Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Preboard
Uploaded by
no accountCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Preboard
Uploaded by
no accountCopyright:
Available Formats
PREBOARD EXAMINATION
SESSION: 2023-24
SUBJECT: PHYSICS (SET-B)
CLASS: XIl ~
Name of the Studen t:~~ 6.A.JtO' Mu. Marks: 70
th
Day & Date: Monday, 7 D~ember, 2023 Duration: 3 Hrs.
General Jnstroctions:
()) All questions are compulsory. There are 33 questions in all.
(2) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Seel/on E.
• Section A contains 12 MCQs and 4 assertion reasoning MCQs ofJ mark each.
• Section B contains 5 short answer questions of2 marks each
• Section C contains 7 short answer questions of3 marks each,
• Section D contains 2 case-based questions of 4 marks each and
• Section E contains 3 long answer questions of5 marks each.
(3) There is no overall choice. However internal choice is provided You have to attempt only one of
the choices in such questions.
SECTION A
All questions are compulsory.
Q.1 ABC is an equilateral triangle. Charges of +g are placed at each comer The electric field (l]
at centroid O will be:
(a)q/4n t-0-? (b) q/4n t-0 r
(c) Zero (d) 3q/41t t-0 r1
Q.2 Two charged spheres A and B having their radii in the ratio I :2 are connected together {1]
with a conducting wire. The ratio of their surface charge densities [o.Joa] will be:
(a) 1/2 (b) 2
(c) 1/4 (d) 4
Q.3 Electron is projected with velocity 'v' along the axis of a current carrying long solenoid. (1]
Which one of the following statements is true:
(a)The path of the electron will be circular along the axis.
(b)The electron will be accelerated along the axis.
(c) The path of the electron will be helical.
(d) The electron will continue to move with the same velocity 'v' along the axis of the
solenoid.
Q.4 A galvanometer of resistance 25 n gives full scale deflection for a current of IO mA. What (1)
resistance is to be connected in its series so that it can work as a voltmeter of range 10 V?
(a) 10000 !l (b) 10025 n (c) 975 !l (d) 9975 !l
7
Q.S A proton enters a magnetic field of 1.5 Twith the velocity of2xl0 mis at an angle of (1)
30° with the field. The force on the proton will be:
(a) 2.4x 10·12 N (b) 0.24x 10·12 N (c )24x 10·12 N (d)0.024x 10·12 N
Q.6 In a non-uniform magnetic field, a diamagnetic material moves: (1)
(a)From weaker to stronger part of the field.
(b)perpendicular to the field.
(c)from stronger to the weaker part of the field.
(d)in any random direction. A
be w ha t You wan t to be. 8 PRESIDIUM
\
Q.7 A copper ring is held horizontally and a bar magnet is dropped through the ring w·•L .
. ofthe frw1ling magnet wh'1le it is1\11 tta
length along the axis of the ring. The acceIerauon
passing through the ring is :
(a) g
(b)less than g
(c)Greater than g
(d)Depends on the diameter of the ring and length of the magnet.
Q.8 Sinusoidal voltage of peak value 283V and frequency 50 Hz is applied to a series LCR
circuit in which R=3O , 1,;=25.48 mH , and C=796 µF, then the power dissipated at the
resonant condition will be:
(a) 39.70kW (b) 26.70kW (c) 13.35kW (d) zero
Q.9 The maximum intensity of fringes in Young's double slit experiment is 'I'. If one of the (1)
slit is closed, the intensity at that place becomes lo.Which of the following relation is
true?
(a)I=Io (b) 1=210 (c) l=4lo (d) lo =21
Q.10 Lights of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 2 eV and 5 eV [=l]
respectively, successively illuminates the metal of work function l.O eV. The ratio of
maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be:
(a)2:5 (b) 1:5 (c) 1:4 (d) I :2
Q.11 The diagram shows the energy level for an electron in a hydrogen atom. Which transition, [l]
shown here, represents the emissions of a photon of maximum energy?
n=4
-_,L..;;..__ _ _ _ n=3
0
- 1 - - - - - i - - - n=2
A C
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
Q.12 Hydrogen atoms in the ground state {E=-13.6eV) are excited by monochromatic radiation (1)
of photon energy 12.leV. The maximum number of spectral lines emitted by hydrogen
atoms, as per Bohr's theory, will be:
(a)l (b)2 (c) 3 (d) 4
For question numbers 13, 14, 15 and 16, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other
labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and Rare true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false
Q.13 ASSERTION: (1)
In photoelectric effect, on increasing the intensity of incident light, the number of ejected
photoelectrons increases.
