Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7.10 Technical Report: Figure# 7.6 Simulation
7.10 Technical Report: Figure# 7.6 Simulation
Uploaded by
Fawad Shakil AsgharOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7.10 Technical Report: Figure# 7.6 Simulation
7.10 Technical Report: Figure# 7.6 Simulation
Uploaded by
Fawad Shakil AsgharCopyright:
Available Formats
7.
10 Technical report
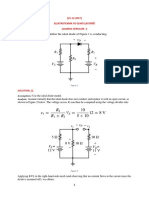
Consider the circuit using figure 7.1 with a resistor of 2.2kohm. when the voltage is positive the diode
(Zener Diode) is reverse biaised. Until the zener potential is reached the diode resistance is very high
and no current flows. In this condition ohm’s law makes the voltage across R zero so all E appear across
the zener. Once the E exceed the zener voltage the remaining E drops across R.
When the input Voltage is 1V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.6
Figure# 7.6 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 2V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.7
Figure# 7.7 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 5V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.8
Figure# 7.8 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 10V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.9
Figure# 7.9 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 15V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.10
Figure# 7.10 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 20V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.11
Figure# 7.11 Simulation
Build the figure 7.2 by using resistor of 2.2Kohm and 4.7Kohm and Zener diodes.
When the input Voltage is 2V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.12
Figure# 7.12 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 5V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.13
Figure# 7.13 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 10V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.14
Figure# 7.14 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 15V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.15
Figure# 7.15 Simulation
When the input Voltage is 20V then the output across Zener Diode is in figure 7.16
Figure# 7.16 Simulation
You might also like
- 5V DC Power SupplyDocument6 pages5V DC Power SupplyTarik Imran100% (2)
- Determine Whether The Ideal Diode of Figure 1 Is ConductingDocument10 pagesDetermine Whether The Ideal Diode of Figure 1 Is Conductingserkan1234No ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Zener Diode Voltage RegulationDocument11 pagesLab 3 - Zener Diode Voltage Regulationeyob100% (1)
- Electronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Document34 pagesElectronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Kylle SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- Yanbu University College: Electronics (CSE 252)Document6 pagesYanbu University College: Electronics (CSE 252)Raed AlRuwaili100% (1)
- Laboratory #1 Power Diode CharacteristicsDocument11 pagesLaboratory #1 Power Diode CharacteristicsJohn Laurence Gonzaga AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Study of Zener Diode As A Voltage RegulatorDocument4 pagesStudy of Zener Diode As A Voltage RegulatorVolodya Smolyak33% (3)
- LBYEC76 Experiment 2Document22 pagesLBYEC76 Experiment 2Yob YnnosNo ratings yet
- 183 Eee202s Exp1Document13 pages183 Eee202s Exp1Shamsul HaqueNo ratings yet
- BEE NPTEL NotesDocument183 pagesBEE NPTEL NotesMahesh PatilNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Semiconductor Diodes and Applications P-N Junction Diode Characteristics and ParametersDocument14 pagesUNIT-1 Semiconductor Diodes and Applications P-N Junction Diode Characteristics and ParametersPRATHAP_CNo ratings yet
- Ecr207 L7Document14 pagesEcr207 L7Md Mahamudul Hasan HimelNo ratings yet
- Diode CircuitsDocument23 pagesDiode CircuitsSurendra BachinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 (Analogue Electronics I)Document8 pagesLecture 4 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 ZenerDocument12 pagesLab 2 ZenerDoaa HegazyNo ratings yet
- Eletronics Lab Report - Zener DiodesDocument3 pagesEletronics Lab Report - Zener DiodesThan Lwin Aung71% (7)
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial 4Document5 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial 4Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Sir HenryDocument4 pagesExp 2 Sir HenryPercival Cylas CabralesNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 02Document4 pagesExperiment No 021101 MilonNo ratings yet
- 6.zener Diode As A Voltage RegulatorDocument3 pages6.zener Diode As A Voltage Regulatorshakti sindhuNo ratings yet
- Constant Voltage and Current Power Supply Circuit Design Using BJT and Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesConstant Voltage and Current Power Supply Circuit Design Using BJT and Zener DiodeArct John Alfante ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Tutorials Sheet No 1 Phys 225 Nasey Fev 2021Document5 pagesTutorials Sheet No 1 Phys 225 Nasey Fev 2021jordantoulepiNo ratings yet
- 1 ADocument50 pages1 AArunkuma81No ratings yet
