Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Philosophies of Education Matrix
Uploaded by
Kk RiosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Philosophies of Education Matrix
Uploaded by
Kk RiosCopyright:
Available Formats
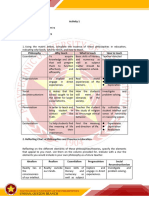
PHILOSOPHIES OF EDUCATION
PHILOSOPHIES OF EDUCATION
ESSENTIAL COMPONENTS
IDEALISM REALISM PRAGMATISM EXISTENTIALISM PERENNIALISM ESSENTIALISM PROGRESSIVISM SOCIAL RECONSTRUCTION
Reality exists independently of human Stresses the preservation of existing
Reality is mentally constructed; ideas Focuses on action and asserts that Reality is subjective, based on individual Embraces change as an inherent part of Developed from pragmatism and
experience, determined scientifically or Believes in timeless, unchanging truths culture and societal norms as essential
1. Philosophical Treatises are the reliable form of reality due to the ideas and actions must align; rejects perceptions. Opposes objective reality life, viewing education as a tool to existentialism, serving as an extension
empirically, focusing on the physical that persist despite changes over time. for societal survival and personal
changing physical world. absolute, unchanging truth. advocated by realism. manage and adapt to societal change. of Progressivism.
world. satisfaction.
Focused on the transmission of Focuses on the individual learner, aiming Focuses on societal change and
Focus on character development through Aims for understanding the unchanging Encourages learners to learn through Emphasizes self-definition, giving Aims to develop human rationality,
essential knowledge, attitudes, and to teach problem-solving, adaptability, rebuilding society, aiming to address
2. Aims of Education absorbing ideas and personal discipline, world through inquiry and verifying ideas their own experiences, reconstructing learners control over academic decisions focusing on intellectual growth through
skills of life, emphasizing social values and practical skills necessary for an societal issues and drive social reform
teaching timeless wisdom. in the physical world. experiences to solve problems. and personal growth. the transmission of classical knowledge.
and cultural heritage. ever-changing world. through education.
Favors inductive and problem-solving Emphasizes critical pedagogy, social
Emphasis on deductive logic, rote Emphasizes inductive processes, Emphasizes experiential learning, Promotes self-realization through Emphasizes testing, periodic Relies on demonstration, drill, recitation,
techniques, emphasizes cooperative analysis, problem-based learning, and
3. Educational Methods memory, Socratic method, and lecture teaching for mastery of facts, through individualized instruction, and practical journals, portfolios, and self-paced assessment, and a structured "one size memorization, and standardized testing
learning, reflection, and experiential community-based projects to analyze
discussions. experimentation, drills, and exercises. activities over lectures. learning with teachers as facilitators. fits all" teaching approach. to impart knowledge and skills.
learning methods. and address societal issues.
Centers around socioeconomic and
Centered on dialogue and "textbook Focuses on humanities, psychology, Values Great Books and liberal arts, Emphasizes the "3 R's" - reading, Features a flexible and integrated
Science, mathematics, and vocational Personalized curriculum based on political problems, focusing on social
knowledge" in literature, arts, arts, self-actualization through diverse focusing on timeless classical writings in writing, arithmetic, and basic skills in curriculum focusing on practical
4. Curriculum Features subjects are prioritized, focusing on learners' experiences, focuses on the sciences and problem-based
philosophy, history, religion, and activities, less emphasis on math and subjects like philosophy, literature, and literature, history, mathematics, and problem-solving and group activities that
practical knowledge and skills. process of learning rather than content. approaches that examine societal
humanities. science. arts. science. adapt to societal changes.
issues, past, present, and future.
Teachers serve as trustees of cultural Teachers act as facilitators guiding Teachers act as catalysts of social
Transmit objective knowledge free from Present principles without bias, Teachers act as "sages on stage,"
Act as authorities and moral character Act as facilitators, guides, and and educational heritage, guiding learners in active, relevant, and realistic change, facilitating critical discussions
5. Role of Teachers personal biases, teaching regularities encouraging critical examination and imparting knowledge and controlling the
models, dispensing knowledge. challengers, students and prescribing the essential experiences, preparing them to handle on societal problems, suggesting
and rhythms of nature. personal value development. learning experiences of students.
curriculum. challenges in the real world. solutions, and promoting social reform.
Active participants engaged in
Encourages learners to explore, think,
Central to the educative process, Encouraged to discover themselves, Learners are seen as empty vessels to understanding broader societal issues,
Passive receivers expected to memorize Trains senses in analyzing the physical Learners receive knowledge as passive and experience the world around them,
learning by doing, understanding that control their education, value be filled with essential knowledge and encouraged to use personal experiences
6. Role of Learners classics and emulate teachers' world, focuses on scientific reasoning recipients, focusing on mastering basic allowing them to reflect on personal
truth is what works and is proven through individuality, and take accountability for must adhere to prescribed curriculum to uncover and address social problems,
questioning and reflection. and acquiring scientific skills. subjects for intellectual cultivation. experiences and solve problems based
personal experiences. actions. without exploration or questioning. preparing learners to actively participate
on their perspectives.
in society as agents of change.
Evaluates learners based on problem-
Prefers assessment tools like journals, Emphasizes achievement test scores, Assessments center on gauging
Subjective evaluation via essays, Prefers standardized testing and Opposes standardized testing, values Stresses periodic testing, standardized solving abilities, learning by doing,
simulations, portfolios, and fieldwork to standardized testing, and mastery of students' critical-thinking, problem
7. Learning Assessment reflection papers, focusing on logical competency testing, evaluating learners intrinsic motivation over grades, and assessments, and mastery of timeless individualized assessments tailored to fit
integrate personal experiences and prescribed subject matter through solving, and active involvement in
rigor. using quantitative measures. promotes authentic learning. knowledge for reasoning. learning styles, emphasizing practical
course material. rigorous evaluation. addressing real-world issues.
application of knowledge.
Teacher-led environment with a Classroom environment focuses on Encourages cooperative, democratic A forum for discussing pressing social
Subject-centered, less focus on learner Learner-friendly, democratic, where both Nurtures individuality, rejects conformity
Authoritarian with restrictive discipline, structured approach and a focus on lecturing, standardized textbooks, environments, promotes divergent issues, encouraging curiosity, critical
8. Classroom Atmosphere interests and emotions, filled with teachers and learners collaborate in to group norms, fosters diverse activities
limiting learners' freedom. acquiring important information and assignments, and prioritizes order and thinking, challenges, and practical thinking, and active engagement with the
teaching and learning materials. defining rules and procedures. and free thinking.
principles. discipline. learning experiences. world.
Raises awareness of societal problems,
Provides scientific, technical, and Emphasizes practical thinking, fosters Maximizes intellectual development, Creates societal stability, promotes empowers learners to participate in
Creates an orderly classroom, gives Focuses on individual growth and
vocational education, preparing learners social reform, and teaches problem- Emphasizes individuality, autonomy, and clear focus on transmitting enduring consistency in education, and provides a solving these issues, emphasizes social
9. Advantages teachers control, ensures coverage of development, promotes adaptability and
for practical and beneficial solving skills aligned with learner optimism in developing learner potential. knowledge, and orderly teaching strong foundation of basic knowledge sciences for understanding societal
essential topics. preparation for a fast-changing society.
competencies. experiences. environment. and skills. dynamics and fostering civic
competence.
While promoting societal reform, it
Neglects holistic learning, de- May emphasize individuality to the May neglect emotional and practical Passivity of learners, potential loss of Potential challenges in underprivileged doesn't define specific means to achieve
Resists change, focuses on mental emphasizes ideals, values, feelings, and Criticized for lacking fixed aims and detriment of sociality, leads to multiple development, emphasizes Western memory due to rote learning, restriction communities due to financial this change, and it places sole
10. Disadvantages development, neglects diverse learning socialization, perceived as overly discipline, as well as over-reliance on curricula and challenges in preparing for knowledge over local culture, and can to traditional basics, and potential lag in constraints, may lack finality in students' responsibility on education, whereas
needs. objective and neglectful of subjective personal experiences for learning. citizenship, neglects the utilitarian limit students' engagement and self- addressing contemporary needs and conclusions due to constant testing and societal change requires the
knowledge. aspect of education. expression. changes. experimentation. collaborative effort of various sectors
beyond education.
