Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hyperbola
Uploaded by
JERLYN MACADO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesConic_Section: Hyperbola
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConic_Section: Hyperbola
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesHyperbola
Uploaded by
JERLYN MACADOConic_Section: Hyperbola
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
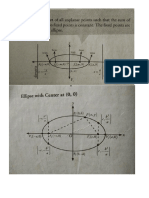
Hyperbolas are conic sections that are not commonly encountered formally.
Its graph consists of
two unbounded branches which extends in different directions.
A hyperbola is a set of all coplanar points such that the difference of its distance from two fixed
points is called the foci of the ellipse.
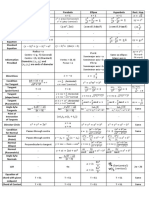
Standard Equations of Hyperbolas with Center at Origin
Hyperbola with foci on the Hyperbola with foci on the
Center (0,0)
x-axis (Horizontal) y-axis (Vertical)
Equation 𝒙 𝟐 𝒚𝟐 𝒚𝟐 𝒙𝟐
− =𝟏 − =𝟏
𝒂𝟐 𝒃𝟐 𝒂𝟐 𝒃𝟐
Where 𝑐 = √𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 and 𝑐 > 𝑎 Where 𝑐 = √𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 and 𝑐 > 𝑎
Vertices Coordinates: (±𝑎, 0) Coordinates: (0, ±𝑎)
(Transverse Axis) Length: 2𝑎 Length: 2𝑎
Location: On the x-axis Location: On the y-axis
Foci Coordinates: (±𝑐, 0) Coordinates: (0, ±𝑐)
Coordinates: (0, ±𝑏) Coordinates: (±𝑏, 0)
Conjugate Axis Length: 2𝑏 Length: 2𝑏
Location: On the y-axis Location: On the x-axis
Asymptotes 𝑏 𝑎
𝑦=± 𝑥 𝑦=± 𝑥
𝑎 𝑏
Latus Rectum Endpoints: (𝑐, ±
𝑏2
) and (−𝑐, ±
𝑏2
) Endpoints: (±
𝑏2
, 𝑐) and (±
𝑏2
, −𝑐)
𝑎 𝑎 𝑎 𝑎
2𝑏2 2𝑏2
Length: Length:
𝑎 𝑎
Equation: 𝑥 = ±𝑐 Equation: y= ±𝑐
Direction: Vertical Direction: Horizontal
Auxiliary Rectangle Dimension: 2𝑎 x 2𝑏 Dimension: 2𝑎 x 2𝑏
Standard Equations of Hyperbolas with Center at h,k
Hyperbola with foci on the Hyperbola with foci on the
Center (h,k)
x-axis (Horizontal) y-axis (Vertical)
Equation (𝒙 − 𝒉)𝟐 (𝒚 − 𝒌)𝟐 (𝒚 − 𝒌)𝟐 (𝒙 − 𝒉)𝟐
− =𝟏 − =𝟏
𝒂𝟐 𝒃𝟐 𝒂𝟐 𝒃𝟐
Where 𝑐 = √𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 and 𝑐 > 𝑎 Where 𝑐 = √𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 and 𝑐 > 𝑎
Vertices Coordinates: (ℎ ± 𝑎, 𝑘) Coordinates: (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑎)
(Transverse Axis) Length: 2𝑎 Length: 2𝑎
Equation: 𝑦 = 𝑘 Equation: x= ℎ
Location: On the x-axis (Horizontal) Location: On the y-axis (Vertical)
Foci Coordinates: (ℎ ± 𝑐, 𝑘) Coordinates: (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑐)
Coordinates: (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑏) Coordinates: (ℎ ± 𝑏, 𝑘)
Length: 2𝑏 Length: 2𝑏
Conjugate Axis
Equation: 𝑥 = ℎ Equation: 𝑦 = 𝑘
Location: On the y-axis (Vertical) Location: On the x-axis (Horizontal)
Asymptotes 𝑏 𝑎
𝑦 = 𝑘 ± (𝑥 − ℎ) 𝑦 = 𝑘 ± (𝑥 − ℎ)
𝑎 𝑏
Latus Rectum Endpoints: (ℎ + 𝑐, 𝑘 ±
𝑏2
) and Endpoints: (ℎ ±
𝑏2
,𝑘 + 𝑐) and
𝑎 𝑎
𝑏2 2
(ℎ − 𝑐, 𝑘 ± ) 𝑏
𝑎 (ℎ ± , 𝑘 − 𝑐)
2𝑏2
𝑎
Length: 2𝑏2
𝑎 Length:
𝑎
𝑏2
Equation: 𝑥 = 𝑘 ± 𝑏2
𝑎 Equation: y= ℎ ±
𝑎
Auxiliary Rectangle Dimension: 2𝑎 x 2𝑏 Dimension: 2𝑎 x 2𝑏
You might also like
- EllipseDocument2 pagesEllipseJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Geometry Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesGeometry Cheat SheetiannybearNo ratings yet
- Summary (WS3-5)Document5 pagesSummary (WS3-5)Mohammed KhalilNo ratings yet
- The Line Integral of The Scalar Field: Math301 Summary (A. Fathy)Document3 pagesThe Line Integral of The Scalar Field: Math301 Summary (A. Fathy)Mohammed KhalilNo ratings yet
- M2 T3 EllipseDocument7 pagesM2 T3 EllipseKurianPaulNo ratings yet
- STT MATH201 Lecture 01Document3 pagesSTT MATH201 Lecture 01basheermazari4No ratings yet
- REVISIONDocument8 pagesREVISIONBún CáNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12apr18Document4 pagesLecture 12apr18kashish goyalNo ratings yet
- Math ExamDocument9 pagesMath ExamMalik AsadNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Memory of Acoustic Oud DesignDocument18 pagesDescriptive Memory of Acoustic Oud DesignDario Martin LobosNo ratings yet
- Physics 1301 Equation SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics 1301 Equation Sheeth.krijestoracNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument16 pagesCoordinate GeometrySLNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument6 pagesCircleMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document6 pagesLecture 7College Application CenterNo ratings yet
- 10 Waveguides GeneralApproachDocument28 pages10 Waveguides GeneralApproachRounak MandalNo ratings yet
- 10 Waveguides GeneralApproach PDFDocument28 pages10 Waveguides GeneralApproach PDFKOTTI NIKHITHANo ratings yet
- 1301 Formula SheetDocument2 pages1301 Formula Sheetdivitimaniteja999786No ratings yet
- T1 - Vectors, Graphs of MotionDocument6 pagesT1 - Vectors, Graphs of MotionGGNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29-Revision of Unit5 and MCQ PracticeDocument28 pagesLecture 29-Revision of Unit5 and MCQ PracticeAerra ManirajNo ratings yet
- Robotics Course: LR02.3:: 3 Dimensional Homogenous TransformationDocument17 pagesRobotics Course: LR02.3:: 3 Dimensional Homogenous TransformationThiha Ye ThwayNo ratings yet
- Feature ExtractionDocument90 pagesFeature Extractionsai tejasNo ratings yet
- Maths 3 Application Powerpoint (Amended)Document27 pagesMaths 3 Application Powerpoint (Amended)lerato guguNo ratings yet
- Pre CalDocument3 pagesPre CalLeon NyNo ratings yet
- Solution For HOMEWORK 4Document5 pagesSolution For HOMEWORK 4Rau Lance CunananNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 EllipseDocument18 pagesLesson 4 Ellipsejarenhndsm.placiegoNo ratings yet
- Precalculus q1 FormulasDocument1 pagePrecalculus q1 FormulasGeronimo LucesNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document12 pagesModule 5Monique UnicoNo ratings yet
- Module Introduction:: This Module Aims That The Students Will Be Able To Learn The FollowingDocument12 pagesModule Introduction:: This Module Aims That The Students Will Be Able To Learn The FollowingRaven Evangelista CanaNo ratings yet
- Application of Partial Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesApplication of Partial Differential EquationsventhiiNo ratings yet
- SimplySupportedBeam PointloadDocument6 pagesSimplySupportedBeam PointloadNeelakantheswar KunkulaguntaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Math Rule Summary (Week 1 To 6)Document9 pagesEngineering Math Rule Summary (Week 1 To 6)Raghad Al-ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Week 11Document76 pagesWeek 11snaaaoNo ratings yet
- Elective Mathematics 10 Module Tangent Line of 4th QTRDocument14 pagesElective Mathematics 10 Module Tangent Line of 4th QTRMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- L Note - V (Updated)Document5 pagesL Note - V (Updated)Updirahman MohamoudNo ratings yet
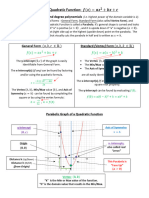
- Graphing A Quadratic FunctionDocument4 pagesGraphing A Quadratic FunctionAbo MoussaNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus ConicsectionsDocument1 pagePre Calculus ConicsectionsBCamacho UrielNo ratings yet
- Neo Neet 11 p1 Phy H Motion in 1d s08Document67 pagesNeo Neet 11 p1 Phy H Motion in 1d s08gecbchebbecbebvebNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Three-Dimensional Geometric TransformationDocument15 pagesUnit 4 Three-Dimensional Geometric TransformationBino100% (1)
- Easy Notes On Mechanics Moment of Inertia PDFDocument48 pagesEasy Notes On Mechanics Moment of Inertia PDFFaisal Shabbir0% (2)
- Problem Set 8: Proof. Let Be A Differentiable Function Whose Value Is Never Zero, and ConsiderDocument3 pagesProblem Set 8: Proof. Let Be A Differentiable Function Whose Value Is Never Zero, and ConsiderSarah TseungNo ratings yet
- Harold's Precalculus Rectangular - Polar - Parametric "Cheat Sheet"Document7 pagesHarold's Precalculus Rectangular - Polar - Parametric "Cheat Sheet"HarshNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus ReviewerDocument4 pagesPre-Calculus Reviewertravisagpasa123No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3Hamza HussineNo ratings yet
- M2 T4 HyperbolaDocument7 pagesM2 T4 HyperbolaKurianPaulNo ratings yet
- Mathematics NotesDocument3 pagesMathematics Notespicnic dayNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Stokes TheoremDocument4 pages3.6.1 Stokes TheoremSyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods FormulaDocument17 pagesNumerical Methods FormulaKhaymon UmaliNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series and TransformDocument16 pagesFourier Series and TransformSalvacion BandoyNo ratings yet
- Parametrized Surfaces: Vector Calculus (MATH-243) Instructor: Dr. Naila AmirDocument23 pagesParametrized Surfaces: Vector Calculus (MATH-243) Instructor: Dr. Naila AmirRakhmeen GulNo ratings yet
- HYPERBOLADocument12 pagesHYPERBOLAYsham KamidNo ratings yet
- Math Methods SummarisationDocument10 pagesMath Methods SummarisationYM GaoNo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument4 pagesAnalytical Geometrymaneskin488No ratings yet
- VectorsDocument27 pagesVectorsSuthara SudhakaranNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument3 pagesAnalytic GeometryJennifer JumaquioNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations: TypesDocument30 pagesUnit 3 Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations: TypesBinoNo ratings yet
- Equation Appendix Final ExamDocument5 pagesEquation Appendix Final ExamDhanush raoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-5Document44 pagesLecture 1-5KeroNo ratings yet
- SL-Topic-4-Forms of Straight LinesDocument2 pagesSL-Topic-4-Forms of Straight LinesSwapnendu SikdarNo ratings yet
- RotationDocument5 pagesRotationKaren GardoseNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- LAS ParabolaDocument2 pagesLAS ParabolaJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- LAS AnnuitiesDocument2 pagesLAS AnnuitiesJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- LAS - Stocks and BondsDocument2 pagesLAS - Stocks and BondsJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Gen - Math - Answersheet (Module 8)Document2 pagesGen - Math - Answersheet (Module 8)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Answersheet Module6Document2 pagesAnswersheet Module6JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem - LASDocument2 pagesBinomial Theorem - LASJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- GenMath11 - Q1 - Mod8 - Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities - Version 4 FinalDocument24 pagesGenMath11 - Q1 - Mod8 - Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities - Version 4 FinalJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 4Document8 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 4JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Conic Section - Problem SolvingDocument1 pageConic Section - Problem SolvingJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet Q2 Module 9Document5 pagesLearning Worksheet Q2 Module 9JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 5Document2 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 5JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 6Document7 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 6JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PRECALCULUS TOS-MidtermDocument2 pagesPRECALCULUS TOS-MidtermJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PC Answersheet (Q2 M1-2)Document2 pagesPC Answersheet (Q2 M1-2)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Precalculus - ANSWERSHEET Q1 M7 8Document2 pagesPrecalculus - ANSWERSHEET Q1 M7 8JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PC Answersheet (Q2 M6-7)Document3 pagesPC Answersheet (Q2 M6-7)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Ma 302 SyllabusDocument3 pagesMa 302 Syllabusapi-262576508No ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter Summative Test in Math 10Document1 page2ND Quarter Summative Test in Math 10milafer daban0% (1)
- Vardhaman Mahaveer Open University, Kota: Differential Geometry and Tensors-1Document358 pagesVardhaman Mahaveer Open University, Kota: Differential Geometry and Tensors-1Rahul NayakNo ratings yet
- Latitude and LongitudeDocument18 pagesLatitude and LongitudeSheryl BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Intro To Conic Sections and Circles 1Document11 pagesLesson 1 Intro To Conic Sections and Circles 1Markkhian GeveroNo ratings yet
- 061 - General Navigation - QuestionsDocument47 pages061 - General Navigation - QuestionsEASA ATPL Question Bank100% (3)
- FC Math Test - Google FormsDocument11 pagesFC Math Test - Google FormsManoj GuruNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Maths CH 11.conic SectionDocument3 pagesHsslive Xi Maths CH 11.conic SectionChrlesNo ratings yet
- ME401T CAD Ellipse Algorithm - 5Document29 pagesME401T CAD Ellipse Algorithm - 5AnuragShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal - Learner - S Packet Q1 Week 1Document17 pagesPre Cal - Learner - S Packet Q1 Week 1Gladys Angela ValdemoroNo ratings yet
- Mat 70Document100 pagesMat 70ChilsonHangadZerdaNo ratings yet
- 2 Integral DefinidaDocument3 pages2 Integral DefinidaDarío HidalgoNo ratings yet
- MTH404 (Dynamics) Notes For Final TermDocument59 pagesMTH404 (Dynamics) Notes For Final Termjutt sabNo ratings yet
- Tangent & Secant SegmentDocument15 pagesTangent & Secant SegmentAllyson AguilaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Arc Length and Arc Length Parametrization - ClassDocument25 pages3 - Arc Length and Arc Length Parametrization - ClassTszkin WongNo ratings yet
- Plane GeometryDocument3 pagesPlane GeometryKenneth Peña JavierNo ratings yet
- Ace Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5Document10 pagesAce Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5James OoiNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: Pre-CalculusDocument46 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Pre-CalculusLeah Mae France100% (2)
- VECTORDocument13 pagesVECTORDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Udaan Class XI Maths Part 1Document168 pagesUdaan Class XI Maths Part 1Tejas PagareNo ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry For BeginnersDocument234 pagesAnalytical Geometry For Beginnersscubadru100% (3)
- REVIEW TEST IB QUESTIONS SOLUTIONS Linear Simultaneous Equations Relations Functions Oct 2012Document8 pagesREVIEW TEST IB QUESTIONS SOLUTIONS Linear Simultaneous Equations Relations Functions Oct 2012megaordinarydayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - CurvesDocument24 pagesChapter 5 - CurvesHassan YousifNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument119 pagesConic SectionsAbid KhanNo ratings yet
- Calculus Assignment No 1Document4 pagesCalculus Assignment No 1Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Final Test - 1Document6 pagesAnalytic Geometry Final Test - 1Brenda MontañezNo ratings yet
- The Rectangular Coordinate SystemDocument25 pagesThe Rectangular Coordinate SystemFrancis LagramaNo ratings yet
- 10 03 Lengths of Tangent PDFDocument5 pages10 03 Lengths of Tangent PDFSri DNo ratings yet
- ParabolasDocument2 pagesParabolasnooluoitNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Coordinate SystemDocument14 pagesRectangular Coordinate SystemMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet