Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculus Standards
Uploaded by
Mahmud Alam NauOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculus Standards
Uploaded by
Mahmud Alam NauCopyright:
Available Formats
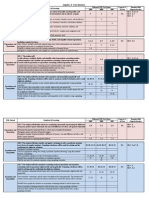
KASC ACADEMIC STANDARDS CHECKLIST
MATHEMATICS
User’s Name:
Use the columns as a checkoff or a place to take notes to track any curriculum issue. For instance,
you might list the unit or marking period in which a standard was mastered, the areas where teachers
want additional professional development opportunities, or any issue you need to analyze as you work
to enhance your students’ performance. See the folder labeled Ideas for Usage for further suggestions
on ways to use the checklists and cards.
HIGH SCHOOL Calculus
Calculus-Limits
Understand the concept of the limit of a function
Understand limits.
HS.C.1 a. Apply limits to a variety of functions, including piecewise functions.
b. Prove that the limit of a function exists, based upon the definition of a limit.
Demonstrate an understanding of limits by estimating and finding the limit of a function at a point
HS.C.2 graphically, numerically and algebraically.
HS.C.3 Apply properties and theorems of limits, including limits of indeterminate forms.
HS.C.4 Communicate understanding of limits using precise mathematical symbols and language.
Calculus-Function Behavior
Describe the asymptotic and unbounded behavior of functions
Describe asymptotic behavior (analytically and graphically) in terms of infinite limits and limits at
HS.C.5 infinity.
Discuss the end behavior of functions; identify representative functions for each type of end
HS.C.6 behavior using precise mathematical symbols and language.
Calculus-Continuity
Develop an understanding of continuity as a property of functions
Understand and use the limit definition of continuity to determine whether a given function is
HS.C.7 continuous at a specific point.
Define and identify different types of discontinuity – removable (hole) or non-removable (jump,
HS.C.8 asymptote) – in terms of limits.
Understand and apply continuous function theorems.
HS.C.9 a. Apply the Intermediate Value Theorem to continuous functions.
b. Apply the Extreme Value Theorem to continuous functions.
HS.C.10 Communicate an understanding of continuity using precise mathematical symbols and language.
KASC KAS Checklist
Calculus-Understanding the Derivative
Demonstrate an understanding of the derivative
Define derivatives.
a. Define the derivative of a function as the limit of the difference quotient.
HS.C.11 b. Understand this limit of the difference quotient can be interpreted as an instantaneous rate of
change or the slope of a tangent line.
HS.C.12 Use average rate of change to estimate the derivative from a table of values or a graph.
HS.C.13 Understand the derivative as a function.
HS.C.14 Apply the definition of derivative to find derivative values and derivative functions.
HS.C.15 Explain why differentiability implies continuity yet continuity does not imply differentiability.
Understand and apply the Mean Value Theorem, including numerical, graphical and algebraic
HS.C.16 representations.
Understand the relationship between the concavity of a function and the sign of the second
HS.C.17 derivative.
HS.C.18 Understand Rolle’s Theorem as a special case of the Mean Value Theorem.
Calculus-Applications of Derivatives
Apply differentiation techniques
HS.C.19 Efficiently find derivatives of functions with and without technology.
Understand and use derivative rules for sums, differences, products and quotients of two functions
HS.C.20 and calculate the derivative of a composite function using the chain rule.
HS.C.21 Use implicit differentiation to find a derivative in an equation of two variables.
HS.C.22 Use implicit differentiation to find the derivative of the inverse of a function.
Understand the relationship between the increasing and decreasing behavior of a function and the
HS.C.23 sign of the first derivative of the function.
HS.C.24 Use the first derivative to analyze curves and identify relative extrema.
HS.C.25 Understand the relationship of concavity to the second derivative.
HS.C.26 Use the second derivative to find points of inflection.
Use the second derivative to analytically locate intervals on which a function is concave up, concave
HS.C.27 down or neither.
Describe how graphical characteristics of a given function, the first derivative of that function and the
HS.C.28 second derivative of that function interrelate.
HS.C.29 Use derivatives to express rate of change in a variety of contexts.
Use derivatives to solve a variety of problems including related rates, optimization, tangent line
HS.C.30 approximations and growth and decay models.
HS.C.31 Use differentiation to solve problems involving velocity, speed and acceleration.
Understand and apply differential equations.
a. Verify solutions to differential equations and use them to model real-world problems with and
HS.C.32 without technology.
b. Solve separable differential equations and use them in modeling real-world problems with and
without technology.
KASC KAS Checklist
Calculus-Understanding Integration
Demonstrate understanding of a definite integral
Understand the definite integral of a function over an interval. Interpret a definite integral as a limit of
HS.C.33 Riemann Sums and as net accumulation of change.
HS.C.34 Write a Riemann sum that represents the definition of a definite integral.
Calculate the values of Riemann Sums over equal subdivisions to approximate definite integrals of
HS.C.35 functions represented graphically and numerically (using tables). Use left-hand sums, right- hand
sums, midpoint sums and trapezoidal sums.
HS.C.36 Recognize differentiation and integration as inverse operations.
Understand how the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus connects differentiation and integration and
HS.C.37 use it to evaluate definite and indefinite integrals and to represent particular antiderivatives.
HS.C.38 Perform analytical and graphical analysis of functions using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
Understand and use the definite integral of a function over an interval and understand its use as a
HS.C.39 mathematical tool.
Calculus-Applications of Integration
Apply techniques of integration
Find antiderivatives of a variety of basic functions including power, exponential, logarithmic and
HS.C.40 trigonometric and apply basic properties of definite integrals.
HS.C.41 Use substitution techniques and change of limits of integration to find antiderivatives.
HS.C.42 Find particular antiderivatives given initial conditions.
Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles
Model, solve and interpret applications of antiderivatives including finding area, velocity, acceleration
HS.C.43 and volume of a solid.
HS.C.44 Apply integration to solve problems including particle motion and exponential growth and decay.
Describe the application of integration to a variety of problems using precise mathematical language
HS.C.45 and notation.
KASC KAS Checklist
You might also like
- Grade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksLindaNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 7 Learning Competency K-12Document4 pagesMath Grade 7 Learning Competency K-12Lino Garcia63% (8)
- OCS Call Detail Record Reference (V100R002C02LG0237 - 26) (Pakistan, Ufone) PDFDocument354 pagesOCS Call Detail Record Reference (V100R002C02LG0237 - 26) (Pakistan, Ufone) PDFMuhammad Saad Farooq0% (1)
- MSC Aerospace Engineering PresentationDocument14 pagesMSC Aerospace Engineering PresentationMahmud Al HassanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Integral Calculus: Systematic Studies with Engineering Applications for BeginnersFrom EverandIntroduction to Integral Calculus: Systematic Studies with Engineering Applications for BeginnersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Basic CalculusDocument88 pagesBasic CalculusJulyvia Danila75% (4)
- Metal DetectorsDocument54 pagesMetal DetectorsAchmad Fadhillah Kurniawan100% (2)
- DCN Manual 2019Document74 pagesDCN Manual 2019Suhani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The Need For DigitizationDocument7 pagesThe Need For DigitizationMariza AgustinaNo ratings yet
- 954 Math T (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusDocument4 pages954 Math T (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesLesson PlanAnnmarie McGonagleNo ratings yet
- Ap Calculus BC SyllabusDocument15 pagesAp Calculus BC Syllabusapi-306402864No ratings yet
- Coordinate Algebra Unit 3Document8 pagesCoordinate Algebra Unit 3crazymrstNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade StandardsDocument8 pages7th Grade Standardsapi-251069371No ratings yet
- Algebra II Standards Final ChartDocument6 pagesAlgebra II Standards Final Chartapi-273248611No ratings yet
- 8th Grade StandardDocument7 pages8th Grade Standardapi-251069371No ratings yet
- Math 7 Syllabus 2014-2015Document5 pagesMath 7 Syllabus 2014-2015api-266524097No ratings yet
- The Big 50 Revision C3Document5 pagesThe Big 50 Revision C3Jithin RajanNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC Course of StudyDocument12 pagesAP Calculus BC Course of Studydanvelezz100% (1)
- Algebra I Pacing Guides 2015-2016 1Document9 pagesAlgebra I Pacing Guides 2015-2016 1api-252392763No ratings yet
- ST Standards and ObjectivesDocument1 pageST Standards and Objectivesapi-295344110No ratings yet
- 7 Grade Math Ratios & Proportional Relationships CCSS "I Can" StatementsDocument71 pages7 Grade Math Ratios & Proportional Relationships CCSS "I Can" Statementsapi-271033247No ratings yet
- Do Scope and Seq Alg 2 CPDocument6 pagesDo Scope and Seq Alg 2 CPapi-233720080No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 CriticalDocument10 pagesAlgebra 2 Criticalapi-115680157No ratings yet
- Term 4 Maths GR 12Document11 pagesTerm 4 Maths GR 12Simphiwe ShabalalaNo ratings yet
- Hsp-Add Math-F5Document28 pagesHsp-Add Math-F5Azreen DaudNo ratings yet
- End of Instruction - Algebra 1 Content Standards and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesEnd of Instruction - Algebra 1 Content Standards and ObjectivesAhmet OzturkNo ratings yet
- Alg 2 Math Correlations 2010Document6 pagesAlg 2 Math Correlations 2010Harish MulevaNo ratings yet
- Common Core Exponential FunctionsDocument8 pagesCommon Core Exponential Functionsapi-297804475No ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document4 pagesAlgebra 2api-15888876No ratings yet
- A Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionDocument10 pagesA Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionxcrunitccNo ratings yet
- Advanced Algebra Trig Pacing Guide: Big Ideas Enduring Understandings Essential QuestionsDocument11 pagesAdvanced Algebra Trig Pacing Guide: Big Ideas Enduring Understandings Essential Questionsapi-305244588No ratings yet
- Stage 1 - Desired Results: Understanding by DesignDocument3 pagesStage 1 - Desired Results: Understanding by DesignLuis AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Air Molek Form 5 Additional Mathematics Scheme of Work 2013Document15 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Air Molek Form 5 Additional Mathematics Scheme of Work 2013Green QingNo ratings yet
- Ubd QuadraticsDocument3 pagesUbd Quadraticsapi-355509602No ratings yet
- Syllabus 3 AP Calculus BC Course OutlineDocument5 pagesSyllabus 3 AP Calculus BC Course OutlineEbuka EfobiNo ratings yet
- Learning OutcomesDocument2 pagesLearning OutcomeschinesetakeoutNo ratings yet
- Ib Math Standard Level Yr 1 and 2Document7 pagesIb Math Standard Level Yr 1 and 2Tien PhamNo ratings yet
- Overland TrailDocument8 pagesOverland Trailapi-245623862No ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan (2012) Mathematics Form 5Document19 pagesYearly Lesson Plan (2012) Mathematics Form 5Nie Anthon100% (1)
- Ap Calculus Ab Syllabus Course OverviewDocument10 pagesAp Calculus Ab Syllabus Course OverviewanuNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics AM 27: SyllabusDocument15 pagesPure Mathematics AM 27: SyllabusAshley MorganNo ratings yet
- SCCCR AlgebraiDocument2 pagesSCCCR Algebraiapi-269559470No ratings yet
- Mathematics Learning Objectives Years 10 To 11Document5 pagesMathematics Learning Objectives Years 10 To 11Hafidz ArifNo ratings yet
- Calc Ap SyllabusDocument4 pagesCalc Ap Syllabusapi-239856705No ratings yet
- Individual Development Profile Report: Muhammad, TalibahDocument5 pagesIndividual Development Profile Report: Muhammad, TalibahGlamrockFreddy TLCNo ratings yet
- KS3 Mathematics: Curriculum MapDocument20 pagesKS3 Mathematics: Curriculum MapGrace TabfNo ratings yet
- 8 Grade Math The Number System CCSS "I Can" StatementsDocument79 pages8 Grade Math The Number System CCSS "I Can" Statementsapi-271033247No ratings yet
- 8th Grade CcssDocument1 page8th Grade Ccssapi-237059911No ratings yet
- Chapter 111. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills For Mathematics Subchapter C. High SchoolDocument17 pagesChapter 111. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills For Mathematics Subchapter C. High Schoolascap85No ratings yet
- Calculus BC Syllabus 3Document6 pagesCalculus BC Syllabus 3Yohannes GebreNo ratings yet
- K-12 Math Crosswalks Algebra IDocument17 pagesK-12 Math Crosswalks Algebra Iestabloid1169No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Number System StandardsDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Number System Standardsapi-282583504No ratings yet
- Grade 8 MathxDocument5 pagesGrade 8 Mathxapi-2542992270% (1)
- Polynomial Functions Unit PlanDocument10 pagesPolynomial Functions Unit Planapi-255851513No ratings yet
- North Carolina Standard Course of Study North Carolina Math 3Document8 pagesNorth Carolina Standard Course of Study North Carolina Math 3Alex WellmanNo ratings yet
- Overland Trail Curr AnalysisDocument5 pagesOverland Trail Curr Analysisapi-246119961No ratings yet
- Ca Css Math - Content Standards Ca Dept of Education Ap CalculusDocument2 pagesCa Css Math - Content Standards Ca Dept of Education Ap Calculusapi-456572687No ratings yet
- Unit A9Document5 pagesUnit A9mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Analysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5Document20 pagesAnalysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5establoid1169No ratings yet
- Mathematics 8 2022 2023Document8 pagesMathematics 8 2022 2023Princess Mae LumawagNo ratings yet
- 8 ThgradecurriculumDocument5 pages8 Thgradecurriculumapi-254290621No ratings yet
- Mathq Prelim ReviewerDocument4 pagesMathq Prelim Reviewerfujiko galboNo ratings yet
- 0580 Y05 SW 1 2Document3 pages0580 Y05 SW 1 2zurichasNo ratings yet
- Ees ManualDocument191 pagesEes ManualMohd Jamal Mohd MoktarNo ratings yet
- Química de CoordinacionDocument107 pagesQuímica de CoordinacionEMMANUEL ALEJANDRO FERNANDEZ GAVIRIANo ratings yet
- Boiler Other Steam Plant AccessoriesDocument5 pagesBoiler Other Steam Plant AccessoriesCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Assigment1 Jan30-2023Document4 pagesAssigment1 Jan30-2023Vaquas aloNo ratings yet
- XT1C 160 TMD 25-450 4p F F: General InformationDocument3 pagesXT1C 160 TMD 25-450 4p F F: General InformationHenrics MayoresNo ratings yet
- Substance Chemistry Lesson 1Document28 pagesSubstance Chemistry Lesson 1samsonNo ratings yet
- 2.4 GHZ 14 Dbi 90 Degree Vertical Polarized Sector Panel Wireless Lan Antenna - Model: Hg2414Sp-090Document2 pages2.4 GHZ 14 Dbi 90 Degree Vertical Polarized Sector Panel Wireless Lan Antenna - Model: Hg2414Sp-090Giovanni José Huacasi SupoNo ratings yet
- KGF 1146Document7 pagesKGF 1146Dharmawan TohNo ratings yet
- AT2 ERT Installation GuideDocument3 pagesAT2 ERT Installation GuideYordan Silva GomezNo ratings yet
- SV1-10-4/4M/4R: - Solenoid ValveDocument2 pagesSV1-10-4/4M/4R: - Solenoid ValveCORTOCIRCUITANTENo ratings yet
- ASTM B 280-20 STD Spec For Seamless Copper Tubing For Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Field ServiceDocument9 pagesASTM B 280-20 STD Spec For Seamless Copper Tubing For Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Field Servicetomhansen935No ratings yet
- Schedule 90 Days Jee Main Crash Course MathongoDocument3 pagesSchedule 90 Days Jee Main Crash Course MathongoShrish DollinNo ratings yet
- Departemen Statistika, Fakultas Sains Dan Matematika, Universitas DiponegoroDocument12 pagesDepartemen Statistika, Fakultas Sains Dan Matematika, Universitas DiponegoromonicaramadhaniaNo ratings yet
- The Performance and Service Life of Wire Ropes Under Deep Koepe and Drum Winders Conditions - Laboratory SimulationDocument9 pagesThe Performance and Service Life of Wire Ropes Under Deep Koepe and Drum Winders Conditions - Laboratory SimulationRicardo Ignacio Moreno MendezNo ratings yet
- SRM-51-47-00 Fastener Pitch and Edge Distance DataDocument13 pagesSRM-51-47-00 Fastener Pitch and Edge Distance DataJelpi Duvan LariosNo ratings yet
- Light: Year 9 Science Semester RevisionDocument4 pagesLight: Year 9 Science Semester Revisionapi-32133818No ratings yet
- The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics: Postulate 1Document6 pagesThe Postulates of Quantum Mechanics: Postulate 1sgybleeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Iot Networking - I: Dr. Sudip MisraDocument19 pagesBasics of Iot Networking - I: Dr. Sudip MisraMohit KrNo ratings yet
- AWS TCO WorkSpacesDocument16 pagesAWS TCO WorkSpacessantuchetuNo ratings yet
- DTC Table: Caution: Be Sure To Perform Before Starting DiagnosisDocument3 pagesDTC Table: Caution: Be Sure To Perform Before Starting DiagnosisBumbu PermataNo ratings yet
- 6242 01 Rms 20060616Document10 pages6242 01 Rms 20060616UncleBulgariaNo ratings yet
- Understand and Troubleshoot IP Address Management (IPAM) in Windows Server 8 BetaDocument102 pagesUnderstand and Troubleshoot IP Address Management (IPAM) in Windows Server 8 Betacalin bNo ratings yet
- 2155 13572 1 PBDocument8 pages2155 13572 1 PBIliace ArbaouiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Escalation and Intl Conflict Jo CRDocument25 pagesTheory of Escalation and Intl Conflict Jo CRfuckyou321No ratings yet
- P-G-R-T / P-G-R-S Truck: Preventative Maintenance GuideDocument2 pagesP-G-R-T / P-G-R-S Truck: Preventative Maintenance GuideKANG PRIYONo ratings yet