0% found this document useful (0 votes)
422 views33 pagesTeaching Philosophies & Development
1. The document discusses 5 lessons related to personal growth and professional development for teachers. The lessons cover different philosophies of teaching, teaching as a profession, professional links with colleagues, professional reflection, and professional development goals.
2. Key points from the lessons include different categories of teaching philosophies like teacher-centered vs student-centered, qualities of effective teachers, benefits of collaboration among teachers, importance of reflective practice to improve teaching, and how teachers' professional goals change at different stages of their career.
3. The lessons provide guidance to help teachers understand philosophies that guide their practices, develop as professionals through collaboration and reflection, and determine goals for continuous learning and growth in their career.
Uploaded by
Neliza SalcedoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
422 views33 pagesTeaching Philosophies & Development
1. The document discusses 5 lessons related to personal growth and professional development for teachers. The lessons cover different philosophies of teaching, teaching as a profession, professional links with colleagues, professional reflection, and professional development goals.
2. Key points from the lessons include different categories of teaching philosophies like teacher-centered vs student-centered, qualities of effective teachers, benefits of collaboration among teachers, importance of reflective practice to improve teaching, and how teachers' professional goals change at different stages of their career.
3. The lessons provide guidance to help teachers understand philosophies that guide their practices, develop as professionals through collaboration and reflection, and determine goals for continuous learning and growth in their career.
Uploaded by
Neliza SalcedoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
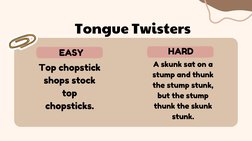
- Personal Growth and Professional Development: Introduces the overarching theme of personal and professional development in the context of teaching.