Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp-6 Speed Control of Induction Motor Drive Using Closed Loop Vbyf Control in MATLAB Simulink.
Uploaded by
Faijal MalekOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp-6 Speed Control of Induction Motor Drive Using Closed Loop Vbyf Control in MATLAB Simulink.
Uploaded by
Faijal MalekCopyright:
Available Formats
G H Patel College of Engineering & Technology
(A Constituent College of CVM University)
Department of Electrical Engineering
EXPERIMENT No.6 DATE: / /
AIM: Speed Control of Induction Motor Drive using Closed Loop V/f (Scalar Control)
Scheme in MATLAB Simulink.
THEORY:
Synchronous speed can be controlled by varying the supply frequency. Voltage induced in
the stator is 1 ∝ Ф where Ф is the air-gap flux and f is the supply frequency. As we can
neglect the stator voltage drop, we obtain terminal voltage 1 ∝ Ф . Thus, reducing the
frequency without changing the supply voltage will lead to an increase in the air-gap flux
which is undesirable.
Hence whenever frequency is varied in order to control the speed, the terminal voltage is
also varied so as to maintain the V/f ratio constant. Thus, by maintaining a constant V/f
ratio, the maximum torque of the motor becomes constant for changing speed.
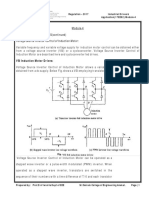
Fig.1: Torque-Speed characteristics for V/f Controlled Induction Motor.
As can be seen from Fig.1, when V/f Control is implemented, for various frequencies inside
the operating region, the maximum torque remains the same as the speed varies. Thus,
maintaining the V/f ratio constant helps us to maintain a constant maximum torque while
controlling the speed as per our requirement.
[ Laboratory Manual ] |102050701_Electrical and Hybrid Vehicles 1
G H Patel College of Engineering & Technology
(A Constituent College of CVM University)
Department of Electrical Engineering
Closed-Loop V/f Control of Induction Motor:
It employs an inner slip speed loop and an outer speed loop as shown in Fig.2.
The slip speed loop acts as inner current control loop. It also ensures the motor to
operate between synchronous speed and the speed at which maximum torque occurs
for all frequencies.
Thus, a high torque will be produced for a small current drawn from supply.
The drive uses a PWM inverter fed from a dc source. Regenerative braking and four
quadrant operation of drive is possible because of the use of PWM inverter.
The speed error is processed through a speed controller, usually a PI controller, and a
slip regulator.
P controller reduces the steady state error and I controller reduces the peak overshoot
and settling time so that the response will be faster.
PI controller gives good steady state accuracy and reduces the noise.
Slip regulator set the slip speed command ωsl*. This command controls the inverter
current to its maximum allowable value.
The synchronous speed obtained by adding actual speed ωm and slip speed ωsl*
determines the frequency of inverter output voltage.
Reference signal V* for controlling the output voltage of inverter is generated using a
flux control block.
This reference signal ensures a constant flux operation below base speed and constant
voltage operation above base speed.
Fig.2: V/f based closed loop speed control an induction motor fed from VSI.
[ Laboratory Manual ] |102050701_Electrical and Hybrid Vehicles 2
G H Patel College of Engineering & Technology
(A Constituent College of CVM University)
Department of Electrical Engineering
If the motor speed is to be increased, then the reference speed ωm* will be set to the
required speed.
Now the comparator compares the actual speed and reference speed and produces a
positive error.
This will set the slip speed command ωsl* at its maximum value.
Hence the motor starts accelerating (i.e., speed increases) at the maximum inverter
current and hence the speed error decreases.
When the actual motor speed reaches the reference value, the drive finally settles at
that speed. At this speed, the motor torque equals the load torque.
If the motor speed is to be decreased, then the reference speed ωm* will be set to the
required speed.
Now the comparator compares the actual speed and reference speed and produces a
negative error.
This will set the slip speed command ωsl* at its maximum negative value.
Hence the motor starts decelerating (i.e., speed decreases) at the maximum inverter
current and hence the speed error decreases. Here regenerative braking is applied.
When the actual motor speed reaches the reference value, the drive finally settles at
that speed. At this speed, the motor torque equals the load torque.
For operation below base speed, the ratio (V/f) is kept constant.
For operation above base speed, the terminal voltage is kept constant, and frequency
is increased.
For low frequency operation, the ratio (V/f) is increased to maintain constant flux
operation.
When a fast response is required, the drive can be made to accelerate at a current
more than the rated current of induction motor.
But the power electronic switches present in the inverter must be selected such that
they can withstand for those high currents. Any device with increased current rating
will be more costly. This will increase the cost of total drive system.
When fast response is not required, current ratings of inverter and rectifier can be
chosen to be marginally higher than that of the motor.
[ Laboratory Manual ] |102050701_Electrical and Hybrid Vehicles 3
G H Patel College of Engineering & Technology
(A Constituent College of CVM University)
Department of Electrical Engineering
MATLAB Simulation:
Power Circuit
[ Laboratory Manual ] |102050701_Electrical and Hybrid Vehicles 4
G H Patel College of Engineering & Technology
(A Constituent College of CVM University)
Department of Electrical Engineering
Control Circuit
Function
PI Controller
Saturation
Result: (Speed_reference Vs time / Speed_actual Vs time)
[ Laboratory Manual ] |102050701_Electrical and Hybrid Vehicles 5
G H Patel College of Engineering & Technology
(A Constituent College of CVM University)
Department of Electrical Engineering
Conclusion:
Post Experiment Exercise:
1. What are the main components of a closed-loop V/F speed control system for an
induction motor?
2. What are the advantages of using V/F control for induction motor speed regulation
compared to other methods?
3. How does the closed-loop V/F control system maintain the desired speed of the
induction motor under varying load conditions?
4. What are the limitations or challenges associated with closed-loop V/F speed control of
induction motors?
5. Provide the examples of real-world applications where closed-loop V/F speed control of
induction motors is commonly used.
Grade/Marks
Obtained
Date of Assessment
Sign of Instructor
[ Laboratory Manual ] |102050701_Electrical and Hybrid Vehicles 6
You might also like
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Exp-5 - To Understand The Concept of Regerative Braking Using MATLAB SimulinkDocument8 pagesExp-5 - To Understand The Concept of Regerative Braking Using MATLAB SimulinkFaijal MalekNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Chapter 1 PDFDocument11 pagesAhmed Chapter 1 PDFيوسف سامي عبد هاديNo ratings yet
- Ijetae 1013 117Document9 pagesIjetae 1013 117rasim_m1146No ratings yet
- Speed Control of Induction Motor Using V PDFDocument5 pagesSpeed Control of Induction Motor Using V PDFNadia Julian PutriNo ratings yet
- Separately Excited DC Motor Speed Control Using Four Quadrant ChopperDocument3 pagesSeparately Excited DC Motor Speed Control Using Four Quadrant ChopperJay S PatelNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor.Document6 pagesInduction Motor.Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction Motor Using Volt/hertz Control For Automotive ApplicationDocument6 pagesSpeed Control of 3-Phase Induction Motor Using Volt/hertz Control For Automotive ApplicationPrabhat KarnNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument59 pagesFinal ReportAzeez SharieffNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Closed Loop Control of Buck Converter Fed DC Motor DriveDocument4 pagesSimulation of Closed Loop Control of Buck Converter Fed DC Motor DriveIJSTENo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction MotorDocument27 pagesClosed Loop Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction MotorRajesh kumar yadavNo ratings yet
- Active Energy Control - Optimum Solution For Maximum Savings: Industry Application IA04008001EDocument4 pagesActive Energy Control - Optimum Solution For Maximum Savings: Industry Application IA04008001ESaju V KumarNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction Motor Using Volt/hertz Control For Automotive ApplicationDocument6 pagesSpeed Control of 3-Phase Induction Motor Using Volt/hertz Control For Automotive ApplicationAlemneh TechiloNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor Using Arduino and V/F TechniqueDocument10 pagesSpeed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor Using Arduino and V/F TechniqueAnonymous oyUAtpKNo ratings yet
- Position-Sensorless Method For Electric Braking Commutation of Brushless DC MachinesDocument13 pagesPosition-Sensorless Method For Electric Braking Commutation of Brushless DC MachinesMalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- Sensorless Control of Induction Motors Using Multi-Level ConvertersDocument11 pagesSensorless Control of Induction Motors Using Multi-Level ConvertersmssmsNo ratings yet
- PID Controller For A Two Quadrant Chopper Fed DC Motor DriveDocument5 pagesPID Controller For A Two Quadrant Chopper Fed DC Motor DriveSalman HabibNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Three Phase Full Bridge Converter Controlled DC MotorDocument45 pagesPerformance Analysis of Three Phase Full Bridge Converter Controlled DC Motoranon_451051243No ratings yet
- Matrix AdvantagesDocument14 pagesMatrix AdvantagesAdeline WinsterNo ratings yet
- VFD Speed ControlDocument7 pagesVFD Speed ControlLICHEN YUNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1 Speed Control of DC Motor Using Matlab SimulinkDocument4 pagesExperiment-1 Speed Control of DC Motor Using Matlab Simulinksameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- PATRADocument46 pagesPATRAAnimesh PatraNo ratings yet
- 17ee82 - Ida - Mod 4 NotesDocument18 pages17ee82 - Ida - Mod 4 NotesManish Kumar SahaniNo ratings yet
- Khodapanah2018 Article EstimatingPowerFactorOfInductiDocument10 pagesKhodapanah2018 Article EstimatingPowerFactorOfInductiodracirggNo ratings yet
- Project Synopsys1Document6 pagesProject Synopsys1jvnsr005No ratings yet
- Modeling, Simulation and Implementation of A Five-Phase Induction Motor Drive SystemDocument6 pagesModeling, Simulation and Implementation of A Five-Phase Induction Motor Drive SystemBook4AllNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Induction Motor Using PI and V/F Scalar Vector ControllersDocument8 pagesSpeed Control of Induction Motor Using PI and V/F Scalar Vector ControllersViorel CatalinNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Induction Motor Drives: SyllabusDocument8 pagesModule 3: Induction Motor Drives: SyllabusManoj SkNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument10 pagesResearch PaperAlok AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PI Controller Based Torque and Speed Control of Five Phase Switched Reluctance MotorDocument6 pagesPI Controller Based Torque and Speed Control of Five Phase Switched Reluctance MotorPasupuleti SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of D C MOTOR Using Chopper-1308Document7 pagesSpeed Control of D C MOTOR Using Chopper-1308Moon3pellNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Improvement With IMdrive With PI ControllerDocument4 pagesEfficiency Improvement With IMdrive With PI ControllerHarsh AnandNo ratings yet
- A MATLAB/Simulink Model of A Self Excited Induction Generator For An Electrical Brake ApplicationDocument5 pagesA MATLAB/Simulink Model of A Self Excited Induction Generator For An Electrical Brake ApplicationbeeshamNo ratings yet
- Unit 7electric TractionDocument35 pagesUnit 7electric TractionVinod KohliNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Control of Three-Phase Induction Motor DriveDocument6 pagesEnergy Efficient Control of Three-Phase Induction Motor DrivenaserhashemniaNo ratings yet
- Four Quadrant Operation of IM Using H - BridgeDocument5 pagesFour Quadrant Operation of IM Using H - Bridgesomnath bhongNo ratings yet
- Mahdipour 2015Document14 pagesMahdipour 2015Yustinus PadmundanaNo ratings yet
- Performance Characteristics of InductionDocument48 pagesPerformance Characteristics of InductionToolit MartineNo ratings yet
- The Installation of AC Drives Can Yield Some Predictable Benefits and Some Not-So-Predictable Side EffectsDocument3 pagesThe Installation of AC Drives Can Yield Some Predictable Benefits and Some Not-So-Predictable Side EffectsJonathan SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science and Technology, An International JournalDocument9 pagesEngineering Science and Technology, An International JournalAnita IonelaNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Eee 20110102 14Document8 pages10 5923 J Eee 20110102 14clide_050793No ratings yet
- 4.5 Energy Performance Assessment of Motors / Variable Speed DrivesDocument24 pages4.5 Energy Performance Assessment of Motors / Variable Speed DrivesranveerNo ratings yet
- 5.5 Retardation Test or Running Down On D.C Machines: Electric Machinery Fundamentals Stephen J. ChapmanDocument8 pages5.5 Retardation Test or Running Down On D.C Machines: Electric Machinery Fundamentals Stephen J. Chapmanjakkoju saitejaNo ratings yet
- Closed-Loop Control of Hybrid Stepper Motor DrivesDocument7 pagesClosed-Loop Control of Hybrid Stepper Motor DrivesChanthu C NairNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Ac Motor Monitoring and Parameter Calculation Using Labview and DaqDocument13 pages3-Phase Ac Motor Monitoring and Parameter Calculation Using Labview and DaqInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Analysis and Simulation of The High-Speed Torque Performance of BrushleDocument10 pagesAnalysis and Simulation of The High-Speed Torque Performance of BrushlePhạm Văn TưởngNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed Control Methods Using MATLAB - Simulink and Their Integration Into Undergraduate Electric Machinery CoursesDocument9 pagesDC Motor Speed Control Methods Using MATLAB - Simulink and Their Integration Into Undergraduate Electric Machinery CoursesWen ZJNo ratings yet
