Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PS Implementation and Best Practices
Uploaded by
mohammedraulmadrid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesPS Implementation and Best Practices
Uploaded by
mohammedraulmadridCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
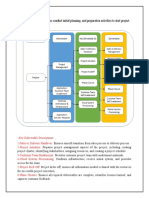
SAP PS Implementation and Best Practices
Implementation
Implementing SAP Project System (PS) involves several steps to ensure a successful
implementation. Here is a general overview of the steps involved in implementing SAP
PS from beginning to end:
1. Project Preparation: a. Define project objectives and scope. b. Identify key
stakeholders and form a project team. c. Conduct a feasibility study and assess
the readiness for SAP PS implementation. d. Develop a project plan, timeline, and
budget.
2. Business Blueprint: a. Conduct a detailed analysis of existing business processes
and requirements. b. Identify gaps between current processes and SAP PS
functionalities. c. Define the future processes and requirements. d. Create a
comprehensive business blueprint document that outlines the scope, processes,
and configuration requirements.
3. System Configuration: a. Configure SAP PS system based on the defined business
blueprint. b. Customize the system settings to align with the organization's
specific needs. c. Define project structures, WBS elements, activity types, network
types, cost elements, and other relevant master data. d. Set up integration points
with other SAP modules or external systems.
4. Development and Testing: a. Develop any necessary enhancements or
customizations to meet specific requirements. b. Conduct unit testing to ensure
the configured system meets the defined specifications. c. Perform integration
testing to verify the integration with other modules and external systems. d.
Conduct user acceptance testing (UAT) to involve end users and validate the
system against real-world scenarios. e. Address any issues or gaps identified
during testing and make necessary adjustments.
5. Data Migration: a. Plan the data migration strategy, including data extraction,
cleansing, and transformation. b. Migrate relevant data from legacy systems to
the SAP PS system, ensuring data accuracy and integrity. c. Validate the migrated
data against the original source and perform reconciliation.
6. Training and User Enablement: a. Develop training materials and conduct training
sessions for end users. b. Train users on SAP PS functionalities, processes, and
best practices. c. Provide ongoing support and guidance to users during the
training period.
7. Change Management and Communication: a. Develop a change management
strategy to manage the transition to the new system. b. Communicate the
benefits of SAP PS to stakeholders and address any concerns or resistance. c.
Implement change management activities, such as communication plans,
stakeholder engagement, and user adoption strategies.
8. Deployment and Go-Live: a. Prepare the system for production use by finalizing
configurations, data, and user roles. b. Conduct a final system readiness check
and ensure all necessary prerequisites are met. c. Execute a cutover plan to
transition from the legacy system to the SAP PS system. d. Perform thorough
testing and verification in the production environment. e. Go live with SAP PS,
making it available for day-to-day project management.
9. Post-Go-Live Support and Optimization: a. Provide post-go-live support to
address any immediate issues or user concerns. b. Monitor system performance,
user feedback, and key metrics. c. Continuously optimize and improve SAP PS
processes based on feedback and lessons learned. d. Conduct periodic system
maintenance, including upgrades and patches.
It's important to note that the specific steps and timeline may vary depending on the
organization's requirements, complexity, and implementation approach. Working with
experienced SAP consultants or partners can help ensure a smooth and successful SAP
PS implementation.
You might also like
- PS Best PracticesDocument2 pagesPS Best PracticesmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- Business Requirements For Congolese CompanyDocument1 pageBusiness Requirements For Congolese CompanyUcheNo ratings yet
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- SAP Business Requirements For Kenyan CompanyDocument1 pageSAP Business Requirements For Kenyan CompanyUcheNo ratings yet
- SAP Business Requirements For Tanzanian CompanyDocument1 pageSAP Business Requirements For Tanzanian CompanyUcheNo ratings yet
- 300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionFrom Everand300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionNo ratings yet
- SAP Business Requirements For Togolese CompanyDocument1 pageSAP Business Requirements For Togolese CompanyUcheNo ratings yet
- Detailed Job Duties_SamplinDocument3 pagesDetailed Job Duties_SamplinRAjesh BoyapallyNo ratings yet
- Review ProjectDocument18 pagesReview ProjectFathima LaisaNo ratings yet
- SAP Activate Methodology For Business Suite and On-Premise-Agile and WaterfallDocument9 pagesSAP Activate Methodology For Business Suite and On-Premise-Agile and WaterfallRamesh Kumar BNo ratings yet
- ASAP MethodologyDocument14 pagesASAP MethodologyTiffany HughesNo ratings yet
- Business Requirements For African CompanyDocument1 pageBusiness Requirements For African CompanyUcheNo ratings yet
- Approach To Run The SapmmDocument20 pagesApproach To Run The Sapmmanwardwh5895No ratings yet
- Metodologija OverwievDocument50 pagesMetodologija Overwievzelimir1No ratings yet
- SAP Implementation Phases GuideDocument3 pagesSAP Implementation Phases GuideAjit GautamNo ratings yet
- Sap-Asap MethodsDocument3 pagesSap-Asap MethodsRavi RebelNo ratings yet
- General Plan For AutomationDocument6 pagesGeneral Plan For AutomationMarko ZeljkoNo ratings yet
- SAP GRC Access Control 5.2 Implementation Guide For Enterprise Role ManagementDocument11 pagesSAP GRC Access Control 5.2 Implementation Guide For Enterprise Role ManagementpenguinfootNo ratings yet
- SAP ImplementationDocument15 pagesSAP ImplementationMohd FadzilNo ratings yet
- Deployment Plan EssentialsDocument31 pagesDeployment Plan Essentialswawa1308No ratings yet
- ASAP Methodology - SAPDocument6 pagesASAP Methodology - SAPShiv MandowaraNo ratings yet
- SAP Asap MethodologyDocument33 pagesSAP Asap Methodologyimvav100% (1)
- SAP Implementation GuideDocument4 pagesSAP Implementation Guideabcabcabcabc4100% (1)
- SM001 - Sol Manager QnsDocument12 pagesSM001 - Sol Manager QnsFrank FrankiesNo ratings yet
- Implementing SAP with ASAP Roadmap MethodologyDocument11 pagesImplementing SAP with ASAP Roadmap MethodologyGifted423No ratings yet
- Different MethodologiesDocument11 pagesDifferent Methodologiesian uzumakiNo ratings yet
- Prepare Phase:: Project Teams Conduct Initial Planning, and Preparation Activities To Start ProjectDocument4 pagesPrepare Phase:: Project Teams Conduct Initial Planning, and Preparation Activities To Start ProjectHarpy AhmedNo ratings yet
- QSandS NTUA SAP MethodologyDocument25 pagesQSandS NTUA SAP Methodologyel_angel_5000No ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration Semester 2 Project Management Assignment Set-1Document32 pagesMaster of Business Administration Semester 2 Project Management Assignment Set-1vbolly12No ratings yet
- AIS Introduction 1-sdlcDocument3 pagesAIS Introduction 1-sdlcjannahNo ratings yet
- Ensured That Business Capabilities and Data Were Adequately Addressed After Corporate Move To SAPDocument3 pagesEnsured That Business Capabilities and Data Were Adequately Addressed After Corporate Move To SAPKarthik BhandaryNo ratings yet
- 1 13936 Fixed Asset Management Evaluation GuideDocument6 pages1 13936 Fixed Asset Management Evaluation GuideRagul MohanNo ratings yet
- ASAP MethodologyDocument9 pagesASAP MethodologysudhaNo ratings yet
- Organizing A su-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesOrganizing A su-WPS Officedameregasa08No ratings yet
- African Railway Centre for Excellence Project Management RPM-(REGM -6007Document27 pagesAfrican Railway Centre for Excellence Project Management RPM-(REGM -6007Kassu JilchaNo ratings yet
- SAP Activate Methodology ExplainedDocument1 pageSAP Activate Methodology ExplainedRasmi Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- SAP Activate Methodology RFP (On-Prem and Managed Cloud) V4Document7 pagesSAP Activate Methodology RFP (On-Prem and Managed Cloud) V4Sam KumarNo ratings yet
- New ASAP 8 MethodologyDocument6 pagesNew ASAP 8 MethodologyJagadish JaganNo ratings yet
- Phases of SDLC, SDLC Models, Design Project InitiationDocument14 pagesPhases of SDLC, SDLC Models, Design Project InitiationBukola BukkyNo ratings yet
- ERPDocument1 pageERPTarwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Guide to Selecting the Right SAP Best Practices Implementation ApproachDocument4 pagesGuide to Selecting the Right SAP Best Practices Implementation ApproachSumeet SharmaNo ratings yet
- BSBADM504 Plan and Implement Administrative Systems Assessment-2Document6 pagesBSBADM504 Plan and Implement Administrative Systems Assessment-2Anzel AnzelNo ratings yet
- SAP Activate Methodology RFP (On-Prem and Managed Cloud) V4Document7 pagesSAP Activate Methodology RFP (On-Prem and Managed Cloud) V4Oktaviana'Panca AdiNo ratings yet
- New Implementation:: SAP ActivateDocument3 pagesNew Implementation:: SAP ActivateKevin Anderson100% (1)
- Sap PMDocument3 pagesSap PMLAXMI VNo ratings yet
- ASAP MethodologyDocument5 pagesASAP MethodologyRohidas Shinde100% (1)
- ASAP Roadmap OffersDocument2 pagesASAP Roadmap OffersSurya NandaNo ratings yet
- 7.BSBADM504 Assessment 2 Learner PDFDocument3 pages7.BSBADM504 Assessment 2 Learner PDFArijit ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- RISE With SAP S4HANA Cloud Private Edition Release NotesDocument7 pagesRISE With SAP S4HANA Cloud Private Edition Release NotesAlexey MartynovichNo ratings yet
- Demystifying SAP ActivateDocument12 pagesDemystifying SAP Activateeason insights100% (1)
- 348 PMP ® Exam Practice Test and Study GuideDocument70 pages348 PMP ® Exam Practice Test and Study GuideObi A AgusioboNo ratings yet
- Process PlanningDocument10 pagesProcess PlanningSudeep Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Preparation Steps-1Document4 pagesPreparation Steps-1Gyas AhmadNo ratings yet
- SAP Solution Manager: PurposeDocument19 pagesSAP Solution Manager: PurposedcNo ratings yet
- BusinessCase On SAP Implementation at Global Retail CompanyDocument13 pagesBusinessCase On SAP Implementation at Global Retail Companysemi_garryNo ratings yet
- ASAP MethodologyDocument27 pagesASAP Methodologymhassim123100% (2)
- Kisi-Kisi Uts Enterprise System Tipe I - Kemungkinan Bisa KeluarDocument16 pagesKisi-Kisi Uts Enterprise System Tipe I - Kemungkinan Bisa KeluarwahyuNo ratings yet
- PS-MM IntegrationDocument2 pagesPS-MM IntegrationmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- Create A Project Vs Create A NetworkDocument3 pagesCreate A Project Vs Create A NetworkmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- Period End and Year End ClosingDocument2 pagesPeriod End and Year End ClosingmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- Asset Under ConstructionDocument2 pagesAsset Under ConstructionmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- CostsDocument1 pageCostsmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- SettlementDocument1 pageSettlementmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- LLM4OGDocument27 pagesLLM4OGShathikaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 "Linear System Identification Using Neural Networks" ObjectiveDocument7 pagesExercise 4 "Linear System Identification Using Neural Networks" Objectiveberkanhzrc67No ratings yet
- Module II Lecture 4Document19 pagesModule II Lecture 4Prateek NayakNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument16 pagesInternship ReportIshita Gaur100% (4)
- Sales Deck-JOPDocument19 pagesSales Deck-JOPsadia.aliNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning For Fluid Mechanics: Steven L. Brunton, Bernd R. Noack and Petros KoumoutsakosDocument32 pagesMachine Learning For Fluid Mechanics: Steven L. Brunton, Bernd R. Noack and Petros KoumoutsakosBaran DenliNo ratings yet
- Training Calendar (2017) : School of Quality: Iso 9001:2015 - Quality Management SystemDocument1 pageTraining Calendar (2017) : School of Quality: Iso 9001:2015 - Quality Management SystemHasbullah MohdNo ratings yet
- Online Complaint Management SystemDocument67 pagesOnline Complaint Management SystemNivetha VNo ratings yet
- BMT HL Critical Path Analysis - Revision SheetDocument9 pagesBMT HL Critical Path Analysis - Revision SheetPeehu AgarwalNo ratings yet
- FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis) : Definition/PurposeDocument3 pagesFMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis) : Definition/PurposehemanthreddyNo ratings yet
- Safe Automotive Software Architecture (SAFE)Document40 pagesSafe Automotive Software Architecture (SAFE)bnd1uNo ratings yet
- MIT2 04AS13 Lecture1Document21 pagesMIT2 04AS13 Lecture1Fabio PelleritoNo ratings yet
- JCC 2021051813373227Document16 pagesJCC 2021051813373227Mukesh PrajapatNo ratings yet
- IATF 16949:2016 Clause 4 Context of The Organization: FD-440-001 Flow Diagram Process InteractionsDocument1 pageIATF 16949:2016 Clause 4 Context of The Organization: FD-440-001 Flow Diagram Process InteractionsNavnath TamhaneNo ratings yet
- Mercury TourDocument23 pagesMercury Tournalinikanta0% (1)
- Docc 9 F 3Document21 pagesDocc 9 F 3demmaaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - Complexity AnalysisDocument18 pages1.2 - Complexity AnalysisAanchal KashyapNo ratings yet
- Lecture TwoDocument36 pagesLecture TwoMostafa RabieNo ratings yet
- EMARO Student Handbook Provides Structure and Key DatesDocument30 pagesEMARO Student Handbook Provides Structure and Key DatesaustinvishalNo ratings yet
- Process Control: Modeling, Design and Simulation: Atlab ImulinkDocument5 pagesProcess Control: Modeling, Design and Simulation: Atlab ImulinksandeepNo ratings yet
- Heuristic or Informed Algorithm1Document61 pagesHeuristic or Informed Algorithm1jhn75070No ratings yet
- INCOSE Requirement EngineeringDocument8 pagesINCOSE Requirement Engineeringxlnc1No ratings yet
- Hyperparameter Tuning For Machine Learning ModelsDocument14 pagesHyperparameter Tuning For Machine Learning Modelsincir kokusuNo ratings yet
- Checlist Audit OKDocument23 pagesCheclist Audit OKKurnia Agustina100% (1)
- A New Four-Scroll Chaotic System With A Self-Excited Attractor and Circuit ImplementationDocument5 pagesA New Four-Scroll Chaotic System With A Self-Excited Attractor and Circuit ImplementationMada Sanjaya WsNo ratings yet
- Observer-Based Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control For Fixed Wing Unmanned Aerial VehicleDocument6 pagesObserver-Based Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control For Fixed Wing Unmanned Aerial VehiclemailtosshettyNo ratings yet
- 2CSE60E14: Artificial Intelligence (3 0 4 3 2) : Learning OutcomesDocument2 pages2CSE60E14: Artificial Intelligence (3 0 4 3 2) : Learning OutcomesB. Srini VasanNo ratings yet
- Ansys-11 0Document3 pagesAnsys-11 0abiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Software Requirement EngDocument31 pagesChapter 6 Software Requirement EngJëbê Béløñgs Tö JêsüsNo ratings yet
- The Advantages of Evolutionary Computation: David B. FogelDocument11 pagesThe Advantages of Evolutionary Computation: David B. FogelNapsterNo ratings yet
- Designing Data-Intensive Applications: The Big Ideas Behind Reliable, Scalable, and Maintainable SystemsFrom EverandDesigning Data-Intensive Applications: The Big Ideas Behind Reliable, Scalable, and Maintainable SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- Excel 2023: A Comprehensive Quick Reference Guide to Master All You Need to Know about Excel Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts with Real-World ExamplesFrom EverandExcel 2023: A Comprehensive Quick Reference Guide to Master All You Need to Know about Excel Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts with Real-World ExamplesNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveFrom EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Data Engineering: Plan and Build Robust Data SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Data Engineering: Plan and Build Robust Data SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Agile Project Management: A Complete Beginner's Guide to Agile Project Management, Learn the Basic Concept and ToolsFrom EverandAgile Project Management: A Complete Beginner's Guide to Agile Project Management, Learn the Basic Concept and ToolsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Change Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemFrom EverandChange Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Creating Online Courses with ChatGPT | A Step-by-Step Guide with Prompt TemplatesFrom EverandCreating Online Courses with ChatGPT | A Step-by-Step Guide with Prompt TemplatesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Learn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIFrom EverandLearn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Notion for Beginners: Notion for Work, Play, and ProductivityFrom EverandNotion for Beginners: Notion for Work, Play, and ProductivityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Excel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetFrom EverandExcel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetNo ratings yet
- A Modern Enterprise Architecture Approach: Enterprise ArchitectureFrom EverandA Modern Enterprise Architecture Approach: Enterprise ArchitectureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Excel 2023 for Beginners: A Complete Quick Reference Guide from Beginner to Advanced with Simple Tips and Tricks to Master All Essential Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, Charts, Tools, & ShortcutsFrom EverandExcel 2023 for Beginners: A Complete Quick Reference Guide from Beginner to Advanced with Simple Tips and Tricks to Master All Essential Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, Charts, Tools, & ShortcutsNo ratings yet
- Product Operations: How successful companies build better products at scaleFrom EverandProduct Operations: How successful companies build better products at scaleNo ratings yet
- Design and Build Modern Datacentres, A to Z practical guideFrom EverandDesign and Build Modern Datacentres, A to Z practical guideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Master Your Data with Power Query in Excel and Power BI: Leveraging Power Query to Get & Transform Your Task FlowFrom EverandMaster Your Data with Power Query in Excel and Power BI: Leveraging Power Query to Get & Transform Your Task FlowRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Balanced Scorecards and Operational Dashboards with Microsoft ExcelFrom EverandBalanced Scorecards and Operational Dashboards with Microsoft ExcelRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)