REASON:
On increasing the intensity oflight, energy of incident light photon increases
accord.in I .
Q.14 ASSERTION: (1)
The images formed by total internal reflections are much brighter than images formed by
mirrors or lenses.
· be what you want to be. S PRESIDIUM
REASON:
Q.15
There is no loss of intensi in
ASSERTION:
° ·
· t taJ internal reflection.
TI1c surface of spherical conductor can be co .d red . (1)
REASON: nst e as an equipotential surface.
In a conductor c cs can easil flow till ·
ASSERTION: tential is same at the entire surface.
Q.16
Silicon is preferred over gennanium for making semicond cto devtces. · (1)
REASON: u r
The energy gap for germanium is more than the energy gap of silicon.
SECTION-B
Q.17 Calculate the_equivalent resistance of the given electrical network between points A and (2)
B from the given figure.
C
Also, calculate the current through CD and ACB, if a 10 Volt d.c. source is connected
between A and B and the value of R is asswned as 2n.
OR
In the electric network shown in the figure, use l(jrchhoff's rules to calculate the power
consumed by the resistance R= 4 n .
c, = 12 V
+ r1 =20
B C
1,
R=40
A D
1, + 12
+ F
E
12 &2 =6V
Q.18 Double convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index l.55, with (2)
both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the
focal length is to be 20 cm?
Q.19 A smalJ telescope has an objective lens of focal length 140 cm and an eyepiece of focal (2)
length 5 cm. What is the magnifying power of telescope for viewing distant object when:
(i) The telescope is in nonnal adjustment (i.e. when the final image is at Infinity)?
(ii)The final image is fonned at the least distance of distinct vision (25 cm)?
Q.20 Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of the electron orbiting in the n=2 state of hydrogen (2)
atom.
be what you want to be. S PRESIDIUM
ons in a nuclear reaction is conserved, in what" '
If both the number of protons and n~utr
Q.21
is mass converted into energy (or vice versa
)? &'Plain giving one example. ~
SECTION C
All uestions are com ulso .
Q.22 3 identical capacitors Cl, C2 and C3 of capaci.tance of 6µF each connected to a 12V
are
battery as shown in the figure . Find:
C1
+
-=-12 v
C2
(a)Charge on each capacitor.
(b) Equivalent capacitance of the network.
(c)Energy stored in the network of capacitors.
Q.23 (a)Define drift velocity,
(b)The number density of free electrons in a copper condu (3)
ctor is 8.5 x 1<>21 m·3 • How long
does an electron take to drift from one end of a wire 3.0 m long
to its other end? The area
of cross section of the wire is 2.0x l 0-6 m2 and is carrying a curren
t of 3A.
Q.24 (a)A moving coil galvanometer of resistance Ro gives a full-sc
ale deflection for current [3]
J1 . Use the suitable circuit diagram to convert it into an amme
ter of range Oto I (I >Ia).
Deduce the expression for the shunt required for this conversion.
Hence, write the
expression for the resistance of the ammeter thus obtained.
Co) A current carrying loop, free to turn, is placed in a unifor
m magnetic field. What will
be its orientation, relative to 'B' in the equilibrium state?
Q.25 AO.Sm long metal rod PQ completes the circuit as shown :
)(
(3)
)( X )( X X
a
)( )( )( X )( )(
2 m s-1
)( X )( )( X X
)( X X X p )( )(
The area of the circuit is perpendicular to the magnetic field of
flmt density O.15 T. If the
resistance of the total circuit is 3Q, calculate the force needed
to move the rod in the
direction as indicated with the speed of 2 m/!r.
Q.26 (a) Considering the case of a parallel plate capacitor being
charged, show how one is [3)
required to generalize Amperes circuital law to include the
term due to displacement
current.
(b) Name the e.m. waves which are suitable for radar system
s used in aircraft navigation.
Write the range of frequency of these waves .
be wha t you wan t to be.
S PRESIDIUM
fa1>loin giving reasons for the following: (31
(a)Photoelectric current in a photocell increases with the increase in the intensity of the
incident radiation.
(b)The stopping potential(Vo) varies linearly with the frequency (v) of the incident
radiation for a given photo sensitive surface with the slope remaining the same for
different surfaces.
(c}Ma.ximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is independent of the intensity of
incident radiation.
I
OR
(a)Show that the de Broglie's wavelength of electrons accelerated for potential V volts
h
can be expressed as, ). = -,- .
v2meV
)What is the de Broglie's wavelength of a 2 kg object moving with the speed of 1 mis?
(a) What happens to the \vidth of depletion layer of p-n junction when [31
(i)it is forward biased,
(ii)reverse biased?
(b) Draw energy band for p type and n type extrinsic semiconductor.
SECTIOND
Questions 29 and 30 are Case Study based questions and are compulsory. Attempt any 4 sub parts from
each question. Each question carries l mark.
Cutting of Lens: Lens maker's fonnula is a fonnula correlating the power P(or focal [4]
length f) of a lens to radii of curvature of the two surfaces of the Jens and the refractive
index oflens material with respect to its surroundings. The fonnula is expressed as:
1 1 1
p = f = (n - l)[Rl - R2]
where n is the refractive index of the material of the lens with respect to its surroundings,
(ordinarily air) and R1 and ~ are the radii of curvature of two surfaces of the lens. The
relation is true under alJ conditions but while applying it we should put values of P,f,R1,
and ~ with their proper signs as per sign convention being followed by us. Let us have a
bi-convex lens and let radii of cUivature of both its curved surface is same. That is IR1 I=
l~l=R{say).
(i)Power P of a biconvex lens may be expressed as:
X'+;yX Y'
(a) p = Zn-1 (b) p = Zn+t (c) p = Z(n- 1) (d)Z(n+l)
R R R R
(ii) Let given biconvex. lens be cut into 2 parts Lt ll.l)d k along a section YY', then
Power Pt of each part will be:
(a) P1 =P (b) P1 =2P (c) P1 = P/2 (d) P1 =4P
(iii) Let given biconvex lens be cut into 2 parts Lt and k obtained in (ii) are joined
a ain as shown in the fi r then the net ower of the combination will be:
be what you want to be. S PRESIDIUM
X'---+ -H---X
(b) P (c) P/2 (d) 3P/2
2
(?)P . . b t ·nto l parts along a section XX', then Power P1
(av) Let given biconvex 1ens e cu •
of each part will be: (c) P (d) 4P
(a) P (b) P/2 2
(v) if l parts of lens obtained in (iv) be joined together as shown. Then the nd power
of the combination will be:
m m(i) (ii)
(a) 2P and P respectively (b) P and P respectively
(c) 2P and 2P respectively (d) 2P and Orespectively
Rectifier- A p-n junction allows current to pass only when it is forward biased. This (4]
property of diode is made use to rectify alternating voltages. If an alternative voltage is
applied across a diode in series with a load, a pulsating voltage appears across the load
only during the half cycle of AC input during which the diode is forward biased. To get
output rectified voltage corresponding to both positive as well as negative half of AC
supply, we arrange the circuit using two diodes. Such an arrangement is called full wave
rectifier. Output of a fuJI wave rectifier is unidirectional but it doesn't have a steady value.
To get a steady DC output we use a filter.
With the help of above comprehension, choose the most appropria te alternativ e for
each of the following questions:
(i)A rectifier is an electronic arrangem ent which:
(a) transforms alternating current into unidirectional current.
(b) transforms direct current into alternating current.
(c)Both a as well as b.
(d)none of these.
(ii) p-n junction diode has a resistance of 20 0 when forward biased and 2x 1()5 O
when reversed biased. The current in the diode for the arrangem ent shown here will
be:
5V 30 Q
·•---~;it--- ~,---OV·
(a)0.4 A (b) l/6A (c) O.lA (d) 25µA
(iii) What is the correct circuit diagram of half wave rectifier?
be what you want to be. e ·PRESIDIUM
+
..
□ CT
'
(a) a.c.
t
(b) a 1-
(r) □a~
(iv) Select the correct statement:
(a)ln a full wave rectifier, 2 diodes work in a complementary mode.
(b)ln a full wave rectifier, 2 diodes work simultaneously.
(c)The efficiency of full and half wave rectifier is same.
(d)Full wave rectifier is bidirectional.
cy of
(v) An AC of frequency 50 Hz is supplied to a full wave rectifier. The frequen
ripple present in output of rectifier is:
(a) 50 Hz (b) 25 Hz (c) IOOHz (d) No ripple is present
SECTI ONE
All uestions are com ulso . In case of internal choices attem tan one.
or of radius 12cm
7
has a charge of 1.6x 10' C distributed /SJ
Q.31 (a)A spherica l conduct
unifonnly on its surface. What is the electric field:
(i) inside the sphere.
(ii) just outside the sphere.
