Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Present Perfect Continuous
Uploaded by
Farah ElbadryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Present Perfect Continuous
Uploaded by
Farah ElbadryCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
Contents
I. PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE(1)...................................................................2
I. FORM:...........................................................................................................................3
II. Time Expressions:..........................................................................................................4
III. PRONUNCIATION:......................................................................................................4
IV. PRACTICE:...................................................................................................................5
II. PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE (2).....................................................................5
I. PRACTICE:...................................................................................................................5
III. THE PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS (3)............................................6
I. Definition.......................................................................................................................6
II. Examples and Observations:..........................................................................................6
III. FORM:...........................................................................................................................7
IV. USE:...............................................................................................................................8
V. EXERCISES:...............................................................................................................10
IV. Important:....................................................................................................................13
VI. Remember Non- Continuous Verb:..............................................................................13
VII. Adverb Placement:.......................................................................................................13
V. REFERENCE (4)...........................................................................................................14
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 1
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
I. PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE (1)
You can use present perfect to talk about unfinished action or situation.
I’ve always known my best friend.
I’ve never been to Africa.
I’ve lived in my flat for five years.
I’ve been a teacher since 2006.
You can also use the present perfect to talk about finished action which is important
now.
I’ve just heard the news about the fire. Isn’t it awful?
We’ve painted the house. It looks lovely.
Don’t use the present perfect which finished time in the past.
Use the past simple:
We painted our house last week.
He saw this film on Monday.
They went to Africa in 1999.
Time expressions:
You often use these time expression with present perfect:
For Since Always Never yet Recently Just Already
You can use:
Always and never to talk about the whole of your life until now.
For and since to talk about part of your life until now.
Recently and just to talk about the short time ago.
I’ve just seen Sopheak. If you hurry you can go with her.
Yet to talk about something that you expect to happen.
Have you finished your homework? No, I’ve started it yet.
Already to talk about something that happened sooner the expect.
He’s already seen this film.
Ever in question means at any time in your life.
. Have you ever had Thai food?
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 2
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
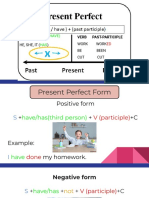
I. FORM:
We can use present perfect:
PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE
Sentences Form Example
Positive S +Have/Has +Past I’ve lived in Siem Reap for
Participle 5 years
Negative S +Have/Has +Not +Past I haven’t lived in Siem Reap
Participle
Question How long have you live in
Siem Reap
Have/Has +S + Past
Participle
II. Time Expressions:
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 3
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
Present perfect + Time expressions
In mid position: For +period of the time At the end of the
Auxiliary Time Since +point in time Sentences
expression+
Past participle
.I has always known my I’ve live in my flat for I ‘haven’t written the
best friend. five years. essay yet.
He’s live in his flat since We have seen her
.I’ve never been to
2005. recently.
Africa.
.I’ve just heard the news
.I has already written the
essay.
Note: some time expression can go in more than one position. Already can also go at
the end of the sentences. I have written essay already. Recently can also go in mid
position in positive sentences. We’ve have recently seen her. It can go in mid position
in negative sentences. We haven’t recently seen her.
III. PRONUNCIATION:
You usually stress the adverb in mid position and at the end of the sentence.
. I’ve always known my best friend.
. I haven’t written the essay yet.
But you don’t stress for or seen
. I’ve lived the flat for five years.
. He’s live in his flat since 2005
IV. PRACTICE:
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 4
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
Add these time expression to the sentences:
For Since Always Already Yet Just Never
1. You have done the homework, haven’t you? Could you help me? You’ve already
done homework....
2. I haven’t finished the report for today’s meeting. I’m very worried.
3. He’s lived in the same house. He was born there.
4. They’ve had that car ten years. It’s broken down.
5. We’ve come back from safari in Kenya. It was an amazing experience.
6. We haven’t seen each other university, but it seems like yesterday.
7. I’ve seen this film. I saw it years ago, when it first came out.
8. I’ve liked spicy food. It’s too hot for me.
II. PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE (2)
The basic purpose of the present perfect simple is to say something about the present by
describing something which happen or start in the past.it can be useful to thing about the
present perfect simple as having more three meaning uses:
1. Describing the period from sometime in the past until now.
I’ve been to Singapore (For whole life)
I’ve seen him a few times since July.
You can use the present perfect simple in this way to summaries experiences and
achievement
2. Describing an activity, state or habit which start in the past and is still going on.
I’ve lived here since 1990.
They’ve learned with the same teacher for ten years.
You often use present perfect simple in this ways to answer the question “How
long.....?”
3. Emphasizing the present result of past events.
I thing I’ve lost my key. (Now I lost it)
I’ve leant a lot so now I can earn a lot of money. (Now I’m rich)
Because the present perfect simple is about the present, you can’t use it with
finished past time expressions. I have been to Thailand in 2000
I. PRACTICE:
Make question and sentences. Use the present perfect simple.
1. have / been/always/I/good at /playing football
2. a couple of degrees/done/in psychology and social work/have/I
3. recently/passed/my driving liecen /I/ have
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 5
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
III. THE PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS (3)
I. Definition:
A verb construction (made up of has been or have been plus the present participle) that
emphasizes the ongoing nature of an action that began in the past and continues in the present.
(The decision to use has been or have been is determined by agreement with the subject.)
The present perfect progressive tense usually conveys the meaning of recently or lately. The
action reported by the present perfect progressive may or may not have been completed.
The present perfect progressive (continuous) is use for an action, which began sometime in
the past and it is still going on at the presence in the moment.
See Examples and Observations below. Also see:
Aspect
Present Perfect
Progressive Aspect
Present Progressive
II. Examples and Observations:
Try to understand how hard he has been trying to make everything better for his family.
(Lorraine Hansberry, A Raisin in the Sun, 1959)
I have been painting with a palette knife because I don't like to wash the brushes.
(Flannery O'Connor, summer 1953. The Habit of Being: Letters of Flannery O'Connor,
1979)
I have been waiting. I have been searching. I am a man under the moon, walking the
streets of earth until dawn. There's got to be someone for me."
(Henry Rollins, Solipsist, 1998)
The ocean has been singing to me, and the song is that of our life together."
(Nicholas Sparks, Message in a Bottle, 1999)
[Even Jerry] Garcia might have been surprised by how many scholars have been
studying the cultural furniture in the Grateful Dead outback."
(Nicholas G. Meriwether, Studying the Dead. Scarecrow, 2013)
My friends and I are a little worried because Stacey hasn't been feeling too great lately.
But she seems to be coping."
(Ann M. Martin, The Baby-Sitters Club: Poor Mallory. Scholastic, 2014)
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 6
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
The PRESENT PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSE indicates a continuous action that
has been finished at some point in the past or that was initiated in the past and continues to
happen. The action is usually of limited duration and has some current relevance: "She has been
running and her heart is still beating fast." The present perfect progressive frequently is used to
describe an event of the recent past; it is often accompanied by just in this usage: "It has just
been raining."
This tense is formed with the modal "HAVE" or "HAS" (for third-person singular
subjects) plus "BEEN," plus the present participle of the verb (with an -ing ending): "I have been
working in the garden all morning. George has been painting that house for as long as I can
remember."
Singular Plural
I have been walking We have been walking
You have been walking You have been walking
He /she /it has been walking They have been walking
Singular Plural
I have been sleeping We have been sleeping
You have been sleeping You have been sleeping
He/she/it has been sleeping They have been sleeping
Singular Plural
There is no present perfect progressive for the "to be" verb. "Have been being" is expressed
simply as "have been": "We have been being successful in the past."
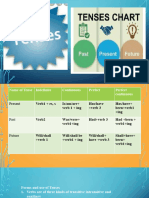
III. FORM:
1. The Form of Present Perfect Progressive (Continue) has or have + been + verbing
(Present Participle).
Subject have/has + been + verb ing rest of sentence
I / You / We / They have been watching TV for three hour
He / She / It has been playing football for two hour
IV. USE:
A. Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)-
Which to use?
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 7
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
In general, use the present perfect simple when the action started in the past and is
relevant to the present.
Ex: This is the third time I’ve written to you. (I wrote twice in the past and now I am writing
again – in the present.)
If it’s an action that started in the past and that same action is still happening now, use the
present perfect progressive.
Ex: I have been meeting for you since 8 am.
Some actions can be expressed in either tense, especially those that started in the past and
still occur in the present on a habitual basis.
Ex: I have lived in this house for 20 years. / I have been living in this house for 20 years.
Both sentences are correct.
B. Contractions in the Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
In general, we contract the subject (the person or thing doing the action) and form of have:
1. I have > I’ve – I’ve been thinking about you since you called.
2. He has > He’s / She has > She’s / It has > It’s – He’s been singing for two hours.
3. We have > We’ve / You have > You’ve / They are > They’ve – We’ve been helping her
out for a few months.
You may have noticed that the 3rd person singular (he, she, it) contractions look like those in
the present progressive. You can tell them apart by the use of been and from the context of the
sentence: he is > He’s eating now. / he has > He’s been eating for two hours.
C. Negative Sentences in the Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
Spelling Tip
When shortening the 3rd person (he, she, it) negative, just remove the o in not and add an
apostrophe (‘)
has not > hasn’t
When creating negative sentences, we use hasn’t or haven’t together with been and the ing
(present participle) form of the verb. Save the long forms (has not, and have not) for when you
want to create emphasis. When speaking, put the stress on ‘not’.
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 8
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
Subject Axillary verb Been verbing Rest of sentence
I / We / You / They haven’t (have not) been lying to you
He / She / It hasn’t (has not) been sleeping well since the accident
1. I haven’t been feeling well lately.
2. Simon hasn’t been attending class regularly since he got a job.
3. The sales team hasn’t been performing at the top of their game.
4. He has not been paying attention!
D. Yes/No Questions in the Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
To create a question that will be answered with a yes or no, start the question with Have or
Has, (Haven’t or Hasn’t for a negative question) then add a subject (the person or thing that has
been doing the action) followed by been and the ing (present participle) form of the verb and
only then add the rest of the sentence.
auxiliary Verb Subject Been + Verbing Rest of Sentence
Have I/you/we/ they Been working Since this morning
Has he / she / it been earning since this morning
Hasn’t he / she / it been helping you clean the house
1. Have you been keeping track of sales?
2. Has Jerry been picking fruit from my trees again?
E. Wh-Questions in the Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 9
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
Wh- questions are questions that require more information in their answers. Typical wh- words
are what, where, when, why, which, who, how, how many, how much.
To create a wh-question, start with the wh-word, then add have or has, then the subject (a person
or thing that has been doing the action), followed by been and the ing (present participle) form of
the verb, and only then add the rest of the sentence.
Wh-Word Auxiliary Verb Subject Been+ verbing Rest of
Sentence
What have I/you/we/ they Been doing Lately
Why has he/she/it Been copying Documents all
day
1. What have you been doing since I left?
2. Why has the phone been ringing for the last two hours?
3. How long has he been waiting?
V. EXERCISES:
Exercises – Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
Fill in the correct for of the Present Perfect Progressive as in the examples.
1. I‘ve been gardening for three hours. (garden) My back is killing me!
2. Tony has been listening to the news non-stop since the conflict began. (listen)
3. Have you been saving the coupons for me? (save)
1. Roger ______ at his mother’s house since his divorce. (stay)
2. How long _____ the dogs ________ like that? (bark)
3. I _______ the football score. (not follow) Are we winning?
4. The students ______ plans for the school party for several weeks. (make)
5. Rachel ________ at that studio for very long. (not dance)
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 10
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
6. _________ Tim _______ that book since January? (not read) I’m waiting to borrow it.
