Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PURPOSIVE
PURPOSIVE
Uploaded by
202202214Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PURPOSIVE
PURPOSIVE
Uploaded by
202202214Copyright:
Available Formats
PURPOSIVE
1. **Definition**: Purposive communication refers to the intentional and goal-oriented exchange of
information to achieve specific objectives or outcomes. It involves conveying messages with clarity,
relevance, and effectiveness to influence, inform, persuade, or engage the audience.
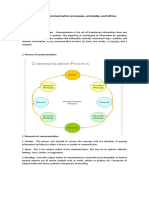
2. **Elements of Purposive Communication**:
- **Sender**: The individual or entity initiating the communication process, responsible for encoding
and transmitting the message.
- **Message**: The information, ideas, or emotions conveyed by the sender to the receiver.
- **Receiver**: The intended audience or recipient of the message, who decodes and interprets the
message.
- **Purpose**: The intended outcome or goal of the communication, which could be to inform,
persuade, entertain, or take action.
- **Channel**: The medium or method used to transmit the message, such as face-to-face interaction,
written documents, digital media, or visual aids.
- **Feedback**: The response or reaction of the receiver to the message, providing valuable
information to the sender and facilitating two-way communication.
- **Context**: The surrounding circumstances or environment in which the communication takes
place, influencing the interpretation and effectiveness of the message.
3. **Types of Purposive Communication**:
- **Informative Communication**: Aimed at providing factual information, explanations, or updates to
educate or clarify understanding.
- **Persuasive Communication**: Seeks to influence attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors by presenting
arguments, appeals, or convincing evidence.
- **Instructional Communication**: Involves giving directions, guidance, or training to instruct others
on how to perform tasks or achieve specific objectives.
- **Transactional Communication**: Focuses on achieving mutual understanding and reaching
agreements in interactions involving exchanges of goods, services, or ideas.
4. **Principles of Effective Purposive Communication**:
- **Clarity**: Ensuring the message is clear, concise, and easily understandable by the intended
audience.
- **Relevance**: Tailoring the message to the interests, needs, and preferences of the audience to
maintain engagement and attention.
- **Credibility**: Establishing trust and credibility by providing accurate information, supporting claims
with evidence, and demonstrating expertise or authority.
- **Adaptability**: Adjusting the communication style, tone, and delivery based on the characteristics
and preferences of the audience.
- **Feedback**: Encouraging feedback and actively listening to the responses of the audience to
assess comprehension, address concerns, and improve future communication.
- **Ethical Considerations**: Respecting the rights, values, and cultural sensitivities of the audience,
and avoiding deceptive or manipulative tactics.
5. **Applications of Purposive Communication**:
- Business communication (e.g., marketing, sales, customer service).
- Academic communication (e.g., lectures, presentations, research papers).
- Public speaking and presentations.
- Interpersonal communication in personal and professional contexts.
By understanding and applying the principles of purposive communication, individuals and organizations
can effectively convey messages, achieve their goals, and build positive relationships with their
audiences.
You might also like
- Let Me See Your Body TalkDocument6 pagesLet Me See Your Body TalkMichael RuesterNo ratings yet
- The Purpose Discovery WorkbookDocument9 pagesThe Purpose Discovery WorkbookAbodunrin Joseph100% (1)
- Adapted Physical Education PDFDocument1,264 pagesAdapted Physical Education PDFSherilyn Em Bobillo94% (17)
- Dan J. Stein - Philosophy of Psychopharmacology - Smart Pills, Happy Pills, and Pep Pills (2008) PDFDocument224 pagesDan J. Stein - Philosophy of Psychopharmacology - Smart Pills, Happy Pills, and Pep Pills (2008) PDFAve ClaudiuNo ratings yet
- First 90 DaysDocument13 pagesFirst 90 Dayssgeorge23100% (3)
- Event Management A New ProfessionDocument7 pagesEvent Management A New ProfessionMustafa Tariq ButtNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Communication in EducationDocument49 pagesCommunication in EducationMakaha RutendoNo ratings yet
- MasturbationDocument17 pagesMasturbationRitesh Chandra17% (6)
- Purposive CommunicationDocument31 pagesPurposive CommunicationPaul Jordan MalateNo ratings yet
- Psychological Capital (Psycap) in Nigeria Adaptation of Luthan's Postive Psychological Capital Questionnaire (Pcq-24) For Nigerian SamplesDocument10 pagesPsychological Capital (Psycap) in Nigeria Adaptation of Luthan's Postive Psychological Capital Questionnaire (Pcq-24) For Nigerian SamplesInternational Journal of Advance Study and Research WorkNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Introduction To CommunicationDocument3 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To CommunicationAlbert Masinde100% (9)
- Communication & Presentation Skills: How to Communicate Effectively in the WorkplaceFrom EverandCommunication & Presentation Skills: How to Communicate Effectively in the WorkplaceNo ratings yet
- Purposes of CommunicationDocument3 pagesPurposes of CommunicationTamil Ka AmutharasanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer DiASsDocument3 pagesReviewer DiASsCruz L AntonioNo ratings yet
- Communication ProcessDocument8 pagesCommunication ProcessMahalakshmi100% (1)
- Purposive CommunicationDocument13 pagesPurposive CommunicationTori Tan100% (1)
- Intro To Public SpeakingDocument7 pagesIntro To Public SpeakingRonald CagampanNo ratings yet
- PC Notes All 5 UnitDocument44 pagesPC Notes All 5 UnitjanhvilkwNo ratings yet
- Comunication PRV Yrs Qtns 12345Document10 pagesComunication PRV Yrs Qtns 12345rajkumarnitesh123No ratings yet
- Mid English WorkDocument7 pagesMid English WorkAsHfAq khanNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication in BusinessDocument2 pagesEffective Communication in BusinessThan Htike SoeNo ratings yet
- Business-communication-Question-SolveDocument67 pagesBusiness-communication-Question-Solvesamaira07islamNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Reviewer MwanDocument2 pagesOral Com Reviewer MwanLasta RainyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document41 pagesLesson 1juliaeduarte6No ratings yet
- Advertisting and Brand ManagementDocument29 pagesAdvertisting and Brand ManagementSantosh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Communication Refers To The Process of Sharing InformationDocument3 pagesCommunication Refers To The Process of Sharing Informationanandkaushik475No ratings yet
- Assignment Naveed Yasin 965Document13 pagesAssignment Naveed Yasin 965naveedyasin1236No ratings yet
- EnglishDocument9 pagesEnglishsarthakraawatNo ratings yet
- Corporate CommunicationDocument17 pagesCorporate CommunicationSanpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Presentation BCDocument44 pagesPresentation BCSubhash SoniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Communication ProcessDocument14 pagesLesson 2 The Communication ProcessNorhaya KalipapaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Muhammad Hendri Kurniawan Prodi: Akuntansi Nim: 212300150Document3 pagesNama: Muhammad Hendri Kurniawan Prodi: Akuntansi Nim: 212300150Ihwan IzzudinNo ratings yet
- DIASS Q2 ReviewerDocument12 pagesDIASS Q2 Reviewerctanedo634No ratings yet
- Unit 2 BM320Document31 pagesUnit 2 BM320osama samiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Asheqin ZafeeraNo ratings yet
- Elements of CommunicationDocument6 pagesElements of CommunicationRoisa JoyNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument4 pagesCommunicationriyo wayneNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument77 pagesBusiness CommunicationFarhanRazaNo ratings yet
- EducationDocument6 pagesEducationAyesha KhiljiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One (Communication Foundation)Document8 pagesChapter One (Communication Foundation)Fatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Revision NotesDocument107 pagesElectrical Engineering Revision Notesabuadano47No ratings yet
- Chapter Two Communication Process PDFDocument17 pagesChapter Two Communication Process PDFAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Main Elements of The Comunication ProcessDocument1 pageMain Elements of The Comunication ProcessRicardo OANo ratings yet
- The Communications Process: Chapter OverviewDocument15 pagesThe Communications Process: Chapter OverviewJatin BhambhuNo ratings yet
- The Theories of Organizational Communication Developed by Claude Shannon and Warren WeaverDocument6 pagesThe Theories of Organizational Communication Developed by Claude Shannon and Warren WeaverAdrian TobonNo ratings yet
- The Theories of Organizational Communication Developed by Claude Shannon and Warren WeaverDocument6 pagesThe Theories of Organizational Communication Developed by Claude Shannon and Warren WeaverAdrian TobonNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal ExplainationDocument12 pagesInterpersonal ExplainationJennifer Maria Suzanne JuanerioNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 CommunicationDocument8 pagesUnit 13 Communicationcvan.tran03No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentSrinu SrinivasNo ratings yet
- The Communication ProcessDocument33 pagesThe Communication ProcessshannoyiaNo ratings yet
- DIASSDocument26 pagesDIASSpascuajanina13No ratings yet
- Business CommunicationsDocument105 pagesBusiness CommunicationsAbdisamed Allaale0% (1)
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1lundubhai010No ratings yet
- Bussiness CommunicationDocument7 pagesBussiness Communicationninjamekwan10No ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument16 pagesBusiness Communicationzachariafrancis3No ratings yet
- Introduction To Effective Oral CommunicationDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Effective Oral CommunicationIanne FabianNo ratings yet
- The 7 CDocument2 pagesThe 7 CNajmus Sahar Saleem SiddiguiNo ratings yet
- Communication Nature, Functions and ScopeDocument25 pagesCommunication Nature, Functions and ScopebasuNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Unit 1Document3 pagesModule 1 - Unit 1Rynkar Uy.No ratings yet
- Sec - Communication in Everyday LifeDocument13 pagesSec - Communication in Everyday LifeMohd kamal saifiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 TCDocument5 pagesUnit 5 TCjarvis123tony123No ratings yet
- GE 5 - Overall Summary.Document6 pagesGE 5 - Overall Summary.Eriane Mae C. SamaneNo ratings yet
- Jean Bernadette O. Sison, I-BSE ENGLISH-A, Purposive CommunicationDocument2 pagesJean Bernadette O. Sison, I-BSE ENGLISH-A, Purposive CommunicationPammieNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Communication Principles Processes and Ethics 3Document33 pagesWeek 1 Communication Principles Processes and Ethics 3rth frtNo ratings yet
- Principles of Social WorkDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Social WorkRocel RoxasNo ratings yet
- Discipline of CommunicationDocument78 pagesDiscipline of CommunicationLheyna AguacNo ratings yet
- Ccs-Unit 1 Concepts of Effective CommuicationDocument16 pagesCcs-Unit 1 Concepts of Effective CommuicationPrajwal Muthanna100% (1)
- Unit II Understanding Communication Process-1Document15 pagesUnit II Understanding Communication Process-1Mohammed ShaffanNo ratings yet
- A Father's MessageDocument6 pagesA Father's Messagejonaz29No ratings yet
- 1.giáo Trình c1 Vstep - Student' S Book-Practice Test-1Document16 pages1.giáo Trình c1 Vstep - Student' S Book-Practice Test-1Hs TonyNo ratings yet
- Research Seminar On Urban Information Systems - SyllabusDocument2 pagesResearch Seminar On Urban Information Systems - SyllabusCoursePinNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Educa On Region III - Central Luzon Schools Division of Tarlac Province Corazon C. Aquino High SchoolDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Educa On Region III - Central Luzon Schools Division of Tarlac Province Corazon C. Aquino High SchoolLuke LucasNo ratings yet
- Brag SheetDocument3 pagesBrag Sheetapi-337682376No ratings yet
- Likhith Kumar C MIT Daily Reporting Format-3Document2 pagesLikhith Kumar C MIT Daily Reporting Format-3Madhusudhan M LNo ratings yet
- Wiring YourbrainDocument1 pageWiring Yourbrainapi-285116042No ratings yet
- Public SpeakingDocument3 pagesPublic SpeakingNirvana OshoNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Indian Society, Diversity in IndiaDocument3 pagesSalient Features of Indian Society, Diversity in IndiaVinit KuwareNo ratings yet
- Addressing Ways of Social InequalitiesDocument28 pagesAddressing Ways of Social InequalitiesSherra Mae NarcisoNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument8 pagesThe Problem and Its BackgroundHamdiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Topic C-Grade 5Document2 pagesModule 1 Topic C-Grade 5api-293753588No ratings yet
- Inspiring Every ChildDocument64 pagesInspiring Every ChildHajrart100% (1)
- Give Your OpinionsDocument3 pagesGive Your Opinions'Al-Ghazali Abu HamidNo ratings yet
- P614 625Document12 pagesP614 625city9848835243 cyberNo ratings yet
- The Agape ProjectDocument23 pagesThe Agape Projectapi-583455523No ratings yet
- Reebok Case StudyDocument2 pagesReebok Case StudySunil Kumar0% (1)
- Indirect Methods of Recruitment - HRDocument18 pagesIndirect Methods of Recruitment - HRAnita Andrew0% (2)
- Advanced Accounting - Volume 1Document4 pagesAdvanced Accounting - Volume 1Samantha Cabugon23% (26)
- Assessment of Learning 2Document3 pagesAssessment of Learning 2Mark Lester Asher RedricoNo ratings yet
- Coaching, Career and Talent ManagementDocument13 pagesCoaching, Career and Talent ManagementCindy KusumaNo ratings yet