Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MAS Tutorial 2A Solutions
Uploaded by
Yashasvi RawatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MAS Tutorial 2A Solutions
Uploaded by
Yashasvi RawatCopyright:
Available Formats
AMA1003 Mathematics for Applied Science
Topic 2 Functions
Tutorial 2A – Solutions
1. Examine the following diagrams and determine if they are one-one functions.
y y
(a) (d)
0 x 0 x
Not One-one function Not One-one function
y y
(b) (e)
0 x 0 x
Not One-one function One-one function
y y
(c) (f)
0 x 0 x
Not One-one function Not One-one function
AMA1003 Mathematics for Applied Science/Tutorial 2A 1
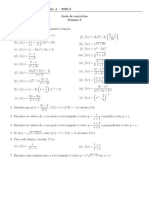
2. Given f(x) = x and g(x) = x 3 , evaluate the following:
(a) f −1 (x) (f) gf(x)
f −1 (x) = 𝐱 gf(x) = 𝐱 𝟑
(b) g −1 (x) (g) f −1 g(x)
𝟑
g −1 (x) = √𝐱 f −1 g(x) = 𝐱 𝟑
(c) f 2 (x) (h) g −1 f(x)
f 2 (x) = (x) = 𝐱 3 𝟑
g −1 f(x) = √(x) = √𝐱
(d) g 2 (x) (i) f(x) ∙ g(x)
g 2 (x) = (x 3 )3 = 𝐱 𝟗 f(x) ∙ g(x) = x ∙ x 3 = 𝐱 𝟒
(e) fg(x) (j) gg −1 (x)
3
fg(x) = (x)3 = 𝐱 𝟑 3
gg −1 (x) = ( √x) = 𝐱
3. Determine the composite function fg(x) and fg(1) of the following functions:
f(x) = 2x + 3 f(x) = x 2 + 2
(a) (b)
g(x) = x 2 + 5 g(x) = x + 4
fg(x) = f(x 2 + 5) = 2(x 2 + 5) + 3 = 𝟐𝐱 𝟐 + 𝟏𝟑
(a)
fg(1) = 2(1)2 + 13 = 𝟏𝟓
fg(x) = f(x + 4) = (𝐱 + 𝟒)𝟐 + 𝟐
(b)
fg(1) = (1 + 4)2 + 2 = 𝟐𝟕
AMA1003 Mathematics for Applied Science/Tutorial 2A 2
4. Given that f(x) = 4 + 3x and g(x) = x 3 . Determine the following:
(a) fg(x) and fg(1) (b) gf(x) and gf(1)
fg(x) = f(x 3 ) = 4 + 3(x 3 ) = 𝟒 + 𝟑𝐱 𝟑
(a)
fg(1) = 4 + 3(1)3 = 𝟕
gf(x) = g(4 + 3x) = (𝟒 + 𝟑𝐱)𝟑
(b)
gf(1) = [4 + 3(1)]3 = 𝟑𝟒𝟑
3
5. Given f(x) = x−2 and g(x) = √x + 2.
(a) Write down the domain for f(x) and g(x).
(b) Find fg(x) and gf(x).
(c) Write down the domain for fg(x) and gf(x).
Domain for 𝐟(𝐱), 𝒙 ≠ 𝟐
(a)
Domain for 𝐠(𝐱), 𝒙 ≥ −𝟐
𝟑
fg(x) = (√𝐱+𝟐)−𝟐
(b)
3 3+2𝑥−4 𝟐𝒙−𝟏
gf(x) = √(x−2) + 2 = √( ) = √ 𝒙−𝟐
𝑥−2
Domain for 𝐟𝐠(𝐱): 𝐱 ≥ −𝟐, 𝐱 ≠ 𝟐
(c) 𝟏
Domain for 𝐠𝐟(𝐱): 𝐱 ≤ 𝐨𝐫 𝐱 > 𝟐
𝟐
4
6. Given that p(x) = √x + 8, determine if the following function input values, p(−24) and
p(248) are in the domain of the function. Write down the domain of the function.
4
p(−24) = √−24 + 8 = 𝐮𝐧𝐝𝐞𝐟𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐝
Since 𝐩(−𝟐𝟒) is undefined, 𝒙 = −𝟐𝟒 is NOT in the domain of 𝐩(𝐱).
4
p(248) = √248 + 8 = 𝟒
Since 𝐩(𝟐𝟒𝟖) is real, 𝒙 = 𝟐𝟒𝟖 is in the domain of 𝐩(𝐱).
Domain for 𝐩(𝐱): 𝐱 ≥ −𝟖
AMA1003 Mathematics for Applied Science/Tutorial 2A 3
7. Find the inverse function of the following:
(a) f(x) = 3x 3 + 3 (b) g(x) = 8x 2 + 5
(c) f(x) = 5x − 7 (d) f(x) = 3 + 4x 2 , x < 0
(a) f(x) = 3x 3 + 3
Method 1 Method 2
Let y = 3x 3 + 3 f(x) = 3x 3 + 3
3x 3 + 3 = y Let y = 𝑓 −1 (𝑥)
3x 3 = y − 3 f(y) = 3y 3 + 3
y−3 x = 3y 3 + 3
x3 =
3
−𝟏 (𝐱)
𝒙 − 𝟑 𝟏/𝟑
𝐲=𝐟 =[ ]
y − 3 1/3 3 y − 3 𝟑
x= ( ) =√
3 3
−𝟏
𝐱 − 𝟑 𝟏/𝟑 𝟑 𝐱 − 𝟑
𝐟 (𝐱) = ( ) =√
𝟑 𝟑
(b) g(x) = 8x 2 + 5
Method 1 Method 2
Let y = 8x 2 + 5 g(x) = 8x 2 + 5
8𝑥 2 = 𝑦 − 5 Let y = g −1 (x)
1 g(y) = 8x 2 + 5
𝑦−5 2 𝑦−5
x=( ) =√ x = 8𝑦 2 + 5
8 8
𝟏
𝟏 𝒙−𝟓 𝟐
𝒙−𝟓 𝒙−𝟓
𝟐 𝒚 = 𝒈−𝟏 (𝒙) = ( )
𝐠 −𝟏 (𝐱) = ( ) =√ 𝟖
𝟖 𝟖
AMA1003 Mathematics for Applied Science/Tutorial 2A 4
(c) f(x) = 5x − 7
Method 1 Method 2
Let y = 5x − 7 f(x) = 5x − 7
5x = y + 7 Let y = f −1 (x)
y+7 f(y) = 5y − 7
x=
5 x = 5y − 7
𝐱+𝟕 𝐱+𝟕
𝐟 −𝟏 (𝐱) = 𝐲 = 𝐟 −𝟏 (𝐱) =
𝟓 𝟓
(d) f(x) = 3 + 4x 2 , x < 0
Method 2
Method 1
f(x) = 3 + 4x 2
2
Let y = 3 + 4x
Let y = f −1 (x)
y−3
x2 = f(y) = 3 + 4y 2
4
1 x = 3 + 4y 2
y−3 y−32
x=( ) =√ 𝟏
4 4 𝐱−𝟑 𝟐
𝑦 = 𝐟 −𝟏 (𝐱) = ( )
𝟏
𝟒
𝐱−𝟑 𝟐 𝐱−𝟑
𝐟 −𝟏 (𝐱) = ( ) =√ 𝐱−𝟑
𝟒 𝟒 =√
𝟒
AMA1003 Mathematics for Applied Science/Tutorial 2A 5
8. The function f(x) is defined by f(x) = x 2 + 2x − 3.
(a) Prove that f(x) is not a one-one function.
(b) Does the inverse function f −1 (x) exists?
(c) Write down the domain of f(x) such that f −1 (x) exists.
(a)
Not one-one function
(b) 𝐟 −𝟏 (𝐱) does not exist.
Domain of 𝐟(𝐱): 𝐱 𝛜 𝐑, 𝐱 ≥ −𝟏
(c) Domain of 𝐟(𝐱): 𝐱 𝛜 𝐑, 𝐱 ≤ −𝟏
AMA1003 Mathematics for Applied Science/Tutorial 2A 6
You might also like
- TRACK B Module 4 - Transcendental FunctionsDocument11 pagesTRACK B Module 4 - Transcendental FunctionsARIANNA YSABEL CHANNo ratings yet
- Chain RuleDocument4 pagesChain RuleJivan KaprielianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.3 - Relation and FunctionDocument12 pagesChapter 2.3 - Relation and FunctionPoeil Sergio MoldezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Operations On FunctionsDocument17 pagesLesson 4 Operations On FunctionsCelestine LunaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Operations On FunctionsDocument17 pagesLesson 4 Operations On FunctionsCelestine LunaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Week 1Document7 pagesGen Math Week 1France Dave Mercado MadrigalNo ratings yet
- ListaS6 CalculoA 2020-2Document2 pagesListaS6 CalculoA 2020-2Yasmin SeloisNo ratings yet
- HK2 2022Document5 pagesHK2 2022lasma.dundureNo ratings yet
- MPE Review: Logarithmic & Exponential FunctionsDocument38 pagesMPE Review: Logarithmic & Exponential FunctionsonyejekweNo ratings yet
- Local Media22262561799390700Document2 pagesLocal Media22262561799390700hence manelsNo ratings yet
- Sample Quiz 1Document3 pagesSample Quiz 1Yogeneswari AppalasamyNo ratings yet
- Real Functions ExercisesDocument2 pagesReal Functions ExercisesИРадојичићNo ratings yet
- MATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 2Document2 pagesMATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 2malafikokamilNo ratings yet
- Paso1 IndividualDocument5 pagesPaso1 IndividualNatalia GuerraNo ratings yet
- MSM 131 Tutorial Sheet 2Document3 pagesMSM 131 Tutorial Sheet 2Kingsley MweembaNo ratings yet
- Composite and Inverse FunctionsDocument12 pagesComposite and Inverse FunctionsAnonymous yPCsBWJG9No ratings yet
- Set 1Document4 pagesSet 1Ka Ho WongNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument4 pagesReviewerjoshua bautistaNo ratings yet
- Functions Example 1:: G (X) Under G. X and G (X) 2x. in This Case, H A H A H A FDocument6 pagesFunctions Example 1:: G (X) Under G. X and G (X) 2x. in This Case, H A H A H A FOGEGA KERUBONo ratings yet
- Calculus IDocument84 pagesCalculus IAli MaithaNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 GenmathDocument35 pagesLesson2 GenmathAshley IgnoNo ratings yet
