Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.2 Basic Integration Rules Part 1
Uploaded by
Me Being RandomOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.2 Basic Integration Rules Part 1
Uploaded by
Me Being RandomCopyright:
Available Formats
INTEGRAL CALCULUS
MODULE 1
INTEGRATION RULES
TOPIC LEARNING OUTCOMES
a. Apply the uses of integration specially in solving engineering problems and present solutions and
techniques in evaluating anti-differentiation problems. (CLO 1)
b. Apply mathematical solutions using different formulae (power, exponential function, trigonometric
function, inverse trigonometric function and integration by parts) in problems involving indefinite
integrals. (CLO 1)
c. Evaluate indefinite integral problems using algebraic and trigonometric substitution and present
solutions involving the integration of rational functions. (CLO 2)
d. Apply mathematical solutions in problems involving definite integrals and demonstrate the use of
Wallis’ Formula in some definite integral problems. (CLO 2)
THE POWER FORMULA
𝑢𝑛+1
∫ 𝑢𝑛 𝑑𝑢 = +𝐶
𝑛+1
𝑛 ≠ −1
Where:
u = function
du = differential of "u“
n = power / exponent
THE EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION
𝑎𝑢
∫ 𝑎𝑢 𝑑𝑢 = +𝐶 ∫ 𝑒 𝑢 𝑑𝑢 = 𝑒 𝑢 + 𝐶
ln 𝑎
Where:
a = constant
e = Euler ′ s number (e ≈ 2.718)
u = function
du = differential of "u“
n = power / exponent
ENGR. JONAYKA T. AZARIAS Page 1
INTEGRAL CALCULUS
THE LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION
𝑑𝑢
∫ = ln𝑢 + 𝐶
𝑢
Where:
𝑢 = function
𝑑𝑢 = differential of "𝑢“
ln( ) = natural logarithm
EXERCISES:
Evaluate:
1. ∫ 𝑥 2 𝑑𝑥
2. ∫ (3𝑥 2 + 2)𝑑𝑥
3. ∫ (3𝑥 2 + 2)𝑑𝑥
4. ∫ 𝑥 2 (𝑥 3 − 1)4 𝑑𝑥
5. ∫ (1 − 2𝑥 2 )2 𝑑𝑥
6. ∫ √𝑦(1 + 𝑦)𝑑𝑦
7. ∫ 𝑒 −3𝑥 𝑑𝑥
2
8. ∫ 2𝑥 𝑥𝑑𝑥
2 −1
9. ∫ 𝑣𝑒 3𝑣 𝑑𝑣
1
𝑒 𝑥 𝑑𝑥
10. ∫ 𝑥2
11. ∫ (𝑒 𝑡 − 𝑒 −𝑡 )2 𝑑𝑡
2𝑑𝑦
12. ∫ 3𝑦−4
(2𝑥−5)𝑑𝑥
13. ∫ 𝑥 2 −5𝑥+3
(1−2𝑥)2
14. ∫ 𝑑𝑥
𝑥
(𝑦−3)𝑑𝑦
15. ∫ 𝑦 2 −6𝑦+1
REFERENCES:
✓ DIFFERENTIAL AND INTEGRAL CALCULUS by LOVE and RAINVILLE 6TH EDITION
ENGR. JONAYKA T. AZARIAS Page 2
You might also like
- CHAPTER 1 Part 1 - Integration ConceptsDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1 Part 1 - Integration ConceptsDianna GwennNo ratings yet
- FormulaSheet SPH3U 2015Document1 pageFormulaSheet SPH3U 2015Jieyi HeNo ratings yet
- Intergal CalculusDocument20 pagesIntergal CalculusElizabeth ErwanNo ratings yet
- ELE8311 - Module 2 - The Z-TransformDocument19 pagesELE8311 - Module 2 - The Z-TransformUmarSaboBabaDoguwaNo ratings yet
- The Power FormulaDocument17 pagesThe Power FormulaLyssa ChoiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.a - 1.c - Integration Concepts & FormulasDocument5 pagesLesson 1.a - 1.c - Integration Concepts & FormulasAishlly Crystal OrtizNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1.1 - Indefinite IntegralDocument9 pagesLESSON 1.1 - Indefinite IntegralAivan Lloyd CapuleNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document2 pagesAssignment 7sameed hussainNo ratings yet
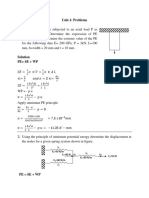
- Unit-1: Problems: K 40 N/M K 80 N/M U U F 60 N F 50 NDocument19 pagesUnit-1: Problems: K 40 N/M K 80 N/M U U F 60 N F 50 NDhruva PatilNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 11b + SolusiDocument5 pagesProblem Set 11b + SolusiIwenda Yudha ImaniNo ratings yet
- LP 1 in Math 2Document23 pagesLP 1 in Math 2Walwal WalwalNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument24 pagesSolutionLoku VelNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus LecturesDocument9 pagesIntegral Calculus LecturesJacob MallariNo ratings yet
- Expo Log IntegrationDocument5 pagesExpo Log IntegrationMatthew JordanNo ratings yet
- Summary of FormulasDocument5 pagesSummary of FormulasMaria Monica Mae MirandaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledAcebuque Arby Immanuel GopeteoNo ratings yet
- ChE Inverse-Trigo-and-Hyperbolic-functionsDocument20 pagesChE Inverse-Trigo-and-Hyperbolic-functionsFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - Review of FundamentalsDocument6 pagesLecture 01 - Review of FundamentalsCaden LeeNo ratings yet
- Calculus of Variations-1Document3 pagesCalculus of Variations-1saleemnasir2k7154No ratings yet
