Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Uploaded by
Adean Ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesstricture and function of organelles
Original Title
structure and function of organelles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentstricture and function of organelles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesComparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Uploaded by
Adean Ahmedstricture and function of organelles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
BASIS FOR
PROKARYOTIC CELLS EUKARYOTIC CELLS
COMPARISON
Size 0.5-3um 2-100um
Kind of Cell Single-cell Multicellular
Cell Wall Cell wall present, comprise of Usually cell wall absent, if
peptidoglycan or present (plant cells and
mucopeptide fungus), comprises of
(polysaccharide). cellulose (polysaccharide).
Presence of Well-defined nucleus is A well-defined nucleus is
Nucleus absent, rather 'nucleoid' is present enclosed within
present which is an open nuclear memebrane.
region containing DNA.
Shape of DNA Circular, double-stranded Linear, double-stranded
DNA. DNA.
Mitochondria Absent Present
Ribosome 70S 80S
Golgi Apparatus Absent Present
Endoplasmic Absent Present
Reticulum
Mode of Asexual Most commonly sexual
Reproduction
Cell Divison Binary Fission, Mitosis
(conjugation, transformation,
transduction)
BASIS FOR
PROKARYOTIC CELLS EUKARYOTIC CELLS
COMPARISON
Lysosomes and Absent Present
Peroxisomes
Chloroplast (Absent) scattered in the Present in plants, algae.
cytoplasm.
Transcription and Occurs together. Transcription occurs in
Translation nucleus and translation in
cytosol.
Organelles Organelles are not Organelles are membrane
membrane bound, if present bound and are specific in
any. function.
Replication Single origin of replication. Multiple origins of
replication.
Number of Only one (not true called as a More than one.
Chromosomes plasmid).
Examples Archaea, Bacteria. Plants and Animals.
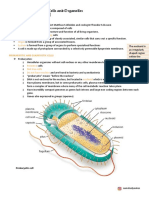
Organelle Structure Function
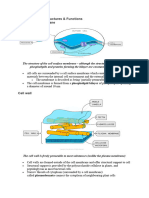
Cell-surface membrane Phospholipid bilayer with proteins The fluid-mosaic model of the membrane
and cholesterol embedded within refers to the fluidity and range of molecules
it. Glycolipids and glycoproteins in the membrane. Cholesterol provides
in the surface. strength and reduces fluidity, proteins are fo
transport and the glycoproteins and
glycolipids are for cell recognition and act a
receptors.
Nucleus Surrounded by a double membrane Nucleolus is the site of rRNA product and
nuclear envelope with nuclear makes ribosomes. DNA replication and
pores. Containing chromosomes, transcription occur in the nucleus.
consisting of protein-bound, linear
DNA, and one or more nucleolus
Mitochondria Double membrane organelle. The Site of aerobic respiration and ATP
inner membrane is folded to form production.
cristae. Contains a fluid centre
called the matrix
Chloroplasts Surrounded by a double The site of photosynthesis. The stroma
membrane. Contains thylakoids, contains enzymes for the light-independent
which are folded membrane stage of photosynthesis
containing chlorophyll pigments.
Contains a fluid centre, the stroma.
Golgi apparatus and Golgi Stacks of membranes creating Proteins and lipids and modified here.
vesicles flattened sacs called cisternae, Carbohydrates can be added to proteins to
surrounded by small round hollow form glycoproteins. Finished products are
vesicles. transported in the Golgi vesicles.
Lysosomes Formed when the Golgi apparatus A type of Golgi vesicle that releases
contains hydrolytic enzymes. lysozymes.
Ribosomes Small granules in cells made of The site of translation in protein synthesis.
protein and rRNA. Made up of a
small and large subunit. 80s in size
in eukaryotes.
Rough endoplasmic Sheets of membranes linked to the RER – site of protein synthesis and
reticulum (RER) and smooth nucleus. The membranes form a glycoprotein synthesis. The proteins can the
endoplasmic reticulum network of cisternae- a network of be transported through the RER. SER –
(SER) tubules and flattened sacs. The create, store and transport lipids and
RER have ribosomes on the outer carbohydrates.
surface.
Cell wall Found in plants, algae and fungi. Provides structural strength to cells and
Consists of polysaccharides, prevents cells from bursting when water
cellulose in plants and chitin in enters by osmosis.
fungi. There is a thin boundary
layer between adjacent cells called
the middle lamella.
Cell vacuole Found in plants. A single To provide support to a cell, store amino
membrane sac filled with fluid acids and sugars and can contain pigments t
containing salts, sugars and amino attract pollinators.
acids. The membrane around a cell
vacuole is called the tonoplast.
You might also like
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument27 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Manifestation of LifeDocument6 pagesStructural and Functional Manifestation of LifeKaila StefanieNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell StructureDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell Structurejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Lec. 1Document27 pagesCell Organelles - Lec. 1Hamza KaisNo ratings yet
- Cells: Electron MicroscopeDocument7 pagesCells: Electron MicroscopeGabriela ZahiuNo ratings yet
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDocument8 pagesCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajNo ratings yet
- Cellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument7 pagesCellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Points To RememberDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4No ratings yet
- Cell_The unit of lifeDocument5 pagesCell_The unit of lifeharifire050No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal CellsCharisse Sheree PuentenegraNo ratings yet
- 1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeDocument100 pages1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and TaxonomyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesDifferences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJess MCDNo ratings yet
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byDocument11 pagesRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byKamlesh RatnamNo ratings yet
- Biology Syllabus NotesDocument92 pagesBiology Syllabus NotesClive Remix BoatengNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsDocument65 pagesThe Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Taxonomyporkypig100% (11)
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-08 Cell: Structure and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-08 Cell: Structure and FunctionsHasharaNo ratings yet
- ER and Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Functions of Key Cell OrganellesDocument5 pagesER and Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Functions of Key Cell OrganellesJohn Rey Bandong100% (1)
- Organelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)Document6 pagesOrganelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- #1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pages#1 Cell Structure and FunctionCharlene EpilepsiaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures and FunctionsPhantomNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Material _xi_22-23-Compressed_0 (1)Document14 pagesBiology Study Material _xi_22-23-Compressed_0 (1)gana63693No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- The Cell StructureDocument7 pagesThe Cell StructureAbcedef Wyn Grey AbrasadoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument16 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationanippoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25No ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Organelles - Structure and FunctionKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- CellDocument17 pagesCellAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles GuideDocument43 pagesCell Organelles GuideMariam Qais100% (1)
- The Cell and Its OrganellesDocument7 pagesThe Cell and Its OrganellesJanine JoverNo ratings yet
- The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDocument45 pagesThe Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument10 pagesCELLMAAYER MUHAMMADNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Botany Notes Part 2Document24 pagesBotany Notes Part 2Rochenick MagoNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 2Document41 pagesمحاضرة 2AbdulNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument25 pagesThe CellmaryshealshealNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesFundamental Unit of Lifechabalalalulama5No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsRosemarie OngNo ratings yet
- Assigment 1 BiologyDocument8 pagesAssigment 1 BiologyshimaabdollahpourNo ratings yet
- Assiginment 2 - 2023-2Document6 pagesAssiginment 2 - 2023-2ashakiobrien0No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PPT 6Document27 pagesCell Structure and Functions PPT 6rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- PL4 Cell CompartmentsDocument11 pagesPL4 Cell CompartmentsJake GopitaNo ratings yet
- A Level Key Words Topic 2 Cells and MembranesDocument4 pagesA Level Key Words Topic 2 Cells and MembranesAlice VitelliNo ratings yet
- CellDocument16 pagesCellanantchouhdary1709No ratings yet
- The Unit of Life WorksheetDocument24 pagesThe Unit of Life WorksheetNeeraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet