Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment 1 - Answer Booklet Haris
Uploaded by
harisali55Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment 1 - Answer Booklet Haris
Uploaded by
harisali55Copyright:
Available Formats
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
NUST School of Business (NBS)
BS Accounting & Finance
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
ASSIGNMENT 1
Allerton Ltd
CMS ID 353797
Name Syed Haris Ali Shah
Date of Issue: 26/10/2023
Date of Submission: 18/11/2023
Note:
All answers to be prepared and presented in this answer book.
The answer book should then be submitted to teacher or over LMS
ANSWER BOOK
NBS Assignment Page 1
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
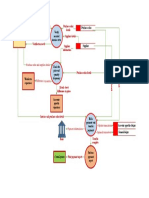
Task 1
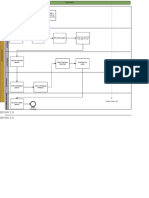
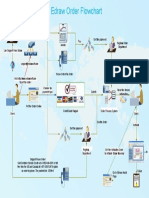
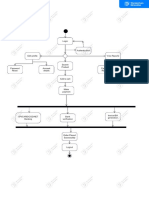
Prepare a flowchart here.
(Use this page – to max 20 marks including 6 marks credit for software use, good style and clear presentation)
Credit card
PAYMENT Card Details
Enter Personal
Details
Start PROCESS
Debit Card
Card Holder
Goods Accept Card Number
Displayed in Email Address
Catalogue Password
Card Security Code
Reject
Accept
Item Payment
Selection Verification at
Reject Bank
No
Add to order Return to
Out of Stock
by clicking buy shopping site or Payment
now exit confirmed?
Itemized order
Yes
Is product Order
No Click “Complete
available? Summary
Total Order Cost order and forward
details
Small (PKR 3.00)
Order
sent.
Order, Weight
and Delivery Medium (PKR
Yes 5.00)
Analysis
Large (PKR 8.00, fixed
2.00/kg variable)
Click “Go to CHECKOUT
checkout”
PROCESS
End
NBS Assignment Page 2
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Allerton Ltd
Task: 2 a.
Prime Costs (planned – November 2023 – To max 6 marks)
Prime costs: Order ‘SUN’ Order ‘MOON’ Order ‘STAR’
Price/
Machining Price/rate Total Total Price/rate Total
Qty Qty rate Qty
department PKR PKR PKR PKR PKR
PKR
Materials 2460 1220 1840
Labour 120 10 1200 160 10 1600 100 10 1000
Expenses 220 7 1540 240 7 1680 180 7 1260
Prime cost: 5200 Prime cost: 4500 Prime cost: 4100
Price/
Painting Price/rate Total Total Price/rate Total
Qty Qty rate Qty
department PKR PKR PKR PKR PKR
PKR
Materials 1360 2760 1160
Labour 160 12 1920 140 12 1680 120 12 1440
Expenses 130 4 520 90 4 360 50 4 200
Prime cost: 3800 Prime cost: 4800 Prime cost: 2800
Price/
Assembly Price/rate Total Total Price/rate Total
Qty Qty rate Qty
department PKR PKR PKR PKR PKR
PKR
Materials 1850 1940 1200
Labour 250 13 3250 270 13 3150 200 13 2600
5
Expenses 80 5 400 90 5 450 100 500
Prime cost: 5500 Prime cost: 5900 Prime cost: 4300
Note to workings (Prime cost (direct costs) – To max 3 marks):
Prime cost = raw material + direct labour
Prime costs are the business’ expenses directly related to the production of a good. E.g., raw
material and labour which are direct costs. We calculated prime costs for all 3 departments, for
all 3 products each.
Materials, Labour,
and Expenses is calculated by multiplying the quantity (except for materials) with the price/rate
and then adding all 3 to find the total prime cost for each department.
NBS Assignment Page 3
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Prime cost (per unit and in total) – To max 2 marks:
=
Total ÷
Prime cost /
Prime costs Units to be
unit
PKR produced
PKR
Order ‘SUN’ 14500 1450 10.00
Order ‘MOON’ 15200 800 19.00
Order ‘STAR’ 11200 1600 7.00
Total ALL products: 40900
Allerton Ltd
Task: 2 b. Total (full) costs of production
(planned – November 2023 – To max 3 marks)
Total Overhead ÷ Overhead
Overhead absorption rates: cost (given) Total basis hours absorption rate
PKR (labour or machine hours) (Oar) PKR / hour
Machining department 10240 640 16.00
Painting department 6300 420 15.00
Assembly department 9360 720 13.00
Total overheads: 25900
Product overheads – To max 4 marks:
Order ‘SUN’ Order ‘MOON’ Order ‘STAR’
Indirect production
overheads: Basis OAR Overhead Basis OAR Overhead Basis OAR Overhead
hours PKR PKR hours PKR PKR hours PKR PKR
Machining 220 16.00 3520 240 16.00 3840 180 16.00 2880
Painting 160 15.00 2400 140 15.00 2100 120 15.00 1800
Assembly 250 13.00 3250 270 13.00 3150 200 13.00 2600
Total: 9170 Total: 9450 Total: 7280
Note to workings (Full production costs / absorption costing – 3 marks):
Full production costs refer to both direct costs and indirect costs added together. The full
product costs are used as the basis of a selling price so that all possible costs can be recovered
through sales.
Absorption costing is a managerial accounting method for capturing all cost associated with
manufacturing a particular product. As the former only includes variable costs, the latter
includes overheads as well (fixed costs) and as such, we absorbed the overheads based on labour
hours or machine hours which was given in the data.
NBS Assignment Page 4
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
We firstly calculate the OAR which is done by dividing total overhead of each department by
labour or machine hours which was mentioned in the data. After OAR is calculated, the basis
hours are absorbed into each department by multiplying the hours with the OAR. Adding all 3
departments overhead gives the total overhead for each product.
Full production costs – To max 4 marks:
+ Indirect
÷ =
Prime costs production = Total (full)
Units Full cost per
B/fwd overheads cost
produced unit
PKR B/fwd PKR
B/fwd PKR
PKR
Order ‘SUN’ 14500 9170 23670 1450 16.32
Order ‘MOON’ 15200 9450 24650 800 30.81
Order ‘STAR’ 11200 7280 18480 1600 11.55
Totals: 40900 25900 66800
Allerton Ltd
Task: 2 c. Finished goods closing inventories / cost of sales
(Planned November 2023 – To max 4 marks)
= Closing Closing
Cost of sales and closing Units Less Cost of sales
inventory inventory
inventory: produced Units sold PKR
(units) PKR
Order ‘SUN’ 1450 900 550 14688 8976
Order ‘MOON’ 800 750 50 23107.5 1540.5
Order ‘STAR’ 1600 1100 500 12705 5775
Totals: 50500.5 16291.5
Note to workings (Cost of sales / closing inventory / Gross profits – absorption system)
(To max 3 marks):
Cost of sales is the amount it takes to manufacture create and sell a product. It is calculated by
multiplying units sold with unit cost (PKR). ‘Moon’ has the highest costs of sales.
Closing inventory is the amount of stock an organisation has at the end of an accounting period.
This can be a combination of finished goods, raw materials or WIP (work in process) goods. Here,
it is calculated by multiplying closing inventory units with unit cost (PKR).
NBS Assignment Page 5
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Gross profit is the profit a company makes after deducting the costs associated with making and
selling its products. Gross profit is calculated by subtracting costs of sales from revenue and is
done after absorption costing.
Allerton Ltd
Task: 2 d. Trading accounts (Gross profits and gross profit margins)
(Planned November 2023 – To max 3 marks)
Order ‘SUN’ Order ‘MOON’ Order ‘STAR’ Totals
Gross profits and margins:
PKR PKR PKR PKR
Sales 81000 26250 77000 184250
Less cost of sales 14688 23107.5 12705 50500.5
Gross profit (Absorption system): 66312 3142.5 64295 133749.5
Gross profit margin: 81.87 11.97 83.50 72.59
Allerton Ltd
Task: 3a Contribution and C/S ratio
(Planned November 2023 – To max 4 marks)
Order ‘SUN’ Order ‘MOON’ Order ‘STAR’
Contributions and profits
PKR PKR PKR
Selling price 90 35 70
Less variable / prime cost per unit 10 19.00 7
= Unit contribution: 80 16 63
C/S ratio: 0.889 0.46 0.90 Total
x Units sold 900 750 1100 PKR
= Total contribution earned: 72000 12000 69300 153300
Less total fixed costs: 25900
NBS Assignment Page 6
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Gross profit (marginal basis): 127400
Note to workings (Gross profits – marginal system / observations – To max 3 marks):
Gross profit is the profit a company makes after deducting the costs associated with making and
selling its products. Gross profit is calculated by subtracting costs of sales from revenue.
It is calculated by subtracting Total contribution (158864) earned with the total fixed costs
(25900 given in question.)
Contribution tells the company the profitability of an individual product, it can be calculated by
subtracting the variable/prime cost from the selling price. C/S ratio is the ratio of Contribution
to Sales C:S. Order ‘Sun’ and ‘Star’ are the most profitable as they have the highest
contributions compared to order Moon which has the lowest contribution.
Allerton Ltd
Task: 3 b.
Reconciliation of profits – (To max 4 marks)
Difference in profits: PKR
Gross profit (absorption system) 133749.5
Gross profit (marginal system) 127400
NBS Assignment Page 7
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Difference (to be reconciled) 6349.5
Order
Reconciliation: Order ‘SUN’ Order ‘STAR’
‘MOON’
Total overhead 9170 9450 7280
÷ Total production (units) 1450 800 1600
= Overhead per unit 6.32 11.81 4.55 Total (as above)
X closing inventory (units) 550 50 500 PKR
= Overhead held in inventory: 3478.23 590.63 2275 6344.16
Note to workings (Reconciliation of profits / explanation – To max 3 marks):
Reconciliation is an accounting procedure that compares two sets of records to check that the
figures are correct and in agreement. Reconciliation also confirms that accounts in a are
consistent and complete. Reconciliation can be used for personal as well as business purposes .
Total overheads were divided by total production units to find unit overhead. This was then
multiplied by closing inventory. Closing inventory overheads were added to find the value of
6344.16.
The gross profit from the absorption system has a higher figure than the marginal system and
the absorption system calculates gross profit using variable costs only, while the marginal system
includes fixed costs, giving us the total production costs.
The difference between the two systems is 6349.5. The difference is reconciled through the
left-over inventory overhead costs that incurred resulting in 6344.16 (difference in values due to
rounding.)
NBS Assignment Page 8
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Allerton Ltd
Task: 4 a. Recalculate gross profit (and margin) if product ‘B’ is removed (deleted)
from the product range – (To max 4 marks)
Order Order Order
Total
Contributions: ‘SUN’ ‘MOON’ ‘STAR’
PKR
PKR PKR PKR
Contribution B/fwd 72000 12000 69300 153300
Less Contribution lost (deletion) 12000 12000
Contribution c/fwd: 72000 0 69300 141300 A
Total
Fixed costs:
PKR
Fixed costs B/fwd 25900
Less fixed costs savings 8000
Fixed costs c/fwd: 17900 B
Adjusted profit (after deletion): PKR
Adjusted profit after deletion (A – B) 123400
Total
Reconciliation:
PKR
Profit (marginal basis) B/fwd 127400
Less contribution lost 12000
Add fixed costs savings 8000
Adjusted profit (as above) c/fwd:
123400
NBS Assignment Page 9
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Task: 4 b. Memo (To max 7 marks)
To: David Jones
From: (Student – Name)
Date: 26th November 2023
Subject: Delete product from range (reply)
Dear David Jones,
It has to my understanding that you have raised an issue concerning to the product "MOON" Your
suggestions to eliminate the product from the range is quite considerate as you have analysed the
company sales manager. I would, however, like to bring to your attention that 'MOON' is among
our products that have the lowest fixed production overheads among our range of products that
we produce, this is in line to the activity-based production analysis done by our finance office on
the range of products we have.
