Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.5 Cloning
3.5 Cloning
Uploaded by
ehodariCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.5 Cloning
3.5 Cloning
Uploaded by
ehodariCopyright:
Available Formats
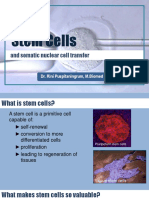
Topic 3.
5: CLONING
Clones
Clones are groups of genetically identical organisms, derived from a single original parent cell
• Various methods of cloning exists for animals and plants, while humans can also clone organisms or tissues artificially
Animal Cloning Human Cloning
Binary Fission Humans can also produce clones via natural mechanisms
• The parental organism divides equally into two clones • Identical twins (monozygotic) are created when fertilised
• Occurs in flatworms (also used by bacteria and protists) eggs split in two, forming two identical embryos
Budding
MONOZYGOTIC TWINS
• Cells split off from parent, generating smaller clones
• Occurs in Hydra, but is also common to yeast
Fragmentation
• New organisms grow from separated fragment of parent
• Common to starfish and some species of annelid worm Zygote
splits
Parthenogenesis Genetically Shared
• Embryos formed from an unfertilised (diploid) ova identical placentas
• Occurs in some species of fish, insect, reptile, amphibian
Plant Cloning
Plants have the capacity for vegetative propagation, whereby small pieces of plant can be induced to grow independently
• This is because adult plants possess totipotent meristematic tissue capable of cellular differentiation
A stem cutting is a separated portion of a plant stem that is used to regrow a new clone via vegetative propagation
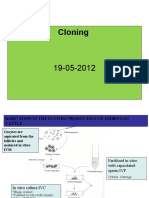
Artificial Cloning
Embryo Cloning Adult Cloning
• Animals can be cloned from an embryo by separating the • Adults can be cloned via the process of somatic cell
embryonic cells into groups nuclear transfer (SCNT)
• As embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, each cell can • The nucleus is removed from an adult body cell (diploid)
potentially form a cloned offspring and fused with an enucleated egg cell
• As this method occurs after random fertilization, it is not • An electric shock stimulates division of the egg cell and
possible to control the genetic features of potential clones the growing embryo is implanted into a surrogate
UV
Early embryo
(identical cells)
Egg cell
enucleated
Clone
Adult cells Nuclei
Clone Clone cultured removed
You might also like
- Clones 19.02.17Document1 pageClones 19.02.17Amos SharpNo ratings yet
- Bioteknologi 110-Stem CellsDocument14 pagesBioteknologi 110-Stem CellsNahla FaridaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell and Its Clinical ImplicationsDocument85 pagesStem Cell and Its Clinical Implications11101955No ratings yet
- Stem Cell Presentation Revised September 2015Document28 pagesStem Cell Presentation Revised September 2015nazım tekerNo ratings yet
- MM2 Cellular DifferentiationDocument2 pagesMM2 Cellular DifferentiationSafiya James100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Unit 3Document16 pagesChapter 2 Unit 3kumar siddhantNo ratings yet
- Subject: Biology Chapter 8: How Do Organisms Reproduce?: Q.1 What Is Reproduction?Document16 pagesSubject: Biology Chapter 8: How Do Organisms Reproduce?: Q.1 What Is Reproduction?AadiveerNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell BasicsDocument73 pagesStem Cell BasicsrosesamanthaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cloning: Artificial Clones in Animals, and A Comparison of Reproductive and Non-Reproductive CloningDocument2 pagesAnimal Cloning: Artificial Clones in Animals, and A Comparison of Reproductive and Non-Reproductive CloningNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Cleavage: The Main Process of Animal DevelopmentDocument123 pagesCleavage: The Main Process of Animal DevelopmentNUR ASMA RIZKYNo ratings yet
- Animal CloningDocument33 pagesAnimal CloningAndi RohandiNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesStem Cells Reading ComprehensionRofi GENo ratings yet
- To Clone or Not To CloneDocument10 pagesTo Clone or Not To CloneShrey SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument34 pagesStem Cells18UGBT055 Surya PrabhaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument34 pagesCell CycleAbi Garcia MolinaNo ratings yet
- Cloning and EthicsDocument9 pagesCloning and EthicsivanaNo ratings yet
- 1-Embryonic-Stem-Cells 1ST LECDocument31 pages1-Embryonic-Stem-Cells 1ST LECrihamazim2018No ratings yet
- Both Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Involve Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesBoth Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Involve Cell DivisionYaneth VargasNo ratings yet
- Explants: Irisan Organ Tanaman Yang Telah Disteril Yang Digunakan Sebagai Bahan Tanam Awal Dalam Kultur in VitroDocument48 pagesExplants: Irisan Organ Tanaman Yang Telah Disteril Yang Digunakan Sebagai Bahan Tanam Awal Dalam Kultur in VitroGerii PitaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument31 pagesMitosis and MeiosisFarah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - The Cell CycleDocument13 pagesLecture 7 - The Cell CycleDequanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - The Cell CycleDocument13 pagesLecture 7 - The Cell CycleDequanNo ratings yet
- Natural Cloning in Animal and PlantsDocument38 pagesNatural Cloning in Animal and PlantsRaniya Khan [Student]No ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument22 pagesPerpetuation of LifeJane Arsus D. DiazNo ratings yet
- CloningDocument11 pagesCloningCindy González100% (1)
- Cloning Technology-Bane or Boon To MankindDocument52 pagesCloning Technology-Bane or Boon To MankindDevain AroraNo ratings yet
- BIO 1 - Module 3Document11 pagesBIO 1 - Module 3kiaraNo ratings yet
- CloningDocument17 pagesCloningPirin Pin PinNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells 1 - Forsyth - 2016Document39 pagesStem Cells 1 - Forsyth - 2016ubaidu dikkoNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell TechnologyDocument16 pagesStem Cell Technologybhaskar sarmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Differentiation: Keynote Speaker: Guan HaiyanDocument46 pagesCell Differentiation: Keynote Speaker: Guan Haiyanthri zonartiNo ratings yet
- Cloning TechniquesDocument2 pagesCloning TechniquesAiman RazaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument31 pagesMitosis and MeiosisDana AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cell SpecialisationDocument1 page1.1 Cell SpecialisationamandineNo ratings yet
- Cloning1Document16 pagesCloning1HarmanWaliaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell-2022-Part-1Document20 pagesStem Cell-2022-Part-1ManikyaMayankNo ratings yet
- Reference Material I 29Document53 pagesReference Material I 29Maru Mengesha Worku 18BBT0285No ratings yet
- Exercise 3 - Embryology LabDocument3 pagesExercise 3 - Embryology LabIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Introduction To Stem CellsDocument12 pages2.3 Introduction To Stem CellsNicholasNo ratings yet
- 10.5 Whole Organism Cloning in Animals COMPLETEDDocument4 pages10.5 Whole Organism Cloning in Animals COMPLETEDhixpatchNo ratings yet
- Cells 1.1-1.4Document6 pagesCells 1.1-1.4bommoNo ratings yet
- 04 STS - Stem CellsDocument44 pages04 STS - Stem CellsAlyza Ashley Tan GallardoNo ratings yet
- Approaching The Topic: Cells: Unit 1Document13 pagesApproaching The Topic: Cells: Unit 1tychrNo ratings yet
- The Role of Reproduction (Part 2)Document8 pagesThe Role of Reproduction (Part 2)Savannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Therapy PDFDocument64 pagesStem Cell Therapy PDFyusuf fathoniNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Cloning, Embyo Stem Cell TechnologiesDocument38 pagesMammalian Cloning, Embyo Stem Cell TechnologiesYash KumarNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument50 pagesCell Cyclesuemie100% (2)
- Cloning of CELLDocument43 pagesCloning of CELLsashaikh1213No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 NRODocument27 pagesLecture 10 NROAnindita MishiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY REVIEWE-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesBIOLOGY REVIEWE-WPS OfficeLeanna DaneNo ratings yet
- CloningDocument13 pagesCloningMA. ALYZANDRA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Stem Cell TechnologyDocument37 pagesIntroduction of Stem Cell TechnologySavitaNo ratings yet
- 4 Science 2 RPK - Chap 5 Cell Division (Part 1)Document58 pages4 Science 2 RPK - Chap 5 Cell Division (Part 1)zanayanNo ratings yet
- Cloning - Human CloningDocument17 pagesCloning - Human CloningAbdur RashidNo ratings yet
- Cell ReproductionDocument62 pagesCell ReproductionLuca DJNo ratings yet
- Animal CloningDocument19 pagesAnimal CloninghyudaristyNo ratings yet
- Zoo301lex2 4 Intros Alviar2017Document2 pagesZoo301lex2 4 Intros Alviar2017Mary Rose SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Cellular ReproductionDocument6 pagesLec 4 Cellular ReproductionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Medicine: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationDocument24 pagesKrok 1 Medicine: Test Items For Licensing Examinationbose_lowe11No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 BOT1LDocument6 pagesChapter 5 BOT1LLovely BalambanNo ratings yet
- The Story of Life: Chapters 7-12 (Evolution) : Thorough With Your Answers! 12points!Document3 pagesThe Story of Life: Chapters 7-12 (Evolution) : Thorough With Your Answers! 12points!Majeda Abdul-JabbaarNo ratings yet
- Study Master Life Sciences Teachers Guide Grade 11 9781107380530ARDocument229 pagesStudy Master Life Sciences Teachers Guide Grade 11 9781107380530ARSimphiwe MpanzaNo ratings yet
- MCQ S EcosystemsDocument6 pagesMCQ S EcosystemsShilajit BaruaNo ratings yet
- What Is Wrong With The Metaphor of Orchids and Dandelions?Document5 pagesWhat Is Wrong With The Metaphor of Orchids and Dandelions?Daniel HowardNo ratings yet
- Nonverbal Communication (1) : Baden EunsonDocument31 pagesNonverbal Communication (1) : Baden EunsonLaiba UzairNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Viruses and Viral Pathogenesis 1Document37 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Viruses and Viral Pathogenesis 1Gabriella CrooksNo ratings yet
- Dawn - paramount.claim.K.K.V5 - DNADocument2 pagesDawn - paramount.claim.K.K.V5 - DNADawn GillisonNo ratings yet
- 03 PharmacometabolomicsDocument11 pages03 PharmacometabolomicsVanessa CarreraNo ratings yet
- Initiate at Buy: Democratizing Synthetic Biology For The MassesDocument34 pagesInitiate at Buy: Democratizing Synthetic Biology For The MassesxueNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Topic 2 QuestionsDocument20 pagesBiology Unit 1 Topic 2 QuestionsMSB Nairobi Academic AdminNo ratings yet
- Outline Cell StructureDocument5 pagesOutline Cell StructureDING ANG BATONo ratings yet
- III Sem Dec-23 Backlog Only 04-12-2023Document8 pagesIII Sem Dec-23 Backlog Only 04-12-2023vepoga6663No ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL & Ic - LTC Neet Grand Test - 10 Paper (02-05-18)Document24 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL & Ic - LTC Neet Grand Test - 10 Paper (02-05-18)Ashutosh PathakNo ratings yet
- Microbial Pathogenesis: Amin - Bakir@hmu - Edu.krdDocument16 pagesMicrobial Pathogenesis: Amin - Bakir@hmu - Edu.krdAsma Muhammed majeedNo ratings yet
- Oral CA Lec (Compatibility Mode)Document48 pagesOral CA Lec (Compatibility Mode)Abubakar sadiqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal PhysiologyDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Animal Physiologyollie tikaNo ratings yet
- Rumah Sakit Umum Muhammadiyah Siti AminahDocument15 pagesRumah Sakit Umum Muhammadiyah Siti AminahLABRSU MUHANo ratings yet
- TUGAS LAPORAN LITERASI BAHASA INGGRIS SEMESTER GenapDocument8 pagesTUGAS LAPORAN LITERASI BAHASA INGGRIS SEMESTER Genapannanta mahassyahNo ratings yet
- Fig. 1 Fig. 1: Correspondence Pathology (2019), 51 (4), JuneDocument3 pagesFig. 1 Fig. 1: Correspondence Pathology (2019), 51 (4), JuneDiego TulcanNo ratings yet
- Polish - English TaskDocument5 pagesPolish - English TaskdaranNo ratings yet
- Segment of DNA Found On Chromosomes That Determines The Inheritance of A Particular TraitDocument9 pagesSegment of DNA Found On Chromosomes That Determines The Inheritance of A Particular TraitJan IceNo ratings yet
- WBI11 01 Que 20190108Document32 pagesWBI11 01 Que 20190108Hadi El HadiNo ratings yet
- Class II Malocclusion: Etiology and DiagnosisDocument19 pagesClass II Malocclusion: Etiology and Diagnosissaradagirish100% (1)
- Into To Soft ComputingDocument20 pagesInto To Soft Computingpallavi shimpiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Aminoacids. Peptides. ProteinsDocument33 pagesLecture 1 - Aminoacids. Peptides. ProteinsEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- Question Booklet & Answer Key For The Recruitment Test of Microbiologist Held On 11.8.2013Document9 pagesQuestion Booklet & Answer Key For The Recruitment Test of Microbiologist Held On 11.8.2013Naivy SidhuNo ratings yet
- BCC - DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Lecture 20Document31 pagesBCC - DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Lecture 20AmyNo ratings yet
- JAC Board Important Questions For Botany - Unit 3Document5 pagesJAC Board Important Questions For Botany - Unit 3AbhishekChowdhuryNo ratings yet