- Active Energy Control Application NoteDocument4 pagesActive Energy Control Application NotemoxlindeNo ratings yet
- Edc Notes Unit 5Document7 pagesEdc Notes Unit 5sushant.sahayee20No ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument84 pagesLab ReportusmanzahidNo ratings yet
- Paper Snptee Digital Twin BertaDocument13 pagesPaper Snptee Digital Twin BertaMarc LangevinNo ratings yet
- RmixedDocument7 pagesRmixedKay KarthiNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Induction Motor Using PI and V/F Scalar Vector ControllersDocument9 pagesSpeed Control of Induction Motor Using PI and V/F Scalar Vector ControllersYesha ShahNo ratings yet
- Regen BrakingDocument32 pagesRegen BrakingMegha SharmaNo ratings yet
- E5G6Document8 pagesE5G6NJ De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Rohini 58172657367Document16 pagesRohini 58172657367Arnab ManasNo ratings yet
- Bharti 2019Document5 pagesBharti 2019Damindu TheekshanaNo ratings yet
- Project Work: Induction Motor in MatlabDocument25 pagesProject Work: Induction Motor in MatlabakshayNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi Applications 13 Hours: Power Electronics - 15EE51T 78Document17 pagesUnit Vi Applications 13 Hours: Power Electronics - 15EE51T 78Shanmukha AkNo ratings yet
- Solar Data Logger ManualDocument4 pagesSolar Data Logger ManualMihirNo ratings yet
- Electronics Industrial TrainingDocument15 pagesElectronics Industrial TrainingShubham MakoneNo ratings yet
- S8VK C06024Document16 pagesS8VK C06024Mạnh VũNo ratings yet
- Abb Acs2000Document204 pagesAbb Acs2000gadgil_vikrant57% (7)
- Solar Energy 207 (2020) 683-692Document10 pagesSolar Energy 207 (2020) 683-692musNo ratings yet
- General EMC GuidelinesDocument8 pagesGeneral EMC GuidelinesnsmikleNo ratings yet
- Varispeed g7Document499 pagesVarispeed g7Victor YosafatNo ratings yet
- DC Inverter Mini ChillerDocument96 pagesDC Inverter Mini Chilleravramus100% (1)
- MCT10 OperatingInstructions MG10R902Document139 pagesMCT10 OperatingInstructions MG10R902Aleksandar StankovićNo ratings yet
- Solar Powered Field Server and Aerator Development For Lake PalakpakinDocument9 pagesSolar Powered Field Server and Aerator Development For Lake Palakpakindragh meh downNo ratings yet
- RefrigeratorDocument101 pagesRefrigeratorRossNo ratings yet
- Electronics For You TruePDF-December 2015 PDFDocument148 pagesElectronics For You TruePDF-December 2015 PDFGeorge Petrakos100% (5)
- 12EE2603 - Power Electronics: Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument72 pages12EE2603 - Power Electronics: Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringMurughesh MurughesanNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument260 pagesManualRogelio ValdezNo ratings yet
- Liebert GXT MT+ RT 1-3kVA Series: User ManualDocument24 pagesLiebert GXT MT+ RT 1-3kVA Series: User ManualJulio Csar da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Solis S5 Mini Series Inverter DatasheetDocument2 pagesSolis S5 Mini Series Inverter Datasheetarehman9999No ratings yet
- Accu Speed: Accuracy With Speed For Semi-Rigid To Rigid SubstratesDocument4 pagesAccu Speed: Accuracy With Speed For Semi-Rigid To Rigid SubstratesVeerapandian ChellakkannuNo ratings yet
- Eset 211 Lab 08 InverterDocument3 pagesEset 211 Lab 08 InverterPhan HiếuNo ratings yet
- AB HPGR BrochureDocument28 pagesAB HPGR BrochurepaoloNo ratings yet
- SP 48v SeriesDocument1 pageSP 48v SeriesEdin EdinNo ratings yet
- EcoEnergy Catalogue 081110Document68 pagesEcoEnergy Catalogue 081110Hummingbird HgcNo ratings yet
- 40-80 kVA 3-Phase UL924 Guide SpecificationDocument16 pages40-80 kVA 3-Phase UL924 Guide SpecificationDiegoJoseMorenoMoralesNo ratings yet
- SPWM Vs SVMDocument11 pagesSPWM Vs SVMpmbalajibtechNo ratings yet
- Bonfiglioli Frekvensomriktare AGL Quick Start Guide VEC651 - r0Document20 pagesBonfiglioli Frekvensomriktare AGL Quick Start Guide VEC651 - r0Mamadou djibril BaNo ratings yet
- Grid-Forming Inverters For Grid-Connected MicrogridsDocument13 pagesGrid-Forming Inverters For Grid-Connected Microgridsveljal6317No ratings yet
- Pvsyst 5Document219 pagesPvsyst 5nexarsolarNo ratings yet
- The Voltech Handbook of Power SuppliesDocument86 pagesThe Voltech Handbook of Power SuppliesDaniel PopaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - DC SystemDocument50 pagesTutorial - DC SystemCarlos PuertoNo ratings yet
- Ups Train3Document157 pagesUps Train3Younes SaifiNo ratings yet