Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TNCT Reviewer 2nd Quarter
Uploaded by
inasalclan45Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TNCT Reviewer 2nd Quarter
Uploaded by
inasalclan45Copyright:
Available Formats
TRENDS NETWORKS AND CRITICAL • SOCIAL DEMOCRACY- Conceived in
THINKING IN THE 21ST CENTURY - the 19th century, it promotes universal
REVIEWER access to health, education, just
LIEZL O. REVILLA compensation for workers, and social
services.
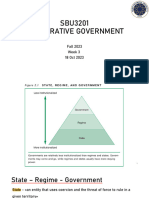
DEMOCRACY DIMENSIONS OF DEMOCRACY
• Means the “power of the people.”It • CIVIL RIGHTS - are the individual
originates from the Greek words demos, person’s right to autonomy and to act
which means “people,” and kratos, which freely without discrimination.
means “strength or power.”
• POLITICAL AND CIVIL RIGHTS - are
• U.S. President Abraham Lincoln limitations to the powers of the
succinctly defined democratic government, government vis-à-vis the sovereign people
in his “Gettsburg Address” delivered in and every individual.
1863, as a “government of the people, by
the people, for the people.” • POLITICAL LEGITIMACY- is
considered a basic condition for governing,
• PARLIAMENTARY DEMOCRACY- A without which a government will suffer
democratic form of government that began legislative deadlock(s) and collapse.
in Great Britain.
• EDUCATIONAL DIMENSION-
-It features a leading party or coalition of dimensions of democracy implies the
parties whose leader becomes the prime equal opportunity of the people in
minister or chancellor. obtaining education.
• JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY- • ECONOMICAL DIMENSION -
Symbolized by Andrew Jackson. It focused dimension of democracy implies economic
on the needs of the ordinary people rather equality as far as possible, satisfaction of
than on the needs of the elite and the the basic needs of the people and equality
educated. of opportunity in undertaking economic
activities.
• LIBERAL OR CONSTITUTIONAL-
Founded on the principles of free and fair • SOCIAL DIMENSION- dimensions of
elections, a universal right to vote, and a democracy, which dimension comprises
competitive political process where the participation of the people in the
qualified people can run and be voted for government.
office.
• ETHNICAL DIMENSION -dimension
• CONSTITUTIONAL MONARCHY- of democracy incorporates equality of all
where the monarch’s power is limited by irrespective of caste, class, color, creed,
the constitution such as in Malaysia, sex and wealth.
Cambodia, Thailand, Japan, Norway,
Sweden, UK, Spain, and the Netherlands. • VOTING SYSTEM- It is a set of rules
that determine how elections and
MONARCHY- Rule by single person who referendums are conducted and how their
inherits power. results are determined.
• FEDERAL REPUBLIC- is composed • REFERENDUM- an event in which
of self- governing states that have the people of a country, state, etc., vote for
consolidated together, thus forming a or against a law that deals with a specific
federation. issue: a public vote on a particular issue.
A referendum is any question, issue, or
• UNITARY REPUBLIC- is run as one
act referred to a vote of the people by the
entity and has a strong central or national
General Assembly, a local government, or
government as exemplified by the
a petition from voters as authorized by
Philippines, Timor-Leste, Vietnam,
law. A referendum includes constitutional
Bangladesh, Egypt, South Korea, Czech
amendments and bond issues.
Republic, Malta, Panama, Uruguay, Peru,
ad Macedonia. • PRIVATE ENTERPRISE- Is an
industry and business which is owned by
individual people or commercial govern. However, there are societies and
companies, and not by the government or governments that discriminates against
an official organization. individual and groups’ tribe or ethnicity,
race, religion, and socioeconomic
- Almost any business can be a
background.
private sector company, with examples
CULTURAL DOMINATION,
including: Digital media companies,
REPRESENTATION AND THE POLITICS
Accountancy firms. Hospitality and
OF
catering businesses.
RECOGNITION
• The wide array of non-governmental -The major cultural groups enjoy more
and not-for-profit organizations that have governments support and priority in terms
a presence in public life, expressing the of development projects, higher
interests and values of their members or representation in government and private
others, based on ethical, cultural, offices, bigger budgetary allocation, and
political, scientific, religious or more seats in governments.
philanthropic considerations.
OTHER FORMS OF UNDEMOCRATIC
• CITIZEN PARTICIPATION- It is the
PRACTICES
most important democratic practice in a
• Vote Buying – is a widespread
country. Many people feel a sense of
phenomenon. It is usually viewed as
commitment to their neighborhood and
a purely economic exchange in
are actively involved in activities to
which the voters sell his/her to the
improve the quality of life there.
highest bidders
• Founded on the principles of free • Bullying – is a form of
and fair elections, a universal right to aggressiveness behaviors in which
vote, and a competitive political process someone intentionally and
where qualified people can run and be repeatedly causes another person
voted for office. injury or discomfort.
• Political corruption –it is the use of
UNDEMOCRATIC PRACTICES power for private gain in the form
-Against or in disagreement with of bribery and embezzlement.
democracy • Abusing power of authority -
These are the practices that affect the misuse of position of power to take
Society and Government in a lot of ways. unjust advantage of individuals,
GENDER BIASES - Refer to the prejudicial organization or government.
act of attitude towards male or females or • Undemocratic practices may not
discrimination between genders always be the best option for a
It is also behavior that shows favoritism number of people, but they work
toward one gender over another. fine in most places where they are
MATRIARCHAL SOCIETY - Is a followed.
characterized by female rule or female • Only you have the power to decide
dominance, including women’s control of which political system works best
property. for you (Democratic or
PATRIARCHAL SOCIETY- Demonstrate the Undemocratic). It’s up to you, but a
social system in which position of factor that should be taken in
dominance and privilege are primarily held consideration is where you live. You
by men. should consider moving to a place
MATRILINEAL SOCIETY- In other hand is where the political views suit you in
where descent or lineage, birthright and a better way and you are
social classification are traced through comfortable with the government.
maternal, rather than paternal lines. REPRESENTATIVE AND
RACE, RELATION, PARTICIPATORY DEMOCRACIES
SUFFRAGE, ANDPOLITICAL
MARGINALIZATION REPRESENTATIVE DEMOCRACY
-Every citizen is entitled to exercise - A person who has been chosen
suffrage or the right to vote people to to act or make decisions on
whom he or she entrust the authority to
behalf of another person or a - MAXRANGE is a data set that analyzes
group of people. political regimes and democratization
REPRESENTATIVE DEMOCRACY processes from the 18th century to the
is also called Indirect present, making it the largest and most
Democracy. comprehensive political regime data set in
A political system where the qualified the world today. Its latest version,
citizens exercise their political power MaxRange2, focuses on seven dimensions,
through representatives. The sovereign including general level of democracy,
power remains on the citizens but its institutional structure, strength of the
exercise is on the representatives they executive, status of the regime,
elect. concentration of powers to the executive,
The power of these representatives is and position of the head of state, as well
limited of balancing measures such as: as a simplified strength variable.
• Constitution MaxRange data set is the creation of Max
• Independent Judiciary Rånge and Mikael Sandberg, who are both
• Referendum associated with Halmstad University in
Sweden.
PARTICIPATORY DEMOCRACY- The
DEMOCRACY INDEX is an evaluation of
action or state of taking part in something.
the state of democracy of countries. It is
PARTICIPATORY DEMOCRACY is also
published by The Economist Intelligence
called Direct Democracy.
Unit based in the UK.
Participatory Democracy is a form of
INTERNATIONAL IDEA- which is based in
government in which citizens participate
Stockholm, Sweden, evaluates the
individually and directly in political
country's quality of democracy. The
decisions and policies that effect their
acronym IDEA stands for Institute for
lives.
Democracy and Electoral Assistance. The
Participatory Democracy is a process of
structure of its assessment framework is
collective decision making that combines
based on popular control over decision
element from both direct and
makers, political equality of those
representative democracy.
exercising control, and seven mediating
One of the most popular demonstration of
values (citizen participation, authorization
Participatory Democracy was the EDSA
of public officials, equal representation of
People Power in 1986.
different groups, accountability of officials,
transparency in government,
REPRESENTATIVE VS PARTICIPATORY
responsiveness to the needs of the public,
DEMOCRACY
and solidarity of the people)..
If the citizen elects representatives to
make laws and policies, it is called a
Representative Democracy.
PRINCIPLES IN SAFEGUARDING
If the people themselves votes directly on
DEMOCRACY
policies and laws, it is called a
Participatory Democracy.
POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY - The power in a
DEMOCRATIC INCLINATION OF
democratic system flows from the people,
INSTITUTIONS
who have the ultimate say in the decisions
- Established democratic institutions
made by their leaders.
possess the core elements of elections,
RULE OF LAW - Everyone is subject to the
political parties, lawmaking bodies,
same laws, including those who make and
interest groups, social movements, and
enforce them. This ensures that no one is
mass just as how democratic a political or
above the law and that justice is applied
social institution is. Moreover, certain
fairly and equally.
values such as respect for human rights
PROPORTIONALITY -principle of
and human dignity, racial and ethnic
safeguarding democracy states that those
equity, equal access to and distribution of
responsible for safeguarding should
wealth and resources, social justice, fair
provide the least intrusive response
trial, and other civil liberties and political
appropriate to the risk presented.
rights are considered as indicators of
democracy and freedom.
PROTECTION- Support and by switching on their mobile devices and
representation for those in greatest need. snapping a photo of a classmate's work,
EMPOWERMENT – People being supported enabling them to copy that homework
and encouraged to make their own almost word for word to avoid doing it
decisions and informed consent. themselves.
PREVENTION- It is better to take action GAMING- There are tons of free gaming
before harm occur. apps and people love them, especially the
PARTNERSHIP- Local solutions through learners. These addictive games can be
services working with their communities. quite a distraction and take away from
ACCOUNTABILITY -Accountability and productivity in learning.
transparency in safeguarding practice.
FUNCTIONS OF ICT
INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION
TECHNOLOGY DATA PROCESSING- The processing is
done in sequence of operations which
ICT- is an extended term for information translates inputs such as geographical
technology (IT) which stresses the role of maps, images, satellite imageries, aerial
unified communications and the photographs or in the form tabular data
integration of telecommunications. The collected from in-site survey, Government
phrase information and communications records or personal observations into
technology has been used by academic output in the form of dimensional model
researchers since the 1980s, and the or in other visual forms.
abbreviation ICT became popular after it DATA CAPTURE- function of ICT is use for
was used in a report to the UK data capturing, storage and transmission
government by Dennis Stevenson in 1997. of important information.
ICT changes how people work, DATA MANIPULATION- functions of ICT,
communicate, learn, and live. which among them it is the process of
ICT transactions like online shopping, summarizing, re-arranging, improving
telemedicine, and social media are now scientific designs achieve either physically
popular because it is easier to buy online or by processor.
and save time. DATA DISPLAY- functions of ICT includes
BENEFITS OF ICT presenting of information in the form of
text, graphics, audio and video.
EDUCATION- Many educators are already DATA STORAGE- function of ICT plays an
using and infusing technology as a issue of covering space, which depends on
teaching-learning pedagogy through the the following factors such as disc space
use of different platforms. and availability and flexibility.
COMMUNICATION- ICT include devices DATA TRANSMISSION- function of ICT is
and applications that provide access to used to transmit data from one pace to
information and enable electronic another place or from one computer to
communications, like sending text another computer.
messages or engaging in video chats. DATA RETRIEVAL- functions of ICT
Mobile phones, smartphones, computers, supports the recovery of information’s
and laptops are typical ICT devices. either in the form of features or
JOB OPPORTUNITY- ICT comprises the characteristics or both in a computer
employees' ability to improve specific jobs, generated form.
be more flexible on working hours, and EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY- function
share ideas with co-workers. And can of ICT includes the provisions of trainings,
easily find a job online. seminars and workshops on how to use
SECURITY BREACH- Students are often technology.
more curious than they are malicious. Infrastructure function - functions of ICT
They want to push the boundaries just to covers network, devices and other related
see if they can. equipment and setups such as those from
CHEATING- Sharing homework answers withdrawing cash from an automated
via IMs, email, text messaging, or any teller machine.
other device.
MANAGEMENT- uses of ICT, refers to the
management information system which
takes care of report writing, home school
links, attendance, examination entries and
target settings.
COMMUNICATION- use of ICT discusses
about projecting the right of image of the
school through its website, which provides
the public idea of the school.
LEARNING- covers the key areas of
research, modeling and simulation, online
courses and revision units,
communication, publishing and
collaboration.
DISADVANTAGE OF THE USE OF ICT:
COST
More and more resources are being put
into ICT in schools the cost of laptops,
wireless broadband, projectors for
example contribute a large percentage of
the school's budget.
Misuse of ICT
Instead of using their laptops or tablets for
their studies and online tests, more often
than not students stray away and visit
social networking sites like Facebook or
Twitter. Students would be too focused on
playing games or visiting social
networking sites resulting to lower
academic grades.
DIGITAL DIVIDE
-natural consequence of advancements in
ICT -discrepancy in peoples access and
skill related to ICT
Factors: geographical location economy
income, age, education, race, and
government support among others.
You might also like
- Sash Shahnashea The Little Green BookFrom EverandSash Shahnashea The Little Green BookNo ratings yet
- Interval DemocracyDocument27 pagesInterval DemocracyJameson EliNo ratings yet
- Local Media6251304588637429313Document6 pagesLocal Media6251304588637429313Rozanne JoyNo ratings yet
- Politics AND SocietyDocument56 pagesPolitics AND SocietyMalik Moammar HafeezNo ratings yet
- Trends - Module 5 - Democratic InterventionsDocument6 pagesTrends - Module 5 - Democratic Interventionserikah100% (1)
- Government Studies Short Hand NotesDocument25 pagesGovernment Studies Short Hand Notesphdunity100% (1)
- Political SelfDocument25 pagesPolitical SelfJEMABEL SIDAYENNo ratings yet
- Formal Sources of DemocraticDocument13 pagesFormal Sources of DemocraticankitlatherstudyNo ratings yet
- DemocracyDocument37 pagesDemocracyJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- DemocracyDocument26 pagesDemocracyKenn CalabriaNo ratings yet
- Political and Leadership StructuresDocument57 pagesPolitical and Leadership StructuresSied ReyesNo ratings yet
- 4.1. Concept of DemocracyDocument9 pages4.1. Concept of DemocracyManish LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Polgov ReviewerDocument5 pagesPolgov Reviewerdobi bearNo ratings yet
- Philippines Politics and GovernanceDocument23 pagesPhilippines Politics and GovernanceHazel ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Understanding DemocracyDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Democracykasandradelossantos121705No ratings yet
- 30 Democracy GovernanceDocument12 pages30 Democracy GovernanceArkim MakhosaNo ratings yet
- Democratic InterventionDocument12 pagesDemocratic InterventionZaira Amarillo RemorozaNo ratings yet
- Democratic InterventionDocument12 pagesDemocratic InterventionZaira Amarillo RemorozaNo ratings yet
- Interacting With OthersDocument32 pagesInteracting With OthersアゼロスレイゼルNo ratings yet
- Democratic InterventionsDocument22 pagesDemocratic InterventionsVivianAlcantaraDelaCruz73% (11)
- Forms of GovernmentDocument2 pagesForms of GovernmentMariniel Gomez LacaranNo ratings yet
- GG Reviewer 3Document11 pagesGG Reviewer 3jhonashsanchez70No ratings yet
- Human Rights, Democracy and Discrimination: Re-Purposed by Joané BotesDocument23 pagesHuman Rights, Democracy and Discrimination: Re-Purposed by Joané BotesMichael PerezNo ratings yet
- DemocracyDocument24 pagesDemocracySabharna ShanjithaNo ratings yet
- Democratic & DictatorshipDocument15 pagesDemocratic & DictatorshipRoyal Raj AligNo ratings yet
- Democratic InterventionDocument26 pagesDemocratic InterventionJoy Caligan PagariganNo ratings yet