You might also like
- Stress Management PresentationDocument80 pagesStress Management PresentationDenish Vaniyawala100% (1)
- Conflict Analysis Tools and TechniquesDocument35 pagesConflict Analysis Tools and TechniquesLancelot Nyamaka100% (2)
- Social Research and Social Work Research: Unit 1Document32 pagesSocial Research and Social Work Research: Unit 1Prudhvi KNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocument11 pagesThe Teacher and The Community School Culture and Organizational LeadershipAlliana Pauline MorallosNo ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument35 pagesFoundations of EducationElla CamelloNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of EducationDocument4 pagesPhilosophy of EducationClaire YingNo ratings yet
- When Talent Development Becomes A Strategic Imperative - Fe MarieRCabantacDocument40 pagesWhen Talent Development Becomes A Strategic Imperative - Fe MarieRCabantacVoltaire M. Bernal100% (1)
- Philosophies of EducationDocument3 pagesPhilosophies of EducationErika Parungao100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Philosophies of EducationImplication To Teachinglearning Process Short NewDocument8 pagesLesson 3 Philosophies of EducationImplication To Teachinglearning Process Short NewMae Therese TaguriganNo ratings yet
- Table of PhilosophiesDocument2 pagesTable of Philosophiesbarliz33% (3)
- Philosophies in TeachingDocument1 pagePhilosophies in TeachingArielle Ariane NacarNo ratings yet
- Make A Table Summary of The Philosophies of EducationDocument3 pagesMake A Table Summary of The Philosophies of Educationabba may dennis88% (69)
- Module 2 - Ped 02 The Teaching Profession 2 (Revised - Final)Document16 pagesModule 2 - Ped 02 The Teaching Profession 2 (Revised - Final)Lawrence DiolaNo ratings yet
- Idealism Realism Pragmatism/ Experimentalism Essentialism Perennialism Progressivism Social Reconstructionism ExistentialismDocument2 pagesIdealism Realism Pragmatism/ Experimentalism Essentialism Perennialism Progressivism Social Reconstructionism ExistentialismRey Pineda100% (1)
- Six Contemporary Educational PhilosophiesDocument2 pagesSix Contemporary Educational PhilosophiesRickyJeciel100% (7)
- PHILOS and EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONSDocument5 pagesPHILOS and EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONSmarnylieNo ratings yet
- Philosohical Thoughts/Doctorines Vis-Avis EducationDocument3 pagesPhilosohical Thoughts/Doctorines Vis-Avis EducationEddie Jr SadamoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document3 pagesActivity 2Romeo Cabrera Jr.No ratings yet
- Philosophical Schools of TaughtDocument7 pagesPhilosophical Schools of TaughtPing HiponiaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy in EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophy in EducationTamarha Natalie VillarealNo ratings yet
- Joshua Eriberto Miguel G. Llames Educ 202 Mercy Grace I. Saliendra, Ph. DDocument3 pagesJoshua Eriberto Miguel G. Llames Educ 202 Mercy Grace I. Saliendra, Ph. DJem LlamesNo ratings yet
- Isnain, Erich C - BSED 1A 08/22/2020: Educational Philosophy Philosophical Roots Idealism Realism PragmatismDocument3 pagesIsnain, Erich C - BSED 1A 08/22/2020: Educational Philosophy Philosophical Roots Idealism Realism PragmatismErichIsnainNo ratings yet
- Educ 206Document5 pagesEduc 206Alliana Pauline MorallosNo ratings yet
- Blept ReviewerDocument7 pagesBlept ReviewerAliya JimenezNo ratings yet
- Government Elementary College of Education (Qasimabad) : Name: Sitara RiazDocument8 pagesGovernment Elementary College of Education (Qasimabad) : Name: Sitara RiazSitara RiazNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Teacher Development: The Teaching ProfessionDocument5 pagesFaculty of Teacher Development: The Teaching ProfessionBarby Ann CarumbaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 11A 1st Exam and Activity1-4 ExercisesDocument3 pagesEDUC 11A 1st Exam and Activity1-4 ExercisesDanilo Malbueso Ebol Jr.No ratings yet
- Idealism Realism: Philosophical TheoryDocument4 pagesIdealism Realism: Philosophical TheoryKristhel Pecolados Rombaoa100% (1)
- Teaching Profession Activity 1 - Realyn D. TanecaDocument5 pagesTeaching Profession Activity 1 - Realyn D. TanecaEya Delos Santos TañecaNo ratings yet
- Discuss Briefly Your Own Understanding of Philosophy and Its Importance in Teaching. Give Examples or Real Life ExperiencesDocument8 pagesDiscuss Briefly Your Own Understanding of Philosophy and Its Importance in Teaching. Give Examples or Real Life Experiencesjhun ecleoNo ratings yet
- Scarlet Educ 109 Mam BambicoDocument6 pagesScarlet Educ 109 Mam BambicoScarlet Elgamo GalantoNo ratings yet
- Almira, Jhanna Mae A. (Task 1) - 1Document3 pagesAlmira, Jhanna Mae A. (Task 1) - 1Jhanna AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of EdDocument36 pagesPhilosophy of Edning setiaNo ratings yet
- Filosofi PendidikanDocument24 pagesFilosofi PendidikanNadia Alima FadhillaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 90 Task 1 & 2Document7 pagesEDUC 90 Task 1 & 2Gliecy OletaNo ratings yet
- Educational Philosophies: IdealismDocument4 pagesEducational Philosophies: IdealismMerryfil ReyNo ratings yet
- EDUC 10 ReflectionDocument5 pagesEDUC 10 ReflectionaksanaNo ratings yet
- Philisophical Orientations TablesDocument3 pagesPhilisophical Orientations TablesunknownNo ratings yet
- Mendoza, Jhamille-Venn-diagram - Philosophical Models of TeachingDocument1 pageMendoza, Jhamille-Venn-diagram - Philosophical Models of Teachingmjhamille7No ratings yet
- Western Colleges: Theory-Proponent Basic Principles Strengths/ Applications Personal Criticism/SDocument3 pagesWestern Colleges: Theory-Proponent Basic Principles Strengths/ Applications Personal Criticism/SShane Catherine FabiocNo ratings yet
- Constructivism PHCPDocument43 pagesConstructivism PHCPAlfredo MagtaanNo ratings yet
- Abueva - Lesson 1-2 Concept MapsDocument2 pagesAbueva - Lesson 1-2 Concept MapsJaye LenizoNo ratings yet
- Meeting The Educational Philosophers: - He Was AnDocument3 pagesMeeting The Educational Philosophers: - He Was AnAlexa GandioncoNo ratings yet
- Educ 101 MAED MathDocument4 pagesEduc 101 MAED MathJean Marie Ga LacsonNo ratings yet
- ProEd 6Document1 pageProEd 6Jirah Joy PeañarNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Conceptions FinalDocument20 pagesPhilosophical Conceptions FinalShishir Prasad AryalNo ratings yet
- Asyncronous Assignment TTP...Document17 pagesAsyncronous Assignment TTP...Kim alexandraNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophies of EducationMae Salazar SajiseNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument7 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentStephanie Joy Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Thoughts On EducationDocument3 pagesPhilosophical Thoughts On EducationDANIELLA JASPIONo ratings yet
- Educational PhilosophiesDocument10 pagesEducational PhilosophiesFrance FuertesNo ratings yet
- ED2Document1 pageED2jeffrey QuezoraNo ratings yet
- 5 Philosophical InfluencesDocument1 page5 Philosophical InfluencesJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- profED2 1-10Document15 pagesprofED2 1-10Mikee SantoNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Theory of Truth Methodology To Arrive at The Truth Theory of What Is Valuable/Goo D Goal of Teaching-LearningDocument4 pagesPhilosophy Theory of Truth Methodology To Arrive at The Truth Theory of What Is Valuable/Goo D Goal of Teaching-LearningVerlyn ReynesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Josh SumabonNo ratings yet
- BEHAVIORISMDocument1 pageBEHAVIORISMEvaine May PizanaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT #3 - Matrix of The Different PhilosophiesDocument6 pagesASSIGNMENT #3 - Matrix of The Different Philosophiesngitngit.jjtNo ratings yet
- Paper Gari 082013Document16 pagesPaper Gari 082013Diya FulwaniNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 14-Dec-2021Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 14-Dec-2021shivani dinkarNo ratings yet
- Discipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences: Culminating ActvityDocument52 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences: Culminating ActvityAriel Brace HabilNo ratings yet
- Empathy and Resilience in Education: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsFrom EverandEmpathy and Resilience in Education: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsNo ratings yet
- Significance Testing (T-Tests)Document3 pagesSignificance Testing (T-Tests)Madison HartfieldNo ratings yet
- New ShowGeneralReportDocument1 pageNew ShowGeneralReportchamundaxerox88No ratings yet
- Non Parametric Chapter 4Document5 pagesNon Parametric Chapter 4Roan Suanque MartirNo ratings yet
- Low Level Reader Protocol (LLRP) 1.1 Conformance Requirements DocumentDocument47 pagesLow Level Reader Protocol (LLRP) 1.1 Conformance Requirements DocumentWagner Porto FerreiraNo ratings yet
- SAP Business One Is Now Localized in Romania and BulgariaDocument2 pagesSAP Business One Is Now Localized in Romania and Bulgariairinaoprea2No ratings yet
- Study Plan: Introduction of My BackgroundDocument3 pagesStudy Plan: Introduction of My BackgroundTonya R BraunNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Qualification AllowanceDocument2 pagesApplication Form For Qualification AllowanceMuhammad WaqasNo ratings yet
- Brian Ferneyhough (En)Document5 pagesBrian Ferneyhough (En)Manuel BaigorriNo ratings yet
- Work Attitude (Integrity) Screening: Sam SampleDocument9 pagesWork Attitude (Integrity) Screening: Sam SampleعديالعربيNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument16 pagesProject ProposalJulie Ann GernaNo ratings yet
- Is PPP Dead?: Jeremy HarmerDocument9 pagesIs PPP Dead?: Jeremy HarmerSherrey WalterNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Font FormatDocument7 pagesResearch Paper Font Formatjzczyfvkg100% (1)
- Presentation Schedule For MBA (IB) IIIrd Sem PDFDocument5 pagesPresentation Schedule For MBA (IB) IIIrd Sem PDFSwapnil ParohaNo ratings yet
- Habit, Choice, and Addiction (Vandaele & Ahmed, 2021)Document10 pagesHabit, Choice, and Addiction (Vandaele & Ahmed, 2021)GokushimakNo ratings yet
- Detailed Thesis Outline SampleDocument5 pagesDetailed Thesis Outline Samplespqeyiikd100% (2)
- Fluent in 3 Months - Notebook Kindle NotesDocument5 pagesFluent in 3 Months - Notebook Kindle NotesGabriella SchmidNo ratings yet
- Honorable Murray Sinclair Poster - AccDocument5 pagesHonorable Murray Sinclair Poster - Accapi-240752690No ratings yet
- Keywords: Health Education, Story Telling and Healthy Snacking BehaviorDocument7 pagesKeywords: Health Education, Story Telling and Healthy Snacking BehaviorKecengNo ratings yet
- Pre-K StandardsDocument24 pagesPre-K Standardsapi-512878676No ratings yet
- The Multidimensional Driving Style Inventory-Scale Construct and Validation PDFDocument15 pagesThe Multidimensional Driving Style Inventory-Scale Construct and Validation PDFCosmin GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Melc Based Eapp DLP Q1 Week 3Document3 pagesMelc Based Eapp DLP Q1 Week 3kimbeerlyn doromasNo ratings yet
- Star Wards 2Document116 pagesStar Wards 2Marion JannerNo ratings yet
- AHL 3.12 Vector DefinitionsDocument98 pagesAHL 3.12 Vector Definitionspelin petekNo ratings yet
- 2015 Filg10q2Document88 pages2015 Filg10q2Zeus D. Reyes100% (1)
- Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Agra: ADMISSION 2019-20Document25 pagesDr. Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Agra: ADMISSION 2019-20Sachin chaharNo ratings yet
- Walking The Tightrope Study GuideDocument9 pagesWalking The Tightrope Study GuidejessilinnNo ratings yet