Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 130 Revesion Exam
Uploaded by
aymanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 130 Revesion Exam
Uploaded by
aymanCopyright:
Available Formats
This is a mock basic calculus exam, it is only meant as practice, it does not represent the actual
test questions.
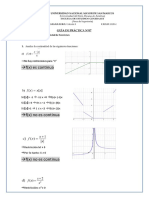
1) Given:
𝑥2 − 9
, 𝑥<4
𝑓(𝑥) = { 𝑥+3
𝑥 − 2, 𝑥=4
ln(𝑥 − 3) + 1, 𝑥>4
Find:
lim 𝑓(𝑥)
𝑥→4
𝑥 2 − 9 42 − 9 16 − 9
lim = = =1
𝑥→4 − 𝑥 + 3 4+3 7
lim ln(𝑥 − 3) + 1 = ln(4 − 3) + 1 = ln(1) + 1 = 1
𝑥→4 +
∴ lim 𝑓(𝑥) = 1
𝑥→4
Is 𝑓(𝑥) continuous at 𝑥 = 4? Explain.
𝐼𝑓 𝑓(𝑥) 𝑖𝑠 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑢𝑜𝑢𝑠 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = 4 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑖𝑡 𝑚𝑢𝑠𝑡 𝑏𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑡 lim 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑓(4)
𝑥→4
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 − 2 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = 4 𝑤ℎ𝑖𝑐ℎ 𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑛𝑠: 𝑓(4) = 2
𝑇𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑑𝑒𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑢𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = 4 lim 𝑓(𝑥) = 1 ≠ 𝑓(4) = 2
𝑥→4
∴ 𝑓(𝑥) 𝑖𝑠 𝒏𝒐𝒕 𝒄𝒐𝒏𝒕𝒊𝒏𝒖𝒐𝒖𝒔 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = 4
1 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
2) Find the following limits:
𝑒 𝑥 + 2𝑥
lim
𝑥→∞ 𝑥 2 + 2𝑥 − 3
𝑒 ∞ + 2(∞) ∞ 𝑒𝑥 + 2 ∞ 𝑒𝑥 ∞
lim → ≝ lim → ≝ lim = =∞
𝑥→∞ (∞)2 + 2(∞) − 3 ∞ 𝑥→∞ 2𝑥 + 2 ∞ 𝑥→∞ 2 2
3𝑥 4 − 2𝑥 6 + 4
lim
𝑥→−∞ 6𝑥 3 − 4𝑥 2 + 1
3(−∞)4 − 2(−∞)6 + 4 ±∞ −2𝑥 6
lim → 𝑒𝑥𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒 ℎ𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑝𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟𝑠 lim
𝑥→−∞ 6(−∞)3 − 4(−∞)2 + 1 ±∞ 𝑥→−∞ 6𝑥 3
−𝑥 3 −(−∞)3
= lim = =∞
𝑥→−∞ 3 3
3 𝑥
lim [ + ]
𝑥→∞ 𝑥 𝑥−1
3 𝑥 𝑥 1
= lim + lim = lim ≝ lim = 1
𝑥→∞ 𝑥 𝑥→∞ 𝑥 − 1 𝑥→∞ 𝑥 − 1 𝑥→∞ 1
(ln 𝑥)3
lim
𝑥→1 𝑥 − 1
1
(ln 1)3 0 3(ln 𝑥)2 ( ) 3(ln 𝑥)2 0
= lim → ≝ lim 𝑥 = lim = =0
𝑥→1 1 − 1 0 𝑥→1 1 𝑥→1 𝑥 1
𝑥2 + 1
lim
𝑥→3 (𝑥 − 3)2
32 + 1 10
lim 2
→
𝑥→3 (3 − 3) 0
𝑥2 + 1 +
𝐿𝑒𝑓𝑡 𝐻𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐿𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑡 = lim− → → +∞
𝑥→3 (𝑥 − 3) 2 + 𝑥2 + 1
2 ∴ lim =∞
𝑥 +1 + 𝑥→3 (𝑥 − 3)2
𝑅𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 𝐻𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐿𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑡 = lim+ → → +∞
{ 𝑥→3 (𝑥 − 3)2 +
2 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
3) Use the four step process (definition of the derivative) to find the derivative of:
𝑓(𝑥) = √𝑥 + 2
The definition of the derivative is:
𝑓(𝑥 + ℎ) − 𝑓(𝑥)
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = lim
ℎ→0 ℎ
So:
√(𝑥 + ℎ) + 2 − √𝑥 + 2
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = lim
ℎ→0 ℎ
(√(𝑥 + ℎ) + 2 − √𝑥 + 2) (√(𝑥 + ℎ) + 2 + √𝑥 + 2)
= lim
ℎ→0 ℎ √(𝑥 + ℎ) + 2 + √𝑥 + 2
((𝑥 + ℎ) + 2) − (𝑥 + 2) 𝑥+ℎ+2−𝑥−2
= lim = lim
ℎ→0 ℎ(√(𝑥 + ℎ) + 2 + √𝑥 + 2) ℎ→0 ℎ(√(𝑥 + ℎ) + 2 + √𝑥 + 2)
ℎ 1 1
= lim == lim =
ℎ→0 ℎ(√(𝑥 + ℎ) + 2 + √𝑥 + 2) ℎ→0 √(𝑥 + ℎ) + 2 + √𝑥 + 2 √𝑥 + 2 + √𝑥 + 2
1
=
2√𝑥 + 2
3 −3𝑥
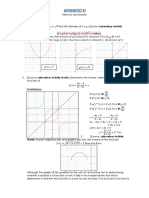
4) Given 𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑒 𝑥 + 1 , find the value(s) of x where the tangent line is horizontal.
3−3𝑥
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 3(3𝑥 2 − 3)𝑒 𝑥
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 0
3−3𝑥
3(3𝑥 2 − 3)𝑒 𝑥 =0
3 −3𝑥
𝑒𝑥 ≠ 0 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑎𝑛𝑦 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑜𝑓 "𝑥"
3𝑥 2 − 3 = 0
3 (𝑥 2 − 1 ) = 0
𝑥 = 1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥 = −1
3 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
5) Find the derivative of the given functions (no need to simplify your answer)
2
𝑓(𝑥) = + 𝑒 2𝑥 − ln(𝑥 + 1) + 𝑒 3
√𝑥
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = ⋯
2−2)
𝑤(𝑥) = (2𝑥 − 1)17 𝑒 (2𝑥
2 −2) 2 −2)
𝑤 ′ (𝑥) = 17(2𝑥 − 1)16 (2)𝑒 (2𝑥 + (2𝑥 − 1)17(4𝑥)𝑒 (2𝑥
𝑒 2𝑥−4 + ln (2)
ℎ(𝑥) =
ln(𝑥 + 1)
1
2𝑒 2𝑥−4 (ln(𝑥 + 1)) + (𝑒 2𝑥−4 + ln(2)) (𝑥 + 1)
ℎ′ (𝑥) =
[ln(𝑥 + 1)]2
𝑗(𝑥) = (ln(2𝑥 2 + 1))8
4𝑥
𝑗 ′ (𝑥) = 8(ln(2𝑥 2 + 1))7 ( )
2𝑥 2 + 1
4 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
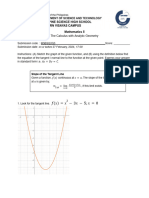
𝑑𝑦
6) Use implicit differentiation to find 𝑑𝑥 and the equation of the tangent line to the curve at
(𝑥, 𝑦) = (−1 , 1)
2𝑦 3 − 9 = 4𝑦𝑥 2
6𝑦 2𝑦 ′ = 4𝑦 ′ 𝑥 2 + 4𝑦2𝑥 → 6𝑦 2 𝑦 ′ − 4𝑥 2 𝑦 ′ = 6𝑥𝑦
6𝑥𝑦
𝑦′ =
6𝑦 2 − 4𝑥 2
6(−1)(1) −6
𝑦′(−1,1) = 2 2
= = −3
6(1) − 4(−1) 2
Then the equation of the line with point (−1,1) 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑚 = −3 is:
𝑦 − 1 = −3(𝑥 + 1)
2𝑥 2 +6
7) Determine the absolute maximum and minimum of the function 𝑓(𝑥) = on the
𝑥+1
interval [0 , 3]
Find the critical values:
2𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 − 6
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) =
(𝑥 + 1)2
2𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 − 6 = 0
2(𝑥 2 + 2𝑥 − 3) = 0
2(𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 − 2) = 0
𝑥 = −3 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥 = 2
In the original function test the end points of the interval and any critical values between them:
𝑓(0) = 6 𝑎𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑚𝑎𝑥
14
𝑓(2) = 𝑎𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑚𝑖𝑛
3
{𝑓 ( 3 ) = 6 𝑎𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑚𝑎𝑥
5 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
8) Given the function 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 2 − 2)(𝑥 − 1) → 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 − 𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 + 1
Find the interval(s) on which 𝑓(𝑥) is increasing and decreasing.
𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 3𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 − 2
2 ± √28 1 + √7 1 − √7
3𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 − 2 = 0 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = → 𝑥= 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥 =
6 3 3
+ - +
1 − √7 1 + √7 𝑥 = 100
3 3
The function is increasing from:
1 − √7 1 + √7
(−∞, ) ∪ ( , ∞)
3 3
The function is decreasing from:
1 − √7 1 + √7
( , )
3 3
Find the interval(s) on which 𝑓(𝑥) is concave up and on which it is concave down.
𝑓 ′′ (𝑥) = 12𝑥 − 2
1
𝑓 ′′ (𝑥) = 0 𝑎𝑡 𝑥=
6
The function is concave up from:
1
( , ∞)
6
And concave down from:
1
(−∞, )
6
6 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
10) Evaluate the following integrals
1 5
∫(2𝑥 3 + − √ 𝑥 3 − + 3𝑒 𝑥 − ln (3)) 𝑑𝑥
𝑥4 𝑥
4
2𝑥 4 𝑥 −3 𝑥 3
= + − − 5 ln(𝑥) + 3𝑒 𝑥 − (ln(3))𝑥 + 𝑐
4 −3 4
3
2−4𝑥 1 1 1 2
∫(2𝑥 − 2)𝑒 2𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = ∫ 𝑒 𝑢 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑒 𝑢 + 𝑐 = 𝑒 2𝑥 −4𝑥 + 𝑐
2 2 2
Let:
𝑢 = 2𝑥 2 − 4𝑥
Then:
𝑑𝑢 = 4𝑥 − 4
1
𝑑𝑢 = (2𝑥 − 2)𝑑𝑥
2
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
𝑥
1 𝑢2 2(2 + 𝑒 𝑥 )2 2(2 + 𝑒 (3) )2 2(2 + 𝑒 (1) )2
∫ 𝑒 √2 + 𝑒 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = ∫ 𝑢 2 𝑑𝑢 =[ ] =[ ] =( )−( )
3 3 3 3
1 1 2 1 1
Let: 𝑢 = 2 + 𝑒 𝑥
Then: 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑒 𝑥 𝑑𝑥
1 1
1 1
17 17 18 17
𝑢19 𝑢18
∫(𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 − 1) 𝑑𝑥 = ∫ (𝑢 + 1 + 1)𝑢 𝑑𝑢 = ∫ 𝑢 + 2𝑢 𝑑𝑢 = [ +2 ]
0 0 19 18 0
0
1
(𝑥 − 1)19 (𝑥 − 1)18 (1 − 1)19 (1 − 1)18 (0 − 1)19 (0 − 1)18
=[ + ] =( + )−( + )
19 9 0
19 9 19 9
(−1)19 (−1)18 −1 1 28
= −( + ) = −( + )=−
19 9 19 9 171
Let: 𝑢 = 𝑥 − 1 → 𝑥 = 𝑢 + 1
Then: 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑑𝑥
7 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
2𝑥 − 1 2(𝑢 − 4) − 1 2𝑢 − 9 2𝑢 9 9
∫ 𝑑𝑥 = ∫ 𝑑𝑢 = ∫ 𝑑𝑢 = ∫ − 𝑑𝑢 = ∫ 2 − 𝑑𝑢
𝑥+4 𝑢 𝑢 𝑢 𝑢 𝑢
= 2𝑢 − 9 ln(𝑢) + 𝑐 == 2(𝑥 + 4) − 9 ln(𝑥 + 4) + 𝑐
Let: 𝑢 = 𝑥 + 4 → 𝑥 = 𝑢 − 4
Then: 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑑𝑥
2𝑥 1
∫ 𝑑𝑥 = ∫ 𝑑𝑢 = ln(𝑢) + 𝑐 = ln(𝑥 2 + 1) + 𝑐
𝑥2+1 𝑢
Let: 𝑢 = 𝑥 2 + 1
Then: 𝑑𝑢 = 2𝑥 𝑑𝑥
11) Suppose the marginal revenue equation is given as 𝑅′ (𝑥) = 4𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 3 − 10. If the revenue
from selling 7 units is 1000 KD, find the total revenue function, 𝑅(𝑥).
4𝑥 3 3𝑥 4
𝑅(𝑥) = ∫ 4𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 3 − 10 𝑑𝑥 = + − 10𝑥 + 𝑐
3 4
Since: 𝑅(7) = 1000
4(7)3 3(7)4 −26245
1000 = + − 10(7) + 𝑐 → 𝑐=
3 4 12
4𝑥 3 3𝑥 4 26245
𝑅(𝑥) = + − 10𝑥 −
3 4 12
8 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
12) Replica oil paintings sell for the price of 𝑝 = 12 − 2𝑥 KD when 𝑥 paintings are sold. If the
cost of selling 𝑥 paintings is 𝐶(𝑥) = 2𝑥 + 5 , write the functions for:
The revenue and profit equations:
𝑅(𝑥) = 12𝑥 − 2𝑥 2
𝑃(𝑥) = −2𝑥 2 + 10𝑥 − 5
Find the number of tickets to be sold to maximize revenue and then find the maximum revenue:
𝑅′ (𝑥) = 12 − 4𝑥
𝑅′ (𝑥) = 0 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑥=3
Since the revenue equation is a parabola opening downwards this is a maximum (make a line test
for the first derivative to show that it is a maximum…)
Then: 3 paintings should be sold to maximize revenue
The maximum revenue is: 𝑅(3) = 12(3) − 2(3)2 = 18
Interpret R’(10)
𝑅′ (10) = −28
Which means the revenue is decreasing at a rate of 28 KD when 10 units are sold.
9 (This is a mock exam, it is only meant as practice)
You might also like
- APM 2611 Assingment 01Document9 pagesAPM 2611 Assingment 01Anonymous 1ZJAxJDp5vNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Homework 6Document11 pagesProblem 1: Homework 6Akansha Kalra0% (1)
- Solution of Mathematics SSC-II (3rd Set)Document7 pagesSolution of Mathematics SSC-II (3rd Set)Javaid100% (1)
- Student Workbook - Unit 2 - Understanding NumberDocument16 pagesStudent Workbook - Unit 2 - Understanding Numberapi-232099327100% (1)
- Smart Algorithms Multimedia ImagingDocument439 pagesSmart Algorithms Multimedia ImagingMukesh PanchalNo ratings yet
- Why Is Mathematics Important in Culinary ArtsDocument2 pagesWhy Is Mathematics Important in Culinary ArtsReiou Regie Manuel25% (4)
- The Derivative As The Slope of The Tangent Line: Grade 11-KeplerDocument17 pagesThe Derivative As The Slope of The Tangent Line: Grade 11-KeplerXzyle1213No ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 One Sided LimitsDocument4 pagesLECTURE 3 One Sided LimitsJoy Rianne HoriqueNo ratings yet
- Unidad III Límites y ContinuidadDocument16 pagesUnidad III Límites y ContinuidadAndy CuaicalNo ratings yet
- Rules of Differentiation: ExampleDocument6 pagesRules of Differentiation: Examplejoshua montoyaNo ratings yet
- Evaluate The Following Limits Without Using A CalculatorDocument3 pagesEvaluate The Following Limits Without Using A CalculatorYasmeen AfifNo ratings yet
- TUGAS II KALKULUS I DERIVATIF DAN INTEGRALDocument5 pagesTUGAS II KALKULUS I DERIVATIF DAN INTEGRALnO NameNo ratings yet
- Actividad Ecuacion de La Recta Normal y TangenteDocument7 pagesActividad Ecuacion de La Recta Normal y TangenteLeidy Susana Romero RojasNo ratings yet
- Tugas MTK (SP)Document4 pagesTugas MTK (SP)teguh imam pradhonggoNo ratings yet
- ACTIVIDAD ECUACION DE LA RECTA NORMAL Y TANGENTEDocument6 pagesACTIVIDAD ECUACION DE LA RECTA NORMAL Y TANGENTELeidy Susana Romero RojasNo ratings yet
- Basic Differentiation Rules CalculusDocument7 pagesBasic Differentiation Rules CalculusJewan Ambadil SampulnaNo ratings yet
- Sol - Recuperatorio Calculo I 1-2023Document3 pagesSol - Recuperatorio Calculo I 1-2023Jair Flores MechanNo ratings yet
- SMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 Answer SchemeDocument5 pagesSMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 Answer SchemeZurainiNo ratings yet
- A.O.D DPPDocument3 pagesA.O.D DPPRishabhNo ratings yet
- Tercer Guia de Calculo Diferencial ....Document4 pagesTercer Guia de Calculo Diferencial ....Sandoval Rendon AlexisNo ratings yet