- Exit Exam UCSPDocument45 pagesExit Exam UCSPvaniiqueNo ratings yet
- POL101 - Lecture 4 - Political Regimes - KNHHDocument29 pagesPOL101 - Lecture 4 - Political Regimes - KNHHSamin hyderNo ratings yet
- Government: Sadia Afrin Assistant Professor, Political Science BSMRSTU, GopalganjDocument48 pagesGovernment: Sadia Afrin Assistant Professor, Political Science BSMRSTU, GopalganjTasnimul IqbalNo ratings yet
- Politics Exam ReviewDocument19 pagesPolitics Exam ReviewokaytemporaryNo ratings yet
- Government and Economy: BY: Rabia KhalidDocument12 pagesGovernment and Economy: BY: Rabia KhalidAhmed Nafees KhanNo ratings yet
- Gen 1o2 - On-Line ClassesDocument45 pagesGen 1o2 - On-Line Classesjust meNo ratings yet
- Democracy 1Document24 pagesDemocracy 1Rijean RecañaNo ratings yet
- Forms of Government in The 21st CenturyDocument74 pagesForms of Government in The 21st CenturyNoli BayaisNo ratings yet
- PGC .PPT PartsDocument240 pagesPGC .PPT PartsFider Gracian0% (1)
- Intro Class Pols 2023Document14 pagesIntro Class Pols 2023lolalelaNo ratings yet
- TNCT 2ND QTR (Long Quiz)Document4 pagesTNCT 2ND QTR (Long Quiz)Catherine Keira IlaganNo ratings yet
- TNCT Democracy 2 GCDocument30 pagesTNCT Democracy 2 GCLorena CabañeroNo ratings yet
- PoliticsDocument15 pagesPoliticsFatima NaqviNo ratings yet
- Comp Govt Week-3Document16 pagesComp Govt Week-3nazrin.eminNo ratings yet
- DemocracyDocument16 pagesDemocracyIrene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Defining DemocracyDocument3 pagesDefining DemocracyYubraj KhatriNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 3Document20 pages09 - Chapter 3Vinay Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit V The Politcal EnvironmentDocument11 pagesUnit V The Politcal EnvironmentMonica Lorevella NegreNo ratings yet
- Trends, Networks and Critical Thinking in The 21St Century Compilation of Topics Presented On Second Quarter by Mrs. Racquel R. DecenaDocument4 pagesTrends, Networks and Critical Thinking in The 21St Century Compilation of Topics Presented On Second Quarter by Mrs. Racquel R. DecenaRacquel DecenaNo ratings yet
- Philippines Politics and GovernanceDocument72 pagesPhilippines Politics and GovernanceMa IsabelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Defining Politics and GovernanceDocument50 pagesLesson 1 - Defining Politics and GovernanceAndre AngkaNo ratings yet
- Becoming A Member of SocietyDocument18 pagesBecoming A Member of SocietyKIZZY MARIE MAG-ISANo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Reviewer in TRENDSDocument7 pages4th Quarter Reviewer in TRENDSCasandra NipayNo ratings yet
- Democracy in Brief KorDocument39 pagesDemocracy in Brief KorGuitelen Siiten100% (1)
- Disciplines in Political ScienceDocument18 pagesDisciplines in Political Sciencejhovin barrientosNo ratings yet
- Democracy DataDocument55 pagesDemocracy DataabdulNo ratings yet
- What Is Democracy PPT Class9Document33 pagesWhat Is Democracy PPT Class9aannoosandhuNo ratings yet
- Trends 1Document13 pagesTrends 1Keren Khate Baniswal NgollobNo ratings yet
- Democratic InterventionDocument42 pagesDemocratic InterventionKienstel GigantoNo ratings yet
- Ds 112 Governance ConasDocument62 pagesDs 112 Governance ConasRamadan ChomeNo ratings yet
- Comparative Government and PoliticsDocument35 pagesComparative Government and PoliticsCloduald Bitong MaraanNo ratings yet
- Political System Process and Forms of GovernmentDocument16 pagesPolitical System Process and Forms of Governmentpidmubataan.2023No ratings yet
- Outcomes of Democracy Class 10 NotesDocument7 pagesOutcomes of Democracy Class 10 Notesdelhitegaming69No ratings yet
- Politics, Governance and Citizenship: GEED 20023Document2 pagesPolitics, Governance and Citizenship: GEED 20023Nico RanuloNo ratings yet
- Links For Document Checklist, Forms & Templates For AffidavitDocument2 pagesLinks For Document Checklist, Forms & Templates For AffidavitVishalNo ratings yet
- ASIRT Decision On Calgary Police Case From 2020Document5 pagesASIRT Decision On Calgary Police Case From 2020Darren KrauseNo ratings yet
- Fractional Share FormulaDocument1 pageFractional Share FormulainboxnewsNo ratings yet
- Generation No 4 Bernabe de Las CAsasDocument94 pagesGeneration No 4 Bernabe de Las CAsastereNo ratings yet
- Pre - Colonial Philippines:: Unit One: The Philippines BeforeDocument19 pagesPre - Colonial Philippines:: Unit One: The Philippines BeforeRachell Villarente ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Good Moral CharacterDocument11 pagesCertificate of Good Moral CharacterAvelino Jr II PayotNo ratings yet
- BL1 1223 - 1230Document2 pagesBL1 1223 - 1230sweetmangoshakeNo ratings yet
- 350 Andhra Pradesh Police Transport Organization Subordinate Service RulesDocument10 pages350 Andhra Pradesh Police Transport Organization Subordinate Service RulesPersonnel Section MTNo ratings yet
- Celpip Questions (Speaking) 3Document3 pagesCelpip Questions (Speaking) 3fuilungwongNo ratings yet
- Governance of Cyber Security Research ProposalDocument1 pageGovernance of Cyber Security Research ProposalAleksandar MaričićNo ratings yet
- Khamis 21.3.24Document2 pagesKhamis 21.3.24razxxfNo ratings yet
- E2language Ielts Topic Toolkit e Bookpdf - CompressDocument103 pagesE2language Ielts Topic Toolkit e Bookpdf - CompressĐỗ Quang Thắng100% (5)
- G.R. No. 111399 November 14, 1994 - ODON PECHO v. SANDIGANBAYAN, ET AL PDFDocument9 pagesG.R. No. 111399 November 14, 1994 - ODON PECHO v. SANDIGANBAYAN, ET AL PDFLucy HeartfiliaNo ratings yet
- Nutty Company Problem 23 - 5 (INTACCS Problem)Document2 pagesNutty Company Problem 23 - 5 (INTACCS Problem)Ya Na100% (1)
- ASYNCHRONOUS Activity - OPPRESSION - STOLEN CHILDREN ACTIVITY STUDENTSDocument3 pagesASYNCHRONOUS Activity - OPPRESSION - STOLEN CHILDREN ACTIVITY STUDENTSywNo ratings yet
- Termination of LeasesDocument28 pagesTermination of Leasesjagwe ronnie lumalaNo ratings yet
- BrowneDocument44 pagesBrowneInsomne88No ratings yet
- Absolute Sale DeedDocument6 pagesAbsolute Sale DeedAbhishek CharanNo ratings yet
- Readphi Capstone RevisedDocument1 pageReadphi Capstone RevisedRosette SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Imp Fillable Form As of June 2022 v1Document13 pagesImp Fillable Form As of June 2022 v1Anna Lyn AnceroNo ratings yet
- 010-Seguritan v. PeopleDocument2 pages010-Seguritan v. PeopleJanineNo ratings yet
- Video Production Proposal Template: Authorized Name AddressDocument8 pagesVideo Production Proposal Template: Authorized Name AddressBeenish YousafNo ratings yet
- EPG Vs CADocument2 pagesEPG Vs CAabbyhwaitingNo ratings yet
- BEF121 Introduction To Development StudiesDocument157 pagesBEF121 Introduction To Development StudiesNguvulu100% (1)
- The Price of Portia's LoveDocument5 pagesThe Price of Portia's LoveHannah BorumNo ratings yet
- E.E EnglishDocument13 pagesE.E EnglishAndrea Miguel100% (1)
- Preliminary Chapter Criminal ProcedureDocument9 pagesPreliminary Chapter Criminal ProcedurewalnutwitchNo ratings yet
- Reed, Deshaya Complaint FinalDocument35 pagesReed, Deshaya Complaint FinalJake DraugelisNo ratings yet
- EOI For Bhubaneswar - Puri Developement CorridorDocument29 pagesEOI For Bhubaneswar - Puri Developement Corridornirmallya kanungoNo ratings yet
- Trial BalDocument5 pagesTrial BalAneel kumarNo ratings yet