(iii)at a point I8cm from the centre of the sphere?
of a solid
(b) Draw a plot showing variation of electric field with distance from the center
conducting sphere of radius R, having a charge Q on its surface.
OR
at a point
(a)Deduce an expression for the electric field E due to dipole of length '2a'
distance 'r' from the centre of the dipole on the axial line.
(b)Draw a graph ofE vs r for r» a.
y represent
(c)Ifthis dipole were kept in a unifonn external electric field E, diagrammaticall
in stable and unstable equilibrium, and write the expression for
the position of the dipole
the to ue actin on the di le in both the cases.
offered by (5)
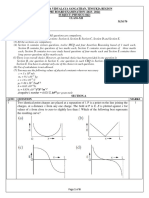
Q.32 (a) The graphs (i) and (ii) shown in the figure represent variation of opposition
of alternating current versus the
the circuit elements, X and Y, respectively to the flow
frequency of the applied emf. Identify the element s X and Y.
~
B E
C: -C:
-
c :C:
v = 0 0
:.:, Q)
·.;; I::
&.a
a.
Q)
'i ~
0.
0 0
i ~Fre quen cy
t - F requenC)I
Ii\ Iii\
of these two
(b) Write the expression for the impedan ce offered by the series combination
elements connected to an AC source of vol e V=Vosi n c.ot.
be what you want to be. 8 PRESIDIUM
(c)Show with the help ofphasordiagrams, the variation of the voltage and the current with
rot in their respective circuits.
OR
(a) Draw a labelled diagram of a step-down transfonner.
(b) Calculator current drawn by the primary coil of a transfonner, which ste~s down 200
volts to 20 volts to operate a device of resistance 20 n. Assume the efficiency of the
·1
transfonner to be 80%.
(c) Mention any two reasons for energy losses in an actual transfonner.
Q.33 (a) Write the conditions under which light sources can be said to be coherent. (5)
(b )Why is it necessary to have coherent sources in order to produce an interference p~em?
(c) Based on Huygen's construction, draw the shape of a plane wavefront as tt gets
refracted on passing through a (i) thin convex lens (ii) a thin prism.
OR
(a) Give two differences between interference and diffraction .
(b) Does the appearance of bright and dark fringes in the interference pattern violate, in
any way, conservation of energy? Explain.
(c)Yellow light(). =6000 A0 ) illuminates a single slit of width 1x I0-4m. Calculate:
(i)the distance between two dark lines on either side of the central maximum when the
diffraction pattern is viewed on a screen, kept 1.5 m away from the slit.
(ii)Anirular soread/oosition of the first diffraction minima.
be what you want to be. S PRESIOIUM
You might also like
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Physics PQ2Document7 pagesPhysics PQ2David BamNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Pre Board Xii Phy 2023-24Document11 pagesPractice Paper Pre Board Xii Phy 2023-24Buvaneswari SriniNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Dec-2023Document12 pagesAdobe Scan 07-Dec-2023Poovaraahan RaghuveeranNo ratings yet
- 12CBSE-Physics-Model - QPDocument11 pages12CBSE-Physics-Model - QPGuestNo ratings yet
- Test paper 8 (answers)Document17 pagesTest paper 8 (answers)ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- COMMON PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION 2022-23 PHYSICSDocument11 pagesCOMMON PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION 2022-23 PHYSICSEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Common Pre-Board Examination 2022-23 Physics (042) Class XIIDocument6 pagesCommon Pre-Board Examination 2022-23 Physics (042) Class XIIEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Bhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1Document9 pagesBhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1niladriputatunda1No ratings yet
- 100 Most Imp Question For Jee MainsDocument23 pages100 Most Imp Question For Jee MainsgopinadhNo ratings yet
- Physics XII QP Set 1Document10 pagesPhysics XII QP Set 1meme MachineNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics Sample Question Paper 1Document42 pagesClass XII Physics Sample Question Paper 1OJASisLiveNo ratings yet
- Physics Final 22Document7 pagesPhysics Final 22AYAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics Support Material Final-1 - Removed - RemovedDocument70 pagesClass XII Physics Support Material Final-1 - Removed - RemovedIshu RaoNo ratings yet
- PB XII Phy QP Nov 2022Document8 pagesPB XII Phy QP Nov 2022Ayushi KayalNo ratings yet
- 14 SQPDocument8 pages14 SQPdipanshu76612No ratings yet
- Sample Paper 2 Word FileDocument12 pagesSample Paper 2 Word FileAtul DubeyNo ratings yet
- Ii Pre Board Class XiiDocument14 pagesIi Pre Board Class XiiPrithibiNo ratings yet
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2Document7 pagesClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2kamali.v777No ratings yet
- Mock PB 23-1Document11 pagesMock PB 23-1Kshitij YadavNo ratings yet
- Class XII Session 2023-24 Subject - Physics Sample Question Paper - 5Document18 pagesClass XII Session 2023-24 Subject - Physics Sample Question Paper - 5krishoreraj23No ratings yet
- BUGKTflSvy9MqZANCjtU 1 7Document7 pagesBUGKTflSvy9MqZANCjtU 1 7ajbros1223No ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument21 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersprismtonicNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2024Document9 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2024s15089a.shubham14646No ratings yet
- Xii QP Physics VSTDocument5 pagesXii QP Physics VSTkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- 2020 12 SP PhysicsDocument22 pages2020 12 SP PhysicsRiya NinanNo ratings yet
- Physics SQPDocument7 pagesPhysics SQPGopa DeyNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - XII - Physics2023-24Document6 pagesSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - XII - Physics2023-24Nandita SharmaNo ratings yet
- XII Physics QP Preboard II - Set 7Document8 pagesXII Physics QP Preboard II - Set 7ABHIK THE GHOULNo ratings yet
- CBSE Physics Class 12 Sample Paper 5Document9 pagesCBSE Physics Class 12 Sample Paper 5Ansh MishraNo ratings yet
- Class XII (H.Y.Exam,) 2020 PhysicsDocument5 pagesClass XII (H.Y.Exam,) 2020 PhysicsPrecisive OneNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 3 2022-23 BoardDocument11 pagesPhysics Set 3 2022-23 BoardKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 12 For Board Exam 2024Document5 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 12 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzNo ratings yet
- 1.Qp - Class 12 - PhysicsDocument12 pages1.Qp - Class 12 - PhysicsEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Cbse SQP Xii Physics Sqp-1Document16 pagesCbse SQP Xii Physics Sqp-1virdishivaliNo ratings yet
- Xii Phy Sample Question Paper 01Document9 pagesXii Phy Sample Question Paper 01Aman DhamiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Apr14 Sample Paper 2023 24Document10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Apr14 Sample Paper 2023 24aisha.lambeNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsDocument8 pagesModel Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsyuvanithanrNo ratings yet
- Scan 06 May 2021Document5 pagesScan 06 May 2021Aditya KavalanekarNo ratings yet
- Test Paper 8Document8 pagesTest Paper 8rajeshsharma4121No ratings yet
- Q.P. - Set-B Physics-First Pre Board-2023Document8 pagesQ.P. - Set-B Physics-First Pre Board-2023Sonal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1Document11 pages12 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- 2022 Mock JEE Main-5 - PaperDocument15 pages2022 Mock JEE Main-5 - PaperAshish GuleriaNo ratings yet
- Physics SQPDocument10 pagesPhysics SQPPankaj SinghNo ratings yet
- QP12PHY02PB23Document8 pagesQP12PHY02PB23Ayush TomarNo ratings yet
- Physics XII - Set 3Document6 pagesPhysics XII - Set 3ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Xii Physics Set-ADocument9 pagesXii Physics Set-AAshik Anamic ShimiyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 5 QuestionsDocument28 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 5 Questionsmr mindNo ratings yet
- Pre Board 1 PhysicsDocument6 pagesPre Board 1 PhysicsMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre Board (2)Document10 pagesPhysics Pre Board (2)izumigamer69No ratings yet
- Sample Papers SolvedDocument185 pagesSample Papers Solvedjovanbhaskaran10No ratings yet
- 1asp MergedDocument73 pages1asp MergedHarrison BennettNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 Sample PaperDocument7 pagesPhysics Class 12 Sample PaperAkhilesh ArdcNo ratings yet
- Pre BoardDocument15 pagesPre Boardfakesmilelover07No ratings yet
- 6.XII Physics Question PaperDocument8 pages6.XII Physics Question PaperEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Physics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionDocument25 pagesPhysics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionA KNo ratings yet
