Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHN (Drug Study) Aj
Uploaded by
Blair Margaux0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views12 pagesCHN (Drug Study) Aj
Uploaded by
Blair MargauxCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
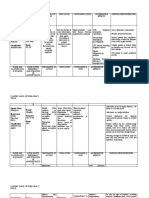
DRUG STUDY
DRUG NAME ROUTE AND MECHANISM INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING
PREPARATION OF ACTION AND PRECAUTION REACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
CNS: unusual Observe and
Generic Name: Route: The exact Initial treatment Contraindicated in tiredness or supervise closely.
mechanism of of active TB wih known
hypersensitivity, weakness Patients should
Pyrazinamide PO other receive at least one
action is
unknown. antituberculotics cross-sensitivity
ethionamide,
with GI:
hepatotoxicity, other effective
or after antituberculosis
Brand Name: Preparation: Pyrazinamide
gets activated treatment failure isoniazid, niacin or
nicotonic acid, anorexia,
diarrhea, nausea, agent concurrently.
Rifater, Tebrazid Preparation to Pyrazinoic with other severe hepatic vomiting Examine patients at
500 mg scored acid in the bacilli primary drugs in damage. regular intervals
where it any form of Use cautiously in : GU: dysuria
Drug Classification: or unscored interferes with active TB. acute gout, DM,
and question about
tablet. acute ittermittent Skin: acne, possible signs of
Anti-mycobacterial fatty acid polyuria, pregnancy itching, toxicity: Liver
class Intermittent synthase FAS I. photosensitivity, enlargement or
dosing at twice This interferes rash tenderness,
Dosage: or thrice weekly with the Metabolic: jaundice, fever,
up to 50 mg/kg bacteriums hyperuricemia anorexia, malaise,
Tablet: 500mg can be given. ability to impaired vascular
Children: synthesize new Musculoskeletal: integrity
30–40 fatty acids, arthralgia, gouty (ecchymoses,
mg/kg/dose. required for arthritis
growth and petechiae,
replication. Hepatic: abnormal bleeding).
jaundice
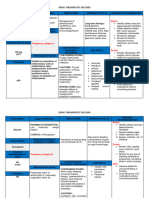
DRUG NAME ROUTE AND MECHANISM INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING
PREPARATION OF ACTION AND PRECAUTION REACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: Route: The mechanism Ethambutol is Contraindicated in CNS: dizziness, Perform visual
of action is not used for the
Ethambutol PO completely treatment of knownhypersensitivity,
fever,
hallucinations,
acuity and color
hydrochloride Preparation: known. pulmonary discrimination tests
Ethambutol tuberculosis with ckilden < 13 years
old, pt with optic headache, before and during
other malaise, mental therapy.
Brand Name: primary may inhibit medications that neuritis confusion,
treatment and synthesis of treat TB (e.g. Use cautiously in : pt peripheral neuritis Ensure that any
Etuibi, prophylaxis: one or more isoniazid) with impaired renal EENT: optic changes in vision
Myambutol Ethambutol
should be matabolites of
susceptible .
function, cataracts,
ecurrent eye neuritis, ireversible don`t result from
underlying
administered in bacteria, inflammation, gout, blindness, condition
a single daily changing cell diabetic retinopathy. decreased visual
Drug oral dose of metabolism acuity Obtain AST and
calssification: 15mg/kg,
concomitant during cell GI: abdominal ALT levels before
Antitubercular drugs being division; pain, anorexia, GI therapy and
agents maintained at bacteriostatic. upset, nausea, monitor these
their vomiting levels every 3 to 4
Dosage: recommended Hematologic: weeks.
dosage levels. thrombocytopenia, In patients with
Tablets: 100 mg, re-treatment: leukopenia, impaired renal
400 mg For the first 60 neutropenia function, base
days of Skin: toxic dosage on drug
treatment, epidermal level
Ethambutol
should be necrolysis, Monitor uric acid
administered in dermatitis, pruritus level, observe
a single daily Musculoskeletal: patient for signs
oral dose of and symptoms of
25mg/kg. joint pain gout
Metabolic:
hyperuricemia
OTHERS:
hypersensitivity
reactions,
precipitation of
acute gout
DRUG NAME ROUTE AND MECHANISM INDICATION CONTRAINDICATI ADVERSE NURSING
PREPARATIO OF ACTION ON AND REACTION RESPONSIBILITI
N PRECAUTION ES
Generic Name: Route: Inhibits DNA- for the treatment Contraindicated in CNS: headache, Monitor hepatic
PO, IV dependent RNA of tuberculosis hypersensitivity to fatigue, function,
Rifampin polymerase, and tuberculosis rifampin
drugs,
or related drowsiness, hematopoietic
(Rifampicin) Preparation: which impairs -related behavioral studies, and uric
Oral - Take RNA synthesis , mycobacterial Use cautiously in : changes, dizziness, acid level.
Brand Name: batericidal. infections pt with liver disease mental confusion,
the capsule or diabetes. inability to In patients with
Rifadin, Rofact on an empty concentrate, existing impaired
stomach, 1 general numbness, hepatic function,
hour before or ataxia, fever monitor LFT
Drug Classification: 2 hours after values, especially
Anti-mycobacterial a meal, with a CV: flushing, shock AST and ALT,
class full glass of before therapy,
EENT: visual then every 2 to 4
Dosage: water disturbances, weeks during
IV infusion - conjunctivitis, sore therapy.
Capsules: Reconstitute mouth or tongue, Watch for and
150mg,300mg the lyophilized tooth discoloration report signs and
powder by GI: epigastric symptoms of
Powder for transferring distress, anorexia, hepatic
infections: 10 mL of nausea, vomiting, impairment.
600mg/vial sterile water
for injection to abdominal pain,
a vial diarrhea, flatulence For TB, a three-
containing Hematologic: drug regimen of
600 mg of rifampin,isoniazid
rifampin for thrombocytopenia, (INH), and
injection transient pyrazinamide is
leukopenia, recommended in
eosinophilia, the initial phase
hemolytic anemia. of short- course
therapy, which is
Hepatic: usually continued
hepatotoxicity for 2 months.
Skin: pruritus, Look alike-sound
urticaria, rash alike: Don't
Musculoskeletal: confuse rifampin
muscular with rifabutin,
weakness, pain in rifaximin,
extremities rifapentine, or
Rifamate.
Metabolic:
hyperuricemia
OTHERS: flulike
syndrome,
discoloration of
body fluids,
porphyria
exacerbation,
hypersensitivity
reactions,
DRUG NAME ROUTE AND MECHANISM OF INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING
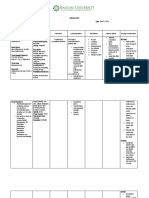
PREPARATION ACTION AND PRECAUTION REACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: Route: Streptomycin’s It's primarily Contraindicated to Black, tarry Lab tests: Obtain C&S
IM mechanism of used as part of patients stools tests prior to and
Streptomycin action is to inhibit the multi-drug hypersensitive to periodically during
Preparation: protein synthesis treatment of streptomycin or other Chest pain course of therapy.
Brand Name: of mycobacteria pulmonary aminoglycosides, Cough
Powder for in the ribosome. tuberculosis. severe In patients with
Rimosidine injection, vial hypersensitivity to Dizziness impaired kidney
containing 1 g of sulfites, concomitant function, frequent
Drug streptomycin live bacterial Chills determinations of
Classification: base, to be vaccines serum drug
Aminoglycoside dissolved in 3.2 Burning concentrations and
Antibiotics ml of water for Itching periodic kidney and
injection to liver function tests are
Dosage: obtain a 250 Numbness advised
Powder for mg/ml solution,
infections: 1g for IM injection. Feeling of Be alert for and report
constant immediately symptoms
injectable movement of ototoxicity
solution: of self or Be aware that auditory
40mg/mL surrounding nerve damage is usually
(pediatric) s preceded by vestibular
Tingling symptoms and high-
feeling pitched tinnitus, roaring
noises, impaired
hearing, sense of
fullness in ears.
Monitor I&O. Report
oliguria or changes in
I&O ratio (possible
signs of diminishing
kidney function).
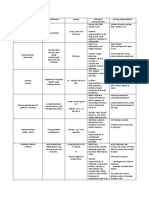
DRUG NAME ROUTE AND MECHANISM INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING
PREPARATION OF ACTION AND CAUTION REACTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: Route: May inhibit cell- it is used for Contraindicated in CNS: peripheral Monitor and
Isoniazid (INH, PO, IM wall the treatment patients with acute neuropathy, interview patients
isoonicotinic acid biosynthesis by of all forms of hepatic disease or seizures, toxic monthly.
hydrazide) Preparation: interfering with tuberculosis or isoniazid- related encephalopathy,
lipid and DNA prevent its liver damage. memory For those patients
Brand Name: PO: synthesis; reactivation. impairment, toxic older than age 35,
Always give drug bactericidal. Use cautiously in psychosis. also measure
Isonarif, with other It can be used older adults, in hepatic enzyme
Isotamine, antituberculotics
to prevent
in combination patients with chronic
with other non-isoniazid-related
EENT: optic
neuritis and atro-
levels before and
periodically
Isotamine B, development of medications liver disease or phy. Gli epigastric throughout
Rifamate, Rifater resistant used to treat chronic alcoholism, distress, nausea, treatment.
Drug organisms. TB. those with seizure vomiting.
Classification disorders (especially Perform
antituberculosis Don't give with if taking phenytoin), Hematologic: mycobacternal
agents food. and those with agranulocytosis, studies and
. severe renal aplastic anemia, susceptibility tests
IM: impairment. thrombocytopenia, prior to and
Dosage: Solution may eosinophilia, periodically during
crystallize at a low hemolytic anemia, therapy to defect
Injection: 100 temperature. . sideroblastic possible resistance
mg/ml. Warm vial to room anemia.
temperature If overdosage
Oral solution: 50 before use to Hepatic: hepatitis, occurs treatment
mg/5 ml. redissolve bilirubinemia, with pyridoxine is
Tablets: 100 mg, crystals. jaundice. instituted.
300 mg Inject deep IM Metabolic:
into a large hyperglycemia,
muscle mass hypocalcemia,
metabolic
acidosis.
Skin: irritation at
injection site.
Other:
gynecomastia,
hypersensitivity
reactions,
pyridoxine
deficiency,
rheumatic and
lupuslike
syndromes
You might also like
- DS & LTsDocument11 pagesDS & LTsLemuel Glenn BautistaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Antituberculot IcDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: Antituberculot IcPrincess Erika C. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibiliti EsDocument12 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibiliti EsdeliejoyceNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyDocument6 pagesNeonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyAlvincent D. BinwagNo ratings yet
- Penicillin G Drug StudyDocument1 pagePenicillin G Drug Studyjean therese100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyMaui LopezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyTanya Victoria Lean ClaudioNo ratings yet
- GENTAMICINDocument2 pagesGENTAMICINlowell cerezoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: GI: Pseudomembranous Colitis, Hematologic: Skin: Pain, Induration, Tenderness Other: Hypersensitivity Reactions, BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: GI: Pseudomembranous Colitis, Hematologic: Skin: Pain, Induration, Tenderness Other: Hypersensitivity Reactions, BeforeKyla Lorena Malate AbelloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanBrythym De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- AmikacinDocument4 pagesAmikacinkristineK100% (1)
- Uep - Edu.ph: Generic NameDocument13 pagesUep - Edu.ph: Generic NameKenneth JazminNo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument3 pagesVancomycinAnika Pleños100% (1)
- Student Drug Study Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesStudent Drug Study Mefenamic AcidJEWEL DEEN VILLARMENTE OQUIANANo ratings yet
- DrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoDocument4 pagesDrugStudy FluconazoleCasilaoArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Document10 pagesDRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Ceria Dorena Fe SeteraNo ratings yet
- Before: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesBefore: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIcel Jean QuimboNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin SulfateDocument2 pagesGentamicin SulfateVlienkCruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cefuroxime CelecoxibDocument3 pagesDrug Study Cefuroxime CelecoxibRem remNo ratings yet
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Drugs Ncp'sDocument12 pagesDrugs Ncp'sanon-849196100% (5)
- Pines City Colleges Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPines City Colleges Drug StudyShannon CabfitNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CSDocument7 pagesDrug Study CSFrancis MendozaNo ratings yet
- DrugggstudyyDocument6 pagesDrugggstudyycataleya mesaNo ratings yet
- Drug TabulationDocument6 pagesDrug TabulationRosemarie Canete Delarita100% (1)
- Antihistamine drug relieves allergy symptomsDocument2 pagesAntihistamine drug relieves allergy symptomsGabby Robles Paje100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudySofia CartallaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SummaryDocument6 pagesDrug Study SummaryAraw GabiNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraDocument15 pagesDRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraCharm Abyss la MorenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesDrug Study and Nursing Care PlanBel CortezNo ratings yet
- Drug study nursing considerationsDocument4 pagesDrug study nursing considerationsMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for common drugsDocument8 pagesNursing responsibilities for common drugsEden Marie FranciscoNo ratings yet
- DS (Ibuprofen)Document6 pagesDS (Ibuprofen)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Loop DiureticDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Loop DiureticNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY New BornDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY New BornNikolai FuncionNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Week 4Document4 pagesDRUG STUDY Week 4Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmpicillinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AmpicillinsebbyenolaNo ratings yet
- NCMB317: RupturedDocument12 pagesNCMB317: RupturedArmand Bong Santiago100% (1)
- Drug Study (Hydrocortisone)Document1 pageDrug Study (Hydrocortisone)Pauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJay Ann Joy PerudaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Drug For H-MoleDocument5 pagesDrug For H-MolesAm_30No ratings yet
- Drug effects and nursing care for acetaminophenDocument3 pagesDrug effects and nursing care for acetaminophenGaerlan Conrado IIINo ratings yet
- TELMISARTANDocument8 pagesTELMISARTANCidny CalimagNo ratings yet
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsDocument6 pagesNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- IV Plan of Care and Drug Study Methyldopa, Cefuroxime, Dexamethasone, HydralazineDocument9 pagesIV Plan of Care and Drug Study Methyldopa, Cefuroxime, Dexamethasone, HydralazineJHoy JhoyThotNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesKat BausaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyNathalia CabalseNo ratings yet
- Generic Name (Brand Name) Classification Dosage Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesGeneric Name (Brand Name) Classification Dosage Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesJoe Anne Maniulit, MSN, RNNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY For SrugeryDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY For SrugeryZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy ParacetamolCasilaoDocument3 pagesDrugStudy ParacetamolCasilaoArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atropine: RecommendedDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Atropine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis 1Document8 pagesDrug Analysis 1Sophia MarieNo ratings yet
