducted.
"True safety behavior is what happens when no one is watching..."
Inspection Frequency:
Daily - inspections
Weekly - inspections
Monthly - inspections
Spot or Special Inspections
Safety Inspection Checklists:
Easiest most convenient method of recording a safety inspection - use a checklist
CRCC HSE PLAN-CO28 TUNNELING 98
Doc. No. 10-136000-4800000241-CRC-HSE-PLN-000002_05
10-136000-4800000241-CRC-HSE-PLN-000002_05
Checklist advantages — reduce inspection time, no need to remember which items to inspect.
Checklist includes all major safety items.
Corrective Action Reports:
Use a checklist 'No' items to develop corrective action report.
Assign corrective actions to persons and / or organization — with timelines.
Prioritize corrective action - 1) major risk, 2) moderate risk, 3) minor risk
Records, Training & Follow-up:
Effective safety inspection program means — "say what we do ... Do as we say ...And prove it.
'Say what we do '- Structured planned safety inspection program.
'Do as we say 'the physical safety inspection with a checklist.
'Prove it' — records & tracking to keep the whole system up to date.
Communication Results:
Hide deficiencies during a safety inspection means that no corrective action takes place — no one
learns from safety mistakes.
No areas can ever have 100% perfect safety - a checklist with all 'yes' items means that deficiencies
have been hidden.
Communicating safety inspection results — means we are doing something to improve safety
reporting nothing means we are doing nothing to improve safety.
Safety Audits:
CRCC - Company's inspection team will conducts periodical safety audits. Once a hazard situation is
identified it should immediately be reported to the concerned personnel. The hazard incident
report is the primary tools of communication for reporting and unsafe condition and unsafe act. All
CRCC.
Personnel will be encouraged to file these reports with the responsible site in-charge and safety
matters and maintained project safety statistics based on the reports. CRCC safety department will
be responsible to maintain a statistical data based on hazards and incidents categorized by type of
infraction, safety violations and other breakdowns. This database will be analyzed for unfavorable
trends to determine which area and work methods are problematic. Solutions then will be targeted
to eliminate the source.
CRCC HSE PLAN-CO28 TUNNELING 99
Doc. No. 10-136000-4800000241-CRC-HSE-PLN-000002_05
10-136000-4800000241-CRC-HSE-PLN-000002_05
20. CRCC-HSE-POLICY
CRCC HSE PLAN-CO28 TUNNELING 100
10-136000-4800000241-CRC-HSE-PLN-000002_05
Doc. No. 10-136000-4800000241-CRC-HSE-PLN-000002_05
You might also like
- Construction Risk in Operational Hospitals: Processes to Ensure Occupant Wellbeing and Minimise DisruptionsFrom EverandConstruction Risk in Operational Hospitals: Processes to Ensure Occupant Wellbeing and Minimise DisruptionsNo ratings yet
- Career Technical Education at Abu Dhabi PolytechnicDocument27 pagesCareer Technical Education at Abu Dhabi PolytechnicAhmed AlamriNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide to Occupational Health and SafetyFrom EverandPractical Guide to Occupational Health and SafetyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Case For Safety - Bowtie AnalysisDocument23 pagesCase For Safety - Bowtie Analysistrau-nuocNo ratings yet
- Security Controls Evaluation, Testing, and Assessment HandbookFrom EverandSecurity Controls Evaluation, Testing, and Assessment HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Occupational Health & Safety PlanDocument113 pagesOccupational Health & Safety PlanAli Akbar100% (1)
- The Effective Security Officer's Training ManualFrom EverandThe Effective Security Officer's Training ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Strategic Safety ObjectivesDocument11 pagesStrategic Safety ObjectivesDivyansh Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Chemical Process SafetyDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To Chemical Process Safetyhitesh bhoiNo ratings yet
- Incident Reporting and Investigation Procedure: Health, Safety and Environment Management SystemDocument5 pagesIncident Reporting and Investigation Procedure: Health, Safety and Environment Management SystemSajidNo ratings yet
- A0T8Y5_-_BRC_EH-S_Handbook_-_Part_5Document69 pagesA0T8Y5_-_BRC_EH-S_Handbook_-_Part_5teguh.setionoNo ratings yet
- Safety Inspection EssentialsDocument29 pagesSafety Inspection EssentialsJeffrey RebonquinNo ratings yet
- SMS Process For Element 8Document5 pagesSMS Process For Element 8Syed AmjadNo ratings yet
- Developing Process Safety Indicators HSE UK GuidlineDocument54 pagesDeveloping Process Safety Indicators HSE UK Guidlinevwagh100% (1)
- Safety Incident ProcedureDocument15 pagesSafety Incident Proceduresivaguruaks100% (1)
- Unit 3 - Major Accident Hazard Control.Document50 pagesUnit 3 - Major Accident Hazard Control.Madhan MNo ratings yet
- Is 104 - Plant and Equipment Safety Appraisal and Control Techniques ContinuationDocument52 pagesIs 104 - Plant and Equipment Safety Appraisal and Control Techniques ContinuationDhârâñî KûmârNo ratings yet
- HAZAN Analysis Full Project ReportDocument53 pagesHAZAN Analysis Full Project Reportthirunavukarasu0% (1)
- Health Safety Plan QCTCDocument54 pagesHealth Safety Plan QCTCFawad KaleemNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Plant & Eqpt. Safety Apprisal & Control Techq.Document147 pagesUnit 1 - Plant & Eqpt. Safety Apprisal & Control Techq.Madhan MNo ratings yet
- LCS English SAMDocument9 pagesLCS English SAMJavier RestrepoNo ratings yet
- P 4 (1 05) PSI Plant Safety Inspection (35) Jul.2012Document35 pagesP 4 (1 05) PSI Plant Safety Inspection (35) Jul.2012Vaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (9)
- gROUP7 - BOSH REPORTT FinalDocument6 pagesgROUP7 - BOSH REPORTT FinalCarlo EguieronNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bow-Tie Method - DubaiDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Bow-Tie Method - DubaiMarcianito Verde100% (1)
- LTVSC046Document15 pagesLTVSC046THARSHANA JERUSALEMNo ratings yet
- CO2: Explain The Measurement and Monitoring TechniquesDocument41 pagesCO2: Explain The Measurement and Monitoring TechniquesSreejith S NairNo ratings yet
- 2020 Draft HSE Plan Ucd CampDocument17 pages2020 Draft HSE Plan Ucd Campbilo198450% (2)
- PR IpercDocument14 pagesPR IpercAbel Bejar EncisoNo ratings yet
- Safety Audit OverviewDocument50 pagesSafety Audit OverviewdimasNo ratings yet
- Bab 13 Safety Audit PDFDocument50 pagesBab 13 Safety Audit PDFfrlolNo ratings yet
- Safety AuditDocument3 pagesSafety AuditAasif EqubalNo ratings yet
- Part 6 Performance MonitoringDocument24 pagesPart 6 Performance Monitoringalex.kollosovNo ratings yet
- 5 (Jeremy Stranks) Health and Safety Pocket BookDocument10 pages5 (Jeremy Stranks) Health and Safety Pocket BookTuralNo ratings yet
- HSE Environmental Hazard Control Procedure 1674601317Document6 pagesHSE Environmental Hazard Control Procedure 1674601317hoangmtbNo ratings yet
- Unit-III SafetyDocument38 pagesUnit-III SafetySudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Safety Case Technical Guidance for Major Hazard InstallationsDocument88 pagesSafety Case Technical Guidance for Major Hazard InstallationszawamaNo ratings yet
- Safety InspectionDocument21 pagesSafety InspectionErnielle Rae Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A study of solid waste managementDocument12 pagesA study of solid waste managementpravinsulakhe74No ratings yet
