Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summarized Ms
Uploaded by
sooyahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summarized Ms
Uploaded by
sooyahCopyright:
Available Formats
NCM1331L | MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING – LECTURE (SUMMARIZED)
MIDTERMS – CARDIO
MR. ROBERT P. ORDONA RM, RN – SCHOOL OF NURSING | 1st SEMESTER A.Y. 2023 - 2024
Week 1:
ASSESSMENT AND
MANAGEMENT FOR
PATIENTS WITH CVD
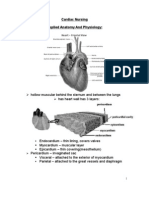
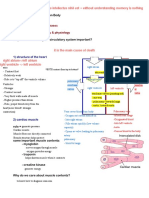
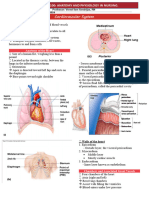
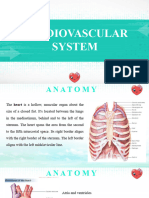
Major function of the heart: Pumps blood to the
tissues supplying them with oxygen and other nutrients
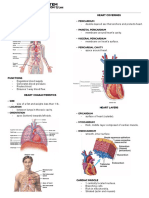
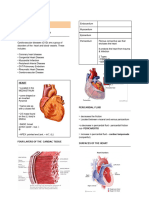
LAYERS OF THE HEART
HEART VALVES
ATRIOVENTRICULA SEMILUNAR
R
1. Mitral (bicuspid) 1. Aortic
2. Tricuspid 2. Pulmonic
CORONARY ARTERIES
HEART CHAMBERS
LEFT CORONARY RIGHT CORONARY
ARTERY ARTERY
a. Left anterior a. Posterior
descending descending
artery artery
b. Left circumflex
artery
PERFUSED DURING DIASTOLE
CORONARY VEINS
Venous blood from these veins returns to the heart
primarily through the CORONARY SINUS
SYSTOLE DIASTOLE Located posteriorly in the right atrium
(CONTRACTION, (RELAXATION,
DEPOLARIZATION) REPOLARIZATION)
- Isovolumetric - Isovolumetric
CONTRACTI RELAXATION
ON phase phase
- EJECTION - FILLING phase
phase
HEART VALVES CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGY
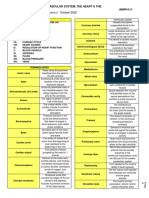
CARDIAC CONDUCTION SYSTEM
NCM1331L | MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING – LECTURE (SUMMARIZED)
MIDTERMS – CARDIO
MR. ROBERT P. ORDONA RM, RN – SCHOOL OF NURSING | 1st SEMESTER A.Y. 2023 - 2024
3. Pulse
4. Paralysis
5. Pressure
6. Pain
Generates and transmits electrical impulses that
stimulate contraction of the myocardium
CARDIAC CONDUCTION SYSTEM
SA NODE Dominant pacemaker of the
hearth
Direct electrical impulses
between SA and AV node
AV NODE Slows conduction
Creates slight delay in impulses
before they reach the ventricles
COMMO Transmits impulses to bundle
N branches
BUNDLE
OF HIS
L&R Left conducts impulses to left
BUNDLE ventricle
OF HIS Right conducts impulses to right
ventricle
PURKINJ Network of fibers that spreads
E FIBERS impulses rapidly
4 CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICAL
IMPULSES
AUTOMACIT Ability of the cell to initiate
Y impulse spontaneously
EXCITABILIT How well the cell responds to
Y electrical stimuli
CONDUCTIVI Ability of the cell to transmit an
TY electrical impulse to another
cardiac cell
CONTRACTIL How well a cell contracts after
ITY receiving a stimulus
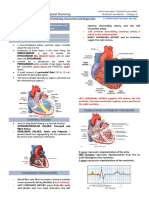
ASSESSING CHEST PAIN
ANGINA Pain spreading across chest
PECTORIS - Bought about by
myocardial ischemia
MYOCARDIA Pain over precordium
L
INFARCTION
PERICARDITI Sharp, severe, substernal pain to
S the left of sternum
PLEAURITIC Pain arises from inferior portion of
PAIN pleura; referred to COSTAL
MARGINS or UPPER
ABDOMEN.
ESOPHAGEA Chest to shoulders
L PAIN
ANXIETY Pain does not radiate
6 Ps
1. Pallor
2. Paresthesia
You might also like
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasFrom EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Wilson, D.S., Hayes, S.C. & Biglan, A. (2018). Evolution and contextual behavioral science an integrated framework for understanding, predicting and influencing human behavior. Oakland Context Press..pdfDocument390 pagesWilson, D.S., Hayes, S.C. & Biglan, A. (2018). Evolution and contextual behavioral science an integrated framework for understanding, predicting and influencing human behavior. Oakland Context Press..pdfjesus100% (3)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Sistema de Conduccion Karen Daniela VelascoDocument3 pagesSistema de Conduccion Karen Daniela Velascoapi-540316757No ratings yet
- Assessing Heart and Neck Vessel Heart Heart Chambers: (Tricuspid & Bicuspid)Document7 pagesAssessing Heart and Neck Vessel Heart Heart Chambers: (Tricuspid & Bicuspid)Dan Floyd FernandezNo ratings yet
- Managing Cardiac Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument29 pagesManaging Cardiac Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsYlanni Coritana100% (1)
- Heart AnatomyDocument178 pagesHeart AnatomysubbuNo ratings yet
- The Heart & Mediastinum: A Fixed Learning Module 2009 Compiled by Assoc Prof DR Hamiadji TanuseputroDocument40 pagesThe Heart & Mediastinum: A Fixed Learning Module 2009 Compiled by Assoc Prof DR Hamiadji TanuseputroQiqin DechrifentoNo ratings yet
- A234 ElectrocardiogramsDocument4 pagesA234 Electrocardiogramsramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Sistema de ConduccionDocument5 pagesSistema de Conduccionapi-543828470No ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy of The Heart - StudentDocument38 pagesApplied Anatomy of The Heart - StudentNatalia RomanNo ratings yet
- CARDIOLOGYDocument15 pagesCARDIOLOGYPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- The Blood and Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesThe Blood and Circulatory SystemChandria ChandriaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Mcon 01 (Lec) A4Document6 pagesCardiovascular System - Mcon 01 (Lec) A4Lemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Sample Transes 2Document11 pagesSample Transes 2Sophia SalamatNo ratings yet
- CARDIODocument17 pagesCARDIORayana Ubas100% (1)
- Dr. Alurkur's Book On Cardiology - 2Document85 pagesDr. Alurkur's Book On Cardiology - 2Bhattarai ShrinkhalaNo ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy & Development in the Middle MediastinumDocument42 pagesHeart Anatomy & Development in the Middle MediastinumVidya BalaNo ratings yet
- External Heart: Arteries That Supply The HeartDocument67 pagesExternal Heart: Arteries That Supply The HeartCliff ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Electrical SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System - Electrical SystemRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Heart and Its External Features For Paramedical StudentsDocument26 pagesHeart and Its External Features For Paramedical Studentslakshmiraman1770No ratings yet
- Cardiac NursingDocument26 pagesCardiac Nursingjgcriste95% (20)
- CV 2 PHDocument22 pagesCV 2 PHaya najemNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cardiovascular System Lecture Outline 1st PeriodDocument16 pagesKami Export - Cardiovascular System Lecture Outline 1st PeriodJada NovakNo ratings yet
- 1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood VesselsDocument9 pages1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood Vessels13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Conduction of The HeartDocument1 pageConduction of The HeartPearlyn John BrittoNo ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation Learning The Basic-JmjDocument89 pagesEcg Interpretation Learning The Basic-JmjJerico Jaranilla100% (1)
- MS NursingDocument75 pagesMS NursingMary Vi IletoNo ratings yet
- w2 Part 1Document30 pagesw2 Part 1farahafiqahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument35 pagesCardiovascular Systemdelacruzchristinejoie.kldNo ratings yet
- Kasus 6 (ADHF Grade II + NSTEMI + HHD + Dislipidemia) - Blok CVS - Tingkat 2 - NRP 1910211099 - REZA RAMADHANSYAHDocument34 pagesKasus 6 (ADHF Grade II + NSTEMI + HHD + Dislipidemia) - Blok CVS - Tingkat 2 - NRP 1910211099 - REZA RAMADHANSYAHReza RamadhansyahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Document26 pagesAnatomy - Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Avi ZychNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Document26 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Buku Saku Pemeriksaan EkgDocument21 pagesBuku Saku Pemeriksaan Ekgpaskah dhNo ratings yet
- 2023 DEFIBRILLATOR 2PDocument58 pages2023 DEFIBRILLATOR 2Ptsarayuth1.2017No ratings yet
- CHAP11Document12 pagesCHAP11Crystal ARIETANo ratings yet
- Crat - Cardio PulmoDocument11 pagesCrat - Cardio PulmoJULIANE MAE BALANGNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument5 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Jantung Lapisan JantungDocument21 pagesAnatomi Jantung Lapisan JantungirineNo ratings yet
- Preview of "Practice Quiz - Heart"Document2 pagesPreview of "Practice Quiz - Heart"Jose Pagan100% (1)
- Heart Valves & CirculationDocument4 pagesHeart Valves & Circulationyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Heart PDFDocument5 pagesMammalian Heart PDFKhaled TurkNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Radiology: FEU-NRMF College of Medicine 2020Document14 pagesCardiac Radiology: FEU-NRMF College of Medicine 2020Shekinah MalimbanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CVSDocument3 pagesIntroduction To CVSapi-3829364No ratings yet
- MS Term 1Document7 pagesMS Term 1Abegail QuintoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Ana & DxticsDocument3 pagesCardiac Ana & Dxticsjames garciaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Sytem of The CatDocument3 pagesCirculatory Sytem of The CatIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cardiovascular SystemDocument36 pagesThe Embryology and Anatomy of the Cardiovascular SystemSofia Nurfadilla BasriNo ratings yet
- Neurologic ComplicationsDocument24 pagesNeurologic ComplicationsMau MillanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Cardiovascular SystemKezzel Grace MaquillaNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsDocument7 pagesPRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- CH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument21 pagesCH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartMadhuri DandamudiNo ratings yet
- The Heart's Chambers and ValvesDocument29 pagesThe Heart's Chambers and ValvesomarNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT CARDIOVASCULARDocument7 pagesASSESSMENT CARDIOVASCULARleih jsNo ratings yet
- FiSIOLOGI JANTUNG ONI Pertemuan 4Document48 pagesFiSIOLOGI JANTUNG ONI Pertemuan 4Ria Fauziah SiswadiNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Cyanide Clean-Up at Chumbwe Gold Mine in ZambiaDocument19 pagesCyanide Clean-Up at Chumbwe Gold Mine in ZambiaRamoutar (Ken) SeecharranNo ratings yet
- Iso 16140 Validation by Afnor On TVC TC and Ec Adria-2 PDFDocument1 pageIso 16140 Validation by Afnor On TVC TC and Ec Adria-2 PDFJuliet RomeroNo ratings yet
- Tips - Microbiology of Meat and Poultry PDFDocument332 pagesTips - Microbiology of Meat and Poultry PDFFadhili DungaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate - MonosaccharidesDocument3 pagesCarbohydrate - MonosaccharidesCheong Yong XuanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1871678419304418 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S1871678419304418 MainGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Bot 121Document4 pagesBot 121Vikki NandeshwarNo ratings yet
- Fleck CVDocument4 pagesFleck CVRoger R. Gonzalo SeguraNo ratings yet
- EX-CELL® EBx® PRO-II Serum-Free Medium Without L-GlutamineDocument2 pagesEX-CELL® EBx® PRO-II Serum-Free Medium Without L-GlutamineSAFC-Global100% (1)
- PASTURE MANAGEMENT - Final PDFDocument101 pagesPASTURE MANAGEMENT - Final PDFDexter Andrew Lyken100% (1)
- M3.1. PTG and Calcium Homeostasis (CC2-LEC)Document5 pagesM3.1. PTG and Calcium Homeostasis (CC2-LEC)Hannah Elizabeth CastroNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 MycologyDocument3 pagesActivity 8 MycologyBrent Lee100% (1)
- Principles of Ecology: 1 Organisms and Their RelationshipsDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Ecology: 1 Organisms and Their RelationshipsRana AtefNo ratings yet
- Novel components of NAD pathways predictedDocument18 pagesNovel components of NAD pathways predictedGuillermo Domínguez HuertaNo ratings yet
- Clown Knifefish Ecological Risk Screening SummaryDocument13 pagesClown Knifefish Ecological Risk Screening SummaryAdi PutraNo ratings yet
- Chrysothemis PulchellaDocument2 pagesChrysothemis PulchellaTharayilsijNo ratings yet
- Package Insert - 06267 - LH - en - 30406 PDFDocument6 pagesPackage Insert - 06267 - LH - en - 30406 PDFadybaila4680No ratings yet
- MC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C03Document9 pagesMC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C03Camille HugoNo ratings yet
- Fantasy Becoming Reality at Kai Tak: On The MoveDocument2 pagesFantasy Becoming Reality at Kai Tak: On The MoveMonique HoNo ratings yet
- Test 3 (3)Document6 pagesTest 3 (3)Blabla HiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1A Hema LecDocument17 pagesQuiz 1A Hema LecAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Madhu VargDocument36 pagesMadhu VargYash GardhariyaNo ratings yet
- Recommended Herbs Per Infection According To Stephen BuhnerDocument3 pagesRecommended Herbs Per Infection According To Stephen BuhnerYannick HsNo ratings yet
- Time 120Document3 pagesTime 120ardhra pNo ratings yet
- Cladistics PDFDocument4 pagesCladistics PDFmanoj_rkl_07100% (1)
- ALL QB's PDFDocument36 pagesALL QB's PDFanimesh0gargNo ratings yet
- Los 12 Pilares de La Inteligencia, Adrian Owen PDFDocument6 pagesLos 12 Pilares de La Inteligencia, Adrian Owen PDFYasmina Itzel Murillo LopezNo ratings yet
- A) State and Describe Various Stages of A Biodegradation StudyDocument6 pagesA) State and Describe Various Stages of A Biodegradation StudyAbdulkadir AlbabaNo ratings yet
- 4d2a1 HD Adequacy Self StudyDocument31 pages4d2a1 HD Adequacy Self StudyWulan SuciNo ratings yet
- Spinal TraumaDocument81 pagesSpinal TraumaharilNo ratings yet