Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lai King Catholic Secondary School 2022-2023 Second Term Examination S.4 Physics Suggested Answers
Uploaded by
CountRatPerson645Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lai King Catholic Secondary School 2022-2023 Second Term Examination S.4 Physics Suggested Answers
Uploaded by
CountRatPerson645Copyright:
Available Formats
LAI KING CATHOLIC SECONDARY SCHOOL
2022-2023
Second Term Examination
S.4 Physics
Suggested Answers
SECTION A
1. D 6. A 11. D 16. A 21. B
2. D 7. C 12. C 17. D 22. C
3. B 8. A 13. A 18. B 23. C
4. B 9. A 14. A 19. D 24. B
5. D 10. A 15. C 20. D
SECTION B
!"
1. (a) 𝑎 = !# = 0.8 m s-2 1M1A
!"$"
(b) (i) # !
$t = 400 1M
t = 40 s 1A
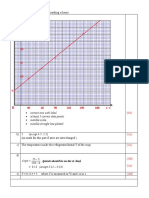
(ii)
20
1A
0 50 200 250
(c) (210 – 25 + 250)(20)/2 1M1A
= 4350 m 1A
S.4 Physics Page 1
%
2. (a) 𝑢(0.1) + !g(0.1)2 = 0.145 1A
\ u + 0.05g = 1.45 … (1)
%
(b) 𝑢(0.2) + g(0.2)2 = 0.145 + 0.24 1M1A
!
\ u + 0.1g = 1.925 … (2) 1A
(c) (2) – (1): 0.05g = 0.475
Þ g = 9.5 1A
(d) The effect of air resistance is not negligible. 1A
3. (a) f(2) = 100(25 sin 20˚) 1M2A
Þ f = 428 N 1A
(b) The force should be perpendicular to the crowbar and acting in the
clockwise direction. 1A
428(2) = F(25) Þ F = 34.2 N 1M1A
4. (a) Since the resistive force (or gravity) in the outer space was negligible, 1A
MRO moved on with a constant velocity due to its inertia. 1A
(b) Atlas V had to travel at a high speed within the Earth’s atmosphere, 1M
its streamlined body could reduce the air resistance. 1A
(c) (i) The thrusters ejected hot gas in the forward direction. 1A
By Newton’s 3rd law, the hot gas would exert a backward force
on MRO and hence slow down MRO. 1A
(ii) Net force exerted on MRO = 1500(1800 – 2900)/27/60 = – 1019 N 1M1A
By Newton’s 3rd law, the force exerted on the hot gas by MRO
was 1019 N (forward). 1A
5. (a) (i) a = 20/10 = 2 1A
T – 1 200 = 500(2) 1M
T = 2 200 N 1A
(ii) T’ = 1 200 N 1A
(b) P = 1 200(20) = 24 000 W 1M1A
(c) Let f be the friction.
Power against friction: f(20) = 60 000 – 24 000 1M
f = 1 800 N 1A
S.4 Physics Page 2
6. (a) 4(300) = 1004 v 1M
v = 1.20 m s-1 1A
(b) Initial K.E. = 0.5(0.004)(300)2 = 180 J 1A
2
Final K.E. = 0.5(1.004)(1.2) = 0.717 J 1A
Percentage loss of K.E. = 99.6% 1A
(c) The loss of K.E. becomes the internal energy of the block and the bullet. 1A
(d) K.E. loss » 0.5(0.004)(3502 – 1002) = 225 J 1M1A
(e) F = 225/0.20 = 1125 N 1M1A
7. (a) Take to the right as positive.
Momentum change of B = 0.5(9 – (–12)) = 10.5 kg m s-1 1M1A
(b) Average force acting on B by A = 10.5/0.3 = 35 N 1M1A
Average force acting on A by B = – 35 N 1A
(c) 0.3(16) + 0.5(–12) = 0.3v + 0.5(9) 1A1M
Þ v = –19 m s-1 (to the left) 1A
(d) Initial K.E. = [0.3(162) + 0.5(122)]/2 = 74.4 J 1A
Final K.E. = [0.3(192) + 0.5(92)]/2 = 74.4 J 1A
Loss in K.E. = 0 1M
\ The collision is elastic.
8. (a)
1A
% 2
m(9.81)(7 cos 30˚) = !mv 1M1A
v = 10.9 m s-1 1A
(b) (i) x = (10.9 cos 30˚)(1.3) = 12.3 m 1M1A
(ii) Vertical distance of C below B
%
= – (10.9 sin 30˚)(1.3) + !(9.81)(1.32) 1M1A
= 1.20 m 1A
S.4 Physics Page 3
You might also like
- S4 Pre X2 AnsDocument5 pagesS4 Pre X2 AnsCountRatPerson645No ratings yet
- SHCC 1718 Phy Mock Sol PDFDocument27 pagesSHCC 1718 Phy Mock Sol PDFVincent haNo ratings yet
- F4 1819 Final Exam MarkingDocument7 pagesF4 1819 Final Exam Marking5B04 CHOW HOI LAMNo ratings yet
- 2014-15 S4phys E1 M PDFDocument3 pages2014-15 S4phys E1 M PDFMa Hau YiNo ratings yet
- F4 Phy Test 1 Solutions and GraphsDocument4 pagesF4 Phy Test 1 Solutions and Graphs陳大明No ratings yet
- Introduction To Vectors and Forces - MiscellaneousDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Vectors and Forces - MiscellaneousJee AspirantNo ratings yet
- Phy Eng MS v4 PDFDocument11 pagesPhy Eng MS v4 PDFHuson 0710No ratings yet
- 2013 F3 Final Exam MSDocument3 pages2013 F3 Final Exam MSjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument12 pagesPhysics Paper 2 SL MarkschemeSaniya DautovaNo ratings yet
- 03 StructDocument8 pages03 Struct。No ratings yet
- (UKS) Physics 2006 (Mock) Paper1 (MS)Document7 pages(UKS) Physics 2006 (Mock) Paper1 (MS)api-19650882No ratings yet
- New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)Document10 pagesNew Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition)Jeffrey YuetNo ratings yet
- Target JEE (Main + Advanced) 2016Document18 pagesTarget JEE (Main + Advanced) 2016Kumar OkumuraNo ratings yet
- 2009 CE Physics Marking SchemeDocument8 pages2009 CE Physics Marking SchemeChoi FungNo ratings yet
- Work Power & Anergy Assignment - StudentDocument3 pagesWork Power & Anergy Assignment - StudentSatish PatelNo ratings yet
- 09 F3 1st Term Exam Marking SchemeDocument3 pages09 F3 1st Term Exam Marking Schemejonas hoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 2023年5月04日Document1 pageAdobe Scan 2023年5月04日阿道夫·希特勒No ratings yet
- Practice TestDocument9 pagesPractice TestDevil NinjaNo ratings yet
- Ans Phy Paper 2 Sgor 2008Document7 pagesAns Phy Paper 2 Sgor 2008Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024F5PHYTermExam1 (E) AnsDocument6 pages2023-2024F5PHYTermExam1 (E) AnsartificialjosemanNo ratings yet
- F4 1920 Year-End Test MarkingDocument4 pagesF4 1920 Year-End Test Marking5B04 CHOW HOI LAMNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion HomeworkDocument32 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion HomeworkPradeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics EveningDocument12 pages11 Physics EveningHimanshu GautamNo ratings yet
- OCR Maths M2 Topic Questions From Papers Energy, Work and Power AnswersDocument9 pagesOCR Maths M2 Topic Questions From Papers Energy, Work and Power Answersjunk filesNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 2022 by S K Mondal 8 MB-edited PDFDocument167 pagesStrength of Materials 2022 by S K Mondal 8 MB-edited PDFRajesh sahaNo ratings yet
- Trial STPM Term 1 Skema Us L6Document5 pagesTrial STPM Term 1 Skema Us L6g-40123326No ratings yet
- 26 June Slot 1Document26 pages26 June Slot 1UroojNo ratings yet
- V V Ms P P Ms E J P JS: Skema Modul Projek Skor A+: Ting 4Document4 pagesV V Ms P P Ms E J P JS: Skema Modul Projek Skor A+: Ting 4Belle RexhaNo ratings yet
- 21S08 Forces Revision 20 Sep 2021 Suggested SolutionsDocument3 pages21S08 Forces Revision 20 Sep 2021 Suggested SolutionsSelvi FatimaNo ratings yet
- PSC Assistant Engg2016Document22 pagesPSC Assistant Engg2016Santanu Mazumdar100% (4)
- Physics Paper 1 Quarter Year Examination 2013 Marking SchemeDocument23 pagesPhysics Paper 1 Quarter Year Examination 2013 Marking SchemeAnonymous IyNfIgG4ZNo ratings yet
- Physics questions with solutionsDocument16 pagesPhysics questions with solutionsKgmasterNo ratings yet
- DPP (30-32) 12th Physics - E - WADocument6 pagesDPP (30-32) 12th Physics - E - WAMeena ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- CHP 6&8 IiDocument10 pagesCHP 6&8 IizhorawalishitaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11-VectorsDocument5 pagesGrade 11-VectorsChetanNo ratings yet
- System of Particles and RotationDocument33 pagesSystem of Particles and RotationLet's work today For better tomorrowNo ratings yet