7. The project manager ________ us to finish the work since Tuesday. (push)
8. ________ you ________ TV all morning? (watch)
9. I_________ to Paris twice a month since the project started. (travel)
10. Jenny ________ customer deadlines since she arrived here. (not meet.) The boss may fire
her.
Answers:
1. has been staying
2. have/been barking
3. haven’t been following
4. have been making
5. hasn’t been dancing
6. Hasn’t/been reading
7. has been pushing
8. Have/been watching
9. I’ve been traveling
10. has not been meeting
F. Examples – Present Perfect Progressive (Continuous)
1. Positive:
1. I have been living in this house for 40 years. (I started living in it 40 years ago and I am
still living in it today.
2. I have been climbing up this mountain for over two hours. (I started climbing up it two
hours ago and at this moment I’m still climbing.)
3. I have been waiting for you since 10 am.
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 11
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
4. I’ve been thinking about you since you called.
5. He’s been singing for two hours.
6. We’ve been helping her out for a few months.
7. I’ve been gardening for three hours. My back is killing me!
8. Tony has been listening to the news ever since the conflict began.
2. Negative:
1. I haven’t been feeling well lately.
2. Simon hasn’t been attending class regularly since he got a job.
3. The sales team hasn’t been performing at the top of their game.
4. He has not been paying attention!
3. Yes/No Questions:
1. Have you been keeping track of sales?
2. Has Jerry been picking fruit from my trees again?
3. Have you been saving the coupons for me?
4. Wh Questions:
1. What have you been doing since I left?
2. How long has he been waiting?
3. Why has the phone been ringing for the last two hours?
Use 1 Duration From The Past Until Now
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 12
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
Past Present Future
We use the present perfect progressive to show that something started in the past and has
continued up until now “For five minutes” “For two week” and “Since Tuesday” are all
duration which are can be used with the present perfect progressive.
Example:
They have been talking for the last hour.
She has been working at that company for three years.
What have you been doing for the last 30 minutes?
Yamin has been teaching at the university since June.
We have been waiting here for over two hour.
Why has Nancy not been talking her medicine for the last three day?
Use 2 Recently lately
Past Present Future
You can also use the preset perfect continuous without a duration such as “Without the
duration; the tense has a more general meaning of “We after use the words” “Lately” or
“Recently” to emphasize meaning.
Example:
Recently, I have been feeling really tired.
She has been watching too much television lately.
Have you been exercising lately?
Yamin has been feeling a little depressed.
Lisa has not been practicing her English.
What have you been doing?
VI. Important
Remember that the present perfect progressive has the meaning of “Lately” or
“Recently” If you use the present perfect progressive in a question such as “Have you been
feeling alright?” it can suggest that the person look sick or Unhealthy. A question such as “Have
you been smoking?” Can suggest that you smell the smoke on the person. Using the tense in a
question suggest you can see, smell, hear, or feel the result of the action. It is possible to result
someone by using this tense on currently.
VII. Remember Non- Continuous Verb
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 13
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA Teach By Out Chanthea
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verb cannot be used in any continuous
tense. Also certain non-continuous meaning for mixed verb cannot be used in continuous tense.
Instead of using present perfect continuous with these verbs, you must use present perfect.
Example:
Sam has been having his car for two years.
= Not Correct
Sam has had his car for two years.
= Correct
VIII. Adverb Placement
The example below show the placement for grammar adverb such as: always; only;
never; ever; still; just; etc.
Example:
You have only been waiting here for one hour.
Have you only been waiting here for one hour?
