0% found this document useful (0 votes)
709 views6 pagesCell Organelles: Functions and Structures
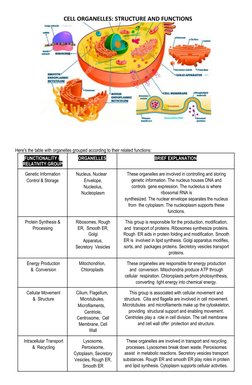
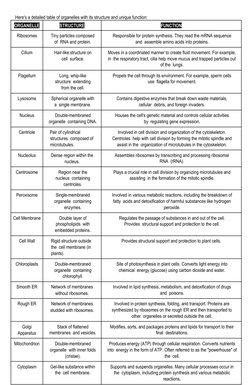
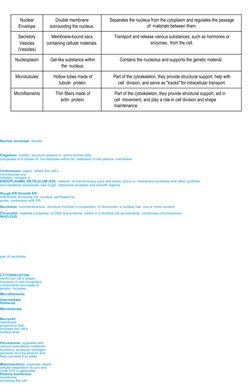
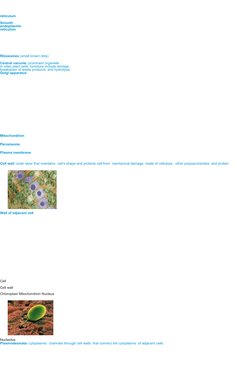
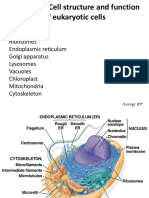
The document describes the structure and functions of various cell organelles grouped into functional categories. It includes a table listing organelles involved in genetic information control and storage like the nucleus, protein synthesis and processing like the ribosomes and Golgi apparatus, energy production and conversion like mitochondria and chloroplasts, and cellular movement and structure like cilia and microtubules. It then provides more detailed descriptions of each organelle's structure and unique functions in protein synthesis, movement, waste breakdown, photosynthesis, and more.
Uploaded by
Karyl Marie Rodas JaminCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
709 views6 pagesCell Organelles: Functions and Structures
The document describes the structure and functions of various cell organelles grouped into functional categories. It includes a table listing organelles involved in genetic information control and storage like the nucleus, protein synthesis and processing like the ribosomes and Golgi apparatus, energy production and conversion like mitochondria and chloroplasts, and cellular movement and structure like cilia and microtubules. It then provides more detailed descriptions of each organelle's structure and unique functions in protein synthesis, movement, waste breakdown, photosynthesis, and more.
Uploaded by
Karyl Marie Rodas JaminCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Overview of Cell Organelles
- Organelles and Their Functions
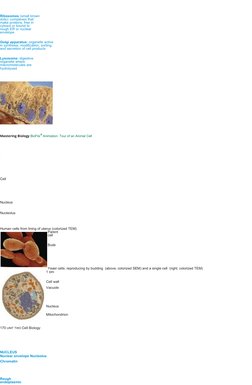
- Mastering Biology: Visual Tours