Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sanjay Ram Project 1st Page
Uploaded by
vallimangala70 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesMy photo
Original Title
sanjay ram project 1st page
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMy photo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesSanjay Ram Project 1st Page
Uploaded by
vallimangala7My photo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
AIM
To Study the Optical Fibre Cable Principle and its Applications.
Important Terms
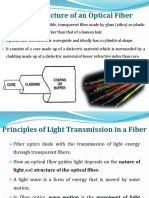
*Optical Fiber: An optical fiber (or fibre) is a glass or plastic fiber that
carries light along its length. Fiber optics is the overlap of applied
science and engineering concerned with the design and application of
optical fibers. Optical fibers are widely used in fiber optic
communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and
at higher bandwidths (data rates) than other forms of Communications.
*Refraction: Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a
change in its speed. This is most commonly observed when a wave
passes from one medium to another. Refraction of light is the most
commonly observed phenomenon, but any type of wave can refract
when it interacts with a medium, for example when sound waves pass
from one medium into another or when water waves move into water of
a different depth
*Reflection: Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an
interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into
the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the
reflection of light, sound and water waves.
Internal Reflection
Scattering: Scattering is a general physical process where some forms
of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to
deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-
uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional
use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle
predicted by the law of reflection.
Attenuation: is the gradual loss in intensity of any kind of flux through
a medium. For instance, sunlight is attenuated by dark glasses, and X-
rays are attenuated by lead.
You might also like
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- To Study The Optical Fibre Cable Principle and Its ApplicationsDocument1 pageTo Study The Optical Fibre Cable Principle and Its ApplicationsSuyash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument21 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsJack HammerNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument8 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsKuronix ArcayaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument23 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsRyan Paul RiwarinNo ratings yet
- Phenomenon of LightDocument5 pagesPhenomenon of LightPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document56 pagesOptics 1hh8860033No ratings yet
- Property of Lights HardDocument6 pagesProperty of Lights HardYippeNo ratings yet
- Unidad 2: Paso 3: Modos de Propagación Y Polarización en Las Ondas ElectromagnéticasDocument16 pagesUnidad 2: Paso 3: Modos de Propagación Y Polarización en Las Ondas ElectromagnéticasJuan Jose PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 3 Waves - AQA Physics A-LevelDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 3 Waves - AQA Physics A-LevelKavay KapoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 As EdexcelDocument91 pagesUnit 2 As Edexcelsadika sabaNo ratings yet
- Isc Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesIsc Physics ProjectBhoomi DhokaNo ratings yet
- Physcis Project On Optical Fibre Cable TDDocument14 pagesPhyscis Project On Optical Fibre Cable TDsoumityachaudharyNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Light: Physical Science - Week 3ADocument28 pagesPropagation of Light: Physical Science - Week 3AJen JvsjvsNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics 2Document49 pagesGen. Physics 2Shelamae MangyaoNo ratings yet
- Diffraction: Diffraction Refers To Various PhenomenaDocument70 pagesDiffraction: Diffraction Refers To Various PhenomenaRizwanbhatNo ratings yet
- Reflection 2Document1 pageReflection 2ShobhitNo ratings yet
- Reflection and RefractionDocument3 pagesReflection and RefractionGokulSubramanianNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument1 pageProjectile MotionYasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- G11 Propagation of LightDocument32 pagesG11 Propagation of LightRyan Dave MacariayNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic CharacteristicsDocument24 pagesFiber Optic CharacteristicssmalyqaNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion and Its ApplicationsDocument24 pagesWave Motion and Its ApplicationsDivya SoodNo ratings yet
- CIVL1180 - 18sep2023Document20 pagesCIVL1180 - 18sep2023jv5gfmjd4xNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument12 pagesContentExtramailNo ratings yet
- Fo 1Document22 pagesFo 1Vijay ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4-New Seca1701Document78 pagesUNIT 4-New Seca1701Venkata naga Sai VarunNo ratings yet
- Doon Public SchoolDocument18 pagesDoon Public SchoolManish HarneNo ratings yet
- 2 Electromagnetic Radiations PDFDocument30 pages2 Electromagnetic Radiations PDFjomel dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument14 pagesFiber OpticsShreeramMohanNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetic Wave?Document3 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetic Wave?Lance Aaron LapuzNo ratings yet
- Institute of Physics Submitted To: Dr. Muhammad Irfan Sahib Submitted By: Hammad Ghaffar Roll No. F20BPHYS3E01009Document8 pagesInstitute of Physics Submitted To: Dr. Muhammad Irfan Sahib Submitted By: Hammad Ghaffar Roll No. F20BPHYS3E01009Hoomi ShbNo ratings yet
- Refraction, Signal Degradation: Reflection &Document4 pagesRefraction, Signal Degradation: Reflection &Colton HutchinsNo ratings yet
- Diffraction TextDocument1 pageDiffraction TextBunty MitraNo ratings yet
- Finals Assignment 1 - Bu3Document3 pagesFinals Assignment 1 - Bu3Jhossa EpondulanNo ratings yet
- Class 2 PPT 1 Unit 1Document83 pagesClass 2 PPT 1 Unit 1ece Ms.G.Bhargavi100% (1)
- Reflection (Physics) : Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument1 pageReflection (Physics) : Jump To Navigationjump To SearchJewel GuintoNo ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument177 pagesOptical FiberManish ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Objectives of LightingDocument20 pagesObjectives of LightingAshrutha HarshiniNo ratings yet
- Refraction 1Document5 pagesRefraction 1murad khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 11th Class P and EDocument51 pagesChapter-2 11th Class P and ErajindertelecomnsqfNo ratings yet
- Physics of Light: de La Luna, Margarette A. Quiros, Ellysa Charise MDocument12 pagesPhysics of Light: de La Luna, Margarette A. Quiros, Ellysa Charise MQueenie Rose MarceloNo ratings yet
- Doc5 Optical PropDocument2 pagesDoc5 Optical PropducdepipoNo ratings yet
- Optics - Igbala VeysalzadeeDocument117 pagesOptics - Igbala VeysalzadeeMəhəmməd MustafazadəNo ratings yet
- Overview (OFC) First Unit Plus SubtopicsDocument8 pagesOverview (OFC) First Unit Plus Subtopicsbabasanta57No ratings yet
- Physics 5Document13 pagesPhysics 5ExtramailNo ratings yet
- Defraction of LightDocument17 pagesDefraction of LightShubh kalathiyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Rehman ZamanNo ratings yet
- LightDocument12 pagesLightapi-3703711100% (1)
- Focus: Light and Geometric Optics: Part I - Content UpdateDocument21 pagesFocus: Light and Geometric Optics: Part I - Content UpdateApril Joyce Ricamora NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument86 pagesFiber OpticsChristopher Oares100% (1)
- Investigation 2.0Document12 pagesInvestigation 2.0GnalixNo ratings yet
- Actvivdidad Pre-saberes-Teoría de OndaDocument3 pagesActvivdidad Pre-saberes-Teoría de OndaCarlos BonetNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of LightDocument16 pagesDiffraction of LightVinayKumarNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Week3Document14 pagesPhysics 2 Week3basurahangyujNo ratings yet
- General Explanation: LightDocument2 pagesGeneral Explanation: LightAzreen Anis azmiNo ratings yet
- Defraction of LightDocument21 pagesDefraction of Lightlyricafiesta1205No ratings yet
- Objective:: To Determine The Wavelength of Yellow Light Emitting From The Na-Lamp.Document14 pagesObjective:: To Determine The Wavelength of Yellow Light Emitting From The Na-Lamp.suleman205No ratings yet
- Physics Project On Optical FiberDocument20 pagesPhysics Project On Optical FiberManas Ranjan PadhanNo ratings yet
- Reasearch PaperDocument2 pagesReasearch Papercallme_thewizNo ratings yet