Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 18 Module
Uploaded by
rose maryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 18 Module
Uploaded by
rose maryCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy Transformation Week 18
Content Standards
The learners demonstrate an understanding of respiration.
Most Essential Learning Competencies
● Differentiate aerobic from anaerobic respiration
● Explain the major features and sequence the chemical events of cellular respiration
● Distinguish major features of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport system, and chemiosmosis
● Describe reactions that produce and consume ATP
● Describe the role of oxygen in respiration and describe pathways of electron flow in the absence of
oxygen
Lesson Presentation/ Discussion
Energy Transformation
Lesson 2: Cellular Respiration
Terminologies:
● ATP- adenosine triphosphate, an energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things
● Pyruvate- a molecule that acts as the transport molecule which carries carbon atoms into the
mitochondria
● Aerobic- requiring air or oxygen for life or survival
● Anaerobic- the absence of oxygen or not requiring oxygen to live
● Autotroph- organisms that can produce their food
● Heterotroph- an organism that cannot manufacture its food and therefore derives its intake of nutrition
from other sources
Living organisms uses the chemical energy found in food in the form of carbohydrate molecules, which
can be traced from photosynthesis. Autotrophs which are energy-producing organisms such as plants can carry
out photosynthesis. On the other hand, heterotrophs such as humans and animals are organisms not capable
of photosynthesis. They require energy from food by consuming other organisms.
Inside the cells are specialized organelles that function for harvesting energy, the mitochondria. It is a
small, specialized organelle that produces energy from food by breaking down carbon-containing molecules
and releasing energy packets in the form of ATP. This provides the chemical fuel that powers the cell to do
certain processes such as moving cells and their parts and copying DNA.
General Biology 1 Page 1 of 3
Energy Transformation Week 18
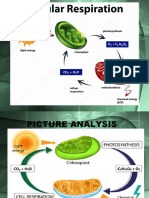
Cellular respiration is the process of releasing energy from the breakdown of glucose; the cell or
organism utilizes chemical energy from nutrients to produce ATP. A cell needs to respire to produce the energy
that they require.
❖ Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic means ‘with air. This type of respiration requires oxygen to facilitate the process.
● Glycolysis
The first stage of aerobic respiration, from the word glycol, means ‘sugar’ and lysis meaning
‘to split. It occurs inside the cytoplasm and does not require oxygen. It begins by breaking down
glucose from food, but only produces a small amount of energy in the form of ATP molecules.
● Krebs Cycle
The next stage of the aerobic pathway is also known as the Citric Acid Cycle. It starts with
the end product of glycolysis, pyruvate, and involves a series of enzyme-controlled processes that
occur inside the mitochondrial matrix.
● Electron Transport Chain
The third part of the process of obtaining energy involves a series of enzyme-controlled
reactions that transfers the chemical energy present in hydrogen electrons to ATP.
General Biology 1 Page 2 of 3
Energy Transformation Week 18
❖ Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is the process of creating energy without the presence of oxygen. Sometimes
the body can’t supply the muscles with the oxygen it needs to create energy – such as in a sprinting
situation. Without the process of anaerobic respiration, there may be no energy supplied to muscles in
times of high demand.
Conclusion/ Summary
● Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy.
● Cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle,
and the electron transport chain.
● Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, while the other two pathways are aerobic. To move from glycolysis
to the citric acid cycle, pyruvate molecules (the output of glycolysis) must be oxidized in a process
called pyruvate oxidation.
References and Supplementary Materials
Online Instructional Videos
1. Cellular Respiration
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Eo7JtRA7lg
2. ATP and Respiration
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=00jbG_cfGuQ
3. Anaerobic vs. Aerobic
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n0uABIlfj44
General Biology 1 Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Earth and Life Science: Humss Grade 11Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science: Humss Grade 11Micaela Castillo100% (4)
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- E 7068 B0 Airmeex De65e0Document5 pagesE 7068 B0 Airmeex De65e0Mehdi HassouneNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- Susatinable ArchitectureDocument10 pagesSusatinable ArchitectureHoney DaveNo ratings yet
- Q2 W1 W2 W3 General Biology 1Document8 pagesQ2 W1 W2 W3 General Biology 1Samantha ManibogNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespDocument3 pagesCellular Resptruckerrr1No ratings yet
- NHM - Ar Etapa 2 - LNDVDocument10 pagesNHM - Ar Etapa 2 - LNDVNatalia Hernandez MontelongoNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in Elementary GradesDocument2 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary GradesJenniferChantengcoCatacutan50% (2)
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Cellular RespirationDraver ZemaNo ratings yet
- BioDocument18 pagesBiomarcneil773No ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument4 pagesBioenergeticsMahnoor MansoorNo ratings yet
- 04 Energy TransformationDocument53 pages04 Energy TransformationlyleandreihendersonNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument21 pagesCellular RespirationAbirami SankarNo ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4Mohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration in Animals.Document4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals.studyklieNo ratings yet
- Mil4ch32 (How Animals Harvest)Document10 pagesMil4ch32 (How Animals Harvest)Muhammad AsadkhanNo ratings yet
- Cellular MetabolismDocument4 pagesCellular Metabolismjanenathaneattl1No ratings yet
- GN 3.3 - Cell RespirationDocument7 pagesGN 3.3 - Cell RespirationJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 7Document4 pagesBiology Class 7Jon Williams100% (4)
- Review ArticleDocument20 pagesReview ArticleAHKI ANTONETTE ABELNo ratings yet
- Cellular1 2Document16 pagesCellular1 2Kaeshamaureen DresNo ratings yet
- BionergeticsDocument4 pagesBionergeticsAriadna Adrienne CaparrosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respirationالتنفس الخلويDocument9 pagesCellular Respirationالتنفس الخلويIraqiNo ratings yet
- Cellular OverviweDocument9 pagesCellular OverviweDannia RoblesNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument214 pagesBiology NotesbloomNo ratings yet
- Jinky Oraiz@deped Gov PHDocument11 pagesJinky Oraiz@deped Gov PHAnnejhel Mae Poralan100% (1)
- Q2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesQ2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationRaph tsuNo ratings yet
- Ange EeeeeDocument4 pagesAnge EeeeeHazel BandayNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument33 pagesCellular RespirationMa. Krizia Tiny ParconNo ratings yet
- Celluar Resp 2009Document58 pagesCelluar Resp 2009Kurt IgotNo ratings yet
- DAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 3: Cellular EnergyDocument33 pagesDAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 3: Cellular EnergyEmilyNo ratings yet
- Slide 1Document1 pageSlide 1NickTheTurtleNo ratings yet
- Week 17 ModuleDocument3 pagesWeek 17 Modulerose maryNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Document5 pagesReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Energy Part 1Document14 pagesHow Cells Release Energy Part 1Jiro SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Atp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesDocument6 pagesAtp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesJhondel GuirrenNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument29 pagesBioenergeticskizzaymenteraNo ratings yet
- 2-Energy and RespirationDocument34 pages2-Energy and RespirationLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- 2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPDocument4 pages2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPTanvir KauraNo ratings yet
- Summary of Aerob RespirationDocument3 pagesSummary of Aerob RespirationHenry AndersonNo ratings yet
- CRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualDocument6 pagesCRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualVanesha AnesNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesCellular RespirationMohammedNo ratings yet
- ATP To ADP - Energy Release: ATP Stands For Adenosine Tri-Phosphate, and Is The Energy Used by An Organism inDocument3 pagesATP To ADP - Energy Release: ATP Stands For Adenosine Tri-Phosphate, and Is The Energy Used by An Organism inlakasNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 14 (PDF)Document12 pagesRespiration in Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 14 (PDF)A. celestianNo ratings yet
- Biochem Week 3Document10 pagesBiochem Week 3divineNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Revision Session 2011Document11 pagesRevision Session 2011glenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q2 Week-5Document6 pagesGB1 Q2 Week-5Leah Jean PonlaonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-14 Respiration in PlantsDocument4 pagesChapter-14 Respiration in PlantsDIVYANSHU KR. XIIC44No ratings yet
- Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesKey ConceptsHikaru IshiiNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Anaerobic Cellular ResDocument21 pagesAerobic Anaerobic Cellular ResRex IanNo ratings yet
- RobatechDocument8 pagesRobatechDavid OnceNo ratings yet
- ST X-Start 4x320Document2 pagesST X-Start 4x320Jorge SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Colding Heating Temperature Controller STC WDocument43 pagesColding Heating Temperature Controller STC Wdedewiki5No ratings yet
- Back Ups Bx750mi MsDocument3 pagesBack Ups Bx750mi MsLuthfi AthoriqueNo ratings yet
- Double Pendulum-2Document17 pagesDouble Pendulum-2Yash TandonNo ratings yet
- Auma - Selection BasisDocument4 pagesAuma - Selection BasisVed Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- 3 Me 20me303 QB1Document5 pages3 Me 20me303 QB1Dhanush kumar NNo ratings yet
- Rotolok Blowing Seal Valve AMD v3Document4 pagesRotolok Blowing Seal Valve AMD v3wijaya adidarmaNo ratings yet
- CIAT Melody MTDocument12 pagesCIAT Melody MTInviairNo ratings yet
- Toyota 7k Engine Repair Manual 18t16633Document10 pagesToyota 7k Engine Repair Manual 18t16633david100% (54)
- Astm D976Document3 pagesAstm D976Eder Fajardo ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Aces Objectives 5 EEDocument5 pagesAces Objectives 5 EEvenjaytabagoNo ratings yet
- SEWHA - SB210 - (WWW - Towzin-Meter - Ir)Document1 pageSEWHA - SB210 - (WWW - Towzin-Meter - Ir)Professional TrustNo ratings yet
- New - Spectronic E-CatalogueDocument58 pagesNew - Spectronic E-CatalogueCARLOS LÓPEZNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: MAN Material Numbers: 11.70123-2073 and 11.70123-0927Document616 pagesUser's Manual: MAN Material Numbers: 11.70123-2073 and 11.70123-0927Ounna PechNo ratings yet
- MS Synopsis Defense Presentation TemplateDocument18 pagesMS Synopsis Defense Presentation TemplatehamzaaltafNo ratings yet
- Explosion ModellingDocument32 pagesExplosion Modellingalviano robertoNo ratings yet
- Pendampingan Pengelolaan Sampah Mandiri Menggunakan Konsep Thermal Insinerasi Di Desa Kebakalan Kecamatan Karanggayam Kebumen Jawa TengahDocument8 pagesPendampingan Pengelolaan Sampah Mandiri Menggunakan Konsep Thermal Insinerasi Di Desa Kebakalan Kecamatan Karanggayam Kebumen Jawa TengahDedi FatchurohmanNo ratings yet
- ECR - E-House Layout - R1Document1 pageECR - E-House Layout - R1thiago fritscheNo ratings yet
- Pumps Motors: Vertical Multistage Openwell Submersible PumpsetsDocument2 pagesPumps Motors: Vertical Multistage Openwell Submersible PumpsetsAtharva KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 - Questioning - Written Assessment - AURETR129Document22 pagesAssessment 1 - Questioning - Written Assessment - AURETR129Sana SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Report Programma Di Sviluppo Delle Nazioni Unite (UNDP)Document320 pagesReport Programma Di Sviluppo Delle Nazioni Unite (UNDP)Davide FalcioniNo ratings yet
- FC113X-C Cummins - Leroy GRDocument7 pagesFC113X-C Cummins - Leroy GRIsrael GomezNo ratings yet
- Sad AliDocument5 pagesSad AliMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- UDCPR Prsentation Patil Sir 12 To 15Document101 pagesUDCPR Prsentation Patil Sir 12 To 15Abhilash ParlikarNo ratings yet
- Carburadoiers y MagnetosDocument73 pagesCarburadoiers y MagnetosFRRNo ratings yet
- Single Phase TransformersDocument48 pagesSingle Phase TransformersBrian MutethiaNo ratings yet
- Technical Data SOLO Transfer BIO-GRINDER HUNGRYGIANT2022Document4 pagesTechnical Data SOLO Transfer BIO-GRINDER HUNGRYGIANT2022Oscar AguirreNo ratings yet