Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Funmath Module 5 - Measurements and Conversions
Uploaded by
Ronelle San buenaventuraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Funmath Module 5 - Measurements and Conversions
Uploaded by
Ronelle San buenaventuraCopyright:
Available Formats
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
MODULE 5 MEASUREMENTS AND CONVERSIONS
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
At the end of this module, the students will be able to:
1. Discuss conversion
2. Solve for measurement and conversion
3. Discuss rounding of numbers
4. Interpret order of operations
5. Simplify problems
INTRODUCTION
In Mathematics, it is required to convert the units while solving many problems. To
carry out the required calculations, mathematical conversions are needed. For example, to
find the area of a triangle, if a base is given in cm, and height is given in meter, and you
are asked to find the area of a triangle in cm, it is necessary to convert the height in meters
into centimetres. Therefore, it is necessary to learn the conversion of units, to convert a
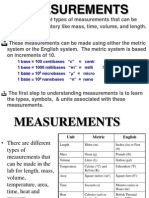
unit into the required unit. Measurement is a process of finding a number that shows the
amount of something.
LESSON
CONVERSION
The use of a unit depends on the situation, such as the area of a room is expressed in
meters but the length of a pencil is expressed in centimetres and its thickness in mm.
Thus, we need to convert one unit to another. Before understanding the concept of
conversion of units we need to understand the relationship between units.
Length and Mass conversion
Mensuration is an ancient concept. Every physical quantity like length, mass, time,
temperature etc, have a specific unit. By definition, a unit is a magnitude of a physical quantity.
There are two systems of units:
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 1
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
1. SI units (International System of Units)
2. Metric system
For example, SI unit of length is a meter (m), while metric units are kilometer (km), meter (m),
decimeter (dm), centimeter (cm) and millimeter (mm).
SI unit of mass is Kilograms (kg).
Importance of Mathematical Conversions
In order to have accuracy and avoid confusion in measurement, we need to convert one unit
to another. For instance, we do not measure the length of a pencil in kilometres, in such case one
have to convert kilometre (km) to centimetre (cm). Generally, the conversion of one unit to another
unit of the same quantity is performed using multiplicative conversion factors. Let’s see how to
convert a different unit of length and mass.
Table for Length Conversion
The table for conversion of length is:
The table for length conversion is given in the figure above. The relation between the
adjacent unit varies by the multiple of 10 (moving left to right) and vice-versa (i.e. moving right to
left).
Example: Convert 2 mm to dam.
Solution: Given 2 mm length.
From the length conversion table, we see dam is 4th position left to mm.
Thus, dividing the given length by 104.
⇒ 2 mm = 2/104 dam
⇒ 2 mm = 0.0002 dam
for Mass Conversion
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 2
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
Similarly, we have mass conversion table which is as follows:
Unit Conversion Table
Let’s have a look at some basic unit conversion of mass and length.
Units of Length Units of Mass
1 km = 10 hm 1 kg = 10 hg
= 100 dam = 100 dag
= 1000 m = 1000 g
1m = 10 dm 1 g = 10 dg
= 100 cm = 100 cg
= 1000 mm = 1000 mg
1 dm = 10 cm 1 dg = 10 cg
= 100 mm = 100 mg
1 cm = 10 mm 1 cg = 10 mg
From the table above we have seen values of units of length are not the same i.e. 1 km
≠ 1m. When 1 km is equal to 1000 m that means we need 1000 meters to make up one
kilometre. This makes kilometre a bigger unit than a meter. This is same for 1 kg = 1000g.
Conversion of units can be done in a few steps.
Points to remember:
To convert bigger units to a smaller unit multiply.
To convert a smaller unit to a bigger unit divide.
Conversion of Units Solved Examples
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 3
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
Example 1: Convert 2 cm to km.
Step 1: Draw a line or box as shown below,
km hm dam m dm cm mm
Step 2: Put 1 at the larger unit to be converted.
Here we want to convert cm to km,
Since km is the larger unit, thus put 1 under the corresponding column (km).
km hm dam m dm cm mm
1
Step 3: Now put 0 till the smaller unit.
Here we want to convert cm to km, put 0 till the corresponding smaller unit.
km hm dam m dm cm mm
1 0 0 0 0 0
We see the conversion is from a smaller to a larger unit. Thus, we need to divide the
given length by 100000 (i.e. 105).
2cm = 2/105 km
⇒2cm = 0.00002 km
Example 2: Convert 5 grams to milligrams.
Solution: We have to convert 5 grams to milligrams.
We know, 1 g = 1000 mg
Thus, 5 g = 5 × 1000 = 5000 mg
MEASUREMENT
There are two major systems of measurement in use today. They are the United States
system and the metric system. Before we describe these systems, let's gain a clear
understanding of the concept of measurement.
Measurement is comparison to some standard.
Standard Unit of Measure
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 4
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
The concept of measurement is based on the idea of direct comparison. This means that
measurement is the result of the comparison of two quantities. The quantity that is used for
comparison is called the standard unit of measure.
Over the years, standards have changed. Quite some time in the past, the standard unit
of measure was determined by a king. For example,
1 inch was the distance between the tip of the thumb and the knuckle of the king.
1 inch was also the length of 16 barley grains placed end to end.
Today, standard units of measure rarely change. Standard units of measure are the
responsibility of the Bureau of Standards in Washington D.C.
Some desirable properties of a standard are the following:
1. Accessibility. We should have access to the standard so we can make comparisons.
2. Invariance. We should be confident that the standard is not subject to change.
3. Reproducibility. We should be able to reproduce the standard so that measurements are
convenient and accessible to many people.
The United States System of Measurement
Some of the common units (along with their abbreviations) for the United States system of
measurement are listed in the following table.
Unit Conversion Table
1 foot (ft) = 12 inches (in.)
Length 1 yard (yd) = 3 feet (ft)
1 mile (mi) = 5,280 feet
1 pound (lb) =16 ounces (oz)
Weight
1 ton (T) = 2,000 pounds
1 tablespoon (tbsp) = 3 teaspoons (tsp)
1 fluid ounce (fl oz) = 2 tablespoons
1 cup (c) = 8 fluid ounces
Liquid Volume
1 pint (pt) = 2 cups
1 quart (qt) = 2 pints
1 gallon (gal) = 4 quarts
Time 1 minute (min) = 60 seconds (sec)
1 hour ( hr) = 60 minutes
1 day (da) = 24 hours
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 5
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
1 week (wk) = 7 days
Conversions in the United States System
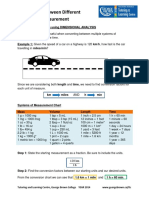
It is often convenient or necessary to convert from one unit of measure to another. For
example, it may be convenient to convert a measurement of length that is given in feet to one
that is given in inches. Such conversions can be made using unit fractions.
Unit Fraction
A unit fraction is a fraction with a value of 1.
Unit fractions are formed by using two equal measurements. One measurement is
placed in the numerator of the fraction, and the other in the denominator. Placement depends
on the desired conversion.
Placement of Units
Place the unit being converted to in the numerator.
Place the unit being converted from in the denominator.
For example,
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 6
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
Sample Set A
Make the following conversions. If a fraction occurs, convert it to a decimal
rounded to two decimal places.
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 7
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
The Advantages of the Base Ten Number System
The metric system of measurement takes advantage of our base ten number sys-
tem. The advantage of the metric system over the United States system is that
in the metric system it is possible to convert from one unit of measure to another
simply by multiplying or dividing the given number by a power of 10. This means
we can make a conversion simply by moving the decimal point to the right or the
left.
Conversion from One Unit to Another Unit
Let's note three characteristics of the metric system that occur in the metric
table of measurements.
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 8
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
1. In each category, the prefixes are the same.
2. We can move from a larger to a smaller unit of measure by moving the
decimal point to the right.
3. We can move from a smaller to a larger unit of measure by moving the
decimal point to the left.
The following table provides a summary of the relationship between the basic
unit of measure (meter, gram, liter) and each prefix, and how many places the
decimal point is moved and in what direction.
kilo hecto deka unit deci centi milli
Basic Unit to Prefix Move the Decimal Point
unit to deka 1 to 10 1 place to the left
unit to hector 1 to 100 2 places to the left
unit to kilo 1 to 1,000 3 places to the left
unit to deci 1 to 0.1 1 place to the right
unit to centi 1 to 0.01 2 places to the right
unit to milli 1 to 0.001 3 places to the right
Conversion Table
Listed below, in the unit conversion table, are some of the common metric units
of measure.