- Lab09 DiodesDocument13 pagesLab09 DiodesChandru BadachiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Study of V - I Characteristics of Zener Diode and Determine Its Voltage Regulation.Document7 pagesExperiment 7 Study of V - I Characteristics of Zener Diode and Determine Its Voltage Regulation.Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diode ProblemsDocument9 pagesDiode ProblemsAravind KarthikNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 P-N DiodeDocument5 pagesLab 01 P-N DiodeyayayehNo ratings yet
- Diode ClipperDocument2 pagesDiode ClipperDr-Jihad BaghdadiNo ratings yet
- M.ABDULLAH FA19-BEE-110 Electronic 1 Lab 2 PDFDocument12 pagesM.ABDULLAH FA19-BEE-110 Electronic 1 Lab 2 PDFAtyia JavedNo ratings yet
- Choo Diode ApplicationDocument10 pagesChoo Diode ApplicationSeanNo ratings yet
- Positive ClamperDocument5 pagesPositive ClamperSudip MondalNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 - Practic Set - With - SolutionDocument13 pagesUnit-5 - Practic Set - With - Solutionantprash727No ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics: I-TheoryDocument4 pagesDiode Characteristics: I-TheoryShubham PatelNo ratings yet
- Zener DRDocument4 pagesZener DRArchana SadanandanNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document6 pagesExp 2MohammedZahidNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument8 pagesAssignment IIArchie BharatriNo ratings yet
- Experimentally Study The IV Curves of DiodeDocument5 pagesExperimentally Study The IV Curves of DiodeMuhammad Tehreem100% (1)
- ELTR 270 - Diode Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument33 pagesELTR 270 - Diode Practice Problems and SolutionsKirk100% (1)
- Lect 16 19EEE111 Rectifier and Zener DiodeDocument38 pagesLect 16 19EEE111 Rectifier and Zener DiodeDenifer DeepNo ratings yet
- Diode ClampersDocument10 pagesDiode ClamperswaleedNo ratings yet
- BEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 6Document31 pagesBEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 6Girish Shankar MishraNo ratings yet
- Takehome 4604Document8 pagesTakehome 4604Hansika KarunathilakeNo ratings yet
- Discussion:: R1 D. R1 DDocument3 pagesDiscussion:: R1 D. R1 DHaziq KlNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Zener DiodDocument34 pagesLab Report - Zener Diodانوارالدين محمد قاسم100% (1)
- Physics PROJ On ZENERDocument10 pagesPhysics PROJ On ZENER04-ADRITO GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Lab ZenerDocument7 pagesLab ZenerMalicke CaseNo ratings yet
- Solution Sheet 1 Electronic CircuitsDocument13 pagesSolution Sheet 1 Electronic CircuitsWajdi BELLILNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2013 SolutionDocument5 pagesMidterm 2013 SolutionArunabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 7 JFET CharacteristicsDocument22 pages7 JFET CharacteristicsAnsar AnsarNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply: King Abdulaziz University Electronics IDocument20 pagesDC Power Supply: King Abdulaziz University Electronics IMohannad S. AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode - Its Principle Working and Example UsageDocument21 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode - Its Principle Working and Example UsageferdinandNo ratings yet
- ECE590 - Tutorial 3 (UiTM)Document5 pagesECE590 - Tutorial 3 (UiTM)NazhammerheartNo ratings yet
- L05 CCE 301 Special Diode CircuitsDocument15 pagesL05 CCE 301 Special Diode CircuitsZakaria MtairekNo ratings yet
- ECE20L - 2 - Expt3Document17 pagesECE20L - 2 - Expt3Niko de LemosNo ratings yet
- Diode Equivalent CircuitsDocument3 pagesDiode Equivalent Circuitssean ballocanagNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems On Semiconductor DiodeDocument8 pagesSolved Problems On Semiconductor DiodeAravind KarthikNo ratings yet
- ECE20L - 2 - Expt7 - DE LEMOS PDFDocument10 pagesECE20L - 2 - Expt7 - DE LEMOS PDFNiko de LemosNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document10 pagesExp 2Enas QtaifanNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Do YrDocument18 pagesDe Do YrFawad Shakil AsgharNo ratings yet
- InspiringDocument10 pagesInspiringFawad Shakil AsgharNo ratings yet
- Title: Hormonal Regulation in Mammalian BodyDocument6 pagesTitle: Hormonal Regulation in Mammalian BodyFawad Shakil AsgharNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument7 pagesProject ReportFawad Shakil Asghar100% (1)
- Quantitative Estimation of Pentose Sugar Present in The Given Solution of Carbohydrates by Bials TesDocument8 pagesQuantitative Estimation of Pentose Sugar Present in The Given Solution of Carbohydrates by Bials TesFawad Shakil Asghar100% (1)
- Find The Latest Mobile Prices in Pakistan - PriceOyeDocument2 pagesFind The Latest Mobile Prices in Pakistan - PriceOyeFawad Shakil AsgharNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Estimation of Pentose Sugar Present in The Given Solution of Carbohydrates by Bials TesDocument12 pagesQuantitative Estimation of Pentose Sugar Present in The Given Solution of Carbohydrates by Bials TesFawad Shakil Asghar100% (1)
- AislabDocument10 pagesAislabFawad Shakil AsgharNo ratings yet
- Shayan Lab 5 EeDocument4 pagesShayan Lab 5 EeFawad Shakil AsgharNo ratings yet