- Paper Ee Solution Set C FinalDocument67 pagesPaper Ee Solution Set C FinalalshifaNo ratings yet
- GATEECERKKanodiaDocument440 pagesGATEECERKKanodiaSri RamNo ratings yet
- RK Kanodia's GATE EC MCQ BookDocument440 pagesRK Kanodia's GATE EC MCQ BookParitam Soni100% (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Settima GR 90 SMT16B L: DimensionsDocument1 pageSettima GR 90 SMT16B L: Dimensionsmahan moradiNo ratings yet
- Sonnax GM 6T40, 6T45, 6T50 Series Identification GuideDocument4 pagesSonnax GM 6T40, 6T45, 6T50 Series Identification GuideAlex DumasNo ratings yet
- សៀវភៅរបាយការណ៍កម្មសិក្សា I3GAR 22 23Document20 pagesសៀវភៅរបាយការណ៍កម្មសិក្សា I3GAR 22 23Ra YutNo ratings yet
- VFD LastDocument31 pagesVFD LastSujith KumarNo ratings yet
- WebastoserviceDocument72 pagesWebastoserviceanasrl2006No ratings yet
- P2061 WebDocument124 pagesP2061 WebElias TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Manual - Growatt - MOD 3 15KTL3 X - Inverters - 2021 - ENGDocument30 pagesInstallation and Operation Manual - Growatt - MOD 3 15KTL3 X - Inverters - 2021 - ENGMarius Constantin VochinNo ratings yet
- KLE Dr M S Sheshgiri College regenerative brakingDocument19 pagesKLE Dr M S Sheshgiri College regenerative brakingRohan PattarNo ratings yet
- HAZID Report FormDocument12 pagesHAZID Report FormElias EliasNo ratings yet
- Campbell HausfeldDocument44 pagesCampbell HausfeldMireya Linares MoriNo ratings yet
- LED Line Flood Lights Specs & DataDocument3 pagesLED Line Flood Lights Specs & DatasvirkomartinkoNo ratings yet
- Furnace Tanur B One Operation ManualDocument7 pagesFurnace Tanur B One Operation ManualLab AkuakulturNo ratings yet
- Grundfos SOLOLIFT2 Sewage Lifting StationsDocument2 pagesGrundfos SOLOLIFT2 Sewage Lifting Stationsacodr83No ratings yet
- Ekip Aircraft (Video) - Ekip Flower Active Specialles - Russian Ufo (7 Photos)Document41 pagesEkip Aircraft (Video) - Ekip Flower Active Specialles - Russian Ufo (7 Photos)flieger horstNo ratings yet
- BS 2151.01, 2151.011-U Manual de ManttoDocument28 pagesBS 2151.01, 2151.011-U Manual de ManttoAndrés Rivera MartínezNo ratings yet
- Parallel Circuits: Prepared By: Alexander T. Montero, Ree, RmeDocument67 pagesParallel Circuits: Prepared By: Alexander T. Montero, Ree, RmeMarc Jairro GajudoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Choke PerformanceDocument45 pagesLecture 1 Choke PerformancearvNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Lab Lab 07: DC Circuits (2) : Section: BEE-10A Group: B4 Group MembersDocument9 pagesApplied Physics Lab Lab 07: DC Circuits (2) : Section: BEE-10A Group: B4 Group MembersAli HaiderNo ratings yet
- Physics20 2ndlawDocument23 pagesPhysics20 2ndlawSamson Bernard Carpio IVNo ratings yet
- PEC PPT BasicsDocument81 pagesPEC PPT BasicsHemanth Peddavenkatappa GariNo ratings yet
- Principles of Sensing: Definition, Classification and Data AcquisitionDocument13 pagesPrinciples of Sensing: Definition, Classification and Data AcquisitionvanithaNo ratings yet
- APFC ProjectDocument52 pagesAPFC Projectपवन वाघNo ratings yet
- What Is The Root Cause of High Vibration On Id Fan: MaintenanceforumsDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Root Cause of High Vibration On Id Fan: MaintenanceforumsYhaneNo ratings yet
- Potabilización de AguaDocument9 pagesPotabilización de AguaSHEILA GINIVA BUSTOS YAIMANo ratings yet
- Hi-Fog For Buildings: Technical IntroductionDocument16 pagesHi-Fog For Buildings: Technical IntroductionEsther TapiaNo ratings yet
- PART TEST-4 (JM-2022) 25-03-2022 (F22 MDP-Seniors) QPDocument11 pagesPART TEST-4 (JM-2022) 25-03-2022 (F22 MDP-Seniors) QPsunny meenuNo ratings yet
- PPSC 2022 Past Paper-1Document23 pagesPPSC 2022 Past Paper-1Hunain ShakirNo ratings yet
- Solar Based Automatic Water Level Sensing and Water Pumping System For Next GenerationDocument5 pagesSolar Based Automatic Water Level Sensing and Water Pumping System For Next GenerationIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Design of a Retractable Electric Propulsion System for SailplanesDocument112 pagesDesign of a Retractable Electric Propulsion System for SailplanesBalashiv KumaranNo ratings yet
- 고전압비와 낮은 전압 스트레스를 가진 단일 스위치와 전압 체배 회로를 이용한 새로운 비절연형 DC-DC 컨버터Document5 pages고전압비와 낮은 전압 스트레스를 가진 단일 스위치와 전압 체배 회로를 이용한 새로운 비절연형 DC-DC 컨버터Armandinho CaveroNo ratings yet