I understand that the products' profit margin is increased with reduced production. Having said
that, I believe that the “MOON” product should remain in the product line. It's worth noting that
the total benefit from all our sales is derived from the contributions of each product. In addition
to this the value of our products to the market and our customers is what we should consider
important, and since some customers prefer 'MOON' we should continue to produce it. We should
prioritise the importance of our goods to the consumer and our consumers, and as some
customers prefer 'MOON' it should stay in the product range.
Thank you,
Yours sincerely
Finance Office Trainee
NBS Assignment Page 10
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Allerton Ltd
Task: 5 a. Explanation of activity – based costing (ABC)
(To max 10 marks)
Activity – Based Costing (ABC)
ABC Costing: - Activity based costing is a costing method that identifies activities in an
organization and assign costs of each activity to all products and services according to the actual
consumption by each. Therefore, this model assigns more indirect costs into direct costs
compared to conventional costing. For example, the full absorption costing method includes
variable costs and fixed costs linked with the production of a good. While on the other hand
activity-based costing includes things like salaries, start-up costs utilities etc. ABC is used to get
a better grasp on costs allowing companies to form a more appropriate pricing strategy. If
Norton were to use activity-based costing method instead of their current method, I believe
they would be more profitable as they can see where the costs of the business are and change
their pricing strategy accordingly. Advantages of ABC costing: -
1). ABC bring accuracy & reliability in product cost determination by focusing on cause-and effect
relationship in the cost incurrence.
2). It identifies the real nature of cost behaviour and helps in reducing costs and identifying
activities which do not add value to the product.
NBS Assignment Page 11
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
3). ABC is concerned with all activities within and beyond the factory to trace more overheads to
the products.
4). ABC traces costs to area of managerial responsibility, processes, customers, departments
besides the product costs.
5). It improves greatly the manager's decision making as they can use more reliable product cost
data.
6). It provides cost driver's rates and information on transaction volumes which are very useful
to management for cost management and performance appraisal of responsibility centres.
Allerton Ltd
Task: 5.b. Recalculate gross profit (and margin) after allocating fixed production
overheads using an ABC system (To max 6 marks)
NBS Assignment Page 12
Intermediate Management Accounting (IMA)
Overhead Order ‘SUN’ Order ‘MOON’ Order ‘STAR’
recovery Recover Recovery Drive Recovery
(ABC Driver Overhead Driver Overhead Overhead
y rate rate r rate
System) Qty PKR Qty PKR PKR
PKR PKR Qty PKR
Set – Ups 30 60 1800 15 60 900 20 60 1200
Inspection
700 8 5600 200 8 1600 650 8 5200
s
Machine
300 10 3000 120 10 1200 250 10 2500
hours
Materials
750 2 1500 150 2 300 550 2 1100
movements
Total overheads: 11900 Total overheads: 4000 Total overheads: 10000
Order Order Order
Total
Profits (Marginal / ABC): ‘SUN’ ‘MOON’ ‘STAR’
PKR
PKR PKR PKR
Sales 81000 26250 77000 184250
Less variable cost of sales 14250 7700 30950
9000
Contribution: 72000 12000 69300 153300
Less Fixed costs (ABC) 11900 4000 10000 25900
Profits (Marginal / ABC): 60100 8000 59300 127400
Profit margin on sales (%) 74.20 30.48 77.01 69.20
Notes to Marginal / ABC profits (Workings / Observations – To max 4 marks):
ABC Costing was used here, and each overhead was calculated by multiplying driver quantity with
their respective overhead recovery rate. For set-ups, 60 was used as recovery rate as it appears
twice with values of 40 and 20. Overheads were then calculated by adding all the cost overheads
of all cost drivers for the products.
To find the contribution, prime costs or variable costs were subtracted from sales. Prime costs
being 10, 18.55 and 7 respectively and multiplying with 900, 750 and 1100 respectively. After
that, we simply subtract fixed overheads which was assigned to each product to find profits for
each product. Margin was calculated by the formula Sales-Total costs/Sales for each product.
