0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views5 pagesCHAPTER 2.1 Complex Numbers
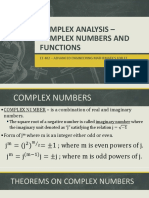
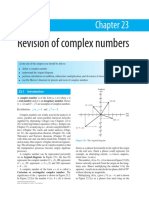
A complex number is a number that can be expressed in the form a + jb, where a is the real part and b is the imaginary part. Complex numbers allow multiplication, addition, subtraction and division using standard algebraic rules. The conjugate of a complex number a + jb is obtained by changing the sign of the imaginary part to a - jb. The product of a complex number and its conjugate is always a real number. Complex numbers find applications in electrical circuits where voltage and current can be represented as complex numbers.
Uploaded by
CT MarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views5 pagesCHAPTER 2.1 Complex Numbers
A complex number is a number that can be expressed in the form a + jb, where a is the real part and b is the imaginary part. Complex numbers allow multiplication, addition, subtraction and division using standard algebraic rules. The conjugate of a complex number a + jb is obtained by changing the sign of the imaginary part to a - jb. The product of a complex number and its conjugate is always a real number. Complex numbers find applications in electrical circuits where voltage and current can be represented as complex numbers.
Uploaded by
CT MarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd