Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TUTORIAL 7 Semiconductor
TUTORIAL 7 Semiconductor
Uploaded by
Nur Aina Sofrina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis document contains 10 questions about p-n junction diodes and their usage in rectifier circuits:
1. It asks how the electric field is arranged across the p-n junction.
2. It asks to explain why the resistance of the p-n junction is low during forward bias and high during reverse bias.
3. It asks why the thickness of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode increases with increasing reverse bias.
Original Description:
tuto
Original Title
TUTORIAL 7 Semiconductor (3)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 10 questions about p-n junction diodes and their usage in rectifier circuits:
1. It asks how the electric field is arranged across the p-n junction.
2. It asks to explain why the resistance of the p-n junction is low during forward bias and high during reverse bias.
3. It asks why the thickness of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode increases with increasing reverse bias.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageTUTORIAL 7 Semiconductor
TUTORIAL 7 Semiconductor
Uploaded by
Nur Aina SofrinaThis document contains 10 questions about p-n junction diodes and their usage in rectifier circuits:
1. It asks how the electric field is arranged across the p-n junction.
2. It asks to explain why the resistance of the p-n junction is low during forward bias and high during reverse bias.
3. It asks why the thickness of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode increases with increasing reverse bias.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
MFT00804 APPLIED PHYSICS
TUTORIAL 8
1. How is the electric field across the p-n junction?
2. Explain why the resistance of the p-n junction is low when forward bias and high when
reverse bias?
3. Why does the thickness of depletion region in a p-n junction diode increases with
increase in reverse bias?
4. When p-n junction is forward bias, then the motion of charges across the barrier is due
to _________ and when it is reverse bias then the motion of charge carriers ________.
5. To forward bias a diode, to which region must the positive terminal of a voltage source
to be connected?
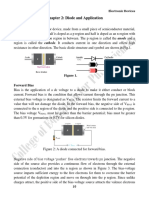
6. Determine whether each diode in Figure 1 is forward bias or reverse bias.
Figure 1
7. Explain the use of p-n junction diode as full wave rectifier. Draw the input and output
waveforms.
8. A full wave p-n junction diode rectifier uses a load resistance 1300 ohm. The internal
resistance of each diode is 9 ohm, find the efficiency of this full wave rectifier.
9. In a half wave rectifier, the sine wave input is 200sin300t. The average value of output
voltage is?
10. A half rectifier is used to supply 50V d.c. to a resistive load of 800 ohm. The diode has
a resistance of 25 ohm. Calculate a.c. voltage required.
You might also like
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- MCQ Semiconductor PDFDocument7 pagesMCQ Semiconductor PDFboomaNo ratings yet
- 3U Magnetism ReviewDocument6 pages3U Magnetism ReviewSanam SheriarNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Half Wave RectifierDocument15 pagesPhysics Project On Half Wave RectifierMaanu Style100% (4)
- Two Mark Questions With AnswersDocument10 pagesTwo Mark Questions With AnswerssenthilNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks With Answers Collection 1Document19 pages2 Marks With Answers Collection 1Guna PriyaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor NotesDocument4 pagesSemiconductor NotesADITYA MAHECHANo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices-Q & A 2023Document7 pagesElectronic Devices-Q & A 2023mackusmockusNo ratings yet
- Electronic DevicesDocument36 pagesElectronic DevicesGiridhar MeruvalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10Document7 pagesExperiment 10Deepan AdakNo ratings yet
- SR Inter IPE Question Bank Chapter-XV (SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS)Document12 pagesSR Inter IPE Question Bank Chapter-XV (SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS)sojakoj867No ratings yet
- Lab Manual Exp 8 - RectifierDocument7 pagesLab Manual Exp 8 - RectifierMohd Fazri SedanNo ratings yet
- 9 - Electronic Devices PDFDocument28 pages9 - Electronic Devices PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- 22223.BEE Tutorial Sheet 1 (Semiconductor Diodes and Applications)Document2 pages22223.BEE Tutorial Sheet 1 (Semiconductor Diodes and Applications)Rajiv SatijaNo ratings yet
- 2054359797-BASIC ELNS-UNIT-1 NOTES-DiodesDocument18 pages2054359797-BASIC ELNS-UNIT-1 NOTES-Diodesajey002hegdeNo ratings yet
- Ece Lab Questons and AnswersDocument6 pagesEce Lab Questons and AnswersAditya AryamNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Q. Paper PB 1Document9 pagesXII Physics Q. Paper PB 1Gillu SinghNo ratings yet
- Eto Handout1 DiodeDocument20 pagesEto Handout1 DiodedawitNo ratings yet
- Physics QDocument2 pagesPhysics QDhruv AroraNo ratings yet
- Bee IiiDocument68 pagesBee IiiTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Diffusion: Which Is The Flow Caused by Variations in The Concentration I.E. Drift: It Is The Movement Caused by Electric FieldsDocument22 pagesDiffusion: Which Is The Flow Caused by Variations in The Concentration I.E. Drift: It Is The Movement Caused by Electric FieldsnagarajudbpNo ratings yet
- 2019Document8 pages2019Roy DeepeshNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Semiconductor 2023Document6 pagesUnit 9 Semiconductor 2023spcodrNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor 4M QuestionsDocument29 pagesSemiconductor 4M Questionsbhanu010420No ratings yet
- Unit: 4 (Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents)Document16 pagesUnit: 4 (Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents)Tuition MasterNo ratings yet
- EEE-182 3-b: Q: Discuss The Revers and Forward Biasing For Silicon Diode. AnsDocument3 pagesEEE-182 3-b: Q: Discuss The Revers and Forward Biasing For Silicon Diode. AnsAfsana KhushiNo ratings yet
- Lab 05Document3 pagesLab 05Juan TarquiNo ratings yet
- BE-201 Practical ExperimentsDocument39 pagesBE-201 Practical ExperimentsKunal DasNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits 1 Marks QuestionsDocument17 pagesSemiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits 1 Marks QuestionsTuition MasterNo ratings yet
- PE Lect2.compressedDocument30 pagesPE Lect2.compressedmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- SEMICONDUCTORS (AutoRecovered)Document7 pagesSEMICONDUCTORS (AutoRecovered)Richard OKNo ratings yet
- Principle of Electronics EnggDocument47 pagesPrinciple of Electronics EnggNilabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Angel Education Society: HALFYEARLY EXAMINATION (2017-20018) Subject: Physics Class - 12 F.M - 70 Time-3 HrsDocument3 pagesAngel Education Society: HALFYEARLY EXAMINATION (2017-20018) Subject: Physics Class - 12 F.M - 70 Time-3 HrsAtul Verma0% (1)
- Publication 12 4795 82Document12 pagesPublication 12 4795 82Saud AloufiNo ratings yet
- EG1108 Tutorial 5: Transformers & Rectifier Circuits - Part 1 EG1108 Tutorial 5: Transformers & Rectifier Circuits - Part 1Document12 pagesEG1108 Tutorial 5: Transformers & Rectifier Circuits - Part 1 EG1108 Tutorial 5: Transformers & Rectifier Circuits - Part 1Leong ssNo ratings yet
- ME1Document5 pagesME1jj012586No ratings yet
- Edc Lab ManualDocument35 pagesEdc Lab ManualYAMINI D SDECT013No ratings yet
- Electron Devices - 1Document12 pagesElectron Devices - 1rajshrimohanksNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PN JunctionDocument8 pagesModule 1 PN JunctionAyush NinaweNo ratings yet
- Diode Valve Effect: Electrical and Electronics LabDocument4 pagesDiode Valve Effect: Electrical and Electronics LabLare ONo ratings yet
- BEEE Precise NotesDocument56 pagesBEEE Precise Noteskurubamailagani ravaliNo ratings yet
- Elec Exam StandDocument14 pagesElec Exam StandDaveyNo ratings yet
- Ec0221 Ed Lab ManualDocument68 pagesEc0221 Ed Lab ManualGoutham ShanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: ElectrostaticsDocument31 pagesChapter - 1: Electrostaticsasha dastagirNo ratings yet
- 2 Mark (ED Questions)Document26 pages2 Mark (ED Questions)Pradeep ravichanderNo ratings yet
- Revision SheetDocument2 pagesRevision Sheetshanugamer0042No ratings yet
- OST De-44Document84 pagesOST De-44princekumar13785No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Diode and ApplicationDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Diode and Applicationসায়েম মুহাম্মাদNo ratings yet
- Negative Resistance DevicesDocument4 pagesNegative Resistance DevicesHasitha Gayan JayasundaraNo ratings yet
- Forward and Reverse Bias of Diode PDFDocument5 pagesForward and Reverse Bias of Diode PDFTapobroto Chatterjee100% (1)
- EI2203 EDC 2marksDocument14 pagesEI2203 EDC 2marksBhanu KodaliNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document14 pagesLab 7Aneema AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-8Document10 pagesChapter 5-8Besu FikadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Constructional Features, Operating Principle, Characteristics and Specification of Power Semiconductor DiodeDocument31 pagesLesson 2 Constructional Features, Operating Principle, Characteristics and Specification of Power Semiconductor DiodeChacko MathewNo ratings yet
- L2 PN Junction DiodeDocument30 pagesL2 PN Junction DiodeMarjia KhatunNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor NotesDocument14 pagesSemiconductor NotesBansariNo ratings yet
- Ec6202-Electronic Devices and Circuits 2 Marks and 16 Marks (Q&A) Unit 1Document31 pagesEc6202-Electronic Devices and Circuits 2 Marks and 16 Marks (Q&A) Unit 1SayiTisanShalomNo ratings yet
- OST Ana214Document96 pagesOST Ana214princekumar13785No ratings yet