- QP Xii PhysicsDocument9 pagesQP Xii PhysicsSufiyan BelimNo ratings yet
- Test paper 7 (answers)Document21 pagesTest paper 7 (answers)ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- XII Physics QPDocument8 pagesXII Physics QPsinghbharat50726No ratings yet
- CLASS XII PRE BOARD Physics QP 2023-24Document19 pagesCLASS XII PRE BOARD Physics QP 2023-24suprajabhupalanNo ratings yet
- Cobalt2 ManualDocument31 pagesCobalt2 ManualSócrates GómezNo ratings yet
- Suruhanjaya Tenaga - Guidelines For Wiring ResidentialDocument55 pagesSuruhanjaya Tenaga - Guidelines For Wiring Residentialkingcloud7100% (24)
- An-CM-302 SPWM Generator For Inverter DesignDocument18 pagesAn-CM-302 SPWM Generator For Inverter DesignRana ThakurNo ratings yet
- P0903BK UnikcDocument5 pagesP0903BK UnikcAmilcar SilvaNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For 110 KVA Switch YardDocument12 pagesMethod Statement For 110 KVA Switch YardCSD shakthiNo ratings yet
- Filter Types: Type Description FC Gain Q/BW Example For Filter ParametersDocument1 pageFilter Types: Type Description FC Gain Q/BW Example For Filter ParametersnopuedorecordarNo ratings yet
- Latha Mathavan Engineering College EEE Ist Internal Exam ResultsDocument3 pagesLatha Mathavan Engineering College EEE Ist Internal Exam Resultspriya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Quotation for 15KW solar system installationDocument3 pagesQuotation for 15KW solar system installationfatima naveedNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Teknis PeralatanDocument23 pagesSpesifikasi Teknis PeralatanHermanNo ratings yet
- Thesis 19 06 2008 Final VersionDocument324 pagesThesis 19 06 2008 Final VersionRatha MbrNo ratings yet
- Technics - RS-TR 979Document34 pagesTechnics - RS-TR 979FernandoNo ratings yet
- WAGO 852-1305enDocument6 pagesWAGO 852-1305enMESSIASNo ratings yet
- GES-6121C: Multiples of Current RatingDocument1 pageGES-6121C: Multiples of Current RatingAdolfo Sotomayor BurgosNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Electric Field DistributiDocument9 pagesCalculation of Electric Field DistributiAbouZakariaNo ratings yet
- 62IN Miniature Circular ConnectorsDocument24 pages62IN Miniature Circular ConnectorsCesar MarquesNo ratings yet
- Amplifier circuits exam questionsDocument4 pagesAmplifier circuits exam questionsjuber mullaNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual JOAN LABDocument2 pagesOperation Manual JOAN LABDoménica Feijoó ChávezNo ratings yet
- Lambda Lab Power Supply ZUP2040Document3 pagesLambda Lab Power Supply ZUP2040michaelbrendenNo ratings yet
- WWW Instructables Com GRBL Offline ControllerDocument9 pagesWWW Instructables Com GRBL Offline ControllerDavid duranNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Multilin Meter EnclosureDocument46 pagesInstruction Manual: Multilin Meter EnclosureGerardo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Dassault Falcon 8X for Sale with 405 Flight HoursDocument19 pagesDassault Falcon 8X for Sale with 405 Flight HoursTesteArquivosNo ratings yet
- Actividad4-Three Circuit Construction Lab Activities PDFDocument12 pagesActividad4-Three Circuit Construction Lab Activities PDFValentina Tascon MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Azionamenti Elettrici SLIDESDocument54 pagesAzionamenti Elettrici SLIDESarnold smithNo ratings yet
- A Bridgeless BHB ZVS-PWM AC-AC Converter For High-Frequency Induction Heating ApplicationsDocument12 pagesA Bridgeless BHB ZVS-PWM AC-AC Converter For High-Frequency Induction Heating ApplicationsBook4AllNo ratings yet
- Concise for Motorola R2600B Radio Communications Analyzer Repair DocumentDocument8 pagesConcise for Motorola R2600B Radio Communications Analyzer Repair DocumentKeith WepkingNo ratings yet
- Guardians of Glxy - Awesome Mix, Volume I.logDocument4 pagesGuardians of Glxy - Awesome Mix, Volume I.logJesenko BurgićNo ratings yet
- Various Light Phenomena: Written Work Activity 1.1Document7 pagesVarious Light Phenomena: Written Work Activity 1.1Mark Chester CuetoNo ratings yet
- Manual de Probador de Alternador, Arranque y BateríaDocument42 pagesManual de Probador de Alternador, Arranque y BateríaLuis SoporteNo ratings yet
- Oscilla - Excellence Since 1960Document24 pagesOscilla - Excellence Since 1960Pau Choon HockNo ratings yet
- Led-Tv: ServiceDocument121 pagesLed-Tv: ServiceSiengNo ratings yet