Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemistry
Biochemistry
Uploaded by
Ayesha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThis document discusses various topics in biochemistry including:
1) Reducing and non-reducing sugars, inhibitors of the electron transport chain, essential fatty acids, and immunoglobulins.
2) Many diseases and deficiencies related to vitamins and minerals such as scurvy, rickets, beriberi, and iron deficiency anemia.
3) Other conditions mentioned include gallstones, gastroenteritis, lactose intolerance, Wilson's disease, and hemoglobinopathies.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various topics in biochemistry including:
1) Reducing and non-reducing sugars, inhibitors of the electron transport chain, essential fatty acids, and immunoglobulins.
2) Many diseases and deficiencies related to vitamins and minerals such as scurvy, rickets, beriberi, and iron deficiency anemia.
3) Other conditions mentioned include gallstones, gastroenteritis, lactose intolerance, Wilson's disease, and hemoglobinopathies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesBiochemistry
Biochemistry
Uploaded by
AyeshaThis document discusses various topics in biochemistry including:
1) Reducing and non-reducing sugars, inhibitors of the electron transport chain, essential fatty acids, and immunoglobulins.
2) Many diseases and deficiencies related to vitamins and minerals such as scurvy, rickets, beriberi, and iron deficiency anemia.
3) Other conditions mentioned include gallstones, gastroenteritis, lactose intolerance, Wilson's disease, and hemoglobinopathies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
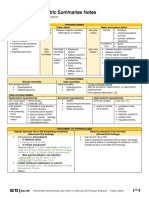
Biochemistry: ▪ Pancreatic enzyme deficiency
❖ Reducing sugar: ➢ Cholelithiasis – 4F – Gall Stone disease
➢ not involved in glycosidic linkage. ▪ Gall Bladder removal
➢ Free function group to show reducing ➢ Gastroenteritis
properties. ▪ Variety of virus attack
➢ all mono and disaccharide ➢ Ulcer
➢ both functional group (aldehyde and ▪ Helicobacter pylori
ketone) ➢ Lactose Intolerance
❖ Non-reducing sugar: ▪ Lactase Enzyme
➢ sucrose ➢ Retrograd Amnesia
➢ glycosidic linkage alpha and beta 2 ▪ Damage in thalamic area
➢ inversion and invert sugar ➢ Hyponetremia
➢ no mutarotation ▪ Excessive water intake or decrease of
➢ no osazone Crystal Na+
❖ Inhibitors of ETC: ➢ Edema
➢ complex I ▪ Excessive water out take or excessive
▪ amyta (barbiturate) Na+
▪ rotenone (insecticide) ➢ Hypokalemia
➢ Complex II: ▪ Excessive K+ conc in cells
▪ Carboxin ➢ Hyperkalemia
➢ Complex III: ▪ Excessive K+ conc outside cells
▪ Antimycin A ➢ Iron Deficiency anemia
➢ Complex IV: ▪ Iron loss, blood loss, hookworm
▪ Cyanide and CO ( carbomonoxide) infection
❖ Natural uncoupling: thermogenin ➢ Hemochromatitis
❖ Synthetic uncouplers: aspirin and salicylates ▪ Iron overload disorder
❖ Essential fatty acids: ➢ Wilson’s disease
➢ linoleic acid (18:2) ▪ Abnormal metabolism of copper
➢ linolenic acid (18:3) ➢ Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
➢ arachidonic acid (20:4) ▪ Zinc deficiency
❖ Semi-essential: ➢ Certinism
➢ Arachidonic acid ▪ Iodine Definciency
❖ Immuglobulins ➢ Beri beri
➢ Glycoproteins ▪ Vit B1 Thiamine
➢ 5 Ig’s based on variations in heavy chains ➢ Wernickee’s Encephalopathy
➢ Ig G is only antibody for placenta transfer ▪ Alcoholics with B1 deficiency
on immunity ➢ Cheilosis, Dermatitis, stomatitis
➢ Ig M is most potent antibody ▪ Vit B2 Riboflavin
➢ Ig A act as mucosal barrier ➢ Pellagra (3D’s)
➢ Ig E is antibody for allergens & parasites ▪ Vit B3 Niacin
➢ Ig D is present on surface of B ➢ Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Lymphocytes ▪ Substitution of Glycine with bulky side
❖ Diseases chains
➢ Burning Food Syndrome ➢ Ehlers Danlos
▪ Vit B5 Pantothenic Acid ▪ Type 3 Collagen (Arteries)
➢ Microcytic Hypochromic Anemia ➢ Marfan
▪ Vit B6 Pyridoxine ▪ Fibrillin
➢ Megaloblastic Anemia, Spinda Bifida ➢ Hemoglobinpathies
▪ Vit B9 Folate ▪ Mutation of Globin gene
➢ Pernicious Anemia ➢ Hydropsfetalis (alpha thalassemia major)
▪ Vit B12 Cobalamin ▪ No synthesis of alpha globin chain
➢ Steatorrhea ➢ Beta thalassemia
▪ Beta globin chain
➢ Sickle Cell Anemia
▪ Mutation of Glutamate to Valine
➢ Chocolate Cynosis
▪ Heme Compenent becomes ferric
state
➢ Atelectasis
▪ Phosphotidyl choline (Lecithin)
➢ Paget’s Disease
▪ Increase calcium level
➢ Hypocalcemia
▪ Vit D, Parathyroid
➢ Osteoporosis
▪ Reduced calcium absorption
➢ Hypernatremia
▪ Dehydration or increase Na+
➢ Alzheimar, Parkinsons
▪ Glogi Complex problem
➢ Mitochondrial Myopathies
▪ Mitochondrial DNA
➢ I-cell Disease
▪ Lysozymes
➢ Zellweger Syndrome / Cerebro-hepato-
renal syndrome
▪ Peroxisomes
➢ Enamel Hypoplasia
▪ Low Vit D
➢ Amelogenesis Imperfecta
▪ Mutation of Amelogenin Gene
➢ Flourosis
▪ Excessive fluoride
➢ Lactose Intolerance
▪ Lactase enzyme
➢ Night Blindness, Xerophthalmia
▪ Vit A
➢ Rickets, Osteomalacia
▪ Vit D
➢ Peripheral Neuropathy, Muscle weakness
▪ Vit E
➢ Hypoprothrombonemia, Increase clotting
time
▪ Vit K
➢ Scurvy
▪ Vit C
You might also like
- Tobin Principles and Practice of Mechanical Ventilation 3rd EditionDocument1,585 pagesTobin Principles and Practice of Mechanical Ventilation 3rd EditionLuis Lopez Reveles77% (22)
- FBCA Biomarkers and ConditionsDocument8 pagesFBCA Biomarkers and Conditionsmet50% (2)
- Cc1-Task 4Document8 pagesCc1-Task 4Joshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure ChartDocument5 pagesBlood Pressure Chartmahajan1963100% (1)
- Psych NCLEX QuestionsDocument16 pagesPsych NCLEX QuestionsPaula Verduzco100% (7)
- HEMATOLOGYDocument17 pagesHEMATOLOGYMA. ANDREA NICOLE BITOINNo ratings yet
- Hematology SBIM Part 1Document7 pagesHematology SBIM Part 1Gousay AlkhazmariNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument15 pagesVitaminsSAURABH PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument20 pagesHematologyJunaid SabirNo ratings yet
- Care Plan 2019Document24 pagesCare Plan 2019api-547212356No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument26 pagesAnemiaJoel CanenciaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Macrocytic Anaemia, Megaloblastic and Nonmegaloblastic AnaemiaDocument43 pages1.3 Macrocytic Anaemia, Megaloblastic and Nonmegaloblastic AnaemiaAlex KamougerosNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used To Treat Anemias: Dr. Redentor B. Magdayao, M.DDocument4 pagesDrugs Used To Treat Anemias: Dr. Redentor B. Magdayao, M.DPham PhamIoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-10-07 at 7.28.18 PMDocument45 pagesScreenshot 2022-10-07 at 7.28.18 PMMohammed Bin EisaNo ratings yet
- Microcytic AnemiaDocument6 pagesMicrocytic AnemiaharideepNo ratings yet
- MLAB 2401: Clinical Chemistry Keri Brophy-Martinez: Plasma ProteinsDocument19 pagesMLAB 2401: Clinical Chemistry Keri Brophy-Martinez: Plasma ProteinsLoulou ApolloNo ratings yet
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument8 pagesAnemia in Pregnancycurry yumeNo ratings yet
- Plabable Gems Endocrine PDF P7aDocument44 pagesPlabable Gems Endocrine PDF P7aayşenur sevinçNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus 1Document5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 1smurplerNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument45 pagesLiver Functionpuno ric100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument9 pagesGastrointestinal DisordersalctheyNo ratings yet
- Hematology Final ExamDocument20 pagesHematology Final ExamAlon GoldfainerNo ratings yet
- Type II Reactions PDFDocument3 pagesType II Reactions PDFRch 19No ratings yet
- Barter Syndrome: Presented ByDocument18 pagesBarter Syndrome: Presented ByFun joyNo ratings yet
- Patient Case - HyponatremiaDocument14 pagesPatient Case - Hyponatremiaapi-611386981No ratings yet
- Chapters 33 and 33: Hematological System Iron Deficiency Anemia Etiology (Cause)Document14 pagesChapters 33 and 33: Hematological System Iron Deficiency Anemia Etiology (Cause)Celena LorenaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins TableDocument1 pageVitamins TableMicah Lou CalambaNo ratings yet
- Newborn Screening, An Update: Learning ObjectivesDocument37 pagesNewborn Screening, An Update: Learning ObjectivesKrenz CatiboNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocument1 pageHemolytic AnemiaVirgile KenmoueNo ratings yet
- Blok 5 Antianaemic DrugsDocument26 pagesBlok 5 Antianaemic DrugsPutri HusnanNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Pedia Blood Disorders StudentDocument39 pagesWeek 5 Pedia Blood Disorders StudentJaslir MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ch15 HyperglycemicEmergenciesDocument30 pagesCh15 HyperglycemicEmergenciesAinil MardiahNo ratings yet
- Renal Tubular AcidosisDocument29 pagesRenal Tubular AcidosisbismahNo ratings yet
- Plabable-Gems-4. Endocrine Plabable GemsDocument44 pagesPlabable-Gems-4. Endocrine Plabable GemsFaizan AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Amenia FinalDocument11 pagesAmenia FinalChihnita ChandanaNo ratings yet
- 18b-VITAMINE DEFFICIENCYDocument26 pages18b-VITAMINE DEFFICIENCYmnouma1612No ratings yet
- Anemia, Ida 1Document131 pagesAnemia, Ida 1zaha shamseerNo ratings yet
- Anemia 07oct FINALDocument77 pagesAnemia 07oct FINALDr pragya joshiNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Anemia: Ainur AbdrakhmanovaDocument15 pagesHereditary Anemia: Ainur AbdrakhmanovaAinur AbdrakhmanovaNo ratings yet
- Anemia FarmakoDocument28 pagesAnemia FarmakoYeniNo ratings yet
- CKD PathophysioDocument1 pageCKD PathophysioNoveeNo ratings yet
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test and Factors Influencing Blood Glucose LevelDocument23 pagesOral Glucose Tolerance Test and Factors Influencing Blood Glucose Levelaziz faydiNo ratings yet
- PEDIA2 2.01b Fluids Electrolytes Summary TablesDocument4 pagesPEDIA2 2.01b Fluids Electrolytes Summary TablesVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Hypercoagulable DisordersDocument6 pagesHypercoagulable DisordersYA M AY100% (1)
- 30 LN Water Soluble Vitamins I BLGDocument39 pages30 LN Water Soluble Vitamins I BLGDakshitha DharmakeerthiNo ratings yet
- Dks HhsDocument16 pagesDks HhsDebora Putri Fernanda SaragihNo ratings yet
- Nursing Clients With Hematologic DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Clients With Hematologic DisordersLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- ANEMIA MS LecDocument2 pagesANEMIA MS Lecsun shineNo ratings yet
- Pathology Week 2 FKHDocument5 pagesPathology Week 2 FKHAnna TohNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 Test 2Document44 pagesMed Surg 2 Test 2Tara ThorntonNo ratings yet
- FCPS Gynae 23 Aug 2023 (M)Document21 pagesFCPS Gynae 23 Aug 2023 (M)Tauseef AfridiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (20 Points)Document8 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (20 Points)ODESSEY SERQUI�ANo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome::one of The Clinical Syndromes With Many Causes and Many Histologic AbnormalitiesDocument8 pagesNephrotic Syndrome::one of The Clinical Syndromes With Many Causes and Many Histologic AbnormalitiesFarhana Fefe Amani FeFeNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & Minerals: Slam Shraf AhmyDocument5 pagesVitamins & Minerals: Slam Shraf AhmyAfsal Ur FriendNo ratings yet
- Clinical PathologyDocument13 pagesClinical Pathologyapi-19710563100% (1)
- PediatricDocument192 pagesPediatricbolt boltNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Tad MiyaDocument41 pagesCase Presentation: Tad MiyaEmily EresumaNo ratings yet
- PHARMA 2 Sir RafDocument1 pagePHARMA 2 Sir Rafshirlenedel cariñoNo ratings yet
- 1.4+5 Sideroblastic Anaemia Inherited and Aquired and PorphyriaDocument43 pages1.4+5 Sideroblastic Anaemia Inherited and Aquired and PorphyriaAlex KamougerosNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument36 pagesVitamins & MineralsMarisha Christin TarihoranNo ratings yet
- Glycogen Storage DiseasesDocument7 pagesGlycogen Storage DiseasesNikhilBhattNo ratings yet
- Anemia 2024Document50 pagesAnemia 2024b9p6vmfnc4No ratings yet
- Deficiency Disorders of Vitamins: RenjiniDocument43 pagesDeficiency Disorders of Vitamins: RenjiniRENJINIRP100% (1)
- Definitions Neuroanatomy VivaDocument3 pagesDefinitions Neuroanatomy VivaAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy VivaDocument10 pagesAnatomy VivaAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Intro To Basic Teachings of QuranDocument28 pagesLecture 5 Intro To Basic Teachings of QuranAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Intro To Basic Teachings of QuranDocument27 pagesLecture 2 Intro To Basic Teachings of QuranAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-6 Quranic StudiesDocument24 pagesLecture-6 Quranic StudiesAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Intro To Basic Teachings of QuranDocument16 pagesLecture 4 Intro To Basic Teachings of QuranAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Pharma FormativesDocument20 pagesPharma FormativesAyeshaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Viral DiagnosisDocument24 pages5 - Viral DiagnosisAyeshaNo ratings yet
- StreptococciDocument43 pagesStreptococciAyeshaNo ratings yet
- 01 MedicalScienceDocument9 pages01 MedicalScienceAyeshaNo ratings yet
- 1 StaphylococciDocument26 pages1 StaphylococciAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative CocciDocument21 pagesGram Negative CocciAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Types of DecelerationsDocument2 pagesTypes of DecelerationsMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- ClubfootDocument4 pagesClubfootDaphne AleliNo ratings yet
- Renal ThresholdDocument3 pagesRenal ThresholdAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Listening TestDocument3 pagesListening TestKhông Trà Trà ĐàoNo ratings yet
- ECG Lead Placement and Lead Reversal GuideDocument2 pagesECG Lead Placement and Lead Reversal Guidealfurlani100% (1)
- Hematocrit A Review of Different Analytical Methods PDFDocument9 pagesHematocrit A Review of Different Analytical Methods PDFEsdras DountioNo ratings yet
- Patient'S Health History: Biographical DataDocument5 pagesPatient'S Health History: Biographical DataLouthor Zyver TanNo ratings yet
- 5 - Stephanurus, Heterakis and SpiruridsDocument78 pages5 - Stephanurus, Heterakis and Spiruridsaniel_bmNo ratings yet
- Patient Record BookDocument1 pagePatient Record BooksumarumNo ratings yet
- UNIT-II SulfonamidesDocument12 pagesUNIT-II SulfonamidesابوبكرNo ratings yet
- ROZA - The Encyclopedia of Drugs and AlcoholDocument188 pagesROZA - The Encyclopedia of Drugs and Alcoholoialexsandro1396100% (4)
- Ebiomedicine: Trevor W. Stone, Megan Mcpherson, L. Gail DarlingtonDocument15 pagesEbiomedicine: Trevor W. Stone, Megan Mcpherson, L. Gail Darlingtoniryasti2yudistiaNo ratings yet
- Critical Illness Claim FormDocument2 pagesCritical Illness Claim FormNarayana MugalurNo ratings yet
- René Leriche PDFDocument2 pagesRené Leriche PDFanon_82494076No ratings yet
- Hymenal MorphologyDocument5 pagesHymenal MorphologyDimple Marie CabiasNo ratings yet
- Pathology QuizDocument11 pagesPathology Quizheshamdhafer04No ratings yet
- Nurses Progress NotesDocument2 pagesNurses Progress NotesCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics GynacologyDocument19 pagesObstetrics GynacologyAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Untitled25 PDFDocument17 pagesUntitled25 PDFElizabeth LeonNo ratings yet
- CSF RhinorrheaDocument10 pagesCSF RhinorrheaDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Emt 100 Question Test VarietyDocument28 pagesEmt 100 Question Test Varietyerickestacio58No ratings yet
- My Co PlasmaDocument70 pagesMy Co Plasmatummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- View Benefits For:: Mediclaim Group InsuranceDocument2 pagesView Benefits For:: Mediclaim Group InsuranceMahesh L SamalaNo ratings yet
- DR Nadia AhmadDocument4 pagesDR Nadia AhmadNadia AhmadNo ratings yet
- Slcog Abstracts 2012Document133 pagesSlcog Abstracts 2012Indika WithanageNo ratings yet
- 14 TH NmcleDocument24 pages14 TH NmclePadam raj pantNo ratings yet