Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unity University Applied
Uploaded by
Sani MohammedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unity University Applied
Uploaded by
Sani MohammedCopyright:
Available Formats
APPLIED MATHS GROUP ASSIGNMENT NOVEMBER 16, 2022
Unity University
College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science
Applied Mathematics I (Math 1012)
Group Assignment (20%)
October, 2022
Instruction: Attempt all questions clearly and neatly
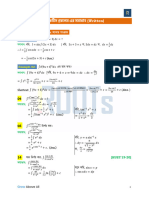
1. Find the limit, if it is exist. If the limit does not exist, explain why?
1
a. 𝑙𝑖𝑚+ √𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 ( 𝑥)
𝑥→0 √
Solution
Using squeeze theorem
1
- We know that -1 ≤ sin( 𝑥) ≤ 1. Next, we can multiply this inequality by √𝑥 without
√
1
changing its correctness. Now we have -√𝑥 ≤ √𝑥 sin( ) ≤ √𝑥
√𝑥
- Take the limit of each part of the inequality.
1
𝑙𝑖𝑚 (-√𝑥) ≤ 𝑙𝑖𝑚 √𝑥 sin( 𝑥) ≤ 𝑙𝑖𝑚 (√𝑥 )
𝑥→0 𝑥→0 √ 𝑥→0
- Next, we know that 𝑙𝑖𝑚 (-√𝑥) = 0 and 𝑙𝑖𝑚 (√𝑥 ) = 0. Thus, we have
𝑥→0 𝑥→0
1
0 ≤ 𝑙𝑖𝑚 √𝑥 sin( 𝑥) ≤ 0
𝑥→0 √
1
- So, we can conclude that 𝑙𝑖𝑚 √𝑥 sin( 𝑥) = 0
𝑥→0 √
- Graphically, the function squeezed
between y = −√𝑥 and y = √𝑥 shows the
same limit
𝟏
❖ 𝒍𝒊𝒎+ √𝒙 𝒔𝒊𝒏 (√𝒙) = 0
𝒙→𝟎
College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science Applied Mathematics I
1
(Math 1012)
APPLIED MATHS GROUP ASSIGNMENT NOVEMBER 16, 2022
2𝑥+4 𝑥
b. 𝑙𝑖𝑚 (2𝑥+3)
𝑥→∞
Solution
2𝑥+4 𝑥 𝑙𝑖𝑚 (2𝑥+4)𝑥
𝑥→∞
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚 ( ) is equivalent to ………… Easily to find the equation (separately)
𝑥→∞ 2𝑥+3 𝑙𝑖𝑚 (2𝑥+3)𝑥
𝑥→∞
2𝑥+4 𝑥
𝑙𝑖𝑚 (2𝑥+4)𝑥 𝑙𝑖𝑚 ( )
𝑥→∞ 𝑥→∞ 2𝑥
- = 2𝑥+3 𝑥
……both the equation divides by 2x to get the form
𝑙𝑖𝑚 (2𝑥+3)𝑥 𝑙𝑖𝑚 ( )
𝑥→∞ 𝑥→∞ 2𝑥
1 𝑥 𝑎 𝑐𝑥 𝑎𝑐
𝑙𝑖𝑚 (1 + 𝑥̇ ) , the value of 𝑙𝑖𝑚 (1 + 𝑏𝑥̇ ) =ⅇ𝑏
𝑥→∞ 𝑥→∞
2x+4 x 2 x 2
lim ( ) lim (1+ ) ⅇ1
x→∞ 2x x→∞ x
- So, 2x+3 x
= 3 x
= 3
lim ( ) lim (1+ ) ⅇ2
x→∞ 2x x→∞ 2x
2 2 3
− 2 3
ⅇ1 ⅇ1 2 3
- 3 = 3 3 …………………….. to simplify the equation, subtract 2 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 ⅇ 1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 ⅇ 2
−
ⅇ2 ⅇ2 2
2 3 1
−
ⅇ1 2 ⅇ2
- 3 3 = ⅇ 0 …………………………….. e0 = 1
−
ⅇ2 2
1 1
1
ⅇ2 ⅇ2
- = = ⅇ 2 = √ⅇ
ⅇ0 1
𝟐𝒙+𝟒 𝒙
❖ 𝒍𝒊𝒎 (𝟐𝒙+𝟑) = √ⅇ
𝒙→∞
|𝑥+5|
c. 𝑙𝑖𝑚
𝑥→−5 𝑥+5
Solution
|𝑥+5|
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚
𝑥→−5 𝑥+5
|𝑥+5| 𝑙𝑖𝑚 |𝑥+5|
𝑥→−5
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚 =
𝑥→−5 𝑥+5 𝑙𝑖𝑚 𝑥+5
̅
𝑥→−5
College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science Applied Mathematics I
2
(Math 1012)
APPLIED MATHS GROUP ASSIGNMENT NOVEMBER 16, 2022
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚 |𝑥 + 5| = 0
𝑥→−5
𝑙𝑖𝑚 𝑥 + 5 = 0
𝑥→−5
𝑙𝑖𝑚 |𝑥+5| 0
𝑥→−5
- = undefined so, we have to evaluate left- and right-hand rule.
𝑙𝑖𝑚 𝑥+5 0
̅
𝑥→−5
|𝑥+5| 𝑥, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 ≥ 0
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚 …………….. absolute value rule |𝑥| = {
𝑥→−5 𝑥+5 −𝑥, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 ≤ 0
|𝑥+5| 𝑥+5 5+5
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚 = = =1
𝑥→−5+ 𝑥+5 𝑥+5 5+5
|𝑥+5| −(𝑥+5) −(5+5)
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚− = = = -1
𝑥→−5 𝑥+5 𝑥+5 5+5
|𝑥+5| |𝑥+5|
- If 𝑙𝑖𝑚+ ≠ 𝑙𝑖𝑚− , then the limit does not exist.
𝑥→−5 𝑥+5 𝑥→−5 𝑥+5
|𝒙+𝟓|
❖ 𝒍𝒊𝒎 = does not exist
𝒙→−𝟓 𝒙+𝟓
2. Show whether f is continuous or discontinuous at “a”.
2𝑥 − 3 , 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥 < 1
𝑓(𝑥) = { 7 , 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥 = 1 ; a =1
3𝑥 − 5 , 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥 > 1
Solution
- A function f(x) is said to be continuous at a point x = a, in its domain if the following
three conditions are satisfied:
1. f(a) exists (i.e., the value of f(a) is finite)
2. 𝑙𝑖𝑚 f(x) exists (i.e., the right-hand limit = left-hand limit, and both are finite)
𝑥→𝑎
3. 𝑙𝑖𝑚 f(x) = f(a)
𝑥→𝑎
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚(7) = 7
𝑥→1
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚 2𝑥 − 3 = 2(1) − 3 = 2 − 3 = −1
𝑥→1−
College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science Applied Mathematics I
3
(Math 1012)
APPLIED MATHS GROUP ASSIGNMENT NOVEMBER 16, 2022
- 𝑙𝑖𝑚 3𝑥 − 5 = 3(1) − 5 = 3 − 5 = −2
𝑥→1+
Conclusion
the right-hand limit ≠ left-hand limit
❖ A function f(x) is discontinuous at a point x = a, a = 1
ⅆ𝑦
3. Use chain rule to find ⅆ𝑥 if
a. 𝑦 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑡𝑎𝑛(𝑙𝑛 𝑥 ))
Solution
Using chain rule
ⅆ
- [𝑓(𝑔(𝑥))] = 𝑓 ′ (𝑔(𝑥)). 𝑔′ (𝑥)
ⅆ𝑥
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥
g(x) = 𝑡𝑎𝑛(𝑙𝑛 𝑥)
1 sⅇc2(ln 𝑥)
𝑔′ (𝑥) = sec 2 (ln 𝑥) ⋅ 𝑥 = 𝑥
ⅆ 𝑠ⅇ𝑐 2 (𝑙𝑛 𝑥) sⅇc2 (ln 𝑥) 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝑙𝑛 𝑥)
- [𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑡𝑎𝑛(𝑙𝑛 𝑥))] = 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝑙𝑛 𝑥) ⋅ =
ⅆ𝑥 𝑥 𝑥
ⅆ 𝐬𝐞𝐜 𝟐 (𝐥𝐧 𝒙) 𝒄𝒐𝒔(𝒕𝒂𝒏 𝒍𝒏 𝒙)
❖ ⅆ𝒙
[𝒔𝒊𝒏(𝒕𝒂𝒏(𝒍𝒏 𝒙))] =
𝒙
b. 𝑦 = 𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥
Solution
- Apply the exponent rule, 𝑎𝑏 = ⅇ 𝑏 𝑙𝑛 𝑎
𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 = ⅇ 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 𝑙𝑛(𝑥) ……………………….. equation 1
College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science Applied Mathematics I
4
(Math 1012)
APPLIED MATHS GROUP ASSIGNMENT NOVEMBER 16, 2022
ⅆ
[ⅇ 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 𝑙𝑛(𝑥) ]
ⅆ𝑥
ⅆ
- Using chain rule, ⅆ𝑥 [𝑓(𝑔(𝑥))] = 𝑓 ′ (𝑔(𝑥)). 𝑔′ (𝑥)
𝑓(𝑥) = ⅇ 𝑥
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = ⅇ 𝑥
g(x) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 𝑙𝑛(𝑥)
ⅆ𝑦 ⅆ𝑦
𝑔′ (𝑥) = (sin 𝑥) ⋅ ln 𝑥 + sin 𝑥 ⋅ (ln 𝑥)
ⅆ𝑥 ⅆ𝑥
𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥
= 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑥 ln 𝑥 + 𝑥
ⅆ 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥
- [ⅇ 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 𝑙𝑛(𝑥) ] = ⅇ 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 𝑙𝑛(𝑥) ⋅ 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑥 ln 𝑥 +
ⅆ𝑥 𝑥
- Substitute equation 1 in ⅇ 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 𝑙𝑛(𝑥) 𝑏𝑦 𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 , because 𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 = ⅇ 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 𝑙𝑛(𝑥)
𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥
𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 (𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑥 ln 𝑥 + )
𝑥
ⅆ 𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝒙
❖ [𝒙𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝒙 ] = 𝒙𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝒙 (𝒄𝒐𝒔 𝒙 𝐥𝐧 𝒙 + )
ⅆ𝒙 𝒙
ⅆ𝑦
4. Use implicit differentiation to find ⅆ𝑥 or 𝑦 ′ 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑦 + 𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑥 = ⅇ
Solution
Use implicit differentiation
ⅆ𝑦
- ⅆ𝑥
( 𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑦 + 𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑥 = ⅇ )
ⅆ𝑦 ⅆ𝑦 ⅆ
- ⅆ𝑥
𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑦 + ⅆ𝑥
𝑦 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑥 = ⅆ𝑥𝑦 ⅇ ……. Differentiate 𝑏𝑜𝑡ℎ 𝑠𝑖𝑑ⅇ 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎⅇ ⅇ𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
ⅆ𝑦 ⅆ𝑦
- 𝑥 cos 𝑦 ⅆ𝑥 + 1 ⋅ sin 𝑦 + ⅆ𝑥 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑥 − 𝑦 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑥 = 0
ⅆ𝑦
- sin 𝑦 − 𝑦 sin 𝑥 + (𝑥 cos 𝑦 + cos 𝑥) = 0 …….. collect like terms
ⅆ𝑥
College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science Applied Mathematics I
5
(Math 1012)
APPLIED MATHS GROUP ASSIGNMENT NOVEMBER 16, 2022
ⅆ𝑦
- (𝑥 cos 𝑦 + cos 𝑥) = −sin 𝑦 + 𝑦 sin 𝑥
ⅆ𝑥
ⅆ𝑦 𝑥 cos 𝑦+cos 𝑥 −sin 𝑦+𝑦 sin 𝑥
- ( 𝑥 cos 𝑦+cos 𝑥 ) = ……Divide both side of the equation by
ⅆ𝑥 𝑥 cos 𝑦+cos 𝑥
𝑥 cos 𝑦 + cos 𝑥
ⅆ𝑦 𝑦 sin 𝑥 −sin 𝑦
- =
ⅆ𝑥 𝑥 cos 𝑦+cos 𝑥
ⅆ𝒚 𝒚 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝒙 −𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝒚
❖ ( 𝒙 𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝒚 + 𝒚 𝒄𝒐𝒔 𝒙 = ⅇ ) = 𝒙 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒚+𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒙
ⅆ𝒙
College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science Applied Mathematics I
6
(Math 1012)
You might also like
- EE518 Midterm Spring 2017 - HWDocument5 pagesEE518 Midterm Spring 2017 - HWCharan KilariNo ratings yet
- Solution of Mathematics SSC-II (3rd Set)Document7 pagesSolution of Mathematics SSC-II (3rd Set)Javaid100% (1)
- Sample MT 1 MckeyDocument6 pagesSample MT 1 MckeytortomatoNo ratings yet
- Once Per Year (RPM Vision Planner) : How To Schedule Your RPM Plan UpdatesDocument1 pageOnce Per Year (RPM Vision Planner) : How To Schedule Your RPM Plan Updatestrav bae0% (1)
- MR Right - Case Study Test - Summer 2018Document7 pagesMR Right - Case Study Test - Summer 2018jadenNo ratings yet
- Ma Education-4th-Engl2115-16-16 PDFDocument39 pagesMa Education-4th-Engl2115-16-16 PDFSameera ZahidNo ratings yet
- 05 Integrating FactorDocument12 pages05 Integrating FactorJoshua Miguel MartirNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1: LimitsDocument6 pagesCalculus 1: LimitsAlie Lee GeolagaNo ratings yet
- UP CIRCUIT Academic Affairs Division: 1. Lim 2. Lim 3. Lim ( ) 4. Lim LimDocument1 pageUP CIRCUIT Academic Affairs Division: 1. Lim 2. Lim 3. Lim ( ) 4. Lim LimJan Adrian Galang FranciscoNo ratings yet
- JEE-Main-2021-Question-Paper-Maths-August-27-Shift-1 2Document9 pagesJEE-Main-2021-Question-Paper-Maths-August-27-Shift-1 2Amit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Universidad Abierta y A Distancia de MéxicoDocument5 pagesUniversidad Abierta y A Distancia de MéxicoMartha Maria Araiza SantiniNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument15 pagesDifferential EquationsHarith HaiderNo ratings yet
- Engineering Analysis - PDFDocument12 pagesEngineering Analysis - PDFbahast faiqNo ratings yet
- Math Part1Document9 pagesMath Part1AlteaAlNo ratings yet
- ACET January 2021 - SolutionDocument11 pagesACET January 2021 - SolutionMeghna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics: Final ExamDocument5 pagesDiscrete Mathematics: Final Exam芮伃No ratings yet
- Soal Kalkulus 112.Document2 pagesSoal Kalkulus 112.misyaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document7 pagesModule 3shaina sucgangNo ratings yet
- Acp - Cbse - Maths - 3 Mark Questions 2023-2024Document4 pagesAcp - Cbse - Maths - 3 Mark Questions 2023-2024Paul KirubainathanNo ratings yet
- IniiDocument5 pagesIniiKoustavRoyNo ratings yet
- 2 Cosh 2 1 Cosh 2 +1: Example 21.1.3Document25 pages2 Cosh 2 1 Cosh 2 +1: Example 21.1.3RaymondNo ratings yet
- 03 - HW Function Limits Problems - SupplDocument3 pages03 - HW Function Limits Problems - SupplMaxNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document11 pagesModule 1Murali Karthik VNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Solving Rational FunctionsDocument14 pagesLesson 6 Solving Rational FunctionscccNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales - Puntos de LaplaceDocument7 pagesEcuaciones Diferenciales - Puntos de LaplaceJuan Pablo Ramirez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Techniques of IntegrationDocument7 pagesTechniques of IntegrationMero MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Analytic Functions of Complex VariableDocument18 pagesAnalytic Functions of Complex VariableUthman MohammedNo ratings yet
- Mathematics MS Class XII SET-1Document9 pagesMathematics MS Class XII SET-1stu.kumkum.yadav23No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Mat183Document9 pagesLesson 2 Mat183itsmeliyaarmyNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesHomogeneous Differential EquationsMay Artemisia SumangilNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 Total Points: 30Document2 pagesHomework 3 Total Points: 30Rayhan KabirNo ratings yet
- The Antiderivative and Indefinite Integral: F (X) The Integrand, C The Constant of The IntegrationDocument2 pagesThe Antiderivative and Indefinite Integral: F (X) The Integrand, C The Constant of The IntegrationVape DrugNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document4 pagesLecture 4owronrawan74No ratings yet
- DPP - Solution - JEE ADVANCED - Differential Equations & AreaDocument8 pagesDPP - Solution - JEE ADVANCED - Differential Equations & AreaSHAKTI SWARUP SAHOONo ratings yet
- K2320022 - Binti Mustamiul Azizah - Tugas 1.2Document6 pagesK2320022 - Binti Mustamiul Azizah - Tugas 1.2binti azizahNo ratings yet
- 2.1 First-Order Differential Equations. Definition 2.1 Separable EquationDocument4 pages2.1 First-Order Differential Equations. Definition 2.1 Separable Equationnadersh019No ratings yet
- Internal Assignment: Name Sneha SankhlaDocument4 pagesInternal Assignment: Name Sneha SankhlaSneha SankhlaNo ratings yet
- Jawab Uts Kalkulus 2020 - TipDocument2 pagesJawab Uts Kalkulus 2020 - TipNurul KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 SolutionDocument2 pagesExam 1 Solutionowronrawan74No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Limits at Infinity and Infinite LimitsDocument5 pagesLecture 4 Limits at Infinity and Infinite LimitsJoy Rianne HoriqueNo ratings yet
- Penmaba Unj 2016: Pembahasan SoalDocument15 pagesPenmaba Unj 2016: Pembahasan SoalAngela OdetioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Take-Home: Brian ShuDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Take-Home: Brian ShuBrian ShuNo ratings yet
- MAT1100 Integral Calculus I - 2020Document6 pagesMAT1100 Integral Calculus I - 2020Potrine MuzumbaNo ratings yet
- File 01Document4 pagesFile 01Atik JoarderNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Limits at Infinity-1Document7 pages2.6 Limits at Infinity-1mostafa ashrafNo ratings yet
- Exam Solution: Zsin ( )Document2 pagesExam Solution: Zsin ( )uipohlklgfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Worked SolutionsDocument172 pagesChapter 12 Worked SolutionsSophia ShiNo ratings yet
- As Pure Maths Revision NotesDocument15 pagesAs Pure Maths Revision NotesAbd Elrhman MohamedNo ratings yet
- DDP Solutions JEE ADVANCED Definite & Indefinite IntegrationDocument8 pagesDDP Solutions JEE ADVANCED Definite & Indefinite Integrationaxiom8750No ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 8th Jan Shift 1 MathsDocument15 pagesJEE Main 2020 8th Jan Shift 1 MathsbhushanNo ratings yet
- Ali Hachem - IntegralsDocument4 pagesAli Hachem - Integralssergedemirdjian1990No ratings yet
- Integral Surface Passing Through A Given CurveDocument8 pagesIntegral Surface Passing Through A Given CurveSaad Ahmed SazanNo ratings yet
- EFI Proof (HW)Document2 pagesEFI Proof (HW)SBNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument19 pagesDifferential EquationsaliNo ratings yet
- Practica 6Document12 pagesPractica 6SERGIO SEBASTIAN BALDERA AMAYANo ratings yet
- Kalkulus 3Document4 pagesKalkulus 3IbadNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Paper: Date of Exam: 9 Time: 9:30 A.M. To 12:30 P.M. Subject: MathematicsDocument14 pagesJEE Main 2020 Paper: Date of Exam: 9 Time: 9:30 A.M. To 12:30 P.M. Subject: MathematicsSakshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Ficha 4 Trigonometria Limites Notáveis 12Document3 pagesFicha 4 Trigonometria Limites Notáveis 12Alexandra OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Integral de Funciones Racionales TrigonometricaDocument6 pagesIntegral de Funciones Racionales Trigonometricajose armando rosas reyesNo ratings yet
- WUC114 Final ExamDocument5 pagesWUC114 Final ExamCAROLINE ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Internal Assignment: Name Sneha SankhlaDocument10 pagesInternal Assignment: Name Sneha SankhlaSneha SankhlaNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Equation1Document7 pagesBernoulli's Equation1James Laroda LaceaNo ratings yet
- Alevelh2maths2008paper2 PDFDocument4 pagesAlevelh2maths2008paper2 PDFLawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Unity University College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science Applied Mathematics I (Math 1012) Group Assignment (20%)Document4 pagesUnity University College of Engineering Technology & Computational Science Applied Mathematics I (Math 1012) Group Assignment (20%)Sani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Maintenance Technicians Admission Process For International Applicants 1Document2 pagesAircraft Maintenance Technicians Admission Process For International Applicants 1dawits065No ratings yet
- Individual 2683202Document13 pagesIndividual 2683202Sani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Our Admission Process: Step 1: ApplicationDocument5 pagesOur Admission Process: Step 1: Applicationhussien amareNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilizationz Unit-5Document14 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationz Unit-5Sani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning and Architecture of Indus CitiesDocument4 pagesUrban Planning and Architecture of Indus Cities23010126230No ratings yet
- Masonery Tools and SafetyDocument6 pagesMasonery Tools and SafetySani MohammedNo ratings yet
- The Last SupperDocument2 pagesThe Last SupperSani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2 Probability and StatisticsDocument24 pagesChapter 1-2 Probability and StatisticsIsokingNo ratings yet
- CH-3 PPT For Basic Stat (Repaired)Document43 pagesCH-3 PPT For Basic Stat (Repaired)Sani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Ch2 StatisticsDocument41 pagesCh2 StatisticsSani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five (Probability) For AnsDocument24 pagesChapter Five (Probability) For AnsSani MohammedNo ratings yet
