Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 TYPE OF SPEECH - Accdeliveryspeechwriting
Uploaded by
Eli ..0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views20 pagesThis document discusses speech delivery and provides information on four types of speech: manuscript reading, memorized speech, impromptu speech, and extemporaneous speech. It also discusses principles of effective speech delivery, including articulation, modulation, stage presence, facial expressions, gestures, movements, and establishing rapport with the audience. The types are defined as reading from notes, reciting a memorized speech, speaking without preparation, and speaking without notes after preparation. Principles emphasize clear pronunciation, vocal tone adjustment, owning the stage, connecting through facial expressions and body language, and engaging with listeners.
Original Description:
LECTURE ON ORAL COMMUNICATION
Original Title
01-TYPE-OF-SPEECH.accdeliveryspeechwriting.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses speech delivery and provides information on four types of speech: manuscript reading, memorized speech, impromptu speech, and extemporaneous speech. It also discusses principles of effective speech delivery, including articulation, modulation, stage presence, facial expressions, gestures, movements, and establishing rapport with the audience. The types are defined as reading from notes, reciting a memorized speech, speaking without preparation, and speaking without notes after preparation. Principles emphasize clear pronunciation, vocal tone adjustment, owning the stage, connecting through facial expressions and body language, and engaging with listeners.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views20 pages01 TYPE OF SPEECH - Accdeliveryspeechwriting
Uploaded by
Eli ..This document discusses speech delivery and provides information on four types of speech: manuscript reading, memorized speech, impromptu speech, and extemporaneous speech. It also discusses principles of effective speech delivery, including articulation, modulation, stage presence, facial expressions, gestures, movements, and establishing rapport with the audience. The types are defined as reading from notes, reciting a memorized speech, speaking without preparation, and speaking without notes after preparation. Principles emphasize clear pronunciation, vocal tone adjustment, owning the stage, connecting through facial expressions and body language, and engaging with listeners.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
SPEECH DELIVERY
•Is the expression in
words of your message,
ideas, thoughts, and
feelings.
4 types
of speech
1. Manuscript Reading
(read)
•A word-for-word iteration of
written message
•Maintains the attention of
the speaker on the printed
page.
2. Memorized Speech
•Recitation of a written message that
the speaker has committed to
memory.
•It can be useful when the message
needs to be exact and the speaker
doesn’t want to be confined by notes.
3. Impromptu Speech
•A talk that you give on the spot
without any preparation.
•A speaker can speak from his
head, commit every word to
memory, read from a script or use
a blended approach.
4. Extemporaneous
Speech
•Spoken or done without any
preparation.
•Same with impromptu
carefully prepared and
delivered without notes.
ACCORDING
TO
DELIVERY
1. Choosing the Topic
•Timely
•Interesting to speaker and listener
•Controversial
•Must be of the level of knowledge of
both the speaker and listener
2. Analysing the Audience
•Get the demographic data of the audience:
Age, Gender, Occupation, Economic status, etc.
•Know the groups which your audience belong
as these groups holds a certain belief and
values.
•Find out how your audience feels about the
topic of your speech.
3. Sourcing the Information
•Newspaper, Magazine, Books,
Journals, search engine like Google,
or any material, and the best
resource which is the people.
4. Outlining and Organizing
the Speech content
•Sort the information into
categories: Statistics, Testimonies,
Opinions, Historical facts, etc.
•Organize the speech itself by
making an outline of it.
PRINCIPLE
OF SPEECH
DELIVERY
1. Articulation
•Pronouncing the words and
speaking with clear diction that
effectively transmits the
message of the speaker.
•The correct way of saying the
word.
2. Modulation
•The capability to adjust or
manipulate the resonance
and timbre of the vocal
tone.
3. Stage Presence
•The ability to own the stage, of the
speaker, being able to fill the space
and project his/her personality to
the audience.
•The opposite of stage presence is
stage fright
4. Facial Expressions
•Builds a connection with your
audience.
•Shows sincerity and credibility to
the message.
•Conveys the feelings of the
speaker.
5. Gestures
•Helps you emphasize a point,
•Express emotions,
•Release tensions,
•And engage with your
audience.
6. Movements
•It adds drama to your
speech.
•Breaks the monotony of
where you are placed.
7. Audience Rapport
•Establishing a
connection with the
listeners or Audience.
END
You might also like
- Types of Speech According To PurposeDocument3 pagesTypes of Speech According To PurposeAiza San Pedro Santos100% (2)
- The Speaker's Handbook: Chapter 1Document35 pagesThe Speaker's Handbook: Chapter 1IrishCrystalBeltran100% (1)
- Study Notes - SOR - BaptismDocument8 pagesStudy Notes - SOR - BaptismYousef Yohanna100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Public-SpeakingDocument31 pagesLesson 2 - Public-SpeakingAshlie JaneNo ratings yet
- Speech: Types of SpeechesDocument5 pagesSpeech: Types of SpeechesJane Sagutaon100% (1)
- Extemporaneous Speech gRADE6Document12 pagesExtemporaneous Speech gRADE6Erika Nicole PascionNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument4 pagesOral Comadrianjayatendido20No ratings yet
- Interviews: (Informative Communication Example)Document29 pagesInterviews: (Informative Communication Example)Francis RaagasNo ratings yet
- Public Communication-S2022Document41 pagesPublic Communication-S2022Aaila AkhterNo ratings yet
- SPEECH DELIVERY PPTXDocument31 pagesSPEECH DELIVERY PPTXAne SierasNo ratings yet
- Communication For Various PurposesDocument3 pagesCommunication For Various PurposesJulianel GocotanoNo ratings yet
- Public SpeakingDocument21 pagesPublic SpeakingEllen AngelNo ratings yet
- Q2 OralComm ReviewerDocument3 pagesQ2 OralComm ReviewerVaughn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Communication For Various PurposesDocument20 pagesCommunication For Various PurposesMaldecida JFNo ratings yet
- Your First Speeches: Getting Started: Febry Siswanto Rizaldi Abrar Eka Novi Dianti Adit NoviyantoDocument23 pagesYour First Speeches: Getting Started: Febry Siswanto Rizaldi Abrar Eka Novi Dianti Adit NoviyantoChandra MajaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Types of SpeechDocument15 pagesPrinciples and Types of SpeechElsie Joy LicarteNo ratings yet
- 3 Selecting The Topic of SpeechDocument15 pages3 Selecting The Topic of SpeechalixamattachNo ratings yet
- Speaking SkillsDocument16 pagesSpeaking Skillslechuhi334No ratings yet
- The Speech Purpose and The Gathering of Suitable MaterialsDocument19 pagesThe Speech Purpose and The Gathering of Suitable MaterialsDawn del SocorroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document30 pagesChapter 3syahida mmaamonNo ratings yet
- TALUMPATIDocument60 pagesTALUMPATIjohnzenurielalquisadaNo ratings yet
- PurpComm Unit 2 Lesson 1 CompressedDocument35 pagesPurpComm Unit 2 Lesson 1 CompressedmercymindioramaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication PPT (Topic 1 Final)Document18 pagesPurposive Communication PPT (Topic 1 Final)Renz LaraNo ratings yet
- Types of Speech According To PurposeDocument3 pagesTypes of Speech According To PurposeAiza San Pedro Santos100% (1)
- No. 5 - Speech DeliveryDocument25 pagesNo. 5 - Speech Deliveryandie hinchNo ratings yet
- Elements of Public SpeakingDocument10 pagesElements of Public Speakingntuyo elvisNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes, Principles, and EthicsDocument28 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles, and Ethicsethics wixNo ratings yet
- Speech WritingDocument18 pagesSpeech WritingRaiza Joy Sarte100% (2)
- 1 Macro Skills ReceptiveDocument26 pages1 Macro Skills ReceptiveDomManigbasNo ratings yet
- Types of Speeches (Context, Style, Act)Document51 pagesTypes of Speeches (Context, Style, Act)silvajunjosephNo ratings yet
- Speaker's Purpose and ToneDocument1 pageSpeaker's Purpose and ToneAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Speeches Preparation and DeliveryDocument12 pages5 Types of Speeches Preparation and DeliveryArmando FaundoNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Speeches Preparation and DeliveryDocument12 pages5 Types of Speeches Preparation and DeliveryNazariah GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context: Mary Sheildred D. AngelesDocument80 pagesOral Communication in Context: Mary Sheildred D. AngelesAbigail Naranjo VillamorNo ratings yet
- 01 Teaching Reading & Writing Education at Primary Level-1Document41 pages01 Teaching Reading & Writing Education at Primary Level-1Nazeeha IhshanNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Speeches Preparation and DeliveryDocument12 pages5 Types of Speeches Preparation and DeliveryRegina Grace Pangilinan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Teaching of Reading 1Document5 pagesTeaching of Reading 1Syrile MangudangNo ratings yet
- Speech MannerDocument3 pagesSpeech MannerRazie MandaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Writing: Realin Packit Escanilla Acosta EllazarDocument45 pagesTeaching Writing: Realin Packit Escanilla Acosta EllazarMica Kimberly UrdasNo ratings yet
- W1 Unit 4.1 4.2 Oral Presentation 2 CLASS SLIDESDocument26 pagesW1 Unit 4.1 4.2 Oral Presentation 2 CLASS SLIDEScmfoo2988897No ratings yet
- Communication Skill CourseDocument116 pagesCommunication Skill Courseowenalex595No ratings yet
- Informational TextsDocument10 pagesInformational TextsKatherine MadridNo ratings yet
- Principles and Types of SpeechDocument17 pagesPrinciples and Types of SpeechElsie Joy LicarteNo ratings yet
- Principles of Speech DeliveryDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Speech DeliveryIcy PallananNo ratings yet
- AIR ORALCOM Lesson3Document18 pagesAIR ORALCOM Lesson3Jeannelle UngrianoNo ratings yet
- Varieties of Written and SpokenDocument16 pagesVarieties of Written and SpokenMary Jane CairelNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm Reviewer 1Document17 pagesOral Comm Reviewer 1maryshealshealNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument12 pagesSpeechmogale.molekwaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Speech WritingDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Speech WritingEmelita CoronelNo ratings yet
- Midterms PurcomDocument3 pagesMidterms PurcomDianne LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Module GECDocument39 pagesModule GECTay Seng FaNo ratings yet
- PrewritingDocument7 pagesPrewritingStar MobileNo ratings yet
- MoralDocument31 pagesMoralKharl Ashley PastorNo ratings yet
- EN+ Midterms ReviewerDocument5 pagesEN+ Midterms ReviewerArvin Kim QuibingcoNo ratings yet
- Principles and Types of SpeechDocument23 pagesPrinciples and Types of SpeechMarichelle Idmilao PurosNo ratings yet
- Reading SkillsDocument35 pagesReading SkillsNivedita PatraNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument8 pagesPurposive CommunicationAliyah MagsinoNo ratings yet
- 3 Public SpeakingDocument21 pages3 Public SpeakingRead this SecretNo ratings yet
