Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 7 Sets
Uploaded by
Azista PharmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 7 Sets
Uploaded by
Azista PharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Galaxy: Class VII
UNIT 7: Sets
Worksheet: Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer.
1. Which one of these is not a set?
a. A group of good tennis players of your school
b. All students of your school who were absent on a particular working
day
c. Letters of the word ‘mathematics’
d. Integers > 100
2. If A represents the set of perfect squares between 2 and 27, then it can
be expressed as
a. A = {4, 16, 25} b. A = {4, 9, 16, 25}
c. A = {4, 9, 10, 25} d. None of these
3. If A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, then its representation would be
a. {x / x is an integer and x < 10}
b. {x / x is a whole number}
c. {x / x is a positive integer and x2 < 100}
d. None of these
4. If Z is the set of integers, then which one of these is not true?
a. 13 Z b. -17 Z c. -103 Z d. 3-1 Z
5. If A = {6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 18}, then its set builder form is
a. {x / x is a composite number & 5 < x < 20}.
b. {x / x is a composite number and x < 20}.
c. {x / x is an even number and x < 20}.
d. none of these.
6. If Z+ is the set of positive integers, then which of these is not true?
a. 11 Z+ b. 0 Z+ c. d.
7. Indicate which of these is a null set.
a. {0} b. {Ø}
c. Ø d. none of these
8. Which one of these is not an infinite set?
a. Set of integers greater than 105
b. Set of integers less than -105
c. Set of all points on a straight line segment of length 10 cm
d. Set of natural numbers less than 105
(c) Oxford University Press
9. If A be the set of vowels in the word ‘mathematician’ then find n (A).
a. 3 b. 6 c. 5 d. 4
10. If A = {-4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {-2, 0, 2, 3}, then find n (A)
+ n (B).
a. 4 b. 13 c. 9 d. 5
11. Find n (A) where A = {x4 / x < 103 & x N}.
a. 10 b. 729 c. 999 d. 1000
12. Find n (A∩B) where A∩B = Ø.
a. 1 b. 2
c. n where n 0 d. 0
For question numbers 13 to 36,
Given are the Universal set U = { -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, a, b, c, d} and
the sets A = {-3, -1, 0, 1, 3 }, B = {0, 1, 3, a, b}, and C = {a, b, c, -1, 0}.
13. Find AU B.
a. {-3, -1, 0, 1, 3, a, b} b. {-3, -1, a, b}
c. {0, 1, 3, a, b, -1} d. None of these
14. Find BUC.
a. {1, 3, a, b, c} b. {0, 1, 3, a, b, c, -1}
c. {0, 1, 3, b, -1} d. None of these
15. Find AUC.
a. {-3, -1, 1, 3, a} b. {-3, -1, 0, 1, a, b}
c. {-3, -1, 0, 1, 3, a, b, c} d. None of these
16. Find A∩B.
a. {0, 1} b. {1, 3} c. {-1, 0, 1} d. {0, 1, 3}
17. Find A∩C.
a. {-1, 0} b. {0, a} c. {0, 1} d. None of these
18. Find B∩C.
a. {1, 0, a, b} b. {0, a, b} c. {a, b, c} d. None of these
19. Find A – B.
a. {0, -1, -3} b. {a, b} c. {-3, -1} d. None of these
20. Find B – A.
(c) Oxford University Press
a. {1, a, b} b. {1, 0, a} c. {2, a, b} d. {a, b}
21. Find C - A.
a. {a, b, c} b. {0, a, b} c. {a, b, -1} d. None of these
22. Find B – C.
a. {0, 1, 3} b. {1, 3} c. {1, 3, a} d. None of these
23. Find C – B.
a. {0, c, -1} b. {c, -1, 3} c. {c, -1} d. {a, b, -1}
24. Find A – C.
a. {-3, 3} b. {3, 1} c. {0, 3, -3} d. {-3, 1, 3}
25. Find n (AUC).
a. 7 b. 8 c. 10 d. None of these
26. Find n (BUC).
a. 10 b. 7 c. 6 d. None of these
27. Find n (BUC).
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
28. Find n (A∩C).
a. 5 b. 4 c. 3 d. 2
29. Find n (A – B).
a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5
30. Find n (C – B).
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
31. Find n (C – A).
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
32. Find n (A∩B).
a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3
33. Find Aʹ.
a. {-4, -2, 2, 4, a, b, c, d} b. {-4, -2, c, d}
c. {3, 4, d} d. None of these
34. Find Bʹ.
(c) Oxford University Press
a. {-2, -1, 2, c, d} b. {-4, -3, -2, -1, 2, c, d}
c. {-1, 2, c, d} d. None of these
35. Find n (Aʹ Cʹ).
a. 4 b. 3 c. 5 d. 2
36. Find n (Bʹ Cʹ).
a. 3 b. 6 c. 4 d. 5
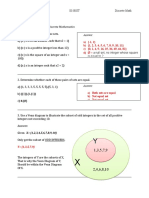
For question number 37 to 40, study the following Venn diagram.
37. Find B – A.
a. {6, 7, 8, 9, 10} b. {0, 1, 2} c. {0, 1, 2, 4} d. None of these
38. Find B ∩ ᵃʹ
a. {0, 1, 2} b. {6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
c. {11, 12} d. {3, 4, 5}
39. Find n (A) + n (B) – n (A B).
a. 5 b. 6 c. n (AUB) d. 14
40. Find n (Aʹ Bʹ).
a. 1 b. 3 c. 6 d. 2
(c) Oxford University Press
You might also like
- Set Class 03Document4 pagesSet Class 03Anvesha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- SS 1 Fmaths 1ST Ca Test First Term 2022Document7 pagesSS 1 Fmaths 1ST Ca Test First Term 2022Akinola OlalekanNo ratings yet
- 9TH Math TestDocument4 pages9TH Math TestSrinivasa PadhiNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Exam For Grade 7 RevisedDocument5 pagesFirst Periodical Exam For Grade 7 RevisedEmelyn V. Cudapas50% (4)
- Grade 7 Quarterly ExamDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Quarterly ExamDavid John JumawanNo ratings yet
- G7 1stprelim 2021Document2 pagesG7 1stprelim 2021Christeus Von SujeroNo ratings yet
- Lab 05 StudentssheetDocument7 pagesLab 05 Studentssheetaoora6No ratings yet
- Automata Revision (1) P1 2021Document15 pagesAutomata Revision (1) P1 2021Kirolos ElkomosNo ratings yet
- Assignment Class 11 Set Theory Board AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignment Class 11 Set Theory Board AssignmentmihirNo ratings yet
- SETS All WoksheetsDocument6 pagesSETS All WoksheetsSelver SadikovicNo ratings yet
- 1 Mathematics Sets & RelationsDocument2 pages1 Mathematics Sets & RelationsHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz # 2Document6 pagesLong Quiz # 2eyaNo ratings yet
- Concept Type Questions: A (1, 3, 5), B (2, 4, 6) and C (0, 2, 4, 6, 8) - Which of TheDocument11 pagesConcept Type Questions: A (1, 3, 5), B (2, 4, 6) and C (0, 2, 4, 6, 8) - Which of TheladduNo ratings yet
- Class9 Alg Test06 Sets Yakup YAZICIDocument5 pagesClass9 Alg Test06 Sets Yakup YAZICIFatos ShuliNo ratings yet
- GEd 102 Problem Set No. 2Document10 pagesGEd 102 Problem Set No. 2six bautistaNo ratings yet
- Ans Ge 104 Midterm Exam BsedDocument6 pagesAns Ge 104 Midterm Exam BsedJA Mie CompbellNo ratings yet
- Operations On SetsDocument9 pagesOperations On SetsDeva sNo ratings yet
- Demo Math7Document31 pagesDemo Math7Jessielou UbaldeNo ratings yet
- 2023 Super Mock Core Maths 1Document7 pages2023 Super Mock Core Maths 1rcvj8hty9cNo ratings yet
- L-2 Extra Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesL-2 Extra Solved ProblemsJohn BlackNo ratings yet
- 3in1 Review Recitation Quiz 1st Q Math 7Document32 pages3in1 Review Recitation Quiz 1st Q Math 7MYRA BACSAFRANo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Score: - /95 Grade & Section: - Teacher: Ms. Joyce Anne T. YabutDocument2 pagesName: - Date: - Score: - /95 Grade & Section: - Teacher: Ms. Joyce Anne T. YabutJoyce Anne Tuala Yabut100% (1)
- English Class X Maths Chapter01Document58 pagesEnglish Class X Maths Chapter01Arman KhanNo ratings yet
- Strictly No Calculators AllowedDocument3 pagesStrictly No Calculators AllowedLhot Bilds Siapno100% (1)
- Mathematics ECAT (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar) - 1Document134 pagesMathematics ECAT (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar) - 1AYESH qureshiNo ratings yet
- SET THEORY and Ven Diagram NTSE QustionDocument12 pagesSET THEORY and Ven Diagram NTSE QustionSrinivasa PadhiNo ratings yet
- The Age of The Earth Is 4, 543, 000, 000 Billion Years. How Is 4, 543, 000, 000 Written in Scientific Notation?Document3 pagesThe Age of The Earth Is 4, 543, 000, 000 Billion Years. How Is 4, 543, 000, 000 Written in Scientific Notation?Tohru00No ratings yet
- Discrete Math ReviewerDocument17 pagesDiscrete Math ReviewerLaurence Kobe B. NavarroNo ratings yet
- Bca Question Paper PDFDocument4 pagesBca Question Paper PDFdrharpreet singh100% (1)
- Assignment / Activity For Discrete MathematicsDocument4 pagesAssignment / Activity For Discrete Mathematicsantonio abanNo ratings yet
- Practiceforgr 9Document4 pagesPracticeforgr 9LalaNo ratings yet
- SJDM Cornerstone College, IncDocument2 pagesSJDM Cornerstone College, IncBetchang AquinoNo ratings yet
- Bawa Edits: Name of Student - Roll No. - Class & Sec.Document4 pagesBawa Edits: Name of Student - Roll No. - Class & Sec.Vicky AgroNo ratings yet
- NUST-NET-Past-Paper-3 EngDocument29 pagesNUST-NET-Past-Paper-3 Engayera fatima100% (1)
- The Pythagorean Theorem Practice NDocument4 pagesThe Pythagorean Theorem Practice NCyril Danica LimareNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Examination in Mathematics ViiDocument2 pagesFirst Periodical Examination in Mathematics ViiApril KylaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet1Document6 pagesTutorial Sheet1Emmanuel Ēzscod TemboNo ratings yet
- Math Entrance Exam (30 Items)Document4 pagesMath Entrance Exam (30 Items)Romano CalderonNo ratings yet
- AImergeDocument343 pagesAImergeKaushal KapureNo ratings yet
- First Periodic Examination Math 7Document5 pagesFirst Periodic Examination Math 7Jonel TuazonNo ratings yet
- UnitTestPracticeAssignment - D01 Feb 2024Document17 pagesUnitTestPracticeAssignment - D01 Feb 2024krishivpatel7108No ratings yet
- Sets - Proposition - UNIT - 1Document25 pagesSets - Proposition - UNIT - 1AKNo ratings yet
- Lets22 Ultimate Math FinalDocument30 pagesLets22 Ultimate Math FinalJudie Jane MuegaNo ratings yet
- Cayambanan National High School: First Quarter Assessment in Mathematics 7Document5 pagesCayambanan National High School: First Quarter Assessment in Mathematics 7Jasmin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- SSLC - Maths - 2 Marks From KalvisolaiDocument12 pagesSSLC - Maths - 2 Marks From Kalvisolaisaravanaajani2012No ratings yet
- Jamb Mathematics 2003Document4 pagesJamb Mathematics 2003Oyinlola AyomideNo ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions: I. Sets and FunctionsDocument12 pagesTwo Mark Questions: I. Sets and FunctionsVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Exam Math7 q1Document3 pagesExam Math7 q1Lovely GuintoNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Examination in Mathematics 7Document2 pagesFirst Periodical Examination in Mathematics 7Nimfa PlazaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Sets - 25 Sep 2020Document6 pagesAssignment - Sets - 25 Sep 2020DeCeNT TuShArNo ratings yet
- MTH 101 2023Document9 pagesMTH 101 2023tnh2mxp69wNo ratings yet
- 11-Maths-B1-Annual Exam 2023-24Document5 pages11-Maths-B1-Annual Exam 2023-24Arunava DuttaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Multiple 1st GradingDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Multiple 1st GradingFresan MagnateNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Discrete MathDocument3 pagesTest 1 Discrete MathMarcus McWile MorningstarNo ratings yet
- 7 - Understanding Summative TestDocument2 pages7 - Understanding Summative Testyusop maligaNo ratings yet
- Topic02 6p2 GalvinDocument31 pagesTopic02 6p2 GalvinIbrahim Abdullah0% (1)
- Set, Relation, Function (Level 1) - Bi8k3ywqsubz3p79x4czDocument5 pagesSet, Relation, Function (Level 1) - Bi8k3ywqsubz3p79x4czRo HitNo ratings yet
- MTH 101 PAST QUESTIONS by ADEBAYO BIM'S 08112601259 ThanksDocument14 pagesMTH 101 PAST QUESTIONS by ADEBAYO BIM'S 08112601259 Thankschisomaugustine29No ratings yet
- Basic Set OperationsDocument13 pagesBasic Set OperationsErica TayapNo ratings yet
- English9 q1 m1 Wk3 Skim-To-Determine-Key-Ideas-And-Authors-PurposeDocument18 pagesEnglish9 q1 m1 Wk3 Skim-To-Determine-Key-Ideas-And-Authors-PurposeMonaliza Pawilan75% (8)
- The Invisalign SystemDocument8 pagesThe Invisalign SystemDr Mohammed Nabeel0% (1)
- How Many Moles of KI Are Present in 500ml of A 0.2 M Solution - QuoraDocument1 pageHow Many Moles of KI Are Present in 500ml of A 0.2 M Solution - QuoraPaytonNo ratings yet
- Artificial InteligenceDocument19 pagesArtificial InteligenceShahnawaz SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Humanistic Therapy Therapy: Group 4Document23 pagesHumanistic Humanistic Therapy Therapy: Group 4Kyra Jane F. DellosaNo ratings yet
- Obstetricia: GabbeDocument1,454 pagesObstetricia: GabbeAstridMeraNo ratings yet
- Prokofievs Chromatic Practice in TheoryDocument22 pagesProkofievs Chromatic Practice in TheoryIlija Atanasov100% (1)
- Your First Day at WorkDocument10 pagesYour First Day at WorkPhu Cong LeNo ratings yet
- Mil Courtesy and DiciplineDocument35 pagesMil Courtesy and DiciplineAlfie Daquiado100% (1)
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusNathaniel BaconesNo ratings yet
- Basics of BSCDocument34 pagesBasics of BSCSushma SelaNo ratings yet
- Abhay Jain Roll No 126Document20 pagesAbhay Jain Roll No 126abhay jainNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Instructional Materials in Teaching and Learning of Financial Accounting in Senior Secondary SchoolsDocument16 pagesAssessment of Instructional Materials in Teaching and Learning of Financial Accounting in Senior Secondary SchoolsArnel MedinaNo ratings yet
- Tle Laboratory ManualDocument7 pagesTle Laboratory ManualAileene Montenegro83% (18)
- Notes On Criminological Research 1Document8 pagesNotes On Criminological Research 1sagesagesausageNo ratings yet
- LSK 1Document306 pagesLSK 1Krish SaiNo ratings yet
- Study of Human Resource Management in Proctor and Gamble Business EssayDocument12 pagesStudy of Human Resource Management in Proctor and Gamble Business EssayRamesh KaliaNo ratings yet
- Kiwi Kids' Good Book Guide 2013Document12 pagesKiwi Kids' Good Book Guide 2013juliaviabeNo ratings yet
- Open House Checklist 18-19Document1 pageOpen House Checklist 18-19api-467926588No ratings yet
- LaclipDocument29 pagesLaclipZhenru LinNo ratings yet
- Weekly Homework Packets For KindergartenDocument5 pagesWeekly Homework Packets For Kindergartenaariozilf100% (1)
- Engineering Library Book Display 2013Document7 pagesEngineering Library Book Display 2013ntulibraryNo ratings yet
- Acca FeeDocument2 pagesAcca FeeKamlendran BaradidathanNo ratings yet
- Applied - Career Opportunities - Career Opportunities - Industrial Technology Advisor (10852)Document15 pagesApplied - Career Opportunities - Career Opportunities - Industrial Technology Advisor (10852)1105195794No ratings yet
- Mattson Alexa Hs Chart 5Document3 pagesMattson Alexa Hs Chart 5api-535398298No ratings yet
- Academic AnxietyDocument31 pagesAcademic AnxietyJuliah TahilNo ratings yet
- Ethical Consideration in TestingDocument9 pagesEthical Consideration in TestingMuhammad Ahmad NaeemNo ratings yet
- How Champions Think (Workshop)Document4 pagesHow Champions Think (Workshop)olha100% (1)
- 12 The Teaching of Construction in Architectural EducationDocument290 pages12 The Teaching of Construction in Architectural EducationRafael SantosNo ratings yet
- Shadow Side of StrengthsDocument2 pagesShadow Side of Strengthsapi-657561077No ratings yet