Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Skeletal and Muscular System Exam: Put The Following Muscle Contraction and Relaxation Steps in Order
Uploaded by
Makiato Maureen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesyeah
Original Title
YAH
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentyeah
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesHuman Skeletal and Muscular System Exam: Put The Following Muscle Contraction and Relaxation Steps in Order
Uploaded by
Makiato Maureenyeah
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
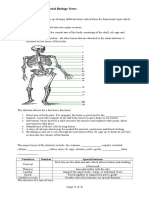
Human Skeletal and Muscular System Exam These two minerals give bones their strength
What are the 4 functions of the skeletal and hardness.
system? The protective layer around the bone.
This can be found inside the center of bones.
These types of bones are primarily used to
What are the 3 general functions of the support weight.
muscular system? What is the primary The scientific name for the breastbone.
function? Your vertebrae are this type of bones.
This type of tissue will absorb shock where
Fill in the missing information about the bones meet.
different types of SYNOVIAL JOINTS Tissue that joins part of the body together.
The scientific name of the thighbone.
TYPE EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION This type of joint allows the most movement
Shoulder & but is susceptible to injury.
Hip A place where two bones meet.
Pivot Joint Moves up & The scientific name for the wrist bones.
down and side The process during which cartilage hardens
to side. into bone.
Hinge Moves in only A type of fracture that does not go all the way
one direction through the bone.
Wrists & A disease that causes the bones to become
Ankles weak and bend.
Thumb The neck is an example of this type of joint.
This part of the skeleton includes the arms,
Describe a fibrous joint? Give an example.
legs, shoulder and pelvis.
A type of fracture where the bone has broken
Describe a cartilaginous joint? Give an example.
all of the way through.
Describe the following joint movements:
Inflammation and swelling of joints could be
Abduction/adduction:
due to this condition.
Elevation:
The knee and elbow are this type of joint.
Extension/flexion:
The scientific name of the kneecap.
Pronation/supination:
A type of fracture where there is a complete
Circumduction/rotation:
break of the bone and the skin.
Fractures:
What is the difference between a complete and The scientific name of the collarbone.
an incomplete fracture? When a bone moves out of position.
What is the difference between a The scientific name of the shoulder blades.
compound/open and a closed/simple fracture? These types of bones are used for small
movements.
What is the difference in how an endochondral These muscles can be found in the lower back.
bone develops and the development of an How many muscles are there in the human
intramembranous bone? body?
Put the following muscle contraction and relaxation This type of muscle can only be found in the
steps in order. heart.
_____ acetylcholine travels across the These connect muscles to bones.
synaptic gap This muscle is often called the calf muscle.
_____ actin and myosin form linkages
_____ calcium ions diffuse into the skeletal
The two protein filaments found in muscle
fiber and bind to troponin fibers.
_____ actin and myosin linkages are broken These tell muscles when to move.
_____ calcium ions diffuse out of the skeletal This type of muscle helps you move when you
muscle want to.
_____ acetylcholine is released from the distal
This type of muscle works without you
end of the motor neuron
_____ cholinesterase decomposes thinking about them.
acetylcholine Also known as striated muscle; moves your
_____ acetylcholine stimulates the skeletal bones.
fiber Type of muscles found in your organs and
_____ muscle relaxes skin.
_____ muscle fiber shortens (contracts)
These muscles can be found in your thigh.
The scientific name of your jawbone. The three things muscles need to stay alive.
These attach bone to bone. The muscles found in the upper chest.
This type of bone protects organs. The category of muscle strain that results in
the complete rupture of the muscle.
This part of the skeleton includes the skull,
ribs, and spinal column. A condition that involves the swelling of the
covering around a tendon.
The end of the muscle that does not move. D. Joint
A condition in which muscles reduce in size
from lack of use. The fibrous bands that connects two bones in a
An injury where the ligament, tendon or joint are
muscle has been pulled or stretched. A. Cartilage
A condition in which muscles increase in size B. Tendons
from being used too much. C. Ligaments
Muscles get short and fat when they do this. D. Strings
When one muscle contracts, its partner does
this. The process in which cartilage is replace by
The end of the muscle that can move. bone is called what?
The muscles found at the back of the thigh. A. Synovial Fluid
B. Ossification
Cartilage is C. Compact bone
A) Infection in the bones D. Fracture
B) Swelling & stiffness in a joint
C) Tough flexible cushion between two bones A break in the bone is called
D) Curvature of the spine A. Fracture
B. Bursitis
Ligaments C. Sprain
A) Strong cord that connects bone to bone D. Torn cartilage
B) Strong cord that connects muscle to bone
Skeletal muscles are
Tendons A. Involuntary
A) Strong cord that connects bone to bone B. Voluntary
B) Strong cord that connects muscle to bone
Your stomach muscle is
Proper care of a sprain is A. Involuntary
A) Bones kept in place B. Voluntary
B) Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation How do muscles work together?
C) Regular exercise and supplementation A. Stretch and pull
B. Up and down
Which of the following is located superior to the C. Contraction and Extension
femur: D. Right and left
A) Metacarpals
B) Fibula
C) Tibia Describe the following parts of a long bone:
D) Humerus Periosteum:
Diaphysis:
A bone is supplied with nutrients by Epiphysis:
A) Yellow Bone Marrow Red bone marrow:
B) Red Bone Marrow Yellow bone marrow:
C) Calcification Articular cartilage:
D) Blood Vessels Epiphyseal disk:
What part of the skeletal system consists of the
skull, breastbone, ribs and vertebrae?
A. Systematic
B. Vertebral
C. Axial
D. Appendicular
The appendicular skeleton consist of what
parts?
A Head, sternum, ribs and vertebrae
B Hands, feet, legs, hips and arms
C Feet, head, legs, ribs and arms
D Hips, head, toes and fingers
The point at which two bones come together is
what?
A. Ligaments
B. Pivot
C. Ossification
You might also like
- SEDS11 Bones Worksheet AnswersDocument13 pagesSEDS11 Bones Worksheet Answersjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular System Review Test Answers PDFDocument9 pagesSkeletal and Muscular System Review Test Answers PDFKabanshi PeterNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PE FinalDocument14 pagesModule 3 PE FinalStephanie De Guzman LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 THE BONES AND MUSCLES A1 and A2Document15 pagesChapter 3 THE BONES AND MUSCLES A1 and A2Marinette Valencia MedranoNo ratings yet
- Principals of Anatomy Energy Systems IncDocument224 pagesPrincipals of Anatomy Energy Systems Inckevinramirezzz365No ratings yet
- 3.1 Skeletal SystemDocument17 pages3.1 Skeletal SystemAndriy GarcíaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesCSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemSamantha ThomasNo ratings yet
- CSEC Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesDocument4 pagesCSEC Form 4 Human and Social Biology Notessmbdy tbhhh100% (1)
- Muscles Anatomy-Dr - NdukuiDocument62 pagesMuscles Anatomy-Dr - Ndukuiglenian560No ratings yet
- The Skeletal and Muscular SystemsDocument39 pagesThe Skeletal and Muscular SystemsMuhamad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo Inglés Médico III UGD 2024Document48 pagesCuadernillo Inglés Médico III UGD 2024gianellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 10Document11 pagesChapter 9 10Ramilyn Villarido ChiongNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument7 pagesJointsbushrashahid208No ratings yet
- Week 10 (A) HSBDocument6 pagesWeek 10 (A) HSBBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument22 pagesJointswazzupwaleedNo ratings yet
- Movement of the Body Requires Muscles to Work in Antagonistic PairsDocument14 pagesMovement of the Body Requires Muscles to Work in Antagonistic PairsReshma DookarranNo ratings yet
- Assessing Musculoskeletal FunctionDocument74 pagesAssessing Musculoskeletal FunctionChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Muscular-Skeletal System Lesson NotesDocument105 pagesMuscular-Skeletal System Lesson NotesMonydit SantinoNo ratings yet
- Joints Lecture 1Document12 pagesJoints Lecture 1Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- 5th Form Biology-Movement - Movement in Man.Document52 pages5th Form Biology-Movement - Movement in Man.Jharell CaravlhoNo ratings yet
- Effectors Organs: LocomotionDocument18 pagesEffectors Organs: Locomotionpuchiti1234No ratings yet
- Joints and Muscles Chapter NotesDocument3 pagesJoints and Muscles Chapter NotesSahithi PNo ratings yet
- Types of Bone Fractures and Clinical ManifestationsDocument10 pagesTypes of Bone Fractures and Clinical ManifestationsFryam BellsNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System NotesDocument4 pagesSkeletal System NotesLeon Abel80% (5)
- Practical Guide To Casting: Author: Matthew Pitt Senior Orthopaedic PractitionerDocument31 pagesPractical Guide To Casting: Author: Matthew Pitt Senior Orthopaedic Practitionerbinod rijalNo ratings yet
- Locomotion Handout 2023Document7 pagesLocomotion Handout 2023rheanna0076No ratings yet
- Anatomy Medical TerminologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy Medical TerminologyNikita GosineNo ratings yet
- The Body in Sport - LearnerDocument31 pagesThe Body in Sport - Learnerplumbs23No ratings yet
- 1.2 TheMuscularSystemDocument60 pages1.2 TheMuscularSystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
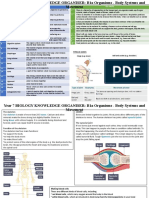
- Year 7 BIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE ORGANISER: B1a Organisms - Body Systems and MovementDocument3 pagesYear 7 BIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE ORGANISER: B1a Organisms - Body Systems and MovementArwind RoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument20 pagesBasic Concepts of The Musculoskeletal SystemTedy FriyadiNo ratings yet
- Lect 1 Intro - MSKDocument75 pagesLect 1 Intro - MSKSivajothyNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Cranial BonesDocument7 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Cranial BonesAsdNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesSkeletal Systemsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular SystemsDocument24 pagesSkeletal and Muscular SystemsMarlyn Laurio-patriarcaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV - All About Muscles: Joint, Muscle, Tendon & LigamentDocument5 pagesChapter IV - All About Muscles: Joint, Muscle, Tendon & LigamentIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Support and MovementDocument8 pagesSkeletal Support and MovementUmme AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ISSA FastTrack Basic and Applied Sciences PDFDocument8 pagesISSA FastTrack Basic and Applied Sciences PDFOlufemi Palmer0% (1)
- ISSA FastTrack Basic and Applied Sciences PDFDocument8 pagesISSA FastTrack Basic and Applied Sciences PDFOlufemi PalmerNo ratings yet
- Anatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingDocument79 pagesAnatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingR DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 4Document67 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 4Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Grade 7-The Human SkeletonDocument19 pagesLesson 2 Grade 7-The Human SkeletonSAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemArlen Joy V. AMPARONo ratings yet
- Muscular System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument32 pagesMuscular System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum MarieNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document22 pagesDocument 5dawidkubiak222No ratings yet
- Movement and Muscle ContractionDocument20 pagesMovement and Muscle ContractionReshma DookarranNo ratings yet
- Chronic Osteomyelitis Case StudyDocument35 pagesChronic Osteomyelitis Case StudyMelissa Gines100% (2)
- Sports Injuries: European SectionsDocument11 pagesSports Injuries: European SectionsBuRiO03No ratings yet
- 1st-Introduction To Anatomy1Document30 pages1st-Introduction To Anatomy1prasun_vNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesSkeletal Systemrheanna0076No ratings yet
- CH 7Document40 pagesCH 7Shreyash PandaNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument11 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemJenielynFerreraArriolaNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2 (4) 2Document5 pages02 Handout 2 (4) 2Senpai LeonNo ratings yet
- Canbridge Checkpoint Grade 7Document25 pagesCanbridge Checkpoint Grade 7seema sarathNo ratings yet
- L345 MusclesBonesJointsDocument17 pagesL345 MusclesBonesJointsmahfa23No ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- 3 Hand HygieneDocument22 pages3 Hand Hygieneasnake DagnewNo ratings yet
- PopoDocument1 pagePopoMakiato MaureenNo ratings yet
- YazazzaDocument33 pagesYazazzaMakiato MaureenNo ratings yet
- Rganisation of BodyDocument2 pagesRganisation of BodyMakiato MaureenNo ratings yet
- Ouline 1 1RDocument3 pagesOuline 1 1RMakiato MaureenNo ratings yet
- Caratative Theory G9Document26 pagesCaratative Theory G9Makiato MaureenNo ratings yet
- Combined Aple CT NotesDocument99 pagesCombined Aple CT NotesFrancis SormahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chemical Basis in LifeDocument38 pagesChapter 2 Chemical Basis in LifeMakiato MaureenNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes & Plant Cell vs. Animal CellDocument24 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 1 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes & Plant Cell vs. Animal CellPercival RiegoNo ratings yet
- P.E.-2-Self-assess Health-Related Fitness StatusDocument9 pagesP.E.-2-Self-assess Health-Related Fitness StatusMaria imelda PanchoNo ratings yet
- RPL Form 4 JHS Learners Checklist of CompetenciesDocument75 pagesRPL Form 4 JHS Learners Checklist of CompetenciesMelody SamsonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueDocument10 pagesCHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueAem TalNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For/Cra : List of Important Topics To Study For Neet-PgDocument1 pageHow To Prepare For/Cra : List of Important Topics To Study For Neet-PgAnushka SoniNo ratings yet
- Congruent Exercise by Bill DeSimone Z-Lib OrgDocument95 pagesCongruent Exercise by Bill DeSimone Z-Lib OrgDima KotNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 2Document12 pagesPhysical Education 2Prince Charles AbalosNo ratings yet
- Unit-7 Physiology and Injuries in SportsDocument73 pagesUnit-7 Physiology and Injuries in Sportsmanishchandel7665No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular FitnessDocument5 pagesCardiovascular FitnessAlieza JimenezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- Nerve Muscle PhysiologyDocument79 pagesNerve Muscle Physiologyroychanchal562100% (2)
- PHYSICAL EDUCATION 01: Self-Testing ActivitesDocument7 pagesPHYSICAL EDUCATION 01: Self-Testing ActivitesEdnalyn Barniza BrecioNo ratings yet
- Four Major Drug TargetsDocument34 pagesFour Major Drug TargetsFlowerNo ratings yet
- FastTwitch Phase3 OS Weeks13 18Document45 pagesFastTwitch Phase3 OS Weeks13 18Melina HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Physical Education in The Tertiary LevelDocument35 pagesPhysical Education in The Tertiary Levelhatsune mikuNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT-1 - Week-1-4 - Learning Module - 033105Document35 pagesPATHFIT-1 - Week-1-4 - Learning Module - 033105knightruzelNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Explained: Skeletal, Cardiac & Smooth Muscle TissueDocument44 pagesMuscular System Explained: Skeletal, Cardiac & Smooth Muscle TissueClaudine Jo B. TalabocNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1Irish Melonie PobladorNo ratings yet
- Health Related FitnessDocument10 pagesHealth Related FitnessKai MeNo ratings yet
- H420-01 QP Jun22Document32 pagesH420-01 QP Jun22Tiya DattaNo ratings yet
- Physio Uhs Solved Past Papers 2nd Year Mbbs WWW Edu Apnafort ComDocument130 pagesPhysio Uhs Solved Past Papers 2nd Year Mbbs WWW Edu Apnafort ComHamza AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sport and Physical Education Dissertation IdeasDocument6 pagesSport and Physical Education Dissertation IdeasPaySomeoneToWriteAPaperForMeCanada100% (1)
- ملزمة احياء جميع الفصولDocument178 pagesملزمة احياء جميع الفصولمحمدNo ratings yet
- Strength Training and Shoulder ProprioceptionDocument4 pagesStrength Training and Shoulder ProprioceptionNico BrantesNo ratings yet
- Unit II Lesson 5Document7 pagesUnit II Lesson 5Jonah SalcedoNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- HY MSK - AnatomyDocument88 pagesHY MSK - AnatomyHumna Younis100% (1)
- 13 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus B2.3 Cell Specialization PowerPointDocument45 pages13 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus B2.3 Cell Specialization PowerPointmike bevnNo ratings yet
- Strength Training Aerobic Exer HGK2007Document7 pagesStrength Training Aerobic Exer HGK2007leal thiagoNo ratings yet