Active/Passive
Example:
Recently, John has been doing the work. Active
Recent, the work has been done by John. Passive
Note: Present Perfect continuous is less commonly used in it passive for
IV. REFERENCE (4)
English Grammar For You By TUT BU In 2001
Cambridge Intermediate
Cambridge Upper-Intermediate
http://grammar.ccc.commnet.edu/grammar/tenses/present_perfect_progressive.htm
http://www.gingersoftware.com/content/grammar-rules/verbs/the-present-perfect-
progressive-tense/
http://www.englishpage.com/verbpage/presentperfectcontinuous.html
GRAMMAR 2014-2015 Page 14
You might also like
- Full Tenses PDFDocument40 pagesFull Tenses PDFsarief100% (2)
- Workbook New Version 2017Document79 pagesWorkbook New Version 2017Dibibi23No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Making Connections BE1 Part 1Document32 pagesUnit 1 Making Connections BE1 Part 1Durga Sri100% (1)
- English Grammar in Use 4th EditionDocument398 pagesEnglish Grammar in Use 4th EditionsebacruztNo ratings yet
- Practical English Usage Book 3Document403 pagesPractical English Usage Book 396 CKNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and ContinuousDocument46 pagesPresent Perfect and Continuouspmalencar100% (1)
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Document8 pagesHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Syazwan ZentNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Are Among UsDocument21 pagesAdverbs Are Among UsashleeNo ratings yet
- English Competency Course ClasesDocument39 pagesEnglish Competency Course ClasesWilmerRiveraVelayarceNo ratings yet
- Simple Past X Pres PerfectDocument28 pagesSimple Past X Pres PerfectAdriano Santos100% (1)
- All Tenses ReviewDocument88 pagesAll Tenses ReviewKsenia GundarovaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple & ContinuousDocument20 pagesPresent Perfect Simple & Continuousbuendia8986% (7)
- 500 Really Useful English Phrases: Intermediate to FluencyFrom Everand500 Really Useful English Phrases: Intermediate to FluencyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Present Perfect - ContinuousDocument23 pagesPresent Perfect - ContinuousAlexander HidalgoNo ratings yet
- GERUND and INFINITIVE Verb Forms ExplainedDocument17 pagesGERUND and INFINITIVE Verb Forms ExplainedSidiq WiranataNo ratings yet
- Compound NounsDocument18 pagesCompound Nounsmoises60% (5)
- Present Perfect Simple ContinuousDocument23 pagesPresent Perfect Simple ContinuousKathrin WolfNo ratings yet
- Direct To FCE Grammar ReferenceDocument19 pagesDirect To FCE Grammar ReferenceDolores Salguero González100% (3)
- Reported Speech For ESL LearnersDocument38 pagesReported Speech For ESL LearnersMieder van Loggerenberg100% (2)
- Verb Tense Review: The Importance of TimeDocument32 pagesVerb Tense Review: The Importance of Timebaba ioana100% (1)
- Topic 1 Simple Present Vs ContinuousDocument31 pagesTopic 1 Simple Present Vs ContinuousMargie ChavezNo ratings yet
- Presentperfect 2ºESODocument21 pagesPresentperfect 2ºESOcamilo sanchezNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument19 pagesPresent Perfect Simpleapi-252190418100% (2)
- The Present Perfect ContinuousDocument14 pagesThe Present Perfect ContinuousNaitali MalikaNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect ContinuousDocument14 pagesThe Present Perfect ContinuousYallyNo ratings yet
- Session 1 A JUST IN TIME Set B1Document24 pagesSession 1 A JUST IN TIME Set B1Jorge MadridNo ratings yet
- Talk about Present Perfect TenseDocument2 pagesTalk about Present Perfect TenseJP SALDAÑANo ratings yet
- Simple Past or Present PerfectDocument17 pagesSimple Past or Present PerfectMarainaNo ratings yet
- Hi, Let's Learn About Present Perfect?Document21 pagesHi, Let's Learn About Present Perfect?João Henrique AlessioNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument64 pagesPresent PerfectmiaNo ratings yet
- B1Document3 pagesB1Daniel YorkeNo ratings yet
- Diapo 2 Ciclo 10 PDFDocument39 pagesDiapo 2 Ciclo 10 PDFDaniyar Quintanilla QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- The Present PerfectDocument26 pagesThe Present PerfectRAYZA ARIEL CURI ALCANTARANo ratings yet
- PRESENTPERFECTTENSEDocument62 pagesPRESENTPERFECTTENSEMuhammad_Al_We_5107100% (1)
- Present Perfect VDocument31 pagesPresent Perfect VelzharahmaelzaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument69 pagesSimple Present TenseStella PayenindiNo ratings yet
- Life 6. Unit 2Document18 pagesLife 6. Unit 2Diana moraNo ratings yet
- Unit Two - Tiempos Perfectos, Parafraseo y ResumenDocument10 pagesUnit Two - Tiempos Perfectos, Parafraseo y ResumenAnibal MartinezNo ratings yet
- Trabalho de InglesDocument18 pagesTrabalho de InglesSabio Maria JulioNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument18 pagesPresent PerfectPopescu DanielaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument19 pagesUNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectOliver TorresNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense: Definition, Rules and Useful ExamplesDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Tense: Definition, Rules and Useful ExamplesAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- VERB TENSE OVERVIEW WITH EXAMPLES Punya Ali PDFDocument165 pagesVERB TENSE OVERVIEW WITH EXAMPLES Punya Ali PDFDila SafiraNo ratings yet
- Ta 2Document12 pagesTa 2ocsenbao64No ratings yet
- Egp Present Perfect 15032023Document20 pagesEgp Present Perfect 15032023Sangri MurugesuNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple ContinuousDocument17 pagesPresent Perfect Simple ContinuousLiliana RaduNo ratings yet
- How Do We Use The Present Perfect Tense?: by Lynn MateasDocument18 pagesHow Do We Use The Present Perfect Tense?: by Lynn MateasFlor LerdaNo ratings yet
- TS 4a B1.1 Unit 1 Interesting LivesDocument90 pagesTS 4a B1.1 Unit 1 Interesting LivesADAMIS LIDUEÑAS BERTELNo ratings yet
- Use of Tenses Guide - Present Perfect, Past Simple, Future Forms ExplainedDocument86 pagesUse of Tenses Guide - Present Perfect, Past Simple, Future Forms Explainedkanwal hafeezNo ratings yet
- Makalah English MinatDocument4 pagesMakalah English MinatNabila KeizaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument7 pagesTensesmanikarthikaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense: or The Most Confusing Tense You Have Ever Tried To Understand !Document14 pagesPresent Perfect Tense: or The Most Confusing Tense You Have Ever Tried To Understand !Sharan DhandaalNo ratings yet
- HND Year 2 Common TextsDocument58 pagesHND Year 2 Common Textsbsonleader5No ratings yet
- HEDVANIADocument14 pagesHEDVANIADjeck CassimoNo ratings yet
- Texto Paralelo InglesDocument58 pagesTexto Paralelo InglesGabriela HernandezNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument59 pagesPresent PerfectAlejandro PrezaNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect Continuous TenseDocument8 pagesFuture Perfect Continuous TenseAtriyusri HanafahNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense - 2Document2 pagesPresent Perfect Tense - 2duru ikinciNo ratings yet
- Elearning Present PerfectDocument14 pagesElearning Present PerfectYosivia YosiNo ratings yet
- Lesson N°2 Present Perfect Simple and Continuous-Grammar RulesDocument7 pagesLesson N°2 Present Perfect Simple and Continuous-Grammar RulesKamil Henriquez100% (1)
- Level 5 - Unit 1: My Class NotesDocument6 pagesLevel 5 - Unit 1: My Class NotesDani AliquintuiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect & Present Perfect Progressive X 4th MeetingDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect & Present Perfect Progressive X 4th MeetingWisely Leo CandraNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple: Use 1 Unspecified Time Before NowDocument6 pagesPresent Perfect Simple: Use 1 Unspecified Time Before NowGabriela ScaeteNo ratings yet
- Material Ive Been Doing My BestDocument41 pagesMaterial Ive Been Doing My BestBLANCA LILIANA SALAZAR SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect - PresentationDocument12 pagesPresent Perfect - PresentationJóse Sandrino Sazo RojoNo ratings yet
- Tatcdr2 - Week 2 - Unit 3 - 4 - SDocument27 pagesTatcdr2 - Week 2 - Unit 3 - 4 - S16-PHẠM THỊ LAN HƯƠNG DHTM13A1No ratings yet
- Charlie and The Chocolate Factory CHPT 2 PDFDocument3 pagesCharlie and The Chocolate Factory CHPT 2 PDFFarah ElbadryNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument7 pagesPresent Perfect TenseFarah ElbadryNo ratings yet
- Charlie and The Chocolate Factory CHPT 3 ..Document2 pagesCharlie and The Chocolate Factory CHPT 3 ..Farah ElbadryNo ratings yet
- Charlie and The Chocolate Factory CHPT 1 ..Document3 pagesCharlie and The Chocolate Factory CHPT 1 ..Farah ElbadryNo ratings yet
- Model Answer (Unit 1 - CW HW)Document11 pagesModel Answer (Unit 1 - CW HW)Farah ElbadryNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egypt ProjectDocument8 pagesAncient Egypt ProjectFarah ElbadryNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument1 pageIrregular VerbsAndrés Guillermo Hoyos MarínNo ratings yet
- Run-On and FregmentsDocument11 pagesRun-On and FregmentsMushtaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Compendio Unit 2-KeniaDocument24 pagesCompendio Unit 2-KeniaIngrid Tahis Conforme MeraNo ratings yet
- Grammar For The Mid-TermDocument5 pagesGrammar For The Mid-TermNatia TughushiNo ratings yet
- Quick guide to English course PDF sectionsDocument1 pageQuick guide to English course PDF sectionsYunus OkumuşNo ratings yet
- Practical Italian GrammarDocument366 pagesPractical Italian GrammarBranko NikolicNo ratings yet
- Physical, Mental & States of Being VerbsDocument4 pagesPhysical, Mental & States of Being VerbsApple DoeNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Ioel Sample PaperDocument2 pagesClass 6 Ioel Sample PaperAlbert CostaNo ratings yet
- Adding EmphasisDocument8 pagesAdding Emphasiswendiwendi100% (1)
- If ConditionalDocument4 pagesIf ConditionalPoer SupadmoNo ratings yet
- Common Affixes Used in Root VerbsDocument8 pagesCommon Affixes Used in Root VerbsTonDaposalaNo ratings yet
- ENGL 1010 - Tarea 4.1Document6 pagesENGL 1010 - Tarea 4.1Andriashaly Rivera RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Learn Adjectives and AdverbsDocument5 pagesLearn Adjectives and AdverbsBebelyn AlquizarNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs 1 - LösungenDocument4 pagesIrregular Verbs 1 - Lösungenсергей кабакNo ratings yet
- Verbs: 1. Transitive VerbDocument4 pagesVerbs: 1. Transitive VerbHdd JohnNo ratings yet
- What Are Correlative Conjunctions?: Conjunction Coordinating Conjunctions Subordinating ConjunctionsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Correlative Conjunctions?: Conjunction Coordinating Conjunctions Subordinating ConjunctionshoneyNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous, Perfect Tenses, Passive Voice & Modal VerbsDocument3 pagesPast Continuous, Perfect Tenses, Passive Voice & Modal Verbsnikola023No ratings yet
- List of Irregular and Regular VerbsDocument6 pagesList of Irregular and Regular VerbsCamila DuranNo ratings yet
- Adjetivos InglesDocument12 pagesAdjetivos InglesDiana C. AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Question Words, Meanings and Example Sentences - English Grammar HereDocument1 pageQuestion Words, Meanings and Example Sentences - English Grammar HereJavierEslNo ratings yet
- WH QuestionsDocument20 pagesWH QuestionsDanny HoiNo ratings yet
- نحو ثالثDocument52 pagesنحو ثالثNatziNo ratings yet
- E Book3Document95 pagesE Book3ေျပာမယ္ လက္တို႔ၿပီးေတာ့No ratings yet