- Chennai - 130: B.E./B.Tech. Degree Examinations, November/December 2013Document29 pagesChennai - 130: B.E./B.Tech. Degree Examinations, November/December 2013B Vignesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Lec#9, Deflection of Beam-Determinate BeamDocument30 pagesLec#9, Deflection of Beam-Determinate Beamchristianborlaza23No ratings yet
- ch8 ProbsDocument4 pagesch8 ProbsEkrem GüldesteNo ratings yet
- 3orca Share Media1664099235094 6979738078155453166Document6 pages3orca Share Media1664099235094 6979738078155453166Angelo GranadaNo ratings yet
- MATH 2 - MODULE 2 - Powers, Logarithmic, and ExponentialDocument9 pagesMATH 2 - MODULE 2 - Powers, Logarithmic, and ExponentialItachi UchihaNo ratings yet
- Module 02 Lesson 02 - Fundamental Differentiation Formula For Algebraic FunctionsDocument8 pagesModule 02 Lesson 02 - Fundamental Differentiation Formula For Algebraic FunctionsKiziahlyn Fiona BibayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Part 5Document18 pagesChapter 7 Part 5Nelson FelixNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.i - 1.j - Integration Concepts & FormulasDocument5 pagesLesson 1.i - 1.j - Integration Concepts & FormulasLester GarciaNo ratings yet
- EovermreportDocument7 pagesEovermreportapi-702743009No ratings yet
- Signals and Systems: Lecture NotesDocument43 pagesSignals and Systems: Lecture NotesVincent GHEROLDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document4 pagesLecture 8Milind BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Homework #5 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHomework #5 SolutionsRUSNIANTI NURNo ratings yet
- Rohini 27786294869Document10 pagesRohini 27786294869Drishti Study CenterNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Discrete-Time State EquationsDocument42 pagesWeek 1 Discrete-Time State EquationsMetin DurmuşNo ratings yet
- KON 509E: Design of Discrete Control Systems Assist. Prof. Dr. İlker ÜstoğluDocument42 pagesKON 509E: Design of Discrete Control Systems Assist. Prof. Dr. İlker ÜstoğluMetin DurmuşNo ratings yet
- Average Case Analysis of Quick SortDocument3 pagesAverage Case Analysis of Quick SortJason David FrankNo ratings yet
- Average Case Analysis of Quick SortDocument3 pagesAverage Case Analysis of Quick SortJason David FrankNo ratings yet
- Q4-STEM-Basic Calculus-Week3Document4 pagesQ4-STEM-Basic Calculus-Week3Llahona FajardoNo ratings yet
- Average Case Analysis of Quick SortDocument3 pagesAverage Case Analysis of Quick SortHitech GaNo ratings yet
- Average Case Analysis of Quick SortDocument3 pagesAverage Case Analysis of Quick SortJason David FrankNo ratings yet
- Natural Response of R-L-C Circuits (Circuit Analysis Without A Voltage Source)Document3 pagesNatural Response of R-L-C Circuits (Circuit Analysis Without A Voltage Source)Huzaifa RehanNo ratings yet
- 4442exercise 3Document2 pages4442exercise 3Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus 3rd Quarter Week 8 MergedDocument11 pagesBasic Calculus 3rd Quarter Week 8 MergedKazandra Cassidy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Xianyu Z.-Z. - Solutions To Peskin & SchroederDocument173 pagesXianyu Z.-Z. - Solutions To Peskin & SchroederAndres100% (3)
- Peskin&Schroeder Solution ManualDocument173 pagesPeskin&Schroeder Solution ManualJerad Williams100% (4)
- 09-25 Problem SetDocument2 pages09-25 Problem SetsonjabottlelawNo ratings yet
- Unit5 Differentiation FormulasDocument11 pagesUnit5 Differentiation FormulasDylan AngelesNo ratings yet
- Integration Sine and CosineDocument13 pagesIntegration Sine and CosinemukondimmagodaNo ratings yet
- RV College of Engineering Department of MathematicsDocument3 pagesRV College of Engineering Department of MathematicsRashmitha raniNo ratings yet
- University of Limpopo: MemorandumDocument6 pagesUniversity of Limpopo: MemorandumNtokozo MasemulaNo ratings yet
- Example Final2013Document17 pagesExample Final2013Pradeep ChauhanNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument4 pagesIntegralHarvey SantosNo ratings yet
- Thermal State of The General Time-Dependent Harmonic OscillatorDocument14 pagesThermal State of The General Time-Dependent Harmonic OscillatorSajjad ZafarNo ratings yet
- 3 - Annotated Notes - Variational Principles - Wed Sept 22, 2021Document8 pages3 - Annotated Notes - Variational Principles - Wed Sept 22, 2021Luay AlmniniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mat455Document36 pagesChapter 2 Mat455Ajaq 98No ratings yet
- CALCULUS 2 FormulasDocument5 pagesCALCULUS 2 FormulasAdi NellascaNo ratings yet
- First Law Definition of Enthalpy: Working Solution Revised 31/10/2013 1Document6 pagesFirst Law Definition of Enthalpy: Working Solution Revised 31/10/2013 1yagoNo ratings yet
- Complex Number (Updated) SummaryDocument2 pagesComplex Number (Updated) SummaryMN4012022 CHIA CHANG YI, AARONNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Lec 07Document6 pagesLec 07Sai Vikyath KomatireddyNo ratings yet
- CS-463 Numerical ComputingDocument4 pagesCS-463 Numerical ComputingAhsan jararNo ratings yet
- Percentage Points of The T-Distribution: This Table Was Generated Using ExcelDocument1 pagePercentage Points of The T-Distribution: This Table Was Generated Using ExcelMohamaad SihatthNo ratings yet
- Spatial Analyst Tools: GIS III: GIS AnalysisDocument23 pagesSpatial Analyst Tools: GIS III: GIS AnalysisRidwan RhydhoNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Laplace TransformDocument86 pagesUnit Iii Laplace TransformArihant DebnathNo ratings yet
- Claims in International Construction Contract: A Case Study of EthiopiaDocument95 pagesClaims in International Construction Contract: A Case Study of EthiopiaDawit yir100% (1)
- Square of Binomial, Product of Sum and Diff, Square of MultinomialDocument11 pagesSquare of Binomial, Product of Sum and Diff, Square of Multinomialacechi iNo ratings yet
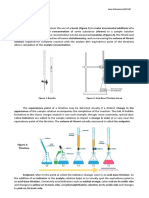
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument9 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectrosamirul azhar80% (10)
- Gauss QuadratureDocument9 pagesGauss QuadratureAnkur ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 01-Data Mining PrimerDocument15 pages01-Data Mining PrimerVivek JainNo ratings yet
- Super RRDocument76 pagesSuper RRIrina UrsachiNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH 4th QUARTER KUYA RIAN JAMES 2122Document4 pagesRESEARCH 4th QUARTER KUYA RIAN JAMES 2122Rechel CanenciaNo ratings yet
- Max. Error Measured Value: Topic: EstimationDocument5 pagesMax. Error Measured Value: Topic: Estimationwei shing zhengNo ratings yet
- Functions Domain RangeDocument24 pagesFunctions Domain RangeAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- B. Arch. 9th Sem. Dissertation (July-Dec 2018)Document104 pagesB. Arch. 9th Sem. Dissertation (July-Dec 2018)Ankit AntilNo ratings yet
- T12 Core Tools - The Alphabet Soup of APQP, PPAP, FMEA, SPC and MSA - JD Marhevko PDFDocument70 pagesT12 Core Tools - The Alphabet Soup of APQP, PPAP, FMEA, SPC and MSA - JD Marhevko PDFrakshithNo ratings yet
- School Level StatisticsDocument280 pagesSchool Level StatisticsganeshedwNo ratings yet
- IE334 Quality Control & Non Destructive Testing LabDocument2 pagesIE334 Quality Control & Non Destructive Testing LabloshidhNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument22 pagesSamplingJema SantillanNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2 SolutionDocument8 pagesMidterm 2 SolutionsdfaewrNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument3 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityNatalie Nicole FernandezNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method An Introduction: Andriya Narasimhulu 9899518264Document18 pagesFinite Element Method An Introduction: Andriya Narasimhulu 9899518264Ankit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shape FunctionDocument2 pagesShape Functionsai100% (1)
- Module 3 Titrimetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesModule 3 Titrimetric AnalysisNikoh Anthony EwayanNo ratings yet
- UAF CGPA CalculatorDocument18 pagesUAF CGPA CalculatorZaYn KakkayZai100% (1)
- Data Mining Graded Assignment: Problem 1: Clustering AnalysisDocument39 pagesData Mining Graded Assignment: Problem 1: Clustering Analysisrakesh sandhyapogu100% (3)
- The DerivativeDocument14 pagesThe DerivativeBiancaMihalacheNo ratings yet
- General Math Weekly Home Learning Plan Week 1Document3 pagesGeneral Math Weekly Home Learning Plan Week 1princeace10100% (1)
- BBBGT Docx2Document19 pagesBBBGT Docx2mengstuhagos1223No ratings yet
- Fractals and The Julia SetDocument14 pagesFractals and The Julia SetJamie100% (2)