- MA5158 Practice Problems-Unit2Document3 pagesMA5158 Practice Problems-Unit2Mithun arjunNo ratings yet
- Aljabar Fungsi dan Komposisi FungsiDocument3 pagesAljabar Fungsi dan Komposisi FungsiAl FandiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledBrenNo ratings yet
- MATH 131 Tutorial 2 2024Document2 pagesMATH 131 Tutorial 2 2024jamakonke8No ratings yet
- Some Fundamental Types of FunctionsDocument12 pagesSome Fundamental Types of Functionsdana alharbiNo ratings yet
- Gabarito Mate 1 GSIDocument8 pagesGabarito Mate 1 GSIDathan NobregaNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS AND COMBINATIONSDocument13 pagesFUNCTIONS AND COMBINATIONSke jia lieuwNo ratings yet
- Math 103 Take-Home Quiz 5Document4 pagesMath 103 Take-Home Quiz 5Brandon CabjuanNo ratings yet
- Math 31 Chapter 10 and 11 LessonsDocument26 pagesMath 31 Chapter 10 and 11 LessonsSam PanickerNo ratings yet
- Notas de Matemáticas - Lista Funciones ElementalesDocument3 pagesNotas de Matemáticas - Lista Funciones ElementalesMickey BMNo ratings yet
- 2019 A M151 X2 AexamDocument10 pages2019 A M151 X2 AexambeefchuckbeefNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading GenMath 2019-2020 v2Document4 pages1st Grading GenMath 2019-2020 v2Mariel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- I. Illustrate The Tangent Line To The Graph of A Function at A Given PointDocument5 pagesI. Illustrate The Tangent Line To The Graph of A Function at A Given Pointrandom potatoNo ratings yet
- M106 Worktext Ch2.Lesson 2Document16 pagesM106 Worktext Ch2.Lesson 2Raymond GarciaNo ratings yet
- GCSEAndIGCSEFM FunctionsDocument5 pagesGCSEAndIGCSEFM FunctionsQWERTYNo ratings yet
- Honors Algebra 2 Inverse Functions ReviewDocument8 pagesHonors Algebra 2 Inverse Functions ReviewMay JayyyNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 - Rules of DerivativesDocument7 pagesCalculus 1 - Rules of DerivativeswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-1 (YMT2002)Document3 pagesProblem Sheet-1 (YMT2002)munnisujliNo ratings yet
- MAT1110 Tutorial 3Document3 pagesMAT1110 Tutorial 3daisymbewe8No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5veen jhana sekaranNo ratings yet
- Calculus1PracticeMidterm1 SolDocument12 pagesCalculus1PracticeMidterm1 SolNgan PhanNo ratings yet
- 1121期中考模擬試題Document3 pages1121期中考模擬試題darron1220No ratings yet
- TOPIC DETAILS 4 POOL 3 Edited VersionDocument7 pagesTOPIC DETAILS 4 POOL 3 Edited VersionUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Worksheet II For Math For NSDocument3 pagesWorksheet II For Math For NSGaaddisaa UsmaanNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Test For Lessons 23 MIDTERMDocument14 pagesAlgebra 2 Test For Lessons 23 MIDTERMqwertyNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math CH 1Document2 pagesDiscrete Math CH 1RS Fashion HouseNo ratings yet
- Functions Its OperationsDocument58 pagesFunctions Its OperationsGame AccountNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-25 9 12-MorpheusDocument148 pagesChapter1-25 9 12-MorpheushauzhiNo ratings yet
- Managerial Mathematics Tutorial 1 FunctionsDocument2 pagesManagerial Mathematics Tutorial 1 FunctionshanisNo ratings yet
- Lista 2-0Document3 pagesLista 2-0guilhermeoliveiramendona123No ratings yet
- HK5 Assigment 5Document3 pagesHK5 Assigment 5lasma.dundureNo ratings yet
- Activity. Relations and FunctionsDocument5 pagesActivity. Relations and FunctionsjejejeNo ratings yet
- Template Week 01Document35 pagesTemplate Week 01Yazish KavinaNo ratings yet
- The Algebra of FunctionsDocument4 pagesThe Algebra of FunctionsMeco BartidoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Advanced Algebra Week 5Document3 pagesGrade 10 Advanced Algebra Week 5Breindell NovoNo ratings yet
- MATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 7: Differentiation RulesDocument3 pagesMATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 7: Differentiation RulesmalafikokamilNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document2 pagesTut 1Batrisya LeeNo ratings yet
- Math 176 Worksheet 1 2011Document2 pagesMath 176 Worksheet 1 2011Greg Levy LevyNo ratings yet
- Shilpa Bhangaleand MMPawarDocument7 pagesShilpa Bhangaleand MMPawarVaishaliNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 10 PDB Orde 2 Tak HomogenDocument7 pagesKuliah 10 PDB Orde 2 Tak HomogenSiti SaraNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform TableDocument2 pagesLaplace Transform TableSuksmatatya ParamestiNo ratings yet
- Rwanda University Module on General and Applied MathematicsDocument166 pagesRwanda University Module on General and Applied MathematicsMasengesho ishimwe PatienceNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Applied Linear Algebra: International University-National University Hochiminh CityDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Applied Linear Algebra: International University-National University Hochiminh CityTrâm TrầnNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Through Solver Tool in ExcelDocument16 pagesLinear Programming Through Solver Tool in Excelami402t0% (1)
- Full Test IDocument7 pagesFull Test IRahul JainNo ratings yet
- MATH1080Document695 pagesMATH1080AaronJay JimankgeNo ratings yet
- Eigen Values & Eigen VectorsDocument34 pagesEigen Values & Eigen VectorsSNEHA AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Course Outline of BS Mathematics in UoKDocument46 pagesCourse Outline of BS Mathematics in UoKMahroz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 5BDocument2 pagesLecture Note 5BRAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- EXAM SOLUTIONSDocument2 pagesEXAM SOLUTIONSNur RafizahNo ratings yet
- Antidifferentiation PDFDocument8 pagesAntidifferentiation PDFDenise Ann CuencaNo ratings yet
- Taylor's TheoremDocument4 pagesTaylor's TheoremTu ShirotaNo ratings yet
- AP 微积分BC Open NoteDocument34 pagesAP 微积分BC Open Note292397677lhxNo ratings yet
- 4024 - 2nd Monthly 2022 - Paper - Maths L1 D1 Chap 5Document2 pages4024 - 2nd Monthly 2022 - Paper - Maths L1 D1 Chap 5Adnan MoeenNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Matrices Index:: Please Click On The Question Number You WantDocument17 pagesIGCSE Matrices Index:: Please Click On The Question Number You WantNad HsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - IVDocument4 pagesMathematics - IVAtish GhoshNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Rotation in Time-Frequency PlaneDocument8 pagesFourier Transform Rotation in Time-Frequency PlaneSatish NaiduNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 OMT 115 PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 5 OMT 115 PDFShaboy De MarionNo ratings yet
- On The Series Å K 1 (3kk) - 1k-nxkDocument11 pagesOn The Series Å K 1 (3kk) - 1k-nxkapi-26401608No ratings yet
- 53205-mt - Optimization TechniquesDocument2 pages53205-mt - Optimization TechniquesSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Oct 2022 P2 QPDocument32 pagesOct 2022 P2 QPZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- PDEDocument39 pagesPDEchandra kantNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-Diagnostic TestDocument7 pagesGrade 10-Diagnostic TestCadigal RoniloNo ratings yet
- 4512 Review2SolutionsDocument4 pages4512 Review2SolutionsaminNo ratings yet
- Competitive Programming - CodeChefDocument9 pagesCompetitive Programming - CodeChefsujith kumarNo ratings yet
- W s-2 Foundation of SetsDocument2 pagesW s-2 Foundation of Setsapi-253679034No ratings yet
- LESSON 8.1:: Rizal National Science High SchoolDocument18 pagesLESSON 8.1:: Rizal National Science High Schooltrisha paclebNo ratings yet
- GenMath Week 6Document2 pagesGenMath Week 6MarlaFirmalino83% (6)