Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revision Worksheet Fun With Magnets
Uploaded by
agarwaladya26Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision Worksheet Fun With Magnets
Uploaded by
agarwaladya26Copyright:
Available Formats
Delhi Public School Agra
(Under the aegis of Delhi Public School Society, East of Kailash, New Delhi)
REVISION WORKSHEET GRADE – VI SUBJECT – SCIENCE
TOPIC: FUN WITH MAGNETS
Answer the following:
1. How will you test that ‘tea dust’ is not adulterated with iron powder?
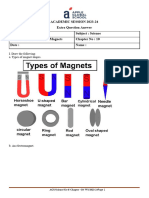
2. Boojho dipped a bar magnet in a heap of iron filings and pulled it out. He found that iron filings got stuck
to the magnet as shown in figure.
(i) Which regions of the magnet have more iron filings sticking to it?
(ii)What are these regions called?
3. A toy car has a bar magnet laid hidden inside its body along its length. Using another magnet i how will
you find out which pole of the magnet is facing the front of the car?
4. You are provided with two identical metal bars. , One out of the two is a magnet. Suggest two ways to
identify the magnet.
5. Describe the steps involved in magnetising an iron strip with the help of a magnet.
6. How should two-bar magnets be kept?
7. Hang a bar magnet with a thread on a stand and rotate the base of stand. What will happen?
8. Why is compass needle kept in a closed glass vessel?
9. Write any four properties of a magnet.
Fill in the blanks:
1. When a bar magnet is broken; each of the broken part will have _________ pole/poles.
2. In a bar magnet, magnetic attraction is _____ near its ends.
3. The south pole of the earth’s magnet is near the geographical _______________ pole.
4. A compass needle always points in ______________ directions.
Give one word:
1. Area around the magnet in which its magnetism can be felt.
2. A magnetic material.
3. Place of discovery of magnet.
4. The property of magnet that helps to find directions.
5. Sure test for magnetism.
Choose the correct option:
1. North pole of a magnet can be identified by ___________.
(a) Another magnet having its poles marked as North pole and South pole.
(b) Another magnet no matter whether the poles are marked or not.
(c) Using an iron bar.
(d) Using iron filings.
2. A bar magnet is immersed in a heap of iron filings and pulled out. The amount of iron filing clinging to the
_____________.
(a) North pole is almost equal to the south pole. (b) North pole is much more than the south pole.
(c) North pole is much less than the south pole. (d) Magnet will be same all along its length.
3. The magnetic properties of a magnet cannot be destroyed by ____________.
(a) hammering (b) heating (c) dropping on a hard surface (d) boiling
4. Which two ends of a magnet are called magnetic poles?
(a) North pole (b) South pole (c) North and south pole (d) Self demagnetisation
You might also like
- Class 6 Fun With Magnets Exercise Question and Answer Plus Inner (Extra) Question and AnswerDocument8 pagesClass 6 Fun With Magnets Exercise Question and Answer Plus Inner (Extra) Question and Answerdebasishnath9593913213No ratings yet
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDocument7 pagesPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierSyed Mairaj Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 SCIENCE MAGNETISMDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 6 SCIENCE MAGNETISMSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Fun With Magnets PDFDocument4 pagesFun With Magnets PDFMohamed SoudhNo ratings yet
- 9th Chapter MagnetismDocument6 pages9th Chapter MagnetismsonafarazmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Fun With MagnetsDocument5 pagesChapter 12 Fun With MagnetsbittuchintuNo ratings yet
- 6th STD Science 3rd Term Notes QuestionsDocument47 pages6th STD Science 3rd Term Notes QuestionsAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- Gr. 6 Ch. 10 Fun With Magnets Extra QuestionDocument6 pagesGr. 6 Ch. 10 Fun With Magnets Extra QuestionManit ShahNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Question BankDocument17 pagesMagnetism Question BankNaveenNo ratings yet
- Jsunil Tutorial, Samastipur: Vi Science Chapter - Fun With Magnets I. Fill in The BlanksDocument1 pageJsunil Tutorial, Samastipur: Vi Science Chapter - Fun With Magnets I. Fill in The BlankspreethaNo ratings yet
- MagnetsDocument5 pagesMagnetssian017No ratings yet
- VI - G.Science - 7 - FUN WITH MAGNETSDocument4 pagesVI - G.Science - 7 - FUN WITH MAGNETS515176No ratings yet
- Chapter - Fun With MagnetsDocument3 pagesChapter - Fun With MagnetsGUGLU GUGLUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Fun With MagnetsDocument11 pagesChapter 13 Fun With Magnets19adityakushwahaNo ratings yet
- PDF 221010 172935Document4 pagesPDF 221010 172935ridha shehimNo ratings yet
- KS3 Magnetism Worksheet: 1) A) Draw The Shape and Direction of The Magnetic Field Around The Barmagnet BelowDocument4 pagesKS3 Magnetism Worksheet: 1) A) Draw The Shape and Direction of The Magnetic Field Around The Barmagnet BelowAmal GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Gr6 Magnets and Their Effects QBDocument8 pagesGr6 Magnets and Their Effects QBplakshmirsmNo ratings yet
- Class 6 - Chapter 13 - Fun With MagnetsDocument4 pagesClass 6 - Chapter 13 - Fun With MagnetskishanrwtNo ratings yet
- (Class 6) Fun With Magnets & Seperation of SubstancesDocument4 pages(Class 6) Fun With Magnets & Seperation of SubstancesSnigdha GoelNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Science Notes Term II Magnets LessonDocument4 pagesGrade 6 Science Notes Term II Magnets LessonShaik Md Shoaib Anas 5A (Shoaib Anas)No ratings yet
- Ok - Science - Magnetic ForceDocument17 pagesOk - Science - Magnetic ForceLovilyn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- STD - Ix: Physics Notes Topic: A: Magnetism & B - Electromagnet and Its UsesDocument9 pagesSTD - Ix: Physics Notes Topic: A: Magnetism & B - Electromagnet and Its Uses209EMohammedYousufAliKhanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Sci4Document2 pagesQuiz 2 Sci4Rizalina LaysonNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun With Magnets Worksheet 1Document2 pagesClass 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun With Magnets Worksheet 1shamshadNo ratings yet
- Magnet and Electric FieldDocument9 pagesMagnet and Electric FieldTranNo ratings yet
- Magnetism NotesDocument27 pagesMagnetism NotestausmanNo ratings yet
- Week 18 - Science 10Document6 pagesWeek 18 - Science 10Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-12-09 at 7.54.33 PDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-09 at 7.54.33 PMadhav JunejaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism SheetDocument2 pagesMagnetism SheetJulius CagampangNo ratings yet
- Obhur International School Second Semester-2020-2021 Revision Worksheet # 5 Science Grade 7Document4 pagesObhur International School Second Semester-2020-2021 Revision Worksheet # 5 Science Grade 7AreumNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 388)Document6 pagesMagnetism: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 388)Jack Kowman80% (5)
- Name: - Class: - DateDocument5 pagesName: - Class: - DateMonalisaNo ratings yet
- ch-4 FUN WITH MAGNETSDocument2 pagesch-4 FUN WITH MAGNETSRakesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 7-Unit8 Electricity and MagnetismDocument33 pages7-Unit8 Electricity and Magnetismelty TanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic CompassDocument5 pagesMagnetic CompassjothipriyagNo ratings yet
- Class - 6 Physics Chapter - 6 Magnets (Exercise Solutions) : ExercisesDocument5 pagesClass - 6 Physics Chapter - 6 Magnets (Exercise Solutions) : ExercisesSumayya P ANo ratings yet
- Science Revision Pack Unit 4 - Magnetism What Have YOU Learnt?Document6 pagesScience Revision Pack Unit 4 - Magnetism What Have YOU Learnt?vinujahNo ratings yet
- Science STD 7 Science Chapter 19 - Properties of A Magnetic FieldDocument3 pagesScience STD 7 Science Chapter 19 - Properties of A Magnetic FieldRiddhi RaneNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Physics Chapter 10 MagnetismDocument4 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 9 Physics Chapter 10 MagnetismrheNo ratings yet
- 06 Science Ncert Ch13 Fun With MegnetsDocument2 pages06 Science Ncert Ch13 Fun With MegnetspreethaNo ratings yet
- Magnet Grade 5 WSDocument7 pagesMagnet Grade 5 WSCatherine JeaneNo ratings yet
- Module 8 MagnetismDocument15 pagesModule 8 MagnetismLouie Jay Alivar KingNo ratings yet
- MAGNETISMDocument52 pagesMAGNETISMUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet (1) Grade 10 Name: Date: Magnetism Worksheet A. Tick The Most Appropriate AnswerDocument3 pagesWork Sheet (1) Grade 10 Name: Date: Magnetism Worksheet A. Tick The Most Appropriate AnswerdodoNo ratings yet
- 8 Magnetism Worksheet PDFDocument3 pages8 Magnetism Worksheet PDFfreanchieNo ratings yet
- Science P3 Unit 4 AkDocument1 pageScience P3 Unit 4 AkAdnes Rida SitorusNo ratings yet
- FUN WITH MAGNETS NOTES ON 2 Edited NoteDocument5 pagesFUN WITH MAGNETS NOTES ON 2 Edited NotebittuchintuNo ratings yet
- Cedar Magnetism Tutorial 1 2018 AnsDocument4 pagesCedar Magnetism Tutorial 1 2018 AnsPrudhoeNo ratings yet
- Exercise-10 (A) : Selina Solutions For Class 9 Physics Chapter 10 - MagnetismDocument15 pagesExercise-10 (A) : Selina Solutions For Class 9 Physics Chapter 10 - MagnetismD.M.X GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Magnets Study GuideDocument3 pagesMagnets Study Guideapi-284403216No ratings yet
- Exercise 10Document21 pagesExercise 10Nithin R NairNo ratings yet
- C) A Magnet Creates An Invisible Area of Magnetism All Around It Called ADocument1 pageC) A Magnet Creates An Invisible Area of Magnetism All Around It Called AAmna AslamNo ratings yet
- Science-4 WHLP WK4Document4 pagesScience-4 WHLP WK4Hazel Mae HabanaNo ratings yet
- Quiz On ElectromagnetismDocument2 pagesQuiz On ElectromagnetismAllan RoyNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field PracticalDocument1 pageMagnetic Field PracticalSophie MiddlebyNo ratings yet
- Module 8 ElectromagnetismDocument35 pagesModule 8 ElectromagnetismMelvin Cabonegro80% (10)
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) Week: - MELC: Characterize Magnetic Force ObjectivesDocument7 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) Week: - MELC: Characterize Magnetic Force ObjectivesGOLDIE TRONGCONo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusNo ratings yet
- Fortified Rice FssaiDocument8 pagesFortified Rice FssaisaikumarNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Fittings DimensionsDocument3 pagesCarbon Steel Fittings DimensionsgiorselNo ratings yet
- 100G OTN Muxponder: Cost-Efficient Transport of 10x10G Over 100G in Metro NetworksDocument2 pages100G OTN Muxponder: Cost-Efficient Transport of 10x10G Over 100G in Metro NetworkshasNo ratings yet
- Dark Elves WarbandDocument9 pagesDark Elves Warbanddueydueck100% (1)
- André Bakker Modeling Flow Fields in Stirred TanksDocument40 pagesAndré Bakker Modeling Flow Fields in Stirred TanksKhalida BekrentchirNo ratings yet
- TM 55 1520 236 23P 1Document843 pagesTM 55 1520 236 23P 1Tod A. Wulff100% (1)
- Cross Border Pack 2 SumDocument35 pagesCross Border Pack 2 SumYến Như100% (1)
- THESISDocument44 pagesTHESISRowena Shaira AbellarNo ratings yet
- 14 Parabola Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument9 pages14 Parabola Formula Sheets QuizrrChandanNo ratings yet
- Bombardier Zefiro Technical Description enDocument15 pagesBombardier Zefiro Technical Description ennickerlesstezla100% (1)
- Elementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 9th Edition Bluman Solutions ManualDocument23 pagesElementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 9th Edition Bluman Solutions Manuala305894328100% (3)
- 03-CircO2 Previous Control Nitric OxideDocument17 pages03-CircO2 Previous Control Nitric OxideVic SpeaksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Area MethodDocument14 pagesChapter 34 Area Methodthorgod941500% (1)
- Exam of Refinery PDF 2Document20 pagesExam of Refinery PDF 2ئارام ناصح محمد حسێن0% (1)
- CHAPTER 48 - Skin Integrity & Wound CareDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 48 - Skin Integrity & Wound CareANo ratings yet
- Table of Content and PrefaceDocument5 pagesTable of Content and PrefaceHaiderEbrahimNo ratings yet
- INERT-SIEX 200-300 IG-100: Design ManualDocument54 pagesINERT-SIEX 200-300 IG-100: Design ManualSaleh Mohamed0% (1)
- Atomic Structure RevisionDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure RevisioncvNo ratings yet
- ISO 13920 - Tolerâncias para Juntas SoldadasDocument7 pagesISO 13920 - Tolerâncias para Juntas SoldadasRicardo RicardoNo ratings yet
- Kyocera Mita KM1505 1510 1810 Series ELITEC EssentialsDocument6 pagesKyocera Mita KM1505 1510 1810 Series ELITEC EssentialsJaime RiosNo ratings yet
- TM 55 1520 400 14 PDFDocument227 pagesTM 55 1520 400 14 PDFOskar DirlewangerNo ratings yet
- Rewoquat We 45 TDS 12 02 01Document3 pagesRewoquat We 45 TDS 12 02 01chintanictNo ratings yet
- E9sht I C C I W D SDocument213 pagesE9sht I C C I W D SMAMBO95TLNo ratings yet
- Lover Album LyricsDocument34 pagesLover Album LyricsMichael PlanasNo ratings yet
- Microbiology QuestionsDocument5 pagesMicrobiology QuestionsNaeem AminNo ratings yet
- Bergeron Et Al 2023 Use of Invasive Brain Computer Interfaces in Pediatric Neurosurgery Technical and EthicalDocument16 pagesBergeron Et Al 2023 Use of Invasive Brain Computer Interfaces in Pediatric Neurosurgery Technical and EthicalPriscilla MelindaNo ratings yet
- Chm130 Test Batch-2Document3 pagesChm130 Test Batch-2misakisuki7No ratings yet
- ASTM D4852-88 (Reapproved 2009) E1Document3 pagesASTM D4852-88 (Reapproved 2009) E1Sandra LopesNo ratings yet
- The Proof of Agricultural ZakatDocument7 pagesThe Proof of Agricultural ZakatDila Estu KinasihNo ratings yet
- 1 An Introduction Basin AnalysisDocument29 pages1 An Introduction Basin AnalysisMuhamadKamilAzharNo ratings yet