Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nucliec
Uploaded by
Lady DanielleOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nucliec
Uploaded by
Lady DanielleCopyright:
Available Formats
Nucleic Acid
Nucleic Acid
Nucleotide – sugar , base, and phosphate
Nucleoside – sugar and base
Backbone – sugar and phosphate
Nucleic acid – is a chain of nucleotide
Bases
Purine – Adenine, Guanine
Pyrimidine – Thymine, uracil, Cytosine
Complementary Base Pairs:
Adenine – Thymine (2 H-bonding)
Uracil – Adenine (2 H-bonding)
Guanine – Cytosine (3 H-bonding) Complementary DNA Strands
8 nucleotide found in DNA & RNA
DNA molecule - a misnomer
Its not neutral, it’s a multicharge ionic matter
The interaction is not covalent but rather a
noncovalent form due to H-bonding.
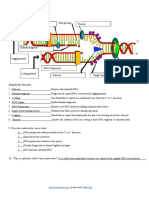
DNA Replication
Primary Structure of the Nucleic Acid
Unwinds by the enzyme DNA helicase
The original strand serve as a template
The pairing occurs one nucleotide at a time
DNA polymerase checks if the pairing is
correct, responsible in forming the daughter
strand, the direction is always 5’ to 3’
(leading strand) in forming the daughter
strand
The 3’ to 5’ (lagging strand) direction forms
Okasaki fragments (nicks) and connected
by DNA ligase Reiji Okasaki
The unwinding can occur in any part of the
DNA strand - bubbles
Protein Synthesis
You might also like
- 6.2 DNA Replication Full NoteDocument44 pages6.2 DNA Replication Full NotejiaenNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - DNA Replication (REVISED)Document6 pagesLesson Plan - DNA Replication (REVISED)Keziah ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- ReplicationDocument45 pagesReplicationAleena MustafaNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument36 pagesObjectivesMARIAN SABENECIONo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisFrezelVillaBasiloniaNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument74 pagesDNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisNabilah Rizky Khairunnisa100% (1)
- General Biology - DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - DNA ReplicationChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- Compressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015Document10 pagesCompressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015SYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaRodriguez MiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Billion of These PairsDocument10 pages3 Billion of These PairsYlooner Quits100% (1)
- Dna Replication Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesDna Replication Lecture NotesAhmad ShyoukhNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Public HealthDocument2 pagesEpidemiology and Public HealthLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument62 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationREYNANTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesDNA ReplicationPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Edited Part1 CENTRAL DOGMA OF GENETICSDocument16 pagesEdited Part1 CENTRAL DOGMA OF GENETICSSyx CameroNo ratings yet
- ReplicacionDocument19 pagesReplicacionIvÀnNo ratings yet
- Genetics Midterm Exam ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenetics Midterm Exam ReviewerChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Identify The StructureDocument3 pagesDNA Replication: Identify The StructureSet FireNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanism of DNA Replication (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument1 pageMolecular Mechanism of DNA Replication (Article) - Khan AcademyShreyansh PareekNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of GeneticsDocument4 pagesCentral Dogma of Geneticsmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- 8b) DNA Replication Summary - 9744 - 2018Document1 page8b) DNA Replication Summary - 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- AbdulrehmanDocument1 pageAbdulrehmanrabia buttNo ratings yet
- 7.1 DNA ReplicationDocument1 page7.1 DNA ReplicationGAVUENo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 EM PDFDocument24 pagesLecture 2 EM PDFhuang SteffiNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication - Prachi.sDocument10 pagesDna Replication - Prachi.sprachishnd74No ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageDNA Structure and Replication Cheat Sheet: by ViaThaboNo ratings yet
- 6.2: Dna ReplicationDocument43 pages6.2: Dna Replicationa200812No ratings yet
- DNA Replication (Prokaryotes) 1 2 PDFDocument54 pagesDNA Replication (Prokaryotes) 1 2 PDFItni Si Baat HyNo ratings yet
- 2.7 7.1DNAReplicationDocument33 pages2.7 7.1DNAReplicationKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument87 pagesDna Replicationspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 CYTO DNA ReplicationDocument4 pagesLesson 5 CYTO DNA ReplicationTherese TimbalNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument24 pagesDNA ReplicationEnzoLangkildeNo ratings yet
- Topic 4a - Protein Synthesis - Stu v2Document65 pagesTopic 4a - Protein Synthesis - Stu v2Angel LimNo ratings yet
- Quiz Microbial Genetics TortoraDocument17 pagesQuiz Microbial Genetics TortorapascabioNo ratings yet
- 5 Replikasi Dna 1 - RizkyDocument15 pages5 Replikasi Dna 1 - RizkyNadya TsaneeNo ratings yet
- Biosistematika Tumbuhan 2Document51 pagesBiosistematika Tumbuhan 2Novie NANo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and RepublicationDocument2 pagesDNA Structure and RepublicationimaniNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication: Replication Forks. A Protein Called Single-StrandedDocument1 pageDna Replication: Replication Forks. A Protein Called Single-StrandedShivani HenryNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic DNA ReplicationDocument31 pagesProkaryotic DNA ReplicationAnonymous Ef3jslp8No ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument46 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationAcyl HoteitNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: AP BiologyDocument30 pagesDNA Replication: AP BiologyFearless AngelNo ratings yet
- 4 Bioc1600-DnaDocument68 pages4 Bioc1600-DnaKellyNo ratings yet
- Bio Cha 7Document1 pageBio Cha 7Ilakia UNo ratings yet
- 5 - DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument85 pages5 - DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationJustina VillageNo ratings yet
- 004 DNA Replication EnzymesDocument16 pages004 DNA Replication EnzymesFavio CocaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Maintenance: Removal of Falsely AttachedDocument2 pagesDNA Replication: Maintenance: Removal of Falsely AttachedKurt BiduaNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication: By: Jayson I. Gula Student - M.A. Ed., Biological ScienceDocument18 pagesDna Replication: By: Jayson I. Gula Student - M.A. Ed., Biological ScienceJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: THINK: Why Does DNA Need To Replicate?Document33 pagesDNA Replication: THINK: Why Does DNA Need To Replicate?AkshiNo ratings yet
- (L-4) - Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Jan 19Document52 pages(L-4) - Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Jan 19AyazNo ratings yet
- Slide 3Document36 pagesSlide 3OdaiNo ratings yet
- 6 Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pages6 Nucleic AcidsTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance and Regulation ReviewerDocument7 pagesInheritance and Regulation ReviewerAngelo LopezNo ratings yet
- 02 DNA Replication ReadingDocument1 page02 DNA Replication Readinglightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Enzyme in The Leading Strand in The Lagging Strand: DNA HelicaseDocument1 pageEnzyme in The Leading Strand in The Lagging Strand: DNA HelicaseKee Chen JieNo ratings yet
- 1 - DNADocument15 pages1 - DNAGilbert Kangleon Jr.No ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument45 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationSıla DenizNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesDNA Structure DNA ReplicationBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- Intradermal Administration PRDocument2 pagesIntradermal Administration PRLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Controlling Microbial Growth in VitroDocument5 pagesControlling Microbial Growth in VitroLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Microparasitology IntroDocument36 pagesMicroparasitology IntroLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Chaps 9 and 2Document65 pagesChaps 9 and 2Lady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Chap 1&3Document51 pagesChap 1&3Lady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Chapters 5 and 6Document56 pagesChapters 5 and 6Lady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemDocument16 pagesIntroduction To BiochemLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Chapters 4 and 10Document56 pagesChapters 4 and 10Lady DanielleNo ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument4 pagesENZYMESLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Organic For NursingDocument6 pagesOrganic For NursingLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Our WorldDocument1 pageMathematics in Our WorldLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument7 pagesLIPIDSLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Florence NightingaleDocument3 pagesFlorence NightingaleLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Unpacking The SelfDocument4 pagesUnpacking The SelfLady DanielleNo ratings yet