Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brief Summary Sheet - AP Chem
Uploaded by
racheljchongOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brief Summary Sheet - AP Chem
Uploaded by
racheljchongCopyright:
Available Formats
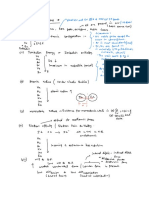
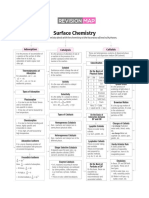
summary sheet
A hydrate is no longera hydrate when mass stops decreasing
Octet rate Exceptions
AI Xe H B
EX AlH3
Negativeformal Charge on mostelectronegative
Sigma o bonds counteverysinglebondandonefromdoubleortriplebond
T1 bonds 1fromdouble2fromtriple
steric number 0 bonds t lonepairs
Stericnumbertellsushowmany orbitalsweneed
IMF Tsurfacetensionf viscosityIn
Hydrogenbonds
Musthave a lonepairand Abond
Kinetic molecular theory
PVNRT
Elasticcollisionwhenparticleshit wall
V is conserved
1Gashasparticlesinconstantrandommotion
2Thevolumeofparticles isnegligiblecomparedtototalvolume
3Particlesexert no forcesupononeanother
4 Particlecollisionsareelastic
5 KEared 1Kelvin
Hightemplargevolume same volume
Lowtemp Hightemp
I small
T volume
a
Closeto ideal condensationpoint
attraction
Pt than idealgaslaw PT thanideal
Distillate lowerBP gaslaw
Mustslowlyincreasetemp
becauseamountofdistillate
decreases
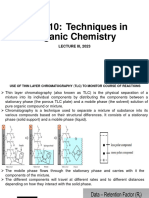
Thin layer chromatography TLC
silipfarousseland Retention factor
polar disafeweadepf.lu
solvent
substance pastorigin
I I Dip in lesspolarsolution
If it is more mobilephase
polar it won'ttravel Morepolarlower
as far RF
column chromatography
LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE
0
Ut silicagel
Solubility Attractionbetween soluteandsolvent
Ions dissociate can'tdissolveHexane in H2O because Hzo moreattractedtoitself
Spectrophotometry
B immonen
Mostchloridebromideandiodidesaltsare soluble in water
EXCEPT AgtHgit Pb
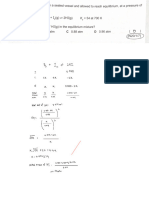
1st Order Half life
ln AIt Kt ten ATo t tht
k
2ndorder reaction
Kt t.to
zero order reaction
A t A o Kt
Bondenergy 0 energywhenbond
Bondenergy Lo energywhenbondbreaks
DHrxn EBE ofbondsbroken EBE of bondsformed
positive negative
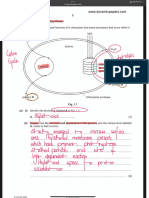
Reaction Rates
Solidsand liquids are not inthereactionquotient
ONLYGASESAND AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS
K is so largethereactiongoesin forwarddirection goestocompletion
If you reverse thereaction take theinverse of K All apply to Q
Soluble salts Ksp 1
Compare 5 NOT K to comparesolubility
Greaters moresoluble
Will a precipitate form
Qsp from initialconcentration
Qsp L Ksp NO PRECIPITATE
Qsp Ksp PRECIPITATE
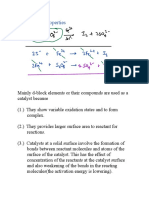
COMMON Ion Effect
In presence of commoniconsolubilitydecreases
ionization4 as molarity Iv
ionizationtellsyouwhat of ionreacted withH2O
If youwant a biggerbufferhavehigherinitialconcentration
Equivalence point molBase MolAcid
AcidBase indicator rightafterequivalencepoint
Useindicator withpKaclosetopH at equivalencepoint
Half equivalencepoint All ofthe acid is equivalent to theconjugate base
EquivalencepointAHacidconverted to theconjugatebase
When buffering capacity is exceededrapidchange in pH
Buffercapacity
Increasingconcentration ofbuffercomponentsdoesn'tchange pH butit increases
theamount the buffer neutralize aslongas ratio is constant
pH of solutionis relative of molesof acidand conjugatebase
Diluting a buffer will not changepH
More conjugateacid thanbasegreatercapacity foraddedbasethanacid
Moreconjugatebase than acid greatercapacityforaddedacidtha
Applications of thermodynamics
D8reaction ESO
products Eso
reactants
GibbsFreeEnergy
Describeswhether a reactionisfavorableor unfavorable
SG LO thermodynamicallyfavorable DGoreaction EGO
reactants EDGopro
ducts
DGoesHo Tss
DHo Favorable
SH0 Unfavorable
DS is favorable SS Unfavorable
SG n F EEell n number of molesof electrons
You might also like
- List of Periodic Table Elements Sorted by Atomic NumberDocument3 pagesList of Periodic Table Elements Sorted by Atomic NumberKrishnaMehta100% (2)
- John Deere Mangueiras PDFDocument43 pagesJohn Deere Mangueiras PDFAmanda Rezende100% (1)
- Master Summary Sheet - AP ChemDocument17 pagesMaster Summary Sheet - AP ChemnoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Inorganic Chemistry 09 May 2022Document5 pagesGroup 2 - Inorganic Chemistry 09 May 2022Defaults rulezNo ratings yet
- Minimum Learning Material CBSE ChemistryDocument50 pagesMinimum Learning Material CBSE ChemistryAntur RakhaNo ratings yet
- Minimum Learning MaterialDocument50 pagesMinimum Learning MaterialGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Group 17 - Inorganic ChemistryDocument7 pagesGroup 17 - Inorganic ChemistryDefaults rulezNo ratings yet
- 29-Dec-2022 OilDocument1 page29-Dec-2022 OilGajulaNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Analytical Techniques: An Overview of Chromatography and SpectrosDocument52 pagesInstrumental Analytical Techniques: An Overview of Chromatography and SpectrosK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry 2Document8 pagesSurface Chemistry 2SITENDER NARWALNo ratings yet
- 12 - Surface Chemistry (Notes)Document27 pages12 - Surface Chemistry (Notes)DivyanshNo ratings yet
- Group 18 (P Block)Document20 pagesGroup 18 (P Block)Celestial GhandatNo ratings yet
- Hayati Chem Book f4 KSSM Version 2Document2 pagesHayati Chem Book f4 KSSM Version 2Ithrah MadihahNo ratings yet
- Module 1 SummaryDocument99 pagesModule 1 SummaryyafagNo ratings yet
- Alkenes - Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesAlkenes - Organic ChemistryDefaults rulezNo ratings yet
- 4 PriciptationDocument30 pages4 PriciptationUsamNo ratings yet
- Hydrogel RheologyDocument24 pagesHydrogel RheologyAna Clara SoaresNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Roult's LawDocument2 pagesSolutions: Roult's LawSsNo ratings yet
- U5 OrganicDocument25 pagesU5 OrganicyuNo ratings yet
- Solutions 2Document29 pagesSolutions 2Lawrence CarlNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Problems - Freezing Point Depression and Other Solution Properties With AnswersDocument16 pagesAP Chemistry Problems - Freezing Point Depression and Other Solution Properties With AnswersCameron Kaye ColamboNo ratings yet
- EntropyDocument5 pagesEntropyabdelrahman moatazNo ratings yet
- SCH 410 Lecture Iii 2023Document21 pagesSCH 410 Lecture Iii 2023Samuel MutisyaNo ratings yet
- CG5052 BPE 3.1 - 4.1 Crystal UL-DSP (20240227)Document56 pagesCG5052 BPE 3.1 - 4.1 Crystal UL-DSP (20240227)RRNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics - MergedDocument13 pagesChemical Kinetics - MergedABLC Any body can learn CubingNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument19 pagesS Block ElementsLurkingMangoNo ratings yet
- Day 6 - Chemical Kinetics NotesDocument49 pagesDay 6 - Chemical Kinetics NotesDeepak KapaNo ratings yet
- Practical 3 6Document9 pagesPractical 3 6saudaminipadhan423No ratings yet
- Writing Assignment 10: Ishani Jain 2013CH10082 Group 5Document4 pagesWriting Assignment 10: Ishani Jain 2013CH10082 Group 5Nakul BahmaniaNo ratings yet
- Lead-Acid Battery ComponentsDocument41 pagesLead-Acid Battery ComponentsBalakrishnan Pedda Govindier100% (1)
- Chem Eqm and Reaction Kinetics TopicalDocument12 pagesChem Eqm and Reaction Kinetics TopicalAaditya MKNo ratings yet
- Solutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020 v2Document80 pagesSolutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020 v2hazo hazNo ratings yet
- Group-18 (Noble Gases) NotesDocument8 pagesGroup-18 (Noble Gases) NotesShashwatNo ratings yet
- Solution in One PageDocument2 pagesSolution in One Pageraiprisha06No ratings yet
- Simple Mixtures Colligative Properties: Chapter 7: SlideDocument32 pagesSimple Mixtures Colligative Properties: Chapter 7: SlideputriNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamics or How To Study The Structure of A Protein You Haven't CrystallizedDocument22 pagesHydrodynamics or How To Study The Structure of A Protein You Haven't Crystallizedchaitanya kumarNo ratings yet
- Note 6 Feb 2024Document28 pagesNote 6 Feb 2024hs87s6smtnNo ratings yet
- 2001 SolutionDocument12 pages2001 SolutionSaghar FaridNo ratings yet
- Solutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020Document80 pagesSolutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020hazo hazNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 SolutionsDocument26 pagesCh. 9 SolutionsPriscila AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- 3 PRECIPITATION - UpdatedDocument80 pages3 PRECIPITATION - Updatedoğuz cantürkNo ratings yet
- P Block 12th - Recap 2 PDFDocument18 pagesP Block 12th - Recap 2 PDFAnandam NagalaxmiNo ratings yet
- GOC-I CompleteDocument59 pagesGOC-I CompleteAPARNA GANGWARNo ratings yet
- Solutions Mind Map PDFDocument4 pagesSolutions Mind Map PDFvashuy091No ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry NotesDocument1 pageSurface Chemistry NotesRohit PatilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Electrons Heterolytic Bond Cleavage Anions CationsDocument7 pagesChemistry Electrons Heterolytic Bond Cleavage Anions CationsSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides - Organic Chemistry-1Document17 pagesAlkyl Halides - Organic Chemistry-1Defaults rulezNo ratings yet
- ELV1-L50-d Block-21092021 - 220419 - 143525Document12 pagesELV1-L50-d Block-21092021 - 220419 - 143525Aditya VijayvargiyaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - SP-2000Document32 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - SP-2000diego isaacNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 12 FormulasDocument46 pagesChemistry Class 12 FormulasabdulbasithmaricarNo ratings yet
- WJL Oc C6 3 5Document4 pagesWJL Oc C6 3 5yang maNo ratings yet
- MB Rationale m1Document15 pagesMB Rationale m1Selena MoonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Experiment - 3Document5 pagesChemistry Experiment - 3Tóñèy StàrkNo ratings yet
- Olefination ReactionDocument65 pagesOlefination ReactionTùng SuNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Colores PDFDocument21 pagesTabla de Colores PDFSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Ways of Expressing Concentrations of SolutionsDocument57 pagesWays of Expressing Concentrations of SolutionsKearly Joy VictorioNo ratings yet
- A2 Organic ReactionsDocument12 pagesA2 Organic ReactionsSafwan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument7 pagesColligative Propertiesakshatjn100% (1)
- 04 - To Investigate The Difference in Acidity of The Alcohols, Phenols and The Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pages04 - To Investigate The Difference in Acidity of The Alcohols, Phenols and The Carboxylic AcidsTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Free Radicals - 5th ClassDocument14 pagesFree Radicals - 5th ClassRijan MrtNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 5Document17 pagesModule 1 Lecture 5Amirs AmjadNo ratings yet
- Crystal Growth: International Series on the Science of the Solid StateFrom EverandCrystal Growth: International Series on the Science of the Solid StateBrian R. PamplinNo ratings yet
- (Chaaban & Muzze, 1991) - Finite Element Analysis of Residual Stresses in Threaded End ClosuresDocument4 pages(Chaaban & Muzze, 1991) - Finite Element Analysis of Residual Stresses in Threaded End Closureschristos032No ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics C211 PDFDocument173 pagesApplied Thermodynamics C211 PDFSubham AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Jotafloor Damp BondDocument4 pagesJotafloor Damp BondMohamed FarhanNo ratings yet
- Nano Material Synthesis Techniques Top-Down and Bottom-Up Nanofabrication, Synthesis ofDocument6 pagesNano Material Synthesis Techniques Top-Down and Bottom-Up Nanofabrication, Synthesis ofsanthoshNo ratings yet
- Matter PowerPointDocument37 pagesMatter PowerPointkmay0517No ratings yet
- 2.5 Eadie (1942) Measured The Initial Reaction Rate of Hydrolysis of Acetylcholme (Substrate) byDocument6 pages2.5 Eadie (1942) Measured The Initial Reaction Rate of Hydrolysis of Acetylcholme (Substrate) byRoxan Bueno MoraNo ratings yet
- Documents - MX - 96209 Fibra Cruda en Alimentos para Animales y Mascotas PDFDocument3 pagesDocuments - MX - 96209 Fibra Cruda en Alimentos para Animales y Mascotas PDFArellanes JmzNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics of Solid SolutionsDocument289 pagesChemical Thermodynamics of Solid SolutionsSatyanarayana MadasuNo ratings yet
- Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument80 pagesSterilization and Disinfectiondr parveen bathlaNo ratings yet
- AMT 2203 Finals Learning Module 01Document16 pagesAMT 2203 Finals Learning Module 01jose santiagoNo ratings yet
- Loctite PC 7210-ENDocument4 pagesLoctite PC 7210-ENYuvarajNo ratings yet
- Lysosome Study GuideDocument2 pagesLysosome Study Guideapi-318784000No ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument11 pagesCoulomb's LawAftab Ahmad100% (1)
- Water Treatment Lecture 6Document45 pagesWater Treatment Lecture 6pramudita nadiahNo ratings yet
- Soil Test Interpretation Guide: D.A. Horneck, D.M. Sullivan, J.S. Owen, and J.M. HartDocument12 pagesSoil Test Interpretation Guide: D.A. Horneck, D.M. Sullivan, J.S. Owen, and J.M. Hartabarrios78100% (1)
- PHYSICAL Metallugy of Titanium by I.I. KornilovDocument358 pagesPHYSICAL Metallugy of Titanium by I.I. Kornilovlram70No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument530 pagesChemistrythearinnewsNo ratings yet
- 3D MECHANISTIC MODEL by Petalas&AzizDocument16 pages3D MECHANISTIC MODEL by Petalas&AzizKirat Purohit100% (2)
- Chemical Reactions Chapter 6Document31 pagesChemical Reactions Chapter 6R.S.HNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Polymer SolutionsDocument7 pagesThermodynamics of Polymer SolutionsQwkutiubb100% (1)
- CO Corrosion Rate Calculation Model: Norsok StandardDocument20 pagesCO Corrosion Rate Calculation Model: Norsok Standardnorman1968No ratings yet
- CoromandelDocument8 pagesCoromandelAnirban BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Metode Analisa FCC 88 - New LogoDocument4 pagesMetode Analisa FCC 88 - New LogoyurinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PropellantDocument8 pagesChapter 3 PropellantGabriel Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- AASHTO T 217 SpeedyDocument6 pagesAASHTO T 217 SpeedyDaniel RodasNo ratings yet
- 3580Document2 pages3580prastowoNo ratings yet
- Production and Purification of Glutamic Acid A Critical Reviewtowards Process Intensification PDFDocument13 pagesProduction and Purification of Glutamic Acid A Critical Reviewtowards Process Intensification PDFGooi Ming YanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Gomes Et Al 2023 Recent Advances in Processing and Preservation of Minimally Processed FoodDocument11 pagesJurnal Gomes Et Al 2023 Recent Advances in Processing and Preservation of Minimally Processed Foodluthfiharits39No ratings yet