NBS Assignment Page 13
You might also like
- HW3 Solutions 2017 SpringDocument4 pagesHW3 Solutions 2017 SpringAtaush Sabuj100% (1)
- DET-2 Service ManualDocument105 pagesDET-2 Service Manualkriotron50% (2)
- Use Case DiagramDocument5 pagesUse Case DiagramShubhamBhardwajNo ratings yet
- Boq Medical Services Obs™ PDFDocument3 pagesBoq Medical Services Obs™ PDFKyle Levic SalaguintoNo ratings yet
- Amazon Fresh Customer Order Process BPMN DiagramDocument3 pagesAmazon Fresh Customer Order Process BPMN DiagramKeerthi MenonNo ratings yet
- SOP User Guide - Check Customer IDDocument30 pagesSOP User Guide - Check Customer IDDella GbedemahNo ratings yet
- Cart - Wish - ComDocument2 pagesCart - Wish - ComAnonymous G1iPoNOKNo ratings yet
- Proof of Payment CodeKece Creative StudioDocument1 pageProof of Payment CodeKece Creative StudioIing the m.rollesNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Match The Words at The Bottom To The Appropriate Part of The Online Order ProcessDocument2 pagesInstructions: Match The Words at The Bottom To The Appropriate Part of The Online Order ProcessKevin BNo ratings yet
- HDFC Regalia UnlockedDocument4 pagesHDFC Regalia UnlockedMayank RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Boq Medical Services Obs™ PDFDocument3 pagesBoq Medical Services Obs™ PDFKyle Levic SalaguintoNo ratings yet
- PI YemenDocument2 pagesPI Yemenابوايمن العمراني ايمنNo ratings yet
- Transaction - Receipt 10 Feb, 2023 06 - 47 PMDocument1 pageTransaction - Receipt 10 Feb, 2023 06 - 47 PMAmrit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturers, Suppliers, Exporters & Importers From The World's Largest Online B2BDocument1 pageManufacturers, Suppliers, Exporters & Importers From The World's Largest Online B2Bsjuntha77No ratings yet
- Echeque Confirmation: View InboxDocument1 pageEcheque Confirmation: View InboxKumar MNo ratings yet
- Safety OralDocument1 pageSafety OralNarsinh WalvoikarNo ratings yet
- Oral4 PDFDocument1 pageOral4 PDFram prasanthNo ratings yet
- My AliExpress - Manage OrdersDocument1 pageMy AliExpress - Manage OrdersStrahinja SkoboNo ratings yet
- Drop Shipment ProcessDocument10 pagesDrop Shipment Processprabhu181No ratings yet
- Order Details for #10 EnvelopesDocument2 pagesOrder Details for #10 Envelopestriveda propertiesNo ratings yet
- Order Flowchart PDFDocument1 pageOrder Flowchart PDFSanthosh Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Order FlowchartDocument1 pageOrder FlowchartkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument1 pageCase StudyShivam DubeyNo ratings yet
- Cheque Payment JourneyDocument2 pagesCheque Payment JourneylasercrazerNo ratings yet
- Shopee Seller Centre Cust #10 (Jazliza)Document2 pagesShopee Seller Centre Cust #10 (Jazliza)anisNo ratings yet
- Track sales orders with Aptec's SOPDocument2 pagesTrack sales orders with Aptec's SOPShrikant GhadageNo ratings yet
- A003808324 - Your Order Invoice - Pizza Hut - Sri LankaDocument1 pageA003808324 - Your Order Invoice - Pizza Hut - Sri LankasinavimartNo ratings yet
- MyBill 11.21.2023Document18 pagesMyBill 11.21.2023jiahui.jianggNo ratings yet
- Bennet WinchDocument1 pageBennet WinchRhytham SoniNo ratings yet
- BillSummary - 2021 09 22Document48 pagesBillSummary - 2021 09 22iyas14No ratings yet
- 8889 20221031 StatementDocument4 pages8889 20221031 Statementacftravel23No ratings yet
- Inv169781253 A15173581 10052022Document3 pagesInv169781253 A15173581 10052022Nanie RNo ratings yet
- Bangalore Fluid System Components Pvt Ltd Purchase Payment ProcessDocument2 pagesBangalore Fluid System Components Pvt Ltd Purchase Payment Processlakshmi kbNo ratings yet
- ReceiptDocument1 pageReceiptsandeepgurung0001No ratings yet
- Repair - Benji Inv. 79713 - 211221Document1 pageRepair - Benji Inv. 79713 - 211221minkqeeNo ratings yet
- Purchase Order Details Suppliers Details Suppliers InformationDocument1 pagePurchase Order Details Suppliers Details Suppliers InformationThanh LâmNo ratings yet
- Procurement To Pay Future Process of Widget Inc.: Create Purchase Requisition Automated DemandDocument1 pageProcurement To Pay Future Process of Widget Inc.: Create Purchase Requisition Automated DemandGowri J BabuNo ratings yet
- Invoice KosliDocument1 pageInvoice KosliIPTV GangNo ratings yet
- Rizki Aditya Wiratama 2018230096Document1 pageRizki Aditya Wiratama 2018230096Annisa OriNo ratings yet
- Blanket Requisition ProcessDocument1 pageBlanket Requisition ProcessAndrow zulfikar AlNo ratings yet
- Week 4 (Process Management - Complete)Document42 pagesWeek 4 (Process Management - Complete)AHSAN ANSARINo ratings yet
- Stop Payment of Cheque (Corporate)Document1 pageStop Payment of Cheque (Corporate)Ram Mohan MishraNo ratings yet
- Thank You For Your Order: Order Details Order SummaryDocument1 pageThank You For Your Order: Order Details Order SummaryBen YoganathanNo ratings yet
- Order Confirmation PDFDocument1 pageOrder Confirmation PDFBen YoganathanNo ratings yet
- BSNL DecDocument3 pagesBSNL DectrivenitataNo ratings yet
- BillSummary - 2021 08 22Document28 pagesBillSummary - 2021 08 22iyas14No ratings yet
- Flujograma Grupo 6Document1 pageFlujograma Grupo 6ALESSANDRA MARIA ASMAT CENTENONo ratings yet
- Bill of Supply for Basic Health Screening PackageDocument1 pageBill of Supply for Basic Health Screening PackageSudip SinghNo ratings yet
- MAT Inc. Customer Payment Processing FlowchartDocument1 pageMAT Inc. Customer Payment Processing FlowchartShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Order & Account Information: Order # 000153720 (The Order Confirmation Email Is Not Sent)Document3 pagesOrder & Account Information: Order # 000153720 (The Order Confirmation Email Is Not Sent)vinuatanimalzoneNo ratings yet
- FEDEX Poster GMDocument2 pagesFEDEX Poster GMmitrax1pNo ratings yet
- Veem InvoiceDocument1 pageVeem Invoiceworkwithjoana.cNo ratings yet
- FICO Integration With Logistics: Process Flows, Accounting, and Valuation SimplifiedDocument36 pagesFICO Integration With Logistics: Process Flows, Accounting, and Valuation SimplifiedHridya PrasadNo ratings yet
- 43e8e3fc-1962-4f91-8a8e-7dbe4ce67670Document2 pages43e8e3fc-1962-4f91-8a8e-7dbe4ce67670Lost WriterNo ratings yet
- Payables Process - VSMDocument1 pagePayables Process - VSMAzmi MahamadNo ratings yet
- Activity DigramDocument1 pageActivity DigramPoonam BhakreNo ratings yet
- CIMB ClicksDocument1 pageCIMB Clicksniyazharraz5mNo ratings yet
- Shopee Seller Centre Cust #5Document2 pagesShopee Seller Centre Cust #5anisNo ratings yet
- Address ProofDocument4 pagesAddress ProofYash GaurkarNo ratings yet
- Use CasesDocument192 pagesUse Casesapi-3759584No ratings yet
- Pangan LestariDocument1 pagePangan LestariKurnia RiasmaNo ratings yet
- Trade Register 2017 2022Document9 pagesTrade Register 2017 2022CatherineNo ratings yet
- đề 3Document12 pagesđề 3Vi CầmNo ratings yet
- Steel Cargoes GuidanceDocument64 pagesSteel Cargoes GuidanceAamir SirohiNo ratings yet
- Lom LogDocument15 pagesLom LogMarco AntonioNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Applying The ANSI/ ISA 18.2 Alarm Management StandardDocument260 pagesUnderstanding and Applying The ANSI/ ISA 18.2 Alarm Management StandardHeri Fadli SinagaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument3 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementShubakar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Balancing Uncertainty in Structural DecisionDocument10 pagesBalancing Uncertainty in Structural DecisionAfifi MohammadNo ratings yet
- 14 Month Old Milestones and DevelopmentDocument6 pages14 Month Old Milestones and Developmentjovilene.abrinaNo ratings yet
- Disaster ClassificationDocument8 pagesDisaster Classificationaggrey noahNo ratings yet
- KUBOTA MU5501 4WD Tractor - T-1037-1562-2016Document9 pagesKUBOTA MU5501 4WD Tractor - T-1037-1562-2016Prashant PatilNo ratings yet
- Botulinum Toxin in Aesthetic Medicine Myths and RealitiesDocument12 pagesBotulinum Toxin in Aesthetic Medicine Myths and RealitiesЩербакова ЛенаNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of 2006 WSEAS Conference on Heat and Mass TransferDocument7 pagesProceedings of 2006 WSEAS Conference on Heat and Mass TransferAnonymous knICaxNo ratings yet
- Content Focus (And Interaction) : Example: Live Lecture (Online or On Campus)Document6 pagesContent Focus (And Interaction) : Example: Live Lecture (Online or On Campus)Dominic LibradillaNo ratings yet
- Teltonika Networks CatalogueDocument40 pagesTeltonika Networks CatalogueazizNo ratings yet
- Core Java AdvancedDocument103 pagesCore Java AdvancedRavi Chandra Reddy MuliNo ratings yet
- China's Lenovo: A Case Study in Competitiveness and Global SuccessDocument3 pagesChina's Lenovo: A Case Study in Competitiveness and Global SuccessIlse Torres100% (2)
- Get Involved American Edition Level Intro Student S Book Unit 4Document8 pagesGet Involved American Edition Level Intro Student S Book Unit 4KeilaNo ratings yet
- Human Factors Cabin CrewDocument18 pagesHuman Factors Cabin CrewMiko Judael TaperlaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 SandwichesDocument10 pagesCH 6 SandwichesKrishna ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Seaskills Maritime Academy: Purchase OrderDocument8 pagesSeaskills Maritime Academy: Purchase OrderSELVA GANESHNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning Vol: 09Document21 pagesDistance Learning Vol: 09Madrasa-Tul-Qaaim [a.s]83% (6)
- (Nick Lund - Grenadier) Fantasy Warriors Special RulesDocument11 pages(Nick Lund - Grenadier) Fantasy Warriors Special Rulesjasc0_hotmail_it100% (1)
- Review Movie: Title:the Conjuring 2: The Enfield PoltergeistDocument2 pagesReview Movie: Title:the Conjuring 2: The Enfield PoltergeistBunga IllinaNo ratings yet
- (PREP SƯU TẦM) Destination B1-22-25Document4 pages(PREP SƯU TẦM) Destination B1-22-25hanhuNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Rectangular Travelling Wave (Unit Step Function at Transition Points-Typical CasesDocument1 pageBehaviour of Rectangular Travelling Wave (Unit Step Function at Transition Points-Typical CasesAngela VaughnNo ratings yet
- Dryspell+ ManualDocument71 pagesDryspell+ ManualAldo D'AndreaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of NOx in Ambient AirDocument12 pagesAnalysis of NOx in Ambient AirECRDNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument18 pagesChapter Oneحيدر محمدNo ratings yet