- Green and Brown Types of Speech Style PresentationDocument14 pagesGreen and Brown Types of Speech Style PresentationMaricel Racimo ParallagNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Cases - Mcqs CH 1 Cases - McqsDocument55 pagesCH 1 Cases - Mcqs CH 1 Cases - McqsChaudhary AdeelNo ratings yet
- Profit Loss Account TemplateDocument4 pagesProfit Loss Account TemplatesnehaNo ratings yet
- 2006 Amc8Document12 pages2006 Amc8Yuhang HeNo ratings yet
- FY EDC 2020 Decor-Combinations en EASTDocument14 pagesFY EDC 2020 Decor-Combinations en EASTCristian VasileNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Software Engineering Course OutlineDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Software Engineering Course Outlinebetelhem yegzawNo ratings yet
- List of Affilited CollegesDocument28 pagesList of Affilited Collegesuzma nisarNo ratings yet
- Communityhealth 141122094330 Conversion Gate02Document22 pagesCommunityhealth 141122094330 Conversion Gate02Titser JoNo ratings yet
- 6to Present Continuous AllDocument1 page6to Present Continuous AllEliana VogtNo ratings yet
- BearingsDocument52 pagesBearingsrahul singhNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of DerivativesDocument12 pagesA Brief History of DerivativesPranab SahooNo ratings yet
- Darfur Now Not On Our Watch Teaching UnitDocument73 pagesDarfur Now Not On Our Watch Teaching UnitFacing History and Ourselves100% (12)
- Background: The Islamic World of Academy of ScienceDocument5 pagesBackground: The Islamic World of Academy of ScienceNusrat MaqboolNo ratings yet
- FRC Team 2637, Phatnom Catz, Techbinder 2023 - 2024 CrescendoDocument17 pagesFRC Team 2637, Phatnom Catz, Techbinder 2023 - 2024 CrescendoShrey Agarwal (Drago Gaming)No ratings yet
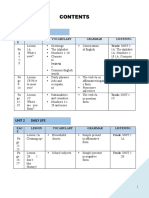
- Unit 1 Hello There!: PAG E Lesson Vocabulary Grammar Listening Track: UNIT 1Document10 pagesUnit 1 Hello There!: PAG E Lesson Vocabulary Grammar Listening Track: UNIT 1Analia SanlongNo ratings yet
- Forced Quenching Improves Three-Transistor FM Tuner: Lyle WilliamsDocument4 pagesForced Quenching Improves Three-Transistor FM Tuner: Lyle WilliamsbaymanNo ratings yet
- Vision N MissionDocument8 pagesVision N MissionIshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Haal E Safar Az Farsh Ta Arsh or Read OnlineDocument174 pagesHaal E Safar Az Farsh Ta Arsh or Read OnlineHaal e Safar100% (4)
- Image Steganography ScopeDocument13 pagesImage Steganography ScopeMUHAMMAD FARAZ HAIDERNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documenthakimfriends3No ratings yet
- Bank of South Sudan Act, 2011 - Bank of South SudanDocument59 pagesBank of South Sudan Act, 2011 - Bank of South SudanAnnadevaraNageswararaoNo ratings yet
- Second SundayDocument6 pagesSecond SundayAlfred LochanNo ratings yet
- Gehman Mennonite Church: Let's Walk With Jesus Personally, Locally, and GloballyDocument1 pageGehman Mennonite Church: Let's Walk With Jesus Personally, Locally, and GloballyGehman Mennonite ChurchNo ratings yet
- Organ TransplantationDocument36 pagesOrgan TransplantationAnonymous 4TUSi0SqNo ratings yet
- 13 Datasheet Chint Power Cps Sca5ktl-Psm1-EuDocument1 page13 Datasheet Chint Power Cps Sca5ktl-Psm1-EuMARCOS DANILO DE ALMEIDA LEITENo ratings yet
- Hammer Pulse TempDocument12 pagesHammer Pulse Temppeter911cm100% (1)
- Task Performance EuthenicsDocument3 pagesTask Performance EuthenicsKimberly MarquezNo ratings yet
- First Responder ManualDocument69 pagesFirst Responder ManualCristina Joy Vicente Cruz100% (3)
- Candi MerakDocument2 pagesCandi MerakEdi YantoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Admax CataDocument30 pages2019 Admax CataEVENTIA AFRICANo ratings yet