Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digital Electronic Circuit
Uploaded by
Kaviarasan KaviarasanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digital Electronic Circuit
Uploaded by
Kaviarasan KaviarasanCopyright:
Available Formats
DIGITAL ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
ELECTRICAL
ENGINEERING
PROF. GOUTAM SAHA
Department of Electrical Engineering
IIT Kharagpur
TYPE OF COURSE : New | Core | UG COURSE DURATION : 12 weeks (28 Jan’19-19 Apr’19)
INTENDED AUDIENCE : BE/ME(EE/CS/EC) EXAM DATE : 27 April 2019
PRE-REQUISITES : Basic understanding of diode, transistor operation. If this is not covered in 10+2 Board of the
students then the same may be studied from Basic Electronics or Analog Electronic Circuits course.
COURSE OUTLINE :
There is a flux of terms in recent times that starts with the word ‘digital’. Examples are digital camera, digital watch,
digital weighing machine, digital signature, digital payment, digital art and so on. The digital prefix associates a term
with digital technology and is considered a step up in the delivered performance at a given cost. The world of digital
provides easy storage and reproduction, immunity to noise and interference, flexibility in processing, different
transmission options, and very importantly, inexpensive building blocks in the form of integrated circuits. Digital
systems represent and manipulate digital signals. Such signals represent only finite number of discreet values. A
signal can be discreet by nature whereas, a continuous signal can be discretized for digital processing and then
converted back. Manipulation and storage of digital signal involves switching. This switching is done through
electronic circuits. Basic gates made from electronic circuits are primary building blocks of digital systems. These
gates combine in different ways to develop digital circuits that are associated with different functionalities.
ABOUT INSTRUCTOR :
Goutam Saha, BTech, PhD from IIT Kharagpur had a short Management Training at XLRI, Jamshedpur. During
1990-1994, he worked with Tata Steel. He joined as faculty member in the Dept. of Electronics and Electrical Commu-
nication Engineering at IIT Kharagpur in 2002. In 2006 fall semester, he served University of Southern California, USA.
His research interest includes biomedical and speech signal processing with collaborations from India and abroad.
COURSE PLAN :
Week 01 : Introduction; Relation between switching and logic operation; Use of Diode and Transistor as switch;
Concept of noise margin, fanout, propagation delay; TTL, Schottky TTL, Tristate; CMOS Logic,Interfac-
ing TTL with CMOS
Week 02 : Basic logic gates, Universality of NAND, NOR gates, AND-OR-Invert gates, Positive and Negative Logic;
Boolean Algebra axioms and basic theorems; Standard and canonical representations of logic
Week 03 : Minimization using Entered Variable Map, Minimization of multiple output functions, Minimization
using QM algorithm
Week 04 : Multiplexer; Demultiplexer / Decoder, BCD to 7-segment decoder driver; Encoder, Priority encoder;
Parity generator and checker
Week 05 : Number systems-binary, Signed binary, Octal, hexadecimal number; Binary arithmetic, One’s and two’s
complements arithmetic
Week 06 : Carry look ahead adder; Magnitude comparator; ALU; Error detecting and correcting codes
Week 07 : Bistable latch, SR, D, JK, T Flip-Flop: level triggered, edge triggered, master – slave, Various representa-
tions of flip-flops
Week 08 : Register, Shift register, Universal shift register; Application of shift register: ring counter,
Week 09 : Up and down counter, Ripple (asynchronous) counters, Synchronous counters; Counter design using
flip flops,
Week 10 : Design of synchronous sequential circuit using Mealy model and Moore model
Week 11 : Digital to analog converters: weighted resistor/converter, binary ladder, converter, accuracy and
resolution; Analog to digital converter
Week 12 : Memory organization and operation, Memory expansion; Memory cell; Different types of memory
151
You might also like
- Rms2dc Ltc1968 Demo Circuit-Dc427b A B CDocument4 pagesRms2dc Ltc1968 Demo Circuit-Dc427b A B CsastrakusumawijayaNo ratings yet
- Ies Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesIes Syllabus PDFKrishanjeet BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus B.tech (ECE) January 2021Document69 pagesSyllabus B.tech (ECE) January 2021Lipi RajNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Basic ElectronicsDocument17 pagesLesson Plan Basic Electronicspratima kadekar100% (1)
- Power Electronics - Course NPTELDocument4 pagesPower Electronics - Course NPTELRithi VishwanathanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Dept 2019-20Document22 pagesElectrical Dept 2019-20Qazi Yasir AzamNo ratings yet
- 9 - 28 - 0 - 0 - 40 - 5th Electrical DE&MPDocument165 pages9 - 28 - 0 - 0 - 40 - 5th Electrical DE&MPvijay kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFArpit PatelNo ratings yet
- DSP SyllabusDocument3 pagesDSP SyllabusAnkit BhuraneNo ratings yet
- ITPE-101-Digital-Electronics - Module 1Document25 pagesITPE-101-Digital-Electronics - Module 1Ivan LeeNo ratings yet
- ETR3C2Document2 pagesETR3C2Pankaj MagarNo ratings yet
- Vitae Dec 2010Document11 pagesVitae Dec 2010Andes PutraNo ratings yet
- B.tech Ec Ei 2nd Year 2018-19Document17 pagesB.tech Ec Ei 2nd Year 2018-19umesh vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Digital ElectronicsDocument228 pagesDigital ElectronicsMujeeb AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Few Words About Digital Protection RelayDocument5 pagesFew Words About Digital Protection RelayPierre Enrique Carrasco FuentesNo ratings yet
- ES108LDocument1 pageES108LSATISH PATINo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19useless9925No ratings yet
- Courses Taken at Durham CollegeDocument9 pagesCourses Taken at Durham Collegeapi-311704518No ratings yet
- Lecture Zero - ECE249 - 20222023Document34 pagesLecture Zero - ECE249 - 20222023Asmin OthuruNo ratings yet
- Switching Thoery and Logic DesignDocument159 pagesSwitching Thoery and Logic DesignamarNo ratings yet
- Digital SystemsDocument390 pagesDigital SystemsKetan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Multi-Functional Electronics Calculator ReportDocument49 pagesMulti-Functional Electronics Calculator Reportguddu kambleNo ratings yet
- IEEE Xplore Download 135Document9 pagesIEEE Xplore Download 135Madalina MejdreaNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Electronics Trainer KitDocument42 pagesDesign and Construction of A Electronics Trainer KitToheebdareNo ratings yet
- Student Name:-Ali Bilal Sultan: Teacher: - Naqaa Luqman MohammedDocument11 pagesStudent Name:-Ali Bilal Sultan: Teacher: - Naqaa Luqman Mohammedالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- Digital ElectronicsDocument2 pagesDigital ElectronicsretheeshvkmNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Ece Compli 54 60Document7 pagesSyllabus Ece Compli 54 60Rasha HasoonNo ratings yet
- DSD Syll - Merged DSD GtuDocument8 pagesDSD Syll - Merged DSD GtuSandeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Alok MauryaNo ratings yet
- DDE 1313 Digital Electronics 1 LODocument6 pagesDDE 1313 Digital Electronics 1 LOAhmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- Aligarh Muslim UniversityDocument35 pagesAligarh Muslim UniversityvtechvishnuNo ratings yet
- I - Sem - Syllabus - EE IoT - 2022-23Document8 pagesI - Sem - Syllabus - EE IoT - 2022-23Sourabh KumarNo ratings yet
- PUC EEE-311 Class-1Document24 pagesPUC EEE-311 Class-1Supreme FfNo ratings yet
- EEE-365 L3T2 17eee Class-1Document20 pagesEEE-365 L3T2 17eee Class-1MortuzaNo ratings yet
- Team 15Document11 pagesTeam 15kishore s v EEE 020No ratings yet
- Semester-III: EC 301 Category Core CoursesDocument18 pagesSemester-III: EC 301 Category Core CoursesSahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Course 9Document2 pagesCourse 9faster123No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics (3CS3 Digital Electronics (3CS3 Zero Lecture Digital Electronics (3CS3-04) Digital Electronics (3CS3-04) Zero LectureDocument19 pagesDigital Electronics (3CS3 Digital Electronics (3CS3 Zero Lecture Digital Electronics (3CS3-04) Digital Electronics (3CS3-04) Zero LectureRajkumar JainNo ratings yet
- Lecture 0 Updated Aug2023Document45 pagesLecture 0 Updated Aug2023Nguyễn Long VũNo ratings yet
- Switching Theory and Logic Design PDFDocument159 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic Design PDFSai TejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Lab (3CS4-24) Zero Lab: Presented ByDocument24 pagesDigital Electronics Lab (3CS4-24) Zero Lab: Presented ByRajkumar JainNo ratings yet
- Bti 402 Digital ElectronicsDocument1 pageBti 402 Digital ElectronicsSanjay Kr SinghNo ratings yet
- L1 EEE 2022 - ElectronicsDocument6 pagesL1 EEE 2022 - ElectronicsSuresh ThanakodiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Zero 2324Document25 pagesLecture Zero 2324lpuprinceyadavNo ratings yet
- Target-GATE: Tell Your FriendsDocument4 pagesTarget-GATE: Tell Your FriendsAth SydNo ratings yet
- Major Project Synopsis: Group No: 92 Group Name: Bakerstreet BoysDocument6 pagesMajor Project Synopsis: Group No: 92 Group Name: Bakerstreet BoysPenrose LearningNo ratings yet
- 2.4-DTSSP OptimizedDocument165 pages2.4-DTSSP Optimizedtamizh kaviNo ratings yet
- Sampad Sir C1Document5 pagesSampad Sir C1Efaz AfnanNo ratings yet
- Ijett V47P284Document7 pagesIjett V47P284Maalmalan KeekiyyaaNo ratings yet
- S.Y. B. Sc. (Electronic Science) - 17.062020Document14 pagesS.Y. B. Sc. (Electronic Science) - 17.062020RoshanNo ratings yet
- Research Profile 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesResearch Profile 2019 PDFMd. Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Electronics: RationaleDocument4 pagesSyllabus in Electronics: RationaleRonnel Asuncion CatoltolNo ratings yet
- STLD NotesDocument159 pagesSTLD NotesanithaNo ratings yet
- Logic Gates ExercisesDocument6 pagesLogic Gates ExercisesSachidananda SwarNo ratings yet
- Dr. N.G.P. Institute of Technology - Coimbatore-48: Analog and Digital Integrated CircuitsDocument48 pagesDr. N.G.P. Institute of Technology - Coimbatore-48: Analog and Digital Integrated CircuitsMrs.S.Divya BMENo ratings yet
- (Tutorials in Electronic Materials, Circuits and Devices) Milin Zhang, Zhihua Wang, Jan Van Der Spiegel, Franco Maloberti - Advanced Tutorial On Analog Circuit Design-River Publishers (2023)Document449 pages(Tutorials in Electronic Materials, Circuits and Devices) Milin Zhang, Zhihua Wang, Jan Van Der Spiegel, Franco Maloberti - Advanced Tutorial On Analog Circuit Design-River Publishers (2023)PANKAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- Robo 2Document4 pagesRobo 2Fernando PlazaNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem ETDocument18 pages6th Sem ETArman VermaNo ratings yet
- Linearization and Efficiency Enhancement Techniques for Silicon Power Amplifiers: From RF to mmWFrom EverandLinearization and Efficiency Enhancement Techniques for Silicon Power Amplifiers: From RF to mmWNo ratings yet
- Callate Gate2Document0 pagesCallate Gate2zagafNo ratings yet
- Types of Mixers in Radar ReceiversDocument23 pagesTypes of Mixers in Radar ReceiversFarin Mahzabeen50% (2)
- Introduction To LVDS, PECL, and CMLDocument17 pagesIntroduction To LVDS, PECL, and CMLSurajRGuptaNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifiersDocument37 pagesOperational Amplifiersearl pannilaNo ratings yet
- FETbiasDocument4 pagesFETbiasRichard LeeNo ratings yet
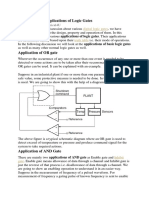
- Uses of Logic GatesDocument3 pagesUses of Logic Gatesjinil shahNo ratings yet
- Latches, Flip-Flops and TimerDocument44 pagesLatches, Flip-Flops and TimerAbushe SolomonNo ratings yet
- LS7183 / LS7184: Encoder To Counter Interface ChipsDocument3 pagesLS7183 / LS7184: Encoder To Counter Interface ChipsAgim ZilkicNo ratings yet
- MC14536B Programmable Timer: PDIP-16 P Suffix CASE 648Document16 pagesMC14536B Programmable Timer: PDIP-16 P Suffix CASE 648djorjuelaNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer ICDocument20 pages555 Timer ICZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Transistors TO-39 CaseDocument1 pageSmall Signal Transistors TO-39 CasePetr ggaNo ratings yet
- Active FIltersDocument41 pagesActive FIltersG RAJESHNo ratings yet
- Taller01 FullDocument4 pagesTaller01 FullAlexander DitestaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits - 5Document4 pagesElectrical Circuits - 5KumarNo ratings yet
- PW 1979 02Document93 pagesPW 1979 02mplennaNo ratings yet
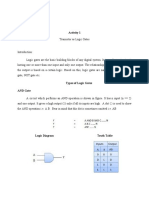
- Activity 1 - Introduction of Logic GatesDocument5 pagesActivity 1 - Introduction of Logic GatesBTOB MelodyNo ratings yet
- SuperLite Amp Schematic and Similar Topology AmpsDocument12 pagesSuperLite Amp Schematic and Similar Topology AmpsesantucciNo ratings yet
- Implementation of 1-Bit Full Adder Circuit Using Pass Transistor LogicDocument11 pagesImplementation of 1-Bit Full Adder Circuit Using Pass Transistor LogicIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Analog ModuleDocument13 pagesAnalog ModuleNgọc Đặng VănNo ratings yet
- PQ09RF11 Sharp PDFDocument7 pagesPQ09RF11 Sharp PDFVictor GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Programmable Array Logic (Denil)Document15 pagesProgrammable Array Logic (Denil)VD-ALL IN ONENo ratings yet
- Input Filter Design by EricksonDocument49 pagesInput Filter Design by EricksonshrikrisNo ratings yet
- 10 - RLC Series CKTDocument2 pages10 - RLC Series CKTChirag PatelNo ratings yet
- Photocouplers and Photorelays: Selection Guide 2019Document48 pagesPhotocouplers and Photorelays: Selection Guide 2019jimmy146No ratings yet
- Lab Session # 8 Latches, Gated Latches and Flip-Flops: CircuitsDocument10 pagesLab Session # 8 Latches, Gated Latches and Flip-Flops: Circuitsmaraim4eveNo ratings yet
- Pragati Engineering College (Autonomous) Mini Project ReviewDocument12 pagesPragati Engineering College (Autonomous) Mini Project ReviewmukeshNo ratings yet
- DTTTDocument528 pagesDTTTMỹ Phước NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 0 60V LM317 Variable Power Supply CircuitDocument6 pages0 60V LM317 Variable Power Supply Circuitdewidewi76No ratings yet
- Tarjetas Amplificadoras de Los Equipos Del CentroDocument4 pagesTarjetas Amplificadoras de Los Equipos Del CentrochineaNo ratings yet