- DactinomycinDocument1 pageDactinomycinIvanne Hisoler0% (2)
- Small Molecular Immunomodifiers of Microbial Origin: Fundamental and Clinical Studies of BestatinFrom EverandSmall Molecular Immunomodifiers of Microbial Origin: Fundamental and Clinical Studies of BestatinHamao UmezawaNo ratings yet
- BFV WeightDocument8 pagesBFV WeightBhargav PatelNo ratings yet
- Industrial Coupling and HoseDocument57 pagesIndustrial Coupling and HoseCesar CoronelNo ratings yet
- Swiss ReDocument9 pagesSwiss ReTuxedo1982No ratings yet
- Aronne Armanini (Auth.) - Principles of River Hydraulics-Springer International Publishing (2018)Document230 pagesAronne Armanini (Auth.) - Principles of River Hydraulics-Springer International Publishing (2018)Matija LozicNo ratings yet
- Purifying Water: Study of MethodsDocument21 pagesPurifying Water: Study of MethodsRohit Thirupasur100% (2)
- Probability As A General Concept Can Be Defined As The Chance of An Event OccurDocument14 pagesProbability As A General Concept Can Be Defined As The Chance of An Event OccurMuhammad Adnan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Olympian G60F1 G75F1 Spec SheetDocument6 pagesOlympian G60F1 G75F1 Spec Sheetkman548No ratings yet
- Tips On Fatigue - NAVWEPS 00-25-559Document123 pagesTips On Fatigue - NAVWEPS 00-25-559Mark Evan SalutinNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 11-Oct-2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 11-Oct-2022onkarkumarsolankiNo ratings yet
- Pokemon Emerald CheatDocument7 pagesPokemon Emerald CheatDimitri Iman P.No ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 Graphing Linear Functions by The Point Plotting MethodDocument4 pagesLesson 2.2 Graphing Linear Functions by The Point Plotting MethodAliah GombioNo ratings yet
- Savage Worlds of Shadowrun FinalDocument29 pagesSavage Worlds of Shadowrun Finaljasonstierle100% (4)
- Trắc nghiệm phần thì trong tiếng anh tổng hợp with keysDocument3 pagesTrắc nghiệm phần thì trong tiếng anh tổng hợp with keysMs ArmyNo ratings yet
- Diagram PLTA SLJDocument4 pagesDiagram PLTA SLJMEi Cuiet Luph-LuPhNo ratings yet
- Project Lakaw: Arduino-base Assisted Stick for Visually Impaired PeopleDocument13 pagesProject Lakaw: Arduino-base Assisted Stick for Visually Impaired PeopleEarl MathewNo ratings yet
- Audi 6 3l w12 Fsi EngineDocument4 pagesAudi 6 3l w12 Fsi EngineMarlon100% (54)
- Corn Tastes Better On The Honor System - Robin Wall KimmererDocument53 pagesCorn Tastes Better On The Honor System - Robin Wall Kimmerertristram59100% (1)
- Types of DisasterDocument22 pagesTypes of DisasterKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Abandonship Drill and LSA Training With Newly Join CrewDocument3 pagesAbandonship Drill and LSA Training With Newly Join CrewSashNo ratings yet
- Savannah Air Cargo ComplexDocument2 pagesSavannah Air Cargo Complexsavannahnow.comNo ratings yet
- La Villa Fact Sheet 2021-2022-UpdatedDocument4 pagesLa Villa Fact Sheet 2021-2022-Updatedsweta suresh ganvirNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Charle's LawDocument11 pagesLesson 3 - Charle's LawJoanNo ratings yet
- Concepts of ProbabilityDocument32 pagesConcepts of ProbabilityRushina SinghiNo ratings yet
- Obadiah Final Manuscript 16 01Document50 pagesObadiah Final Manuscript 16 01Zenaida FeliasNo ratings yet
- 6-1 Homework Team 7Document3 pages6-1 Homework Team 7Edgar ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Immuno HistochemistryDocument26 pagesImmuno HistochemistrySAMMYNo ratings yet
- Zoom Basic Functions - FinalDocument31 pagesZoom Basic Functions - FinalWenshy LavadorNo ratings yet
- Major Project ReportDocument49 pagesMajor Project ReportMohini BhartiNo ratings yet
- Humidity Chamber Tek For Fruiting BRF Cakes - Mushroom Cultivation - Shroomery Message BoardDocument15 pagesHumidity Chamber Tek For Fruiting BRF Cakes - Mushroom Cultivation - Shroomery Message BoardABIYA UNIVERSENo ratings yet
- STK6712BMK4: Unipolar Fixed-Current Chopper-Type 4-Phase Stepping Motor DriverDocument11 pagesSTK6712BMK4: Unipolar Fixed-Current Chopper-Type 4-Phase Stepping Motor DriverGerardo WarmerdamNo ratings yet