Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abdulrehman
Abdulrehman
Uploaded by
rabia buttOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abdulrehman
Abdulrehman
Uploaded by
rabia buttCopyright:
Available Formats
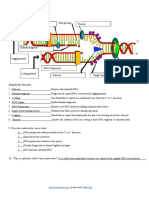
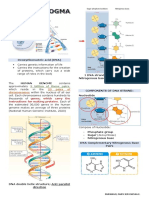
acidic nature of nucleic acis id becauxe of P
group
It is made of two polynucleotide chains.
•
Each chain is a right-handed helix.
The two chains coil around each other to form a
double helix.
•
The chains run in opposite directions – they are
said to be antiparallel.
•
Each chain has a sugar-phosphate backbone with
bases projecting at right angles.
•
The bases in one chain are attracted to the bases of
the other chain by hydrogen bonding between the
bases. This holds the chains together.
•
Because of the way they fit together, like jigsaw
pieces, adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T)
and guanine (G) always pairs with cytosine (C)
(complementary base pairing).
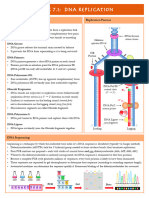
initiation phase leading strand= 5-3
HELICASE ENZYME= lagging strand= 3-5
UNCOILD THE
DOUBLE HELIX
• The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the same
DNA would like Y shaped direction as the replication fork.
• The lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in the
opposite direction of the
primer attaches 3OH group to new nucleotide
Elongation phase
DNA polymerase synthesizes this strand ligase enzyme makes phosphodiestr bone between
continuously in the 5' to 3' direction because it the fragments
can move along the template strand in the
direction of the replication fork.
UUACCGGUA
TTACCGGTA
THREE NUCLEOTIDES CODE FOR ONE AMINO ACID
AATGGCCAT
GCA
CGU
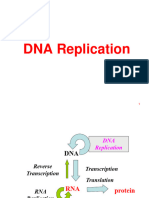
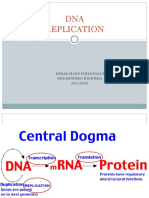
protein synthesis from DNA
amino acid from nucleotides
with the binding of an enzyme called RNA polymerase at
specific site
RNA polymerase unwinds a short stretch of the DNA
double helix near the promoter
exposes the DNA bases, allowing for the synthesis of RNA.
RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template strand
in the 3' to 5' direction, reading the sequence
adds complementary RNA nucleotides (adenine, cytosine,
guanine, and uracil, instead of thymine) to the growing
RNA molecule in the 5' to 3' direction
You might also like
- Biochem Final Exam AnswersDocument12 pagesBiochem Final Exam AnswersTalaMon100% (1)
- Quick Review of Biochemistry For Undergraduates (Questions and Answers) PDFDocument312 pagesQuick Review of Biochemistry For Undergraduates (Questions and Answers) PDFNalini Rooplal100% (4)
- Biological Chemistry. The Bank of MCQ Test Questions) 2016-2017Document32 pagesBiological Chemistry. The Bank of MCQ Test Questions) 2016-2017AGM EBNo ratings yet
- 2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationDocument32 pages2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationALEXANDRA MARIE BUNQUINNo ratings yet
- 5 - DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument85 pages5 - DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationJustina VillageNo ratings yet
- New Strands - High Fidelity (One For Every 10 - 10 Bases) Are Made As Free Nucleotides Combine With Their Complementary BasesDocument2 pagesNew Strands - High Fidelity (One For Every 10 - 10 Bases) Are Made As Free Nucleotides Combine With Their Complementary BasesAciel CruzNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument62 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationREYNANTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 7.1 DNA ReplicationDocument1 page7.1 DNA ReplicationGAVUENo ratings yet
- 6 Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pages6 Nucleic AcidsTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication: By: Jayson I. Gula Student - M.A. Ed., Biological ScienceDocument18 pagesDna Replication: By: Jayson I. Gula Student - M.A. Ed., Biological ScienceJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument87 pagesDna Replicationspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Dna Replication Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesDna Replication Lecture NotesAhmad ShyoukhNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids - ReplicationDocument12 pagesUnit 8 Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids - ReplicationMing mingNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaCahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaCahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta20.020 Cahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Signaling Part 2Document27 pagesSignaling Part 2Wissam AlwazaniNo ratings yet
- One Gene-One Polypeptide Hypothesis: PurinesDocument5 pagesOne Gene-One Polypeptide Hypothesis: PurinesCatalytic AintNo ratings yet
- 15 Lecture 10 (DNA Replication) UpdateDocument44 pages15 Lecture 10 (DNA Replication) Updateacidburn9790No ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudDocument35 pagesDNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudBagus Arya MahartaNo ratings yet
- ReplicationDocument45 pagesReplicationAleena MustafaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudDocument35 pagesDNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudDeni SalmonNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument27 pagesDna ReplicationNida AdilahNo ratings yet
- Biol 200 NotesDocument181 pagesBiol 200 Notessacharlebois7No ratings yet
- Biology (2nd Semester) - Grade 12 ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiology (2nd Semester) - Grade 12 ReviewerPatricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument74 pagesDNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisNabilah Rizky Khairunnisa100% (1)
- DNA Molecule & Central DogmaDocument43 pagesDNA Molecule & Central DogmaJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- Bic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonDocument46 pagesBic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids (HL)Document23 pagesNucleic Acids (HL)Boris-Jeremie-Latyr GueyeNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesDNA Structure DNA ReplicationBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaRodriguez MiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 EM PDFDocument24 pagesLecture 2 EM PDFhuang SteffiNo ratings yet
- Biosistematika Tumbuhan 2Document51 pagesBiosistematika Tumbuhan 2Novie NANo ratings yet
- 21 DNA Replication 2023Document59 pages21 DNA Replication 2023Kurstein FerriolNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationastrogeniusthreeNo ratings yet
- NucliecDocument2 pagesNucliecLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Section 1: General Concepts of DNA ReplicationDocument95 pagesSection 1: General Concepts of DNA ReplicationAqsa YaminNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication FinalDocument85 pagesDNA Replication FinalMahnoor ImranNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation) I) TranscriptionDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation) I) TranscriptionyatiothNo ratings yet
- Slide 3Document36 pagesSlide 3OdaiNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 3 - Dna Replication - Transcription - TranslationDocument14 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 3 - Dna Replication - Transcription - TranslationAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology PresentationDocument239 pagesMolecular Biology PresentationManish SoniNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure, Replication and Repair: V.P.V.Filio, MD, FAMP, FPCP, DPSNDocument67 pagesDNA Structure, Replication and Repair: V.P.V.Filio, MD, FAMP, FPCP, DPSNMad Max FuryNo ratings yet
- Dna Mutation 3Document40 pagesDna Mutation 3Tai PanNo ratings yet
- Case 1 SummeryDocument11 pagesCase 1 SummeryTtNo ratings yet
- VSU-2020-PPT Information Transfer Protein SynthesisDocument78 pagesVSU-2020-PPT Information Transfer Protein SynthesisAndreah BaylonNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Identify The StructureDocument3 pagesDNA Replication: Identify The StructureSet FireNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA and RNADocument42 pagesStructure of DNA and RNAAldrin LupasNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication (Prokaryotes) 1 2 PDFDocument54 pagesDNA Replication (Prokaryotes) 1 2 PDFItni Si Baat HyNo ratings yet
- (1 - 2) - Leading Strand With Helicase - Lagging Strand Opposite HeliaseDocument7 pages(1 - 2) - Leading Strand With Helicase - Lagging Strand Opposite Heliasenevio.wirtgenNo ratings yet
- Bio Cha 7Document1 pageBio Cha 7Ilakia UNo ratings yet
- 3 Billion of These PairsDocument10 pages3 Billion of These PairsYlooner Quits100% (1)
- Chapter 4A: DNA Replication & Protein SynthesisDocument34 pagesChapter 4A: DNA Replication & Protein SynthesisPikuNo ratings yet
- 7.1 DNA ReplicationDocument1 page7.1 DNA ReplicationPolina AbasovaNo ratings yet
- Penang Matriculation College SB015 2018/2019: By: (MS1813362299 / H3P02B)Document11 pagesPenang Matriculation College SB015 2018/2019: By: (MS1813362299 / H3P02B)Yi LingNo ratings yet
- 09NucCM MamalapatDocument1 page09NucCM MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument35 pagesDNA Structure and Replicationcharyl jean cagaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Fatima Parvez 13/117Document24 pagesSubmitted By: Fatima Parvez 13/117Eng CirroNo ratings yet
- Slide 2Document38 pagesSlide 2OdaiNo ratings yet
- Recap:: To Understand The Structure of Mononucleotides and DNADocument17 pagesRecap:: To Understand The Structure of Mononucleotides and DNAmswestNo ratings yet
- 11 - DNA ReplicationDocument32 pages11 - DNA ReplicationR yNo ratings yet
- Eating HintsDocument2 pagesEating Hintsrabia buttNo ratings yet
- 0610 Endocrine System 2 04012023 B14Document1 page0610 Endocrine System 2 04012023 B14rabia buttNo ratings yet
- 0610 Gene Chromosome, Protein 3012024 b14Document1 page0610 Gene Chromosome, Protein 3012024 b14rabia buttNo ratings yet
- 0620 Equilibrium-4 29012024 B14Document1 page0620 Equilibrium-4 29012024 B14rabia buttNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology January Test-1Document1 pageIgcse Biology January Test-1rabia buttNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology January Test-1Document1 pageIgcse Biology January Test-1rabia buttNo ratings yet
- Dietary Guidelines During Cancer Treatment EngDocument2 pagesDietary Guidelines During Cancer Treatment Engrabia buttNo ratings yet
- June 2022 QPDocument20 pagesJune 2022 QPrabia buttNo ratings yet
- Kavish Geography 26 7 2023Document1 pageKavish Geography 26 7 2023rabia buttNo ratings yet
- KavishDocument1 pageKavishrabia buttNo ratings yet
- ;Document1 page;rabia buttNo ratings yet
- KavishDocument1 pageKavishrabia buttNo ratings yet
- YrJI6dPaDzgiPRVj a2whhwejUwSKQ-C5-UNICEF ROSA Are Our Institutions Adolescent FriendlyDocument3 pagesYrJI6dPaDzgiPRVj a2whhwejUwSKQ-C5-UNICEF ROSA Are Our Institutions Adolescent Friendlyrabia buttNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument17 pagesProteinBasira ZolmayNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility ComplexDocument16 pagesMajor Histocompatibility ComplexnikitaNo ratings yet
- Dna and Protein Synthesis CrosswordDocument1 pageDna and Protein Synthesis CrosswordAnthony MoloneyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Tutorial BCH 301: True or False SectionDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Tutorial BCH 301: True or False SectionTheo SantoNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule BrochureDocument1 pageMacromolecule BrochureMohammad IzadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular Biology: Homayoun ValafarDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Biology: Homayoun ValafarJay DansNo ratings yet
- 2 Regulation Gene Expression BalaccoDocument34 pages2 Regulation Gene Expression Balacco9147Indah WulandariNo ratings yet
- BioK DP Notes 2.7Document18 pagesBioK DP Notes 2.7Lal ÖzşahinNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS Gene Expression and RegulationDocument4 pagesANSWERS Gene Expression and RegulationJhoy AmoscoNo ratings yet
- Operonconcept Anoverview PDFDocument16 pagesOperonconcept Anoverview PDFAmbigaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - 1Document12 pagesChapter 11 - 1JeanPaule JoumaaNo ratings yet
- BCH 203 & 202Document28 pagesBCH 203 & 202metasynthronos748No ratings yet
- 02 The Nucleic AcidsDocument18 pages02 The Nucleic AcidsYulia Asri WarlindaNo ratings yet
- Mol Bio SyllabusDocument2 pagesMol Bio SyllabusGandhiraj VNo ratings yet
- unit..1..ge.docxDocument3 pagesunit..1..ge.docxAnonymous CS1QiRCNo ratings yet
- 13 - GluconeogenesisDocument23 pages13 - GluconeogenesischeckmateNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Bruce AlbertsDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Bruce AlbertsJustinReidmajof100% (29)
- L4B Genetics 07Document28 pagesL4B Genetics 07Tofik MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2 DNA Replication IPDocument3 pages2 DNA Replication IPCaitlin EmilioNo ratings yet
- March Rapid AbagrtpcrDocument82 pagesMarch Rapid AbagrtpcrJaycel PazNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESeditedDocument27 pagesBIOMOLECULESeditedMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherDocument26 pagesChapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Structures Differ From One AnotherNeenu RajputNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument15 pagesCitric Acid CyclederhangkerNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument30 pagesVitaminsKamran ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 BiochemistryDocument6 pagesLab 4 BiochemistrySiti Aainaa Sharir100% (1)
- Lab Report DNA PDFDocument8 pagesLab Report DNA PDFpadhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- MCQ 1. in Transcription,: Type of Question: Content FromDocument2 pagesMCQ 1. in Transcription,: Type of Question: Content FromAlex XanderNo ratings yet