0% found this document useful (0 votes)
610 views7 pagesSession 1 - Speed-Time Graph
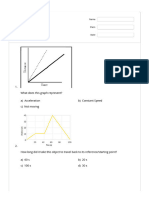
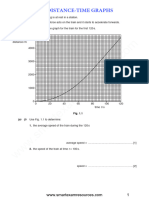
The document discusses speed-time graphs. It explains that speed-time graphs show how an object's speed changes over time. The distance traveled can be found by calculating the area under the graph. If the area forms a triangle, the formula for the area of a triangle is used. If the area is a rectangle, the formula for the area of a rectangle is used. An example speed-time graph is given and used to calculate the total distance and average speed of a car's journey. The document also defines acceleration and provides the formula to calculate acceleration from initial and final velocities and time. It notes that the gradient of a speed-time graph gives the object's acceleration.
Uploaded by
SelvenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
610 views7 pagesSession 1 - Speed-Time Graph
The document discusses speed-time graphs. It explains that speed-time graphs show how an object's speed changes over time. The distance traveled can be found by calculating the area under the graph. If the area forms a triangle, the formula for the area of a triangle is used. If the area is a rectangle, the formula for the area of a rectangle is used. An example speed-time graph is given and used to calculate the total distance and average speed of a car's journey. The document also defines acceleration and provides the formula to calculate acceleration from initial and final velocities and time. It notes that the gradient of a speed-time graph gives the object's acceleration.
Uploaded by
SelvenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd