Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity 1
Activity 1
Uploaded by
EM GinaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 1
Activity 1
Uploaded by
EM GinaCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY 1. MATCH AND PAIR!! ACTIVITY 1. MATCH AND PAIR!!
DIRECTIONS: Match the words in Column A with the DIRECTIONS: Match the words in Column A with the
correct descriptions in Column B. Write the answer on the correct descriptions in Column B. Write the letter on the
space provided to complete the magic word. space provided to complete the magic word.
COLUMN A COLUMN A
P. Zygote P. Zygote
D. Budding D. Budding
D. Sperm cell D. Sperm cell
R. Asexual R. Asexual
E. Regeneration E. Regeneration
U. Binary Fission U. Binary Fission
C. Fertilization C. Fertilization
E. Sex Cells E. Sex Cells
R. Egg Cell R. Egg Cell
O. Sexual O. Sexual
ACTIVITY 2. MATCH AND PAIR!!
COLUMN B ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1. A process by which one organism self-reproduce.
2. The cells that comes from the mother and father during COLUMN B
reproduction.
3. New cell that is formed during fertilization in sexual 1. A process by which one organism self-reproduce.
reproduction. 2. The cells that comes from the mother and father during
4. Sex cell that is coming from the mother. reproduction.
5. Reproduction that requires two parents. 3. New cell that is formed during fertilization in sexual
6. A parent organism produces offspring by growing a tiny of reproduction.
itself. 4. Sex cell that is coming from the mother.
7. An organism divides it body into two where each half 5. Reproduction that requires two parents.
grows into a new organism. 6. A parent organism produces offspring by growing a tiny of
8. A process during reproduction where two sex cells join itself.
together. 7. An organism divides it body into two where each half
9. A method of reproduction wherein an organism can grows into a new organism.
replace or restore their lost or damaged body parts. 8. A process during reproduction where two sex cells join
10. Sex cell that is coming from the father. together.
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 9. A method of reproduction wherein an organism can
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 replace or restore their lost or damaged body parts.
10. Sex cell that is coming from the father.
ACTIVITY 3. RAINING INFO! DIRECTIONS: Complete the ACTIVITY 3. RAINING INFO! DIRECTIONS: Complete the
chart below. Choose your answer in the box provided that chart below. Choose your answer in the box provided that
describes the word. describes the word.
• Requires one parent only • Requires one parent only
• Offspring produced is genetically unique from the parents • Offspring produced is genetically unique from the parents
• Undergoes Fertilization • Undergoes Fertilization
• Undergoes different modes of reproduction • Undergoes different modes of reproduction
• Requires 2 parents • Requires 2 parents
• Offspring is genetically identical to the parent • Offspring is genetically identical to the parent
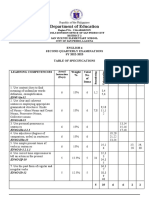
SUMMATIVE TEST 3
1.Which of the following processes determine the DNA of an 13. It is a component of the environment that includes living
offspring? organisms.
A. Asexual reproduction B. Binary fission A. Abiotic B. Biotic
C. Sexual reproduction D. Both A & B C. Consumer D. Producer
2. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of asexual
reproduction? 14. Which of the following is a biotic component of an
A. It is fast ecosystem?
B. It is safe A. Soil B. Warm sun
C. It increases genetic diversity C. Water D. Worm
D. It is a better use of energy 15. It is a non-living component of an ecosystem.
3.Which of the following processes involves a single parent A. Abiotic B. Biotic
in producing offspring? C. Consumer D. Decomposer
A.Fission B.Meiosis 16. Which of the following is an abiotic component of an
C.Sexual reproduction D.Both A and B ecosystem?
4. Which of the following reproductive processes involves A. Ant B. Bacteria
egg and sperm? C. Oxygen gas D. Snail
A. Budding B. Fertilization 17. It is an abiotic component that is needed by plants and
C. Fission D. Pollination trees to make their own food.
5. The genetic material of a zygote is determined A. Carbon dioxide B. Soil
by____________. C. Oxygen D. Temperature
A. An egg cell only 18. It is an abiotic component that is produced by plants
B. sperm cell only through the process of photosynthesis.
C.pollen and a sperm cell A. Oxygen gas B. Soil
D. An egg cell and a sperm cell C. Sunlight D. Water
6. Which of the following structures are NOT involved in 19. The following are abiotic components, EXCEPT
asexual reproduction? __________.
A. Gametes B. Roots A. heat B. oxygen
C. Stems D. Tubers C. water D. water lily
7. What type of reproduction passes genetic information to 20. Which of the following best describes the kinds of things
the future generations? that make up an ecosystem?
A. Sexual reproduction A. All living things and non-living things
B. Asexual reproduction B. Humans and animals
C. Both sexual and asexual C. Only living things
D. none of the above D. Plants only
8. Which process is taking place when a sperm cell unites 21. Which are examples of abiotic components?
with an egg cell? A. chair, desk, window, dog
A. Asexual reproduction B. dog, cat, frog, tree, wood
B. Fertilization C. Dinosaur, paper, pencil
C. Pollination D. plastic, cup, window, rock
D. Vegetative Propagation 22. The biosphere is the part of the Earth that contains life.
9. Which of the following statements is TRUE about asexual Which of the following is a component of the biosphere?
reproduction? I. atmosphere
A. Only one parent is required. II. Earth’s surface
B. A kitten is produced through asexual reproduction. III. water covering most of the planet
C. A mother and father are needed to produce offspring. IV. all of the above
D. The offspring that are produced are genetically unique.
10. Which of the following are modes of asexual A.I only B. I and II C. II and III D. I, II and III
reproduction? 23. Organisms grow in number because of __________.
A. Budding B. Fission A. biotic components
C. Meiosis D. Both A & B B.only abiotic component
11. An organism that is produced ________ can easily adapt C. biotic components
to its environment. D. Both abiotic and biotic components
A. asexually B. sexually 24. Which among the organisms reproduces quickly, saves
C. both A and B D. none of the above energy and not searching for a mate?
A. starfish fertilizing a female
12. In an/a __________, living organisms work along with B. A sea sponge reproducing by mitosis
physical component of a habitat to maintain life. C. A bacterium reproducing by binary fission
D. Both B & C
A. atmosphere B. biosphere 25. Which of the following is an ADVANTAGE of sexual
C. ecosystem D. environment reproduction?
A. It is fast
B. It is safe
C. It is a better use of energy
D. It increases genetic variation
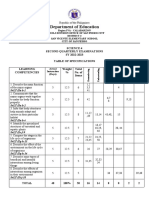
SUMMATIVE TEST 4 A. I only B. II and III only C. I and III only D. II and IV only
1.It is the biotic component that breaks down chemicals 12. An eagle is eating a fish. The eagle is called_____.
from producers and consumers into simpler form. A. commensal C. parasite B. B. host D. Predator
A. Consumer B. Decomposer 13.The ecological relationship of fishes in the aquarium
C. Producer D. Transducer is the same as that of ____.
2. It is an organism that feeds on other organisms A. mosquito and man
because it cannot make its own food. B. a frog and a cricket
A. Consumer B. Decomposer C. a bee and a flower
C. Producer D. Transducer D. carabao grass and bermuda grass in the garden
3. Which of the following two organisms are producers? 14. Which of the following is biotic component?
A. plants and phytoplankton A. decomposer B. light intensity
B. plants and primary consumers C. wind D. humidity
C. secondary consumers and phytoplankton 15. ________ are autotrophic organisms with the ability to
D. Phytoplankton and chlorophyll
carry on photosynthesis and to make food for themselves.
4. A food wed is more realistic than a food chain in
showing the feeding relationships in ecosystem A. Herbivores B. Carnivores
because________. C. Omnivores D. Producers
A. it compares the number of consumers to the number of 16. Examples of consumers include__________
microorganisms in an ecosystem. A. herbivore B. Carnivore
B. food chains use only a small sample of organisms. C. Omnivore D. All of the above
C. a food web explains why there are more producers than
17. An ecosystem possesses_________
consumers.
D. producers are usually eaten by many different consumers A. humas and the animal life we study
and most consumers are eaten by more than one predator. B. both living and non living components
5. Consider this food chain: C. all of the animal and plant life on Earth
Grass----- Grasshopper ---- Frog---- Snake D. just the physical features, such as temperature and
The frog in the food chain is a ____________. moisture that affect life.
A. top carnivore B. tertiary carnivore
18. How does a flower benefit from a bumblebee feeding
C. secondary carnivore D. primary carnivore
6. Which of the following relationships describe on its nectar?
competition? A. it becomes more fragrant.
A. Spider eating mosquito B. It gets protection against parasitic insects.
B. Lions hunting and killing a buffalo C. It gets help with pollination.
C. Tick attaching on the skin of a dog D. It blooms more.
D. An orchid living on a trunk of a mahogany tree
19. A relationship which results in gaining benefits for both
7.Bacteria can be beneficial or harmful to man. Some
bacteria help in digestion others cause diseases. What organisms involved is an example of ________
kind of organisms are those bacteria that cause A. Commensalism B. Mutualism
diseases? C. Parasitism D. Predation
A. Commensal C. Parasite B. Host D. Predator
8. Cat eating rat, bird eating worm and dog eating fish 20-24- Ecological Relationship
are examples of predator-prey relationship. Which of the
following is the complete set of predators?