- Repaso Riemman-1Document5 pagesRepaso Riemman-1Moon PieNo ratings yet
- Araneta All Problem Sets Exams Practice Exams Math 83Document55 pagesAraneta All Problem Sets Exams Practice Exams Math 83Marvince AranetaNo ratings yet
- 7 The Product and Quotient Rules Problem Set Solution v2 1Document3 pages7 The Product and Quotient Rules Problem Set Solution v2 166dancelNo ratings yet
- Limites FinitosDocument11 pagesLimites FinitosCielo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Tugas II Kalkulus IDocument6 pagesTugas II Kalkulus Iendangangel81No ratings yet
- Basic Differentiation RulesDocument10 pagesBasic Differentiation RulesJunelle Christian ObiceNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument33 pagesRevieweranon_422073337No ratings yet
- ACHIEVERS CLASSES TUTORIAL SOLUTIONSDocument16 pagesACHIEVERS CLASSES TUTORIAL SOLUTIONSEve PomeNo ratings yet
- Turunan FungsiDocument9 pagesTurunan FungsiRatna Dewi FPNo ratings yet
- Find limits using theorems and algebraDocument5 pagesFind limits using theorems and algebraMelandry SitorusNo ratings yet
- F (X) Es Continua: No Hay Restricciones para "X"Document12 pagesF (X) Es Continua: No Hay Restricciones para "X"Josue Rojas gutyNo ratings yet
- Parcial #1Document22 pagesParcial #1gloriaNo ratings yet
- Actividad Nivel Inicial Julian ZabaletaDocument7 pagesActividad Nivel Inicial Julian ZabaletaJz PdNo ratings yet
- Section 2.4 Precise Definition of The LimitDocument8 pagesSection 2.4 Precise Definition of The LimitInitsigan KatangkayNo ratings yet
- Upto Mid-TermDocument39 pagesUpto Mid-TermSourav DeNo ratings yet
- Calcular Las Primeras Derivadas ParcialesDocument4 pagesCalcular Las Primeras Derivadas ParcialesBert RTGNo ratings yet
- ZZ_r11_PR_zestaw-ADocument22 pagesZZ_r11_PR_zestaw-AKuba MikusNo ratings yet
- Math22 1ReviewerDerivativeTrigonometricFunctionDocument6 pagesMath22 1ReviewerDerivativeTrigonometricFunctionanon_422073337No ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 LimitsDocument4 pagesLECTURE 2 LimitsJoy Rianne HoriqueNo ratings yet
- Lim Lim Lim Lim Lim 2 + 2 2 ( 1)Document6 pagesLim Lim Lim Lim Lim 2 + 2 2 ( 1)Daniela RamosNo ratings yet
- Week 13-14 - CalcDocument3 pagesWeek 13-14 - CalcFlorenceNo ratings yet
- Juego 1Document18 pagesJuego 1dr1k.strdrNo ratings yet
- Lista 2 (Gabarito)Document5 pagesLista 2 (Gabarito)oDeinoNo ratings yet
- Class 21 - Limits and Continuity - 15.03.2021Document16 pagesClass 21 - Limits and Continuity - 15.03.2021johnathanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Differentiation of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument5 pagesLecture 10 Differentiation of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDally Tabinas GesalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Working With Functions1 1Document8 pagesChapter 2.1 Working With Functions1 1Enkhjin OtgonbatNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document12 pagesModule 3Gerwin MontevirgenNo ratings yet
- Integral 2Document6 pagesIntegral 2Allexa De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Maths August 26 Shift 1Document8 pagesJEE Main 2021 Question Paper Maths August 26 Shift 1Amit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Integration of Algebraic FunctionDocument10 pagesLecture 1 Integration of Algebraic FunctionWendy ManguisiNo ratings yet
- Math 1 Resit Solutions For Students 1Document12 pagesMath 1 Resit Solutions For Students 1jasperNo ratings yet
- Tangent LinesDocument7 pagesTangent LinesKamyl PilarNo ratings yet
- Practico N°2 - RUA 3543Document18 pagesPractico N°2 - RUA 3543Carlos J. F. ChoqueNo ratings yet
- 597 - Correction TD Fonction CirculaireDocument4 pages597 - Correction TD Fonction CirculaireToxic DEVNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Inverse of A FunctionDocument19 pages2.4 Inverse of A FunctionNot.DXcr GaMeRNo ratings yet
- UTN Clase 10 AMI 06 05 2021Document20 pagesUTN Clase 10 AMI 06 05 2021Marcos NahuelNo ratings yet
- DossierrévisionDocument6 pagesDossierrévisionKabeNo ratings yet
- Practico N°2 - RUA 5341Document18 pagesPractico N°2 - RUA 5341Carlos J. F. ChoqueNo ratings yet
- 03-11 ShadevskyiDocument7 pages03-11 Shadevskyihello worldNo ratings yet
- Integrating factors and exact differential equationsDocument3 pagesIntegrating factors and exact differential equationsJohn GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Limits at Infinity and Theorems on Infinite LimitsDocument5 pagesLimits at Infinity and Theorems on Infinite LimitsJoy Rianne HoriqueNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MotionGen Interactive Design and EditingDocument10 pagesMotionGen Interactive Design and EditingArif SugihartoNo ratings yet
- AES Encryption Algorithm: How the Advanced Encryption Standard WorksDocument46 pagesAES Encryption Algorithm: How the Advanced Encryption Standard WorksY Vara PrasadNo ratings yet
- Apllied Vs Pure 2Document10 pagesApllied Vs Pure 2Tushar RastogiNo ratings yet
- The RSA AlgorithmDocument15 pagesThe RSA AlgorithmveenadivyakishNo ratings yet
- 200 Quadratic Equation QuestionsDocument7 pages200 Quadratic Equation QuestionsLatta SakthyyNo ratings yet
- 04Electrostatic-SenAct 44Document94 pages04Electrostatic-SenAct 44Prashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Topics in MathematicsDocument5 pagesTerm Paper Topics in Mathematicsea44a6t7100% (1)
- MATHS REVIEWDocument5 pagesMATHS REVIEWCristina AmantiadNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North Mathematics Revision W/S - 2019-20 Fractions and Decimals ClassviiDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North Mathematics Revision W/S - 2019-20 Fractions and Decimals ClassviiVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- 8221 - Tutorial 1 Line IntegralDocument6 pages8221 - Tutorial 1 Line IntegralVictor LoongNo ratings yet
- Test Item Analysis 3RD QuarterDocument16 pagesTest Item Analysis 3RD QuarterPevi VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: International Mathematics OlympiadDocument3 pagesSample Paper: International Mathematics OlympiadSarthakNo ratings yet
- Codes and CiphersDocument9 pagesCodes and CiphersMilk BrotherNo ratings yet
- Mathlab FunctionsDocument3 pagesMathlab FunctionsAhmed HaaNo ratings yet
- Bevel ProtractorDocument3 pagesBevel ProtractorAnonymous k0timyBdYNo ratings yet
- STANDARD COSTING With GP VARIANCE ANALYSIS KEY ANSWERSDocument19 pagesSTANDARD COSTING With GP VARIANCE ANALYSIS KEY ANSWERSaziel caith florentinNo ratings yet
- Computational Mathematics and Physics of Fusion Reactors - Paul R. GarabedianDocument5 pagesComputational Mathematics and Physics of Fusion Reactors - Paul R. GarabediandougnovaesNo ratings yet
- Jonnala 2016Document8 pagesJonnala 2016sanjay sNo ratings yet
- Vivarium - Vol. 9, Nos. 1-2, 1971 PDFDocument163 pagesVivarium - Vol. 9, Nos. 1-2, 1971 PDFL'uomo della RinascitáNo ratings yet
- Fta TutorialDocument21 pagesFta Tutorialpj_chaudhary3796No ratings yet
- ARS 131 & ARS 131.1Document33 pagesARS 131 & ARS 131.1Dave FortuNo ratings yet
- A Project Report OnDocument44 pagesA Project Report OnVartika_07100% (1)
- C QuizDocument61 pagesC QuizdasarioramaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - 4000 Essential English Words 1Document6 pagesUNIT 3 - 4000 Essential English Words 1Virginia AlexeNo ratings yet