- OHS ProgramDocument25 pagesOHS ProgramFatimah TuzzahraNo ratings yet
- Safe System of Work PresentationDocument8 pagesSafe System of Work PresentationGilbert GillNo ratings yet
- Safe System of Work PresentationDocument8 pagesSafe System of Work PresentationGilbert GillNo ratings yet
- Metro Hse Plan 01Document49 pagesMetro Hse Plan 01Wasique Nesar100% (1)
- Benchmarking 3Document52 pagesBenchmarking 3ikhsan_ismu10No ratings yet
- Tony Ciliberti, PE: Reliability Dynamics LLCDocument49 pagesTony Ciliberti, PE: Reliability Dynamics LLCTony CilibertiNo ratings yet
- SP 05 Hazard Identification Risk Assessment and Control HIRAC PDFDocument8 pagesSP 05 Hazard Identification Risk Assessment and Control HIRAC PDFDJOERI WANDHAWANo ratings yet
- General risk assessment of TCN facilities in CalabarDocument13 pagesGeneral risk assessment of TCN facilities in CalabarMelwin PaulNo ratings yet
- Unit 16 - Monitoring, Review and Audit by Frank WarehamDocument13 pagesUnit 16 - Monitoring, Review and Audit by Frank WarehamUmar ZadaNo ratings yet
- Implementing Kpis To Improve Process Safety Performance: Background NotesDocument6 pagesImplementing Kpis To Improve Process Safety Performance: Background NotesravisankarNo ratings yet
- Safety-Manual Annexure10Document34 pagesSafety-Manual Annexure10somashekhar. ncclNo ratings yet
- PCM Part 2 Compilation PDFDocument53 pagesPCM Part 2 Compilation PDFmatt jaudianNo ratings yet
- ReactiveDocument2 pagesReactiveTayyab JavedNo ratings yet
- Procedure For HACCP PlanDocument25 pagesProcedure For HACCP PlanSyed Mujtaba Ali Bukhari67% (3)
- BOSH Module 4 Integrating Activity (Synerquest)Document53 pagesBOSH Module 4 Integrating Activity (Synerquest)William BautistaNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 - Risk Assessment ProcedureDocument16 pagesAppendix 1 - Risk Assessment Procedurekaderbouira0No ratings yet
- 3 - Safety - ModDocument180 pages3 - Safety - ModhoolooooooNo ratings yet
- API 580 Training Course NotesDocument43 pagesAPI 580 Training Course Notesjangdini100% (3)
- WDC 2013-14 Health & Safety ReportDocument18 pagesWDC 2013-14 Health & Safety ReportSarah WalkerNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice: Ref Cop Gra Issue 1, Dec 2003 Always Refer To Intranet For Latest Version 1Document15 pagesCode of Practice: Ref Cop Gra Issue 1, Dec 2003 Always Refer To Intranet For Latest Version 1etaNo ratings yet
- Plan Cover PageDocument2 pagesPlan Cover PageSyed AmjadNo ratings yet
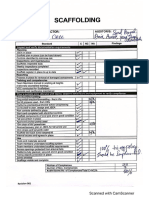
- CRCC Office-Safety-Inspection-ChecklistDocument2 pagesCRCC Office-Safety-Inspection-ChecklistSyed Amjad100% (1)
- Safety Management System Rev 02Document1 pageSafety Management System Rev 02Syed AmjadNo ratings yet
- 29 January 2023 To 30 April 2023 - CRCC - 90-Day Look-Ahead - Rev 25Document3 pages29 January 2023 To 30 April 2023 - CRCC - 90-Day Look-Ahead - Rev 25Syed AmjadNo ratings yet
- Safety Management System Rev 02Document1 pageSafety Management System Rev 02Syed AmjadNo ratings yet
- Plan Cover PageDocument2 pagesPlan Cover PageSyed AmjadNo ratings yet
- Environmental Social Management Plan - Rev 03Document1 pageEnvironmental Social Management Plan - Rev 03Syed AmjadNo ratings yet
- Scaffold Audit ChecklistDocument3 pagesScaffold Audit ChecklistSyed AmjadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 - Parameter and StatisticDocument16 pagesLesson 12 - Parameter and StatisticjenniferNo ratings yet
- Forms of ReasoningDocument28 pagesForms of ReasoningBeatrice AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ambuja Cement's Brand Positioning in BilaspurDocument43 pagesAmbuja Cement's Brand Positioning in BilaspurVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Effects of Group and Situation Factors On Pre-Adolescent Children's Attitudes To School BullyingDocument8 pagesEffects of Group and Situation Factors On Pre-Adolescent Children's Attitudes To School BullyingPAWAT ASAVAPOTIPHANNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Evolution LabDocument4 pagesEvidence of Evolution LabDiego Guardado0% (1)
- Lecture 1 Principles of Six Lecture 1: Principles of Six Sigma SGMDocument48 pagesLecture 1 Principles of Six Lecture 1: Principles of Six Sigma SGMprakulmittal2No ratings yet
- John Jay Magazine (Spring 2010)Document17 pagesJohn Jay Magazine (Spring 2010)jtaverasNo ratings yet
- 16033-Article Text-48226-1-10-20170411Document10 pages16033-Article Text-48226-1-10-20170411Sya'ramdanNo ratings yet
- Install Ocs Glpi CentosDocument9 pagesInstall Ocs Glpi Centoswish_newNo ratings yet
- Change of State: Gaining EnergyDocument5 pagesChange of State: Gaining EnergyRonald DalidaNo ratings yet
- From Structure To Chaos Understanding Marketing StrategyDocument20 pagesFrom Structure To Chaos Understanding Marketing Strategyঅদ্ভুতপাগলীNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Using Guava Leaves As An Alternative Medicine For DiarrheaDocument32 pagesAssessment of Using Guava Leaves As An Alternative Medicine For DiarrheaKamela AliNo ratings yet
- MATH Q1 Lesson 4 Reading and Writing Numbers Up To 100 000 ... MarvietblancoDocument12 pagesMATH Q1 Lesson 4 Reading and Writing Numbers Up To 100 000 ... MarvietblancoAnnaliza QuidangenNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Format For EVSDocument9 pagesLesson Plan Format For EVSsrishaaNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Oxygen-Reduction and Methanol-Oxidation Reactions at The Cathode of A DMFC: A Model-Based Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy StudyDocument7 pagesSimultaneous Oxygen-Reduction and Methanol-Oxidation Reactions at The Cathode of A DMFC: A Model-Based Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy StudyKaustubhNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Computer Science Mark SchemeDocument11 pagesIGCSE Computer Science Mark SchemeJakob HuntingtonNo ratings yet
- Kiss Emoji - Google SearchDocument1 pageKiss Emoji - Google SearchBillieNo ratings yet
- Cyclone FpgaDocument14 pagesCyclone Fpganishanthpv3No ratings yet
- BMCG 1523 Project GuidelinesDocument5 pagesBMCG 1523 Project GuidelinesAssrul YahyaNo ratings yet
- Ghoosing Gerns tlrrough Krishnamurthy padhdhatiDocument3 pagesGhoosing Gerns tlrrough Krishnamurthy padhdhatiBalasubramanian RamaswamiNo ratings yet
- The Story of The Aral Sea: Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesThe Story of The Aral Sea: Reading ComprehensionGreceanu AlinaNo ratings yet
- Preview PDFDocument65 pagesPreview PDFLee ChinghangNo ratings yet
- Dr. Teodora Tiglao Mother of Philippine Public HealthDocument4 pagesDr. Teodora Tiglao Mother of Philippine Public HealthJamie CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lind 18e Chap006Document32 pagesLind 18e Chap006MELLYANA JIENo ratings yet
- Anti FuseDocument2 pagesAnti FuseRahmatullah JatoiNo ratings yet
- 0460 w04 Ms 1 PDFDocument16 pages0460 w04 Ms 1 PDFpNo ratings yet
- Faye Schmidt Teacher Candidate ResumeDocument2 pagesFaye Schmidt Teacher Candidate Resumeapi-452540533No ratings yet
- Siebel Vs Sap-CrmDocument3 pagesSiebel Vs Sap-CrmABANISH10% (1)
- Nrc4596 - Mera - Domenica. Writing PracticeDocument3 pagesNrc4596 - Mera - Domenica. Writing PracticeDomenica MeraNo ratings yet
- Configure CUCME Telephony ServicesDocument6 pagesConfigure CUCME Telephony Servicesluismcano.u2No ratings yet