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 9
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
Distinction Between Mass and Weight
There is a distinction between mass and weight. The weight of a body is
related to gravity whereas the mass of a body is not. For example, your weight
on the earth is different than it is on the moon, but your mass is the same in both
places. Mass is a measure of a body's resistance to motion. The more massive
a body, the more resistant it is to motion. Also, more massive bodies weigh more
than less massive bodies.
Converting Metric UnitsTo convert from one metric unit to another metric unit:
1. Determine the location of the original number on the metric scale
(pictured in each of the following examples).
2. Move the decimal point of the original number in the same direction and
same number of places as is necessary to move to the metric unit you
wish to go to.
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 10
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 11
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
EVALUATION
Name: _____________________________________ Score: __________ Rating: ________
Course Yr. & Sec. ____________________________ Date Submitted: __________________
MEASUREMENTS AND CONVERSIONS
Student Assessment Question
Direction. Answer the following as required. (5 points each)
Using your own words, discuss measurement and conversion.
__________________________________________________________________
_
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________
Briefly discuss the advantage of base ten number system.
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 12
FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
____________
__________________________________________________________________
__
How would you apply the measurement and conversion in your life.
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
______________
Short Quiz:
GO TO THE LINK: https://tinyurl.com/AEMODULETHREE
UP NEXT: COMPUTATION OF GEOMTERIC FIGURES
REFERENCES:
https://byjus.com/maths/conversion-of-units/
https://cnx.org/contents/XeVIW7Iw@4.6:l1jFhipm@2/Measurement-and-the-United-States-System
RONELLE C. SAN BUENAVENTURA, LPT MAEd (CAR) | ronellesb06.svc@gmail.com | 09974820616 |Page 13
You might also like
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Conversion of UnitsDocument9 pagesConversion of UnitsPepper mintNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Q2 Week 2Document17 pagesMath 7 Q2 Week 2Joshrel V. CieloNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversions GuideDocument24 pagesUnit Conversions GuideHermioneNo ratings yet
- Calculating Conversions in ChemistryDocument15 pagesCalculating Conversions in ChemistryMido IzukuNo ratings yet
- Notes 1.1 - Dimensional Analysis-ConversionDocument11 pagesNotes 1.1 - Dimensional Analysis-ConversionBilly JenkinsNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument14 pagesMeasurementOyi Lorenzo-LibanNo ratings yet
- review STEDocument39 pagesreview STEMarisselNo ratings yet
- Units and Dimensional AnalysisDocument5 pagesUnits and Dimensional AnalysisJuan Fernando Cano LarrotaNo ratings yet
- 2018-Quantities, Measurement, Significant Figures, Scientific Notation, Conversion of UnitsDocument50 pages2018-Quantities, Measurement, Significant Figures, Scientific Notation, Conversion of UnitsErika Mae Naparato Pepaño100% (1)
- Objectives:: Imperial SystemDocument9 pagesObjectives:: Imperial SystemTay YpnNo ratings yet
- Local Media5664332096388818018Document38 pagesLocal Media5664332096388818018Freddie NanasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Demo TeachingDocument6 pagesLesson Plan For Demo TeachingPaño Burce MilletNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Unit of Measurement (1)Document22 pagesWeek 1 Unit of Measurement (1)kobep4894No ratings yet
- Netsolving Problems Involving Conversion of Units of MeasurementDocument28 pagesNetsolving Problems Involving Conversion of Units of MeasurementFynn NiallNo ratings yet
- Year VIII Interactive MathsDocument13 pagesYear VIII Interactive MathsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesDimensional Analysis WorksheetDouglas Weber100% (1)
- Module 2 MeasurementDocument13 pagesModule 2 MeasurementEric LucesNo ratings yet
- Imperial System To MetricDocument14 pagesImperial System To MetricVenkatesan SundaramNo ratings yet
- Adm Math7 Quarter2 Module2 Revised Final-V2.0Document22 pagesAdm Math7 Quarter2 Module2 Revised Final-V2.0Jaylor Garido100% (2)
- The English System of UnitsDocument77 pagesThe English System of UnitsAnwer AliNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes:: The Learner Demonstrates Understanding of Key Concepts of MeasurementsDocument34 pagesLearning Outcomes:: The Learner Demonstrates Understanding of Key Concepts of MeasurementsMaricris Galachico GaraoNo ratings yet
- Physics Nist Gov/cuu/unitsDocument1 pagePhysics Nist Gov/cuu/unitsYau Chun LeungNo ratings yet
- Metric System Hand OutDocument3 pagesMetric System Hand OutKenny TothNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Units (Mathematical Conversions) - Tables & ExamplesDocument1 pageConversion of Units (Mathematical Conversions) - Tables & Examplesaadit.25520No ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementDocument39 pagesUnits and MeasurementCyndie AbellaNo ratings yet
- MetricsDocument2 pagesMetricsblackwellbert0% (3)
- Math 6 DLP 63 - Converting From One Unit of Measure To Another PDFDocument11 pagesMath 6 DLP 63 - Converting From One Unit of Measure To Another PDFMelinda Rafael100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument52 pagesPhysicsGONZALES, Ma. Karmelha Adrey B.100% (1)
- LESSON 2.4 UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS v2Document43 pagesLESSON 2.4 UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS v2Reign CallosNo ratings yet
- 1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFDocument35 pages1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFJames PalmonesNo ratings yet
- DLP Physics 1 QTR 1. Module 1Document18 pagesDLP Physics 1 QTR 1. Module 1Shania Joy LaudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Feb 2017Document70 pagesChapter 1 - Feb 2017Firdaus RoslimNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Week 2 LessonsDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Math Week 2 LessonsTina SayconNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math (2nd Quarter)Document22 pagesGrade 7 Math (2nd Quarter)Euclid Pogi100% (1)
- Mat 7 Q2 W1 ModuleDocument9 pagesMat 7 Q2 W1 ModuleRachel Chan100% (1)
- Handouts MeasurementDocument8 pagesHandouts MeasurementfizznbitesNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 7: Pasay-M7-Q2-W2-D1Document20 pagesModule in Mathematics 7: Pasay-M7-Q2-W2-D1Torres Jhon Chriz GabrielNo ratings yet
- Co2 2023-2024Document45 pagesCo2 2023-2024RICHELLE L. HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Introduction Units and MeasurementsDocument46 pagesUnit 1. Introduction Units and MeasurementsAmari JeonNo ratings yet
- Metric System-Reading MaterialDocument8 pagesMetric System-Reading MaterialHasna HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Units of Measurement and ApplicationDocument30 pagesChapter 3 Units of Measurement and ApplicationAaron KirkNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Measurement L - A 1Document30 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Measurement L - A 1Vea Patricia AngeloNo ratings yet
- Understand Measurement Units with the SI SystemDocument16 pagesUnderstand Measurement Units with the SI SystemManish PatelNo ratings yet
- 1.6a DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 1Document41 pages1.6a DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 1Guile MacaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Year 10 Core S 10.1 10.2 Lesson 50Document15 pagesIGCSE Year 10 Core S 10.1 10.2 Lesson 50jonathan abi raadNo ratings yet
- Drilling Calculations CD Complete CourseDocument177 pagesDrilling Calculations CD Complete CoursecarmenNo ratings yet
- Physics1 MeasurementsDocument69 pagesPhysics1 MeasurementsCAITHLENE MARIE ALFONSONo ratings yet
- Convert Units Using Dimensional AnalysisDocument4 pagesConvert Units Using Dimensional AnalysisJeya Plays YTNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Units and MeasurementDocument18 pagesConversion of Units and MeasurementMaria Monica SanielNo ratings yet
- Metric Conversions2013Document12 pagesMetric Conversions2013spreemouseNo ratings yet
- Let's Check Your Understanding!: Are You Ready?Document51 pagesLet's Check Your Understanding!: Are You Ready?Paño Burce MilletNo ratings yet
- Chemical Problem SolvingDocument13 pagesChemical Problem SolvingChristian DuranaNo ratings yet
- Metric System HandoutDocument3 pagesMetric System Handoutflorescu7100% (1)
- How To Use Metric Sytem of MeasurementDocument13 pagesHow To Use Metric Sytem of MeasurementBonnie LumacadNo ratings yet
- Technical Drafting - G7 - 8 - Week 4 LASDocument8 pagesTechnical Drafting - G7 - 8 - Week 4 LASNorman PolilinNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF MEASUREMENTDocument6 pagesPRINCIPLES OF MEASUREMENTAllyah Ross DuqueNo ratings yet
- Personal Tutor FinalDocument100 pagesPersonal Tutor Final신재호No ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS2Document7 pagesFUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS2Ronelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Test Question Funmath PrelimDocument6 pagesTest Question Funmath PrelimRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Pre Test ResultDocument2 pagesPre Test ResultRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 461190231 2nd Quarter Exam in Grade 7 ScienceDocument7 pages461190231 2nd Quarter Exam in Grade 7 ScienceRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Pre Test ResultDocument2 pagesPre Test ResultRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Pre Test ResultDocument2 pagesPre Test ResultRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 587983504-Curriculum-Map-practical-Research-2 (1)Document3 pages587983504-Curriculum-Map-practical-Research-2 (1)Ronelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- TOS-FUNMATH-MIDTERMDocument3 pagesTOS-FUNMATH-MIDTERMRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Tos Funmath PrelimDocument3 pagesTos Funmath PrelimRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Pre Test ResultDocument2 pagesPre Test ResultRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- third-quarter-examination-for-grade-7-englishDocument5 pagesthird-quarter-examination-for-grade-7-englishRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Pre Test ResultDocument2 pagesPre Test ResultRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- toaz.info-eapp-curriculum-map-pr_2100d47cf6de5f90fa833a57a45a346fDocument5 pagestoaz.info-eapp-curriculum-map-pr_2100d47cf6de5f90fa833a57a45a346fRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- PR1-FINALDocument3 pagesPR1-FINALRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 2ND QUARTER EXAM PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2 MULTIPLE CHOICEDocument5 pages2ND QUARTER EXAM PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2 MULTIPLE CHOICEQuennee Ronquillo Escobillo71% (14)
- Grammar and Vocabulary Proficiency of Grade 10 Students in English in Presentacion National High School 2022-2023Document125 pagesGrammar and Vocabulary Proficiency of Grade 10 Students in English in Presentacion National High School 2022-2023Ronelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS2Document7 pagesFUNDAMENTALS OF MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS2Ronelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research TitleDocument8 pagesQuantitative Research TitleRosario OcamiaNo ratings yet
- Malabon National High School Grade 11 Functions LessonDocument2 pagesMalabon National High School Grade 11 Functions Lessonjob moralesNo ratings yet
- 587983504 Curriculum Map Practical Research 2Document3 pages587983504 Curriculum Map Practical Research 2Ronelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 54216384-Lesson-Plan-in-English-I-HomonymsDocument4 pages54216384-Lesson-Plan-in-English-I-HomonymsRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals-of-Mathematics-Midterm-ExamDocument5 pagesFundamentals-of-Mathematics-Midterm-ExamRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- COURSE-SYLLABUS-FOR-OPERATIONS-MANAGEMENT-AND-TQMDocument5 pagesCOURSE-SYLLABUS-FOR-OPERATIONS-MANAGEMENT-AND-TQMRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Course-Syllabus-Living-in-the-IT-EraDocument9 pagesCourse-Syllabus-Living-in-the-IT-EraRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Gas 12sb AwardeesDocument5 pagesGas 12sb AwardeesRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- CONGRATULATIONS-TO-THE-FOLLOWING-LET-TOPNOTCHERSDocument2 pagesCONGRATULATIONS-TO-THE-FOLLOWING-LET-TOPNOTCHERSRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Convergence-CopyDocument1 pageConvergence-CopyRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Pre Test ResultDocument2 pagesPre Test ResultRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 515436547-Graduation-ProposalDocument5 pages515436547-Graduation-ProposalRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Attendace AwardDocument1 pageAttendace AwardRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 8.me331f20 Static Force Analysis ExamplesDocument7 pages8.me331f20 Static Force Analysis ExamplesTaylan KaraçelikNo ratings yet
- Determine Crop Water Needs from Soil SamplesDocument7 pagesDetermine Crop Water Needs from Soil SamplesFaris AhmadNo ratings yet
- CoadaDocument13 pagesCoadaDeny DenisaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Sec: SR Bipc (Chaina & Elite) Neet Model Date: 30-01-2019 Time: 3 Hrs Grand Test-4 Max. Marks: 720MDocument20 pagesPhysics: Sec: SR Bipc (Chaina & Elite) Neet Model Date: 30-01-2019 Time: 3 Hrs Grand Test-4 Max. Marks: 720MShivalgiri GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - II (CE-8402) UNIT-3Document29 pagesStrength of Materials - II (CE-8402) UNIT-3Janarthanan BalakrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- Field Work Report on Social Services at Mukono DistrictDocument36 pagesField Work Report on Social Services at Mukono Districtronny rymes tusubira100% (2)
- PILL CAMERA PPT SeminarsDocument7 pagesPILL CAMERA PPT SeminarsVivek P Thoppil100% (2)
- Dynamics of Cage Floating Breakwater: K. MuraliDocument9 pagesDynamics of Cage Floating Breakwater: K. MuraliSuman.SNo ratings yet
- (9781783475537 - The Neuroscience of Organizational Behavior) IntroductionDocument4 pages(9781783475537 - The Neuroscience of Organizational Behavior) IntroductionMiguelNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Reading Student's Book 6Document13 pagesCambridge Primary Reading Student's Book 6Mari Gold0% (1)
- Time Series Analysis: Solutions to Practice ProblemsDocument82 pagesTime Series Analysis: Solutions to Practice Problemsjuve A.No ratings yet
- Method Water QualityDocument8 pagesMethod Water Qualityazilah harisNo ratings yet
- Kesimira Qonita (18930066)Document12 pagesKesimira Qonita (18930066)Kesimira QonitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter No # 03 Product Innovation CharterDocument11 pagesChapter No # 03 Product Innovation CharterabzuarNo ratings yet
- Densification of Granular Soil by Dynamic CompactionDocument13 pagesDensification of Granular Soil by Dynamic CompactionRobertoLazcanoTrejoNo ratings yet
- Advanced 2 - Discourse MarkersDocument6 pagesAdvanced 2 - Discourse Markersmagur-aNo ratings yet
- 1956 Pritchard JJ, Scott JH, Girgis FG. The Structure and Development ofDocument17 pages1956 Pritchard JJ, Scott JH, Girgis FG. The Structure and Development ofplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- List of Gravitationally Rounded Objects of The Solar SystemDocument12 pagesList of Gravitationally Rounded Objects of The Solar Systemsebastian431No ratings yet
- Automotive Lighting System SimulatorDocument14 pagesAutomotive Lighting System SimulatorAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Kajian Pengaruh Variasi Penambahan Bahan Accelerator Terhadap Parameter Beton Memadat Mandiri Dan Kuat Tekan Beton Mutu TinggiDocument7 pagesKajian Pengaruh Variasi Penambahan Bahan Accelerator Terhadap Parameter Beton Memadat Mandiri Dan Kuat Tekan Beton Mutu TinggiHilda NurhelfitrianingsihNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 1 The Compound MicroscopeDocument16 pagesExercise No. 1 The Compound MicroscopeAndRenNo ratings yet
- V2k (Voice To Skull: Download Free PDFDocument43 pagesV2k (Voice To Skull: Download Free PDFLazlo SecretNo ratings yet
- Sendai Framework For DRRDocument19 pagesSendai Framework For DRRAryaaaNo ratings yet
- Dirac (Bra-Ket) Notation/ FormalismDocument5 pagesDirac (Bra-Ket) Notation/ FormalismIjaz TalibNo ratings yet
- Applied SimulationDocument32 pagesApplied SimulationMeşgulRüyalarımıNo ratings yet
- M4 NSTP1Document2 pagesM4 NSTP1Guki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- IGKO Olympiad Sample Question Paper 1 PDF With Answers For Class 3Document15 pagesIGKO Olympiad Sample Question Paper 1 PDF With Answers For Class 3ARITRA MondalNo ratings yet
- Beneficial Utilisation of Sasol Coal Gasification Ash: Martin Ginster and Ratale H. MatjieDocument5 pagesBeneficial Utilisation of Sasol Coal Gasification Ash: Martin Ginster and Ratale H. MatjieAnonymous fS6Znc9No ratings yet
- Aerated Grit Chamber Design ParametersDocument26 pagesAerated Grit Chamber Design ParametersMarc NguyenNo ratings yet
- 71 International Astronautical Congress (Iac) - The Cyberspace Edition, 12-14 October 2020Document8 pages71 International Astronautical Congress (Iac) - The Cyberspace Edition, 12-14 October 2020John DoeNo ratings yet