25. Write the full name of your adviser
A. Cat, rat, fish `C. Rat, worm, fish
B. Cat, bird, dog D. Rat, worm, dog
9. Which of the following interactions exhibits
commensalism?
A. Man and fish C. Carabao and cow
B. Spider and tree D. Ants and acacia tree
10. The ecological relationship of a sea anemone and
clown fish is the same kind of relationship as that of
___________.
A. the lice and a child C. the pigs in the pigpen
B. a lizard and an insect D. a bee and a flower
11. During harvest time, abundant supply of food is
accompanied by the increase in number of field mice
that eats the rice plant. Snakes that hunt on the field
mice will also increase in number. What could be the
possible outcomes if the farmers get rid of the snakes?
I. The food supply will decrease.
II. The snake population will increase.
III. The rice mice population will double.
IV. The rice mice population will take over the snake
population.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Locating Places On Earth Using A Coordinate SystemDocument28 pagesLocating Places On Earth Using A Coordinate SystemEM GinaNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument27 pagesAccelerationEM GinaNo ratings yet
- Cot ScienceDocument69 pagesCot ScienceEM GinaNo ratings yet
- EDITED ADM-Q4-Week-1-4-edited-FINALDocument24 pagesEDITED ADM-Q4-Week-1-4-edited-FINALEM GinaNo ratings yet
- Valentines'proposalDocument7 pagesValentines'proposalEM GinaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 Class ProgramDocument11 pagesGRADE 7 Class ProgramEM GinaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Athlete RecordDocument3 pages2020 Athlete RecordEM GinaNo ratings yet
- Cot 1-Science 7Document11 pagesCot 1-Science 7EM GinaNo ratings yet
- Action Research Proposal Tle Group 1Document6 pagesAction Research Proposal Tle Group 1EM GinaNo ratings yet
- Summative tEST 4Document17 pagesSummative tEST 4EM GinaNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Friday Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesCatch Up Friday Lesson PlanEM Gina100% (6)
- 2nd PT ScienceDocument5 pages2nd PT ScienceEM GinaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 COT 2-SCIENCEDocument10 pagesGrade 7 COT 2-SCIENCEEM GinaNo ratings yet
- 1ST Periodical TestDocument7 pages1ST Periodical TestEM GinaNo ratings yet
- CoverDocument3 pagesCoverEM GinaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W2Document3 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W2EM GinaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 3rd Cot Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesScience 7 3rd Cot Lesson PlanEM Gina67% (3)
- DLL Quarter 2 Week 6 Jan. 04-06Document43 pagesDLL Quarter 2 Week 6 Jan. 04-06EM GinaNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test Q2 Mapeh 4 Melc BasedDocument11 pagesPeriodical Test Q2 Mapeh 4 Melc BasedEM GinaNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 4 - Q4 - W2Document6 pagesDLL - English 4 - Q4 - W2EM GinaNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test Q2 English 4 Melc BasedDocument7 pagesPeriodical Test Q2 English 4 Melc BasedEM Gina100% (1)
- Periodical Test Q2 Science 4 Melc BasedDocument7 pagesPeriodical Test Q2 Science 4 Melc BasedEM GinaNo ratings yet
- Exit TestDocument3 pagesExit TestEM GinaNo ratings yet
- LeaP-Science-G4-Weeks 7-8-Q3 PDFDocument4 pagesLeaP-Science-G4-Weeks 7-8-Q3 PDFEM GinaNo ratings yet
- DLL Quarter 2 Week 8 Jan. 16-20Document47 pagesDLL Quarter 2 Week 8 Jan. 16-20EM GinaNo ratings yet
- DLL Quarter 2 Week 4 - English ScienceDocument13 pagesDLL Quarter 2 Week 4 - English ScienceEM GinaNo ratings yet
- DLL Quarter 2 Week 5 - English ScienceDocument15 pagesDLL Quarter 2 Week 5 - English ScienceEM GinaNo ratings yet
- A. Covid 19 Monitoring ToolsDocument6 pagesA. Covid 19 Monitoring ToolsEM GinaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quater Summative Test 3-4Document12 pages2nd Quater Summative Test 3-4EM GinaNo ratings yet
- Science 4, Quarter 2 Week 6Document38 pagesScience 4, Quarter 2 Week 6EM GinaNo ratings yet