Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nucleic Acid Metabolism+
Uploaded by
ahmedmansy991Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nucleic Acid Metabolism+
Uploaded by
ahmedmansy991Copyright:
Available Formats
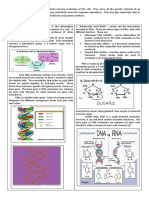
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM
Nucleic acid metabolism is a crucial cellular process that involves the synthesis and degradation of
nucleic acids, which are the building blocks of genetic material in living organisms. There are two main
types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA carries genetic
information, while RNA plays a key role in protein synthesis.
(1)DNA Replication:
• DNA replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its
DNA before cell division.
• It occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the
cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
• Enzymes like DNA polymerase are involved in synthesizing
a complementary strand of DNA.
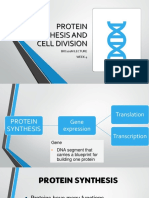
(2)Transcription:
• Transcription is the process by which DNA is used as a template to synthesize RNA.
• RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of RNA strands from
DNA templates.
• The newly synthesized RNA molecule, called
messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic
information from the DNA to the ribosomes for
protein synthesis.
(3)RNA Processing:
• In eukaryotic cells, newly synthesized RNA
molecules undergo processing steps before
becoming functional.
• This includes the addition of a 5' cap and a poly-A
tail, as well as the removal of introns (non-coding
regions) and splicing together of exons (coding
regions).
(4)Translation:
• Translation is the process by which the
information carried by mRNA is used to
synthesize a corresponding protein.
• It occurs on ribosomes, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the
ribosome based on the mRNA codons.
(5)DNA Repair:
• Cells have mechanisms to repair
damaged DNA to maintain genomic
integrity.
• DNA repair mechanisms include base
excision repair, nucleotide excision
repair, and mismatch repair.
(6)Nucleotide Metabolism:
Nucleotide metabolism involves the synthesis
and degradation of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). The
process is complex and includes several key steps:
1. De Novo Synthesis.
2. Salvage Pathway.
3. Conversion of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides.
4. Regulation of Nucleotide Pools.
5. DNA Replication and Repair.
6. RNA Synthesis.
(7)DNA & RNA Degradation :
• Nucleases are enzymes responsible for breaking down DNA and RNA.
• The breakdown products are recycled to be used in the synthesis of new nucleic acids or other
cellular processes.
➢ Causes of degradation:
1. Exonucleases and Endonucleases.
2. Environmental Factors.
3. Oxidative Damage.
4. Chemical Agents.
5. Biological Processes.
6. Microbial Activity.
7. Freeze-Thaw Cycles.
8. Inappropriate pH.
9. RNAse and DNAse Contamination.
You might also like
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument23 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyEros James Jamero100% (1)
- DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisDocument32 pagesDNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisA. Nurul Virninda YusufNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism (Final)Document11 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism (Final)Fatima KhanNo ratings yet
- DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisDocument69 pagesDNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisRomelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien Synthesis 2017Document32 pagesChapter 11 DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien Synthesis 2017dianeNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument56 pagesDna and Rna StructureZeah RealNo ratings yet
- 5 Nucleic AcidsDocument73 pages5 Nucleic AcidsmjmonforteNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 DNA RNA Protein SynthesisDocument24 pagesUnit 7 DNA RNA Protein SynthesisSyed Majid KhanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologyYasin Putra Esbeye100% (2)
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologypathinfoNo ratings yet
- The Nucleic AcidsDocument94 pagesThe Nucleic Acidsmeklit birhanuNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression: Replication, Transcription & Translation: Maya Dian Rakhmawatie FK Unimus - Blok 2 TA 2012/2013Document71 pagesGene Expression: Replication, Transcription & Translation: Maya Dian Rakhmawatie FK Unimus - Blok 2 TA 2012/2013Hera Vinandika PNo ratings yet
- RNA - Cell Physiology...Document13 pagesRNA - Cell Physiology...siddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- 3 5 1 Heredity and Inheritance (DNA RNA)Document17 pages3 5 1 Heredity and Inheritance (DNA RNA)6ix9ine SoulNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument41 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biologyanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid SynthesisDocument9 pagesNucleic Acid SynthesisrosalindaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Name: Miss Rabaya Akter ID: 1922247649Document8 pagesNucleic Acid: Name: Miss Rabaya Akter ID: 1922247649SymumNo ratings yet
- (164446829) Molecular GeneticDocument45 pages(164446829) Molecular GeneticAbdul Rahim Bin AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Bio ToulouseDocument15 pagesBio ToulouseMohamed AlaeddinNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and HeredityDocument42 pagesNucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and HeredityLyssaMarieKathryneEgeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cell Biology: Chapter 7: The Nucleus and DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesFundamentals of Cell Biology: Chapter 7: The Nucleus and DNA ReplicationPlinio GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesBiomolecules - Nucleic AcidsRyan S. CutamoraNo ratings yet
- Summary 4º ESO - Unit 3 - Genetic Information and Nucleic AcidsDocument89 pagesSummary 4º ESO - Unit 3 - Genetic Information and Nucleic AcidsPILARNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 21 Sylvia Mader ModifiedDocument29 pagesBiology Chapter 21 Sylvia Mader ModifiedabdallahNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument20 pagesCell PhysiologySerra ÇevikkanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologySowmya PNo ratings yet
- Sintesis Protein TA 2023-2024Document111 pagesSintesis Protein TA 2023-2024fdla rhmahNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Document69 pagesBasics of Molecular Biology: Tapeshwar Yadav (Lecturer)Nando NanginNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- Nucleic Acid: Structure & FunctionsDocument51 pagesNucleic Acid: Structure & FunctionsManahil SardarNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids - CauntaoDocument68 pagesNucleic Acids - CauntaoMarliza CauntaoNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of LifeDocument9 pagesDna Code of Lifendlovusenamile401No ratings yet
- CH1131 - Biomolecular Engineering - Week 2 - Transcription Translation - Aug 18 21 2015Document49 pagesCH1131 - Biomolecular Engineering - Week 2 - Transcription Translation - Aug 18 21 2015joshuaNo ratings yet
- Nulcleic AcidDocument32 pagesNulcleic AcidhrankhnNo ratings yet
- 2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pages2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic Acidsstu.suman-iftikharNo ratings yet
- III. Molecular Genetics B Landars GroupDocument37 pagesIII. Molecular Genetics B Landars GroupMa.charlina LozadaNo ratings yet
- The Blueprint of Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Blueprint of Protein SynthesislamesaltheamoniqueNo ratings yet
- BIO 111 Lecture 8-Nucleic AcidsDocument47 pagesBIO 111 Lecture 8-Nucleic AcidsChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Disease and The Genome: Genetic, Developmental, and Neoplastic DiseaseDocument24 pagesDisease and The Genome: Genetic, Developmental, and Neoplastic DiseaseMegan CatilinaNo ratings yet
- Biological Functions and Properties of Nucleosides, NucleotidesDocument30 pagesBiological Functions and Properties of Nucleosides, NucleotidesOlerhime BlessingNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument20 pagesProtein Synthesisabrielle dytucoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologySubash SubaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocument69 pagesBasics of Molecular BiologySubash SubaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Nucleic AcidDocument80 pagesChapter 5 Nucleic AcidSaya KacakNo ratings yet
- H.-Nucleic AcidsDocument69 pagesH.-Nucleic AcidsBrianna Pauline BantugNo ratings yet
- DNA Manipulative EnzymesDocument17 pagesDNA Manipulative EnzymesZain Ul AbedienNo ratings yet
- Week 4 NotesDocument13 pagesWeek 4 NotesGHEIST INC.No ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Lecture DNA and RNADocument2 pagesScience-10 Q3 Lecture DNA and RNAbruh669No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument35 pagesProtein SynthesisDaryl GumacalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Genetic ControlDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Genetic ControlCor GuerreroNo ratings yet
- C1 W15 NucleicAcidsDocument68 pagesC1 W15 NucleicAcidsJasmine Kaye CuizonNo ratings yet
- 05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeDocument48 pages05-02-Genetika MikroorganismeKinad DanikNo ratings yet
- The Central DogmaDocument7 pagesThe Central DogmaTobias Domenite P.No ratings yet
- Dogma Central Biology Pertemuan 4Document18 pagesDogma Central Biology Pertemuan 4Rizky BluesNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and The Code of LifeDocument2 pagesNucleic Acids and The Code of LifeAg GabrielNo ratings yet
- Ch. 12 & 13 DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument34 pagesCh. 12 & 13 DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisSemeraNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Perform Different FunctionsDocument16 pagesDNA and RNA Perform Different FunctionsTamanda SekarNo ratings yet
- Cyto Unit 3Document3 pagesCyto Unit 3Vince CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism+Document2 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism+ahmedmansy991No ratings yet
- Amoeba PDFDocument2 pagesAmoeba PDFahmedmansy991No ratings yet
- Amoeba PDFDocument2 pagesAmoeba PDFahmedmansy991No ratings yet
- Amoeba PDFDocument2 pagesAmoeba PDFahmedmansy991No ratings yet
- Amoeba PDFDocument2 pagesAmoeba PDFahmedmansy991No ratings yet
- Ap & TS - SR Elite Neet Grand Test - 2 Paper - 14-03-2022Document28 pagesAp & TS - SR Elite Neet Grand Test - 2 Paper - 14-03-2022srsoumyaranjantareiNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingKent100% (2)
- Grade 12 Biology Module3Document87 pagesGrade 12 Biology Module3Genevieve MerroNo ratings yet
- POGIL - Gene - Expression Translation SDocument8 pagesPOGIL - Gene - Expression Translation Sandrew fortneyNo ratings yet
- The Rafiki MapDocument72 pagesThe Rafiki MapAnonymous Y2qwEuANo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Teacher Answer Key: Code CrackingDocument10 pagesProtein Synthesis: Teacher Answer Key: Code CrackingMariana SuescúnNo ratings yet
- DNA QuizDocument2 pagesDNA QuizDee YipNo ratings yet
- Med Sciences III Exam Ans Key-DönüştürüldüDocument8 pagesMed Sciences III Exam Ans Key-DönüştürüldüZeynep Etka ÇelikkıranNo ratings yet
- Transcripción Alberts 2014 PDFDocument240 pagesTranscripción Alberts 2014 PDFLaliito LeNo ratings yet
- Translation WORKSHEETDocument2 pagesTranslation WORKSHEETPol Marasigan BanzonNo ratings yet
- Biology: Paper 9700/11 Multiple ChoiceDocument59 pagesBiology: Paper 9700/11 Multiple ChoiceAngel XxNo ratings yet
- Dhanasekaran, Dharumadurai PanneErselvam, A. Thajuddin, Nooruddin Antimicrobials Synthetic and Natural CompoundsDocument532 pagesDhanasekaran, Dharumadurai PanneErselvam, A. Thajuddin, Nooruddin Antimicrobials Synthetic and Natural CompoundsKima MadNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 STARS REVIEWERDocument12 pagesGrade 10 STARS REVIEWERjulianna startNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Genetics 2020Document67 pagesBacterial Genetics 2020Ntobi ThomasNo ratings yet
- Transcription & Translation Notes PDFDocument20 pagesTranscription & Translation Notes PDFManas RjNo ratings yet
- Biology Final ExamDocument7 pagesBiology Final ExamJillian FajardoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following:: 9. What Are The Stop Codons? (Use Your mRNA Chart) UAA UAG UGADocument7 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Following:: 9. What Are The Stop Codons? (Use Your mRNA Chart) UAA UAG UGAJamesBuensalidoDellava100% (1)
- Transcription Translation ProtocolDocument13 pagesTranscription Translation ProtocolMrNewbsNo ratings yet
- Transfer RNA and Protein Building Paper LabDocument7 pagesTransfer RNA and Protein Building Paper LabYESMI GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Dams CBT 2015 Test 1Document173 pagesDams CBT 2015 Test 1Mitvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Biorevise Notes MAINDocument34 pagesBiorevise Notes MAINRS JNo ratings yet
- H1 Revision Notes DNA and GenomicsDocument6 pagesH1 Revision Notes DNA and GenomicsJiaLi XieNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Genetics PDFDocument19 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Genetics PDFAsh MiNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-4 Week-5Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-4 Week-5Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Modern BiotechnologyDocument272 pagesModern BiotechnologyRen Jamal Bo100% (4)
- Science Grade 10 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience Grade 10 3rd Quarter ReviewerDiego ConopioNo ratings yet
- MCAT BiologyDocument167 pagesMCAT BiologyChris WongNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Biol 1700 Winter 2021 FinalDocument13 pagesAssignment 1 Biol 1700 Winter 2021 Finalapi-546520104No ratings yet
- Physics of Transport and Traffic Phenomena in Biology-From Molecular Motors and Cells To OrganismsDocument35 pagesPhysics of Transport and Traffic Phenomena in Biology-From Molecular Motors and Cells To OrganismsMike WazowskiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acid ProjectPramod Etarvi100% (7)