- CH 1-2 Basic Statistics-2Document48 pagesCH 1-2 Basic Statistics-2Sani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Masonery Tools and SafetyDocument6 pagesMasonery Tools and SafetySani MohammedNo ratings yet
- Other Emerging Technologies: Chapter SevenDocument57 pagesOther Emerging Technologies: Chapter SevenGetachew HussenNo ratings yet
- Sony DVR-VX2000 ManualDocument92 pagesSony DVR-VX2000 ManualHenryNo ratings yet
- KuchhbhiDocument6 pagesKuchhbhiAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Midterm: Attendance Quiz 1 Quiz 2Document6 pagesMidterm: Attendance Quiz 1 Quiz 2Sohaib ArifNo ratings yet
- Declaration KitDocument4 pagesDeclaration KitJITANSHUCHAMPNo ratings yet
- Đề MINH HỌA Số 11 Luyện Thi Tốt Nghiệp THPT 2023Document7 pagesĐề MINH HỌA Số 11 Luyện Thi Tốt Nghiệp THPT 2023Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- Grade Filipino 7 Week 1-2Document10 pagesGrade Filipino 7 Week 1-2SALEM DE LA CONCEPCIONNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping Services NCII Quarter 3 PDF HousekeepingDocument1 pageHousekeeping Services NCII Quarter 3 PDF HousekeepingSalve RegineNo ratings yet
- A Study On Five International Scientists: Micro Project ReportDocument18 pagesA Study On Five International Scientists: Micro Project ReportAishwarya MohanNo ratings yet
- Why Are Engineers Considered An Important Segment of The Society?Document2 pagesWhy Are Engineers Considered An Important Segment of The Society?Angellete D. GacayanNo ratings yet
- Independent University, BangladeshDocument8 pagesIndependent University, BangladeshMD. Akif RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Norwegian Oil Experience:: Helge RyggvikDocument58 pagesThe Norwegian Oil Experience:: Helge RyggvikhiyeonNo ratings yet
- Virtue Ethics: Deficiency ExcessDocument1 pageVirtue Ethics: Deficiency ExcesschristianNo ratings yet
- Final Verbal Agression ResearchDocument26 pagesFinal Verbal Agression ResearchLucañas PhilipNo ratings yet
- Spatial Association Effect of Regional Pollution Control2019journal of Cleaner ProductionDocument13 pagesSpatial Association Effect of Regional Pollution Control2019journal of Cleaner ProductionArthur PimentelNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques NcatDocument191 pagesQuantitative Techniques NcatJeremiah AkonyeNo ratings yet
- ICT Basic Types of ComputerDocument7 pagesICT Basic Types of ComputerMomina B KhanNo ratings yet
- Applied Linerar Algebra FinalDocument193 pagesApplied Linerar Algebra FinalAslesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Positive Mental AttitudeDocument83 pagesPositive Mental AttitudemuetanianNo ratings yet
- Introducing Python Programming For Engineering Scholars: Zahid Hussain, Muhammad Siyab KhanDocument8 pagesIntroducing Python Programming For Engineering Scholars: Zahid Hussain, Muhammad Siyab KhanDavid C HouserNo ratings yet
- Critical Study of Richard Dawkins, The God DelusionDocument10 pagesCritical Study of Richard Dawkins, The God DelusionJuan Pablo Pardo BarreraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 ADVANCED ANIMATION AS3Document11 pagesLecture 01 ADVANCED ANIMATION AS3Febb RoseNo ratings yet
- Essay My Favourite FoodDocument6 pagesEssay My Favourite Foodafabfasaf100% (2)
- Weatherford OEPS BrochureDocument5 pagesWeatherford OEPS BrochureZharick RojasNo ratings yet
- G11 - ENGPROF - Week 9Document11 pagesG11 - ENGPROF - Week 9Shendy Acosta100% (1)
- Module 2Document28 pagesModule 2Vaishnavi CNo ratings yet
- 3.2.5.applying The Normal Curve Concepts in Problem Solving PDFDocument3 pages3.2.5.applying The Normal Curve Concepts in Problem Solving PDFJhasmin Jane LagamayoNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Holiday HomeworkCOMPETENCY BASED 20230519124608767Document56 pagesClass 10 Maths Holiday HomeworkCOMPETENCY BASED 20230519124608767Itz me KARTIKKKNo ratings yet