Professional Documents
Culture Documents
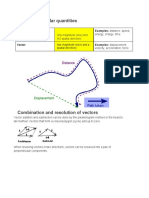
Scalars and Vectors
Uploaded by
Paris MarcanoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scalars and Vectors
Uploaded by
Paris MarcanoCopyright:
Available Formats
1
SCALARS AND VECTORS
Vector quantities have both magnitude and direction, whereas scalar quantities have magnitude only.
SCALARS VECTORS
Temperature, potential difference, distance, time, Displacement, velocity, force (weight),
speed, power, mass, length, energy (work), acceleration, momentum, electric field strength,
pressure, volume, charge, density torque, angular momentum, moments
Addition of Vectors
The resultant of two or more vectors is the single vector which produces the same effect (in both
magnitude and direction).
Parallelogram Rule
If two vectors, and are represented in magnitude and direction by the side OA and OB of a
parallelogram OACB, then represents their resultant.
2
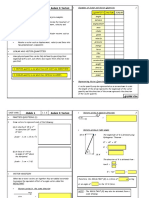
Question
Find the resultant of two forces, 8N and 6N acting at an angle of 380 to each other using both scale
drawing and calculation.
Components of Vectors
Question
Using components, find the resultant of two forces of magnitude 6N and 8N acting at 38 0 to each other.
Lami’s Theorem
If three forces A, B and C are in equilibrium, then
3
A/sin a = B/sin b = C/sin c (similar to the sin Rule). See also Triangle of Forces and Polygon of Forces in
Text.
You might also like
- Physics For Remedial Program Lectures NoteDocument201 pagesPhysics For Remedial Program Lectures NoteNesredin Teshome100% (5)
- Engineering Physics L-1: (Electromagnetic Theory) Quantum MechanicsDocument23 pagesEngineering Physics L-1: (Electromagnetic Theory) Quantum MechanicsVijay ReddyNo ratings yet
- Scalar and Vector ApplicationsDocument15 pagesScalar and Vector ApplicationspraharshdevNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Scalars and Vectors Vector Addition Using Triangle Law and Parallelogram Law For AdditionDocument18 pagesLecture 2 - Scalars and Vectors Vector Addition Using Triangle Law and Parallelogram Law For AdditionNasrullah AwalNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document26 pagesCH 1Opsops123No ratings yet
- 1 emDocument54 pages1 emDr. Neha KondalNo ratings yet
- PDF 12nov23 1123 SplittedDocument14 pagesPDF 12nov23 1123 Splittedtwoderos8abebeNo ratings yet
- Chap IDocument56 pagesChap ICybertron BadeeNo ratings yet
- 01 EE 224 Vector - AlgebraDocument37 pages01 EE 224 Vector - AlgebraEge ArslanNo ratings yet
- KR10203 Chapter 1Document64 pagesKR10203 Chapter 1RINA RINANo ratings yet
- Statics - Chapter 2Document103 pagesStatics - Chapter 2Abdulraof MatturNo ratings yet
- 20014109-012 Phy - 117 ASSIGNMENT # 1Document15 pages20014109-012 Phy - 117 ASSIGNMENT # 1hassan sandhuNo ratings yet
- 01-ES202 - Topic1Document18 pages01-ES202 - Topic1Moguri OwowNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two DimensionsDocument15 pagesMotion in Two DimensionssridhardelcamNo ratings yet
- 1 Vectors, Components, Operation On Vectors, Unit VectorsDocument26 pages1 Vectors, Components, Operation On Vectors, Unit VectorsklNo ratings yet
- Same Direction Are Said To Be Equal No Matter: B A C B A CDocument1 pageSame Direction Are Said To Be Equal No Matter: B A C B A CVanesa Faye De LeonNo ratings yet
- Presented by Presented To: Name:Walid Bin Kader, Lecturerof PhysicsDocument16 pagesPresented by Presented To: Name:Walid Bin Kader, Lecturerof PhysicsJubayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Presented by Presented To: Name:Walid Bin Kader, Lecturerof PhysicsDocument16 pagesPresented by Presented To: Name:Walid Bin Kader, Lecturerof PhysicsJubayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Statics NoteDocument47 pagesStatics NoteJibril omarNo ratings yet
- INFORME 8 Física MecánicaDocument18 pagesINFORME 8 Física Mecánicabecsan57No ratings yet
- Module1 ACEE4EmagsDocument21 pagesModule1 ACEE4Emagsjosephryanbeloria45No ratings yet
- Vectors: Vectors and Their ComponentsDocument22 pagesVectors: Vectors and Their ComponentsdrfefvdsfNo ratings yet
- Vector and Scalar Quantities: Scalar Examples: Distance, SpeedDocument2 pagesVector and Scalar Quantities: Scalar Examples: Distance, SpeedAzadsinh VaghelaNo ratings yet
- PHYS 102 First Lecture August 5, 2020 PDFDocument24 pagesPHYS 102 First Lecture August 5, 2020 PDFUtsav PathakNo ratings yet
- 01 VectorsDocument49 pages01 VectorsZohaib IkramNo ratings yet
- Review of Vector Algebra and Co-Ordinate SystemsDocument77 pagesReview of Vector Algebra and Co-Ordinate SystemsmumamaduraiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document42 pagesChapter 3gosinbradNo ratings yet
- Handout For Mechanics EIABCDocument47 pagesHandout For Mechanics EIABCmikeygena1879No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document21 pagesUnit 1DeribaNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies: Esci 123 - Engineering Mechanics 1Document24 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies: Esci 123 - Engineering Mechanics 1Jeslyn MonteNo ratings yet
- KK Sir - VectorsDocument18 pagesKK Sir - VectorsKunal KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Vector AlgebraDocument22 pages1 Vector AlgebraJunaid ZakaNo ratings yet
- Vectors, Phasors and Complex NumbersDocument21 pagesVectors, Phasors and Complex NumbersReza SalfaniNo ratings yet
- Mathematical MethodDocument11 pagesMathematical MethodPrathmeshNo ratings yet
- PHY01 - Course Outcome 1Document85 pagesPHY01 - Course Outcome 1Karylle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Vectors, Operation On Vectors, Component MethodDocument16 pagesLec 1 - Vectors, Operation On Vectors, Component MethodColeen AmadoNo ratings yet
- Basic MechanicsDocument22 pagesBasic MechanicsBin MassoudNo ratings yet
- Scalar and Vector QuantitiesDocument21 pagesScalar and Vector QuantitiesJustin MonoyNo ratings yet
- P6 ReviewerDocument4 pagesP6 ReviewerMisha ArquizaNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies Module 1Document16 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies Module 1Jeffrey CachoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument184 pagesLecture Notes On Statics of Rigid BodiesLeandro S. DaceraNo ratings yet
- SCI 2 - Physics For Engineers. Lesson 1Document57 pagesSCI 2 - Physics For Engineers. Lesson 1fortxtonly80No ratings yet
- Physics QPDocument92 pagesPhysics QPGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Week 1Document10 pagesElectromagnetics Week 1john jkillerzsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1abadittadesseNo ratings yet
- CH 02 EsDocument32 pagesCH 02 EsAngelloNo ratings yet
- CH 1. Basic Math (Phy +1)Document48 pagesCH 1. Basic Math (Phy +1)Satyam KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2 Scalars and VectorsDocument7 pages1.1.2 Scalars and VectorsMohammad Jahangir AlamNo ratings yet
- 2 Vectors, Components, OperationDocument36 pages2 Vectors, Components, Operationana valenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Cal CV00 Dot Cross ProdDocument7 pagesCal CV00 Dot Cross ProdRamNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Questions and Answers - Addition of A System of Coplanar ForcesDocument3 pagesEngineering Mechanics Questions and Answers - Addition of A System of Coplanar ForcesAnonymous FHYNiBNo ratings yet
- Scalars & VectorsDocument32 pagesScalars & VectorsHope MuzzNo ratings yet
- Final - CBP 2020 Chapter 1 Section 1-5 To 1-6 ModuleDocument8 pagesFinal - CBP 2020 Chapter 1 Section 1-5 To 1-6 ModuleFahad SBNo ratings yet
- Vectors NotesDocument1 pageVectors NotesAryan KapoorNo ratings yet
- Fuerza y VectoresDocument2 pagesFuerza y VectoresKarla ChavarriaNo ratings yet
- Motion in PlaneDocument15 pagesMotion in PlaneKajol HNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biophysics I 2021Document91 pagesIntroduction To Biophysics I 2021Erdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Open ES-1-Handout 2Document61 pagesOpen ES-1-Handout 2JANINA CHRISTELLE ORMITANo ratings yet
- Affective Domain Lesson Plan Conserving Electrical EnergyDocument5 pagesAffective Domain Lesson Plan Conserving Electrical EnergyParis MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Lust A Forbidden Age Gap Romance Purity Book 3 by SkylerDocument230 pagesLust A Forbidden Age Gap Romance Purity Book 3 by SkylerParis MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry I.A Group ProjectDocument4 pagesChemistry I.A Group ProjectParis MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Draft Cs SbaDocument1 pageDraft Cs SbaParis MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 1 Paper 2 Answers - 231129 - 191638Document102 pagesChem Unit 1 Paper 2 Answers - 231129 - 191638Paris MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab 2 and 3Document4 pagesBiology Lab 2 and 3Paris MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Physics Draft Lab #3Document5 pagesPhysics Draft Lab #3Paris MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Physics Draft Lab #3Document5 pagesPhysics Draft Lab #3Paris MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Trafficking in Human Beings For The Purpose Of.99944Document5 pagesTrafficking in Human Beings For The Purpose Of.99944Paris MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Biology #4Document9 pagesBiology #4Paris MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Physics Draft Lab #3Document4 pagesPhysics Draft Lab #3Paris MarcanoNo ratings yet
- 2014 P01Document8 pages2014 P01Paris MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Aspects of BiochemistryDocument21 pagesAspects of BiochemistryParis MarcanoNo ratings yet