Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is The Difference Between A Prokaryote and Eukaryote
Uploaded by
jocelynmillano1150 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
What is the difference between a prokaryote and eukaryote
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Prokaryote and Eukaryote
Uploaded by
jocelynmillano115Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
a.
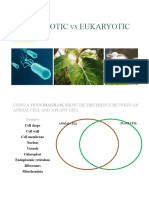
What is the difference between a prokaryote and eukaryote (you
may attach the PDF file of your answer in tabular form or in a Venn
Diagram)?
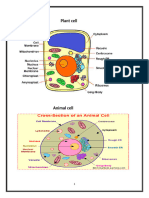
b. Illustrate the typical animal and plant cell and state the function of
the most important organelles (you mat attach the PDF file of your
illustration and the stated function of each organelles).
c. What are the classification of the organisms today?
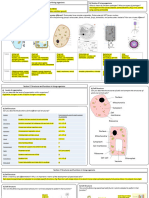
Comparison Chart
BASIS FOR
PROKARYOTIC CELLS EUKARYOTIC CELLS
COMPARISON
Size 0.5-3um 2-100um
Kind of Cell Single-cell Multicellular
Cell Wall Cell wall present, comprise Usually cell wall absent, if
of peptidoglycan or present (plant cells and
mucopeptide fungus), comprises of
(polysaccharide). cellulose (polysaccharide).
Presence of Well-defined nucleus is A well-defined nucleus is
Nucleus absent, rather 'nucleoid' is present enclosed within
present which is an open nuclear memebrane.
region containing DNA.
Shape of DNA Circular, double-stranded Linear, double-stranded
DNA. DNA.
Mitochondria Absent Present
Ribosome 70S 80S
Golgi Apparatus Absent Present
Endoplasmic Absent Present
Reticulum
BASIS FOR
PROKARYOTIC CELLS EUKARYOTIC CELLS
COMPARISON
Mode of Asexual Most commonly sexual
Reproduction
Cell Divison Binary Fission, Mitosis
(conjugation,
transformation,
transduction)
Lysosomes and Absent Present
Peroxisomes
Chloroplast (Absent) scattered in the Present in plants, algae.
cytoplasm.
Transcription Occurs together. Transcription occurs in
and Translation nucleus and translation in
cytosol.
Organelles Organelles are not Organelles are membrane
membrane bound, if bound and are specific in
present any. function.
Replication Single origin of replication. Multiple origins of
replication.
Number of Only one (not true called More than one.
Chromosomes as a plasmid).
Examples Archaea, Bacteria. Plants and Animals.
You might also like
- Prokaryotic and EukaryoticDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryoticG- 6 ODL Trisha Mae Clemente100% (1)
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesProkaryotes EukaryotesSayyeda SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic Cell: Comparison ChartDocument5 pagesEukaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic Cell: Comparison ChartMission Aid100% (1)
- Difference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsMuhammed Sabdat100% (1)
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Arsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document14 pagesCell (Biology)gigiuobohoNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Document19 pagesCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of OrganellesDocument3 pagesStructure and Function of OrganellesAdean AhmedNo ratings yet
- EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Document2 pagesEUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Alea AicoNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Chimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell: Bacteria and Archaea DNADocument3 pagesEukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell: Bacteria and Archaea DNAsyarifah aryaniNo ratings yet
- Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic CellDocument3 pagesCells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cellgafir1230No ratings yet
- NmatstudyguideupdatedpdfDocument26 pagesNmatstudyguideupdatedpdfRafael GoldbergNo ratings yet
- NMAT Study Guide Updated PDFDocument26 pagesNMAT Study Guide Updated PDFDax Arcega100% (1)
- Eukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell - Difference and Comparison - DiffenDocument11 pagesEukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell - Difference and Comparison - DiffenAdnan Malik100% (2)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 9UWDocument14 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 9UWAlice PavesiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 IntroductionDocument8 pages1.2 IntroductionmiftahNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesDifferences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJess MCDNo ratings yet
- 7 - Cell ModelDocument6 pages7 - Cell ModelshailaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Bacteriology LectureDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNo ratings yet
- 1.2 The Two Types of Cells 12BIODocument25 pages1.2 The Two Types of Cells 12BIOedensatire21No ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document4 pagesCell (Biology)Marella SatorreNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellDocument1 pageDifferences Between Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellSunidhi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of Life Med (+1) BiologyDocument46 pagesCell The Unit of Life Med (+1) BiologySaadiya HussainNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic CellDocument2 pagesEukaryotic CellDayan EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Session 4 (Organelles)Document4 pagesSession 4 (Organelles)MARO BGNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab ReportDocument12 pagesAgr122 Lab ReportNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Terms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesTerms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsSlay SacedaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PPT 6Document27 pagesCell Structure and Functions PPT 6rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Chap No 4 DifferencesDocument10 pagesChap No 4 DifferencesWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument17 pagesDNA Vs RNABeenish MuazzamNo ratings yet
- Prok A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProk A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsAMADO JR BANAWANo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pagesCell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- Genbio m2 Act AnsDocument1 pageGenbio m2 Act Anstamia syNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Lec. 1Document27 pagesCell Organelles - Lec. 1Hamza KaisNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Navigation SearchDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : Navigation Searchsamz95100% (1)
- Cellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Document21 pagesCellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Maryum JavedNo ratings yet
- CeluarDocument7 pagesCeluarJef PerezNo ratings yet
- iGCSE-revision-mindmaps-new-specification-double-award ANSWERS Year 10 ModDocument25 pagesiGCSE-revision-mindmaps-new-specification-double-award ANSWERS Year 10 Modlily wongNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- 1.4.2 Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument6 pages1.4.2 Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Celljumbergy01No ratings yet
- Els NotesDocument2 pagesEls Notesramosinducil05No ratings yet
- GN 1.2 - Classify CellsDocument2 pagesGN 1.2 - Classify CellsJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Biomedical 01Document26 pagesBiomedical 01api-3706483No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic CellDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic CellJake GopitaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-27 at 1.09.50 AMDocument27 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-27 at 1.09.50 AMcfhsmjmdqnNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- And Development in Sport: IdentificationDocument201 pagesAnd Development in Sport: IdentificationAndré OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Should We Diagnose AD Alport in COL4A3 HetsDocument3 pagesShould We Diagnose AD Alport in COL4A3 HetsAlekhya NarravulaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering Has Applications in MedicineDocument6 pagesGenetic Engineering Has Applications in Medicineshiv kapilaNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy ReportDocument2 pagesGene Therapy ReportKaren Jane YapNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument23 pagesGenetic EngineeringAlexander Salas EspaderaNo ratings yet
- 全转录-Construction of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network for Exploring Underlying Mechanisms of Lubrication DisorderDocument11 pages全转录-Construction of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network for Exploring Underlying Mechanisms of Lubrication Disorder张议No ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum Disorders PDFDocument405 pagesAutism Spectrum Disorders PDFSrinivasa Raamaanuja100% (1)
- Bm7 RemodellingDocument105 pagesBm7 RemodellingabdullahshiddiqadamNo ratings yet
- Dna Thesis StatementDocument6 pagesDna Thesis Statementlakeishajonesjackson100% (2)
- (Genetics, Genomics and Breeding of Crop Plants) Christophe Plomion - Jean Bousquet - Chittaranjan Kole-Genetics, Genomics, and Breeding of Conifers (2011)Document476 pages(Genetics, Genomics and Breeding of Crop Plants) Christophe Plomion - Jean Bousquet - Chittaranjan Kole-Genetics, Genomics, and Breeding of Conifers (2011)stand backNo ratings yet
- Bio101 008L Syllabus SP2009Document4 pagesBio101 008L Syllabus SP2009Paul FitzgeraldNo ratings yet
- Cell - 28 March 2013Document270 pagesCell - 28 March 2013Ian De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Genetics LectureDocument46 pagesGenetics LecturePabitra SahaNo ratings yet
- 1st CONS of Gene TherapyDocument12 pages1st CONS of Gene TherapyCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- Rubrics 3D Dna ModellingDocument2 pagesRubrics 3D Dna ModellingRon D. ArtNo ratings yet
- Translation: Protein Biosynthesis Mrna Amino AcidsDocument4 pagesTranslation: Protein Biosynthesis Mrna Amino AcidsMalick AwanNo ratings yet
- Leroi-Gourhan: The Organised Inorganic' by Bernard Stiegler From Cahiers de Mediologie, No. 6, 2e Semestre, 1996Document8 pagesLeroi-Gourhan: The Organised Inorganic' by Bernard Stiegler From Cahiers de Mediologie, No. 6, 2e Semestre, 1996Charlie GereNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diversity Analysis in Novel Self-Incompatible (Si) Lines of Cabbage Based On Morphological Traits and SSR MarkersDocument12 pagesGenetic Diversity Analysis in Novel Self-Incompatible (Si) Lines of Cabbage Based On Morphological Traits and SSR MarkersDr Sandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Gene PredictionDocument24 pagesGene PredictionJUDE serpesNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument4 pagesTranscription and TranslationGerry0% (1)
- Evolution of The Peppered MothDocument3 pagesEvolution of The Peppered MothSayed MikoNo ratings yet
- Summary Practice 5Document5 pagesSummary Practice 5Linh HuynhNo ratings yet
- Dog Coat Colour Genetics - A Review, Saif Et Al. 2020Document11 pagesDog Coat Colour Genetics - A Review, Saif Et Al. 2020Emmanuel A. Sessarego DávilaNo ratings yet
- Panghulo National High SchoolDocument2 pagesPanghulo National High SchoolJobelle TabinasNo ratings yet
- Depression and Genes 99Document12 pagesDepression and Genes 99Rayan BotanyNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 Principles of Life Hillis 184 CH 11 Regulation of Gene Expression 9093Document8 pagesBiology 12 Principles of Life Hillis 184 CH 11 Regulation of Gene Expression 9093Kevin ApodacaNo ratings yet
- Bio6.Blueprint of LifeDocument38 pagesBio6.Blueprint of Lifebenjamin_wang_450% (2)
- Bio130 Lab 2Document3 pagesBio130 Lab 2Ruhi KiflenNo ratings yet
- Devitas Review 4th EdDocument446 pagesDevitas Review 4th Edmudasir61100% (1)
- (Roche) Scanner Ms200 Brochure 2009-12-22Document12 pages(Roche) Scanner Ms200 Brochure 2009-12-22Luong NguyenNo ratings yet