Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ALKANE IUPAC Nomenclature
Uploaded by
Lozada DenverOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ALKANE IUPAC Nomenclature
Uploaded by
Lozada DenverCopyright:
Available Formats
What are Carbon Compounds?
Carbon compounds are present everywhere in the food that we eat, the clothes that we wear and even in the lead of
the pencil by which we write. The atomic number of carbon is 6 and the atomic mass is 12.01gmol-1. Carbon is a
member of the 14th group. According to the data, it is the seventeenth most abundant element found on earth.
Carbon: Unique Among the Elements
Two scientists may be singled out for their important contributions to our understanding of carbon and its compounds.
1. Friedrich August Kekule von Stradonitz - was a German organic chemist. He proposed that carbon forms four
covalent bonds. He also postulated that carbon atoms bond to each other, forming long chains of such atoms.
2. Jacobus van’t Hoff – proposed that in compounds carbon forms a tetrahedral structure, with the carbon atom at the
center of the tetrahedron. It is a testament to the great insight of these scientists that their predictions, made over 50
years before techniques and instrumentation were available to verify them.
Hydrocarbon is a compound consisting of only hydrogen and carbon.
The carbon to carbon can be single, double, or triple bonds. The bonds are always nonpolar.
• Saturated hydrocarbons – contain a single bond.
• Unsaturated hydrocarbons – contain a double and triple bond.
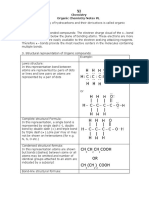
Classification of Hydrocarbons
Unsaturated Unsaturated
Types of Structural Formula
Carbon-to-carbon chains can be:
(A) Straight
(B) Branched
(C) in a closed ring. (Some carbon bonds are drawn longer, but are actually the same length.)
A. molecular formula describes the numbers of different kinds of atoms in a molecule
B. structural formula represents a two-dimensional model of how the atoms are bonded to
each other. Each dash represents a bonding pair of electrons.
Alkanes - are hydrocarbons with only single bonds. Alkanes occur in what is called a
homologous series.
• Each successive compound differs from the one before it only by a CH2
Rules in Naming alkanes:
1. Identify the longest continuous chain.
2. The locations or other groups of atoms attached to the longest chain are identified and numbered by counting from
the end of the molecule which keeps the numbering system as low as possible.
3. Hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the longest continuous chain and named using the parent name and
changing the –ane suffix to –yl.
Prefixes: 1- meth 6-hex
2- eth 7-hept
3-prop 8-oct
4-but 9-non
5-pent 10-dec
4. In some organic compounds, we find the same group occurring more than once on a carbon chain. In this case, we
use a prefix to indicate how often the same group occurs.
5. Sometimes, we find non-alkyl groups attached to carbon atoms. Quite often these will be halogens – Cl, Br, I and F.
These are also named from their position along the carbon chain as in the following example.
Compounds that have the same molecular formula, but different structures (arrangements of the atoms) are
called isomers.
You might also like
- Why Are Chemicals Not Named John? Naming Chemical Compounds 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Are Chemicals Not Named John? Naming Chemical Compounds 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds EditedDocument52 pagesOrganic Compounds EditedbrendonNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesOrganic Chemistrylokeshshetty723No ratings yet
- Saturated Hydrocarbons ReviewerDocument15 pagesSaturated Hydrocarbons ReviewerViaBNo ratings yet
- Leaning Packet 6 Engg Chem 1Document42 pagesLeaning Packet 6 Engg Chem 1Ritchel Conde BoholNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Full Chapter 2022-23Document39 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Full Chapter 2022-23aarishsaifi9811100% (2)
- Intro To Organic Chemistry 2022 Sep 9Document59 pagesIntro To Organic Chemistry 2022 Sep 9SanaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Biochemistry of Life: Chapter 4: Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of LifeDocument44 pagesUnit 2 - Biochemistry of Life: Chapter 4: Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of LifeJeremy CorrenNo ratings yet
- Organic Che-Some Basic PrinciplesDocument20 pagesOrganic Che-Some Basic PrinciplesFarhan Al ZayedNo ratings yet
- 1) Reading Material by Nvs TeacherDocument34 pages1) Reading Material by Nvs Teacherjkc collegeNo ratings yet
- SHREYAAYAKRYFYHURFYGFUGRDocument36 pagesSHREYAAYAKRYFYHURFYGFUGRShreyansh NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Carbon and Its Compounds: Covalent BondsDocument9 pagesChapter - 4 Carbon and Its Compounds: Covalent BondsMaheshNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 - AlkanesDocument10 pagesModule 3.1 - AlkanesNigel HopeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: 1. Organic Chemistry Is The Study of Carbon CompoundsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry: 1. Organic Chemistry Is The Study of Carbon Compoundsreadsalot2012No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2023Document26 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2023sameerakhan8912No ratings yet
- 11chemistry - Organic chemistry-Notes&VLDocument14 pages11chemistry - Organic chemistry-Notes&VLPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture OutlineDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture OutlineMike LockNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: (Part One)Document104 pagesOrganic Chemistry: (Part One)eltoumNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument45 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesJasmine Sloan100% (1)
- Chapter 1 OrganicDocument64 pagesChapter 1 OrganicCatherine VenturaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryEll LynaNo ratings yet
- Mod1 1. Structure and FormulaeDocument50 pagesMod1 1. Structure and FormulaeAntonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument34 pagesOrganic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniquestannie2512No ratings yet
- Orgchem Module Edit 2Document74 pagesOrgchem Module Edit 2Nur-aine HajijulNo ratings yet
- IUPACDocument21 pagesIUPACMihir DhankarNo ratings yet
- SCH4C Organic Chemistry Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesSCH4C Organic Chemistry Cheat SheetSteve M HallNo ratings yet
- CARBON@10Document7 pagesCARBON@10kartikroy0116No ratings yet
- CAPE Unit 2 Chemistry NotesDocument207 pagesCAPE Unit 2 Chemistry NotesAshley Cunningham100% (2)
- Module 1. The Chemistry of Carbon Compounds TOPIC: Structure and FormulaeDocument38 pagesModule 1. The Chemistry of Carbon Compounds TOPIC: Structure and FormulaeOrlanda EllisNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument7 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsMoomin Ahmad DarNo ratings yet
- Session 7Document6 pagesSession 7anthonygchamiNo ratings yet
- CarbonDocument17 pagesCarbonkulbantsingh1507No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Text Book 111CHEMDocument74 pagesOrganic Chemistry Text Book 111CHEMyyoosafe23No ratings yet
- Goc 1641795035Document30 pagesGoc 1641795035joeNo ratings yet
- Basic Organic ChemistryDocument62 pagesBasic Organic ChemistrySempija AaronNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument25 pages2.4 Introduction To Organic ChemistryMin YoonjiNo ratings yet
- 10.1 - Introduction To Organic Chemistry PDFDocument9 pages10.1 - Introduction To Organic Chemistry PDFVũ Đức DuyNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument44 pagesCarbon CompoundriverarafaelljamesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument29 pagesChapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Organic ChemistryDocument92 pagesBasic Concepts in Organic Chemistrymithunkrish2222No ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry Unit 2 ReviewDocument7 pagesCape Chemistry Unit 2 Reviewkayanna100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Definitions Term 3Document4 pagesSTPM Chemistry Definitions Term 3ChooNo ratings yet
- CHMDocument12 pagesCHMgabrf.pascualNo ratings yet
- Kaysonseducation-Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesKaysonseducation-Organic Chemistryankit singhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry - Lecture 1Document59 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry - Lecture 1Humayer MahmudNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 Organic ChemistryDocument51 pagesUNIT 10 Organic ChemistryTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- (8.1) Learning MaterialDocument41 pages(8.1) Learning MaterialLuna VasquezNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument14 pagesOrganic ChemistryStuteeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 12 Cheat SheetDocument25 pagesOrganic Chemistry 12 Cheat SheetVanessa MurphyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Organic Chemistry: 1 Introduction (From Morrison and Boyd)Document17 pagesChapter 4: Organic Chemistry: 1 Introduction (From Morrison and Boyd)DavidNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compound PDFDocument5 pagesCarbon and Its Compound PDFAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Organic I (Chapter 1)Document45 pagesChapter 1 Organic I (Chapter 1)ahmedmustefa773No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument43 pagesHydrocarbonsdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Qt. 2 Week 5Document31 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Qt. 2 Week 5Nina Reca OmisolNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument67 pagesWeek 3 Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesNikol BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds: Presenter: Shannon SmithDocument61 pagesCarbon Compounds: Presenter: Shannon SmithShannon SmithNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques - WatermarkDocument29 pagesOrganic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques - WatermarkPrathviraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Tut Organic ChemistryDocument57 pagesTut Organic ChemistryThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument29 pagesChemistryappugmenonNo ratings yet
- Question WI..Document42 pagesQuestion WI..Indra MansyahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change 7th Edition Silberberg Test BankDocument16 pagesChemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change 7th Edition Silberberg Test Banka4645830560% (1)
- Chemical Engineering BasicsDocument32 pagesChemical Engineering Basicscallielizza100% (5)
- 10 Science t2 sp01Document8 pages10 Science t2 sp01adityasharma6261srNo ratings yet
- Chemistry QuestionsDocument69 pagesChemistry QuestionsChris Pecasales100% (1)
- Cameron Tree Selection Guide - Corrosion at The Wellhead PDFDocument37 pagesCameron Tree Selection Guide - Corrosion at The Wellhead PDFOsama100% (1)
- 0620 s11 QP 22 PDFDocument16 pages0620 s11 QP 22 PDFArasiveluNo ratings yet
- Gas Quality Specifications Fact SheetDocument2 pagesGas Quality Specifications Fact SheetPham LanphuongNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test in Science and HealthDocument1 pageThird Periodical Test in Science and Healthcindy_villamor4308100% (6)
- 01-Operating Manual For 1200 MTPD Ammonia Plant PDFDocument315 pages01-Operating Manual For 1200 MTPD Ammonia Plant PDFAbdulla100% (4)
- Science 8 - Supplementary Lecture Material On Matter (2022-2023)Document152 pagesScience 8 - Supplementary Lecture Material On Matter (2022-2023)Alexis ParcoNo ratings yet
- 018 - 3E - Paper Api 941 AcidenteDocument10 pages018 - 3E - Paper Api 941 AcidenteRicardo BarciaNo ratings yet
- AcetyleneDocument13 pagesAcetyleneImtiaz AliNo ratings yet
- Graphite Data SheetDocument16 pagesGraphite Data Sheetprabin kumar ashishNo ratings yet
- Journal of The Energy Institute: SciencedirectDocument9 pagesJournal of The Energy Institute: SciencedirectChairina SinagaNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Gen Chem 1Document21 pagesSemester 1 Gen Chem 1F. Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Pms 2019 PaperDocument10 pagesPms 2019 PaperarshadNo ratings yet
- Casimiro A. Ynares Sr. Memorial National High School: MM MM MMM MM MM MDocument7 pagesCasimiro A. Ynares Sr. Memorial National High School: MM MM MMM MM MM MIrah PradoNo ratings yet
- Company Profile C Analytics 2018 10 22Document10 pagesCompany Profile C Analytics 2018 10 22awfahaddadinNo ratings yet
- Candle Science - National Candle AssociationDocument3 pagesCandle Science - National Candle AssociationCheahsin TanNo ratings yet
- An Automated Media Fill Microbial InspectionDocument4 pagesAn Automated Media Fill Microbial InspectionTorres XiaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Practice QuestionsBen BarnesNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education ChemistryDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education ChemistryVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Standard Test Method For Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of Petroleum ProductsDocument9 pagesStandard Test Method For Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of Petroleum ProductsGregorio ToroNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class XI Chemistry Sample Paper - 3 Solution Section ADocument13 pagesCbse Class XI Chemistry Sample Paper - 3 Solution Section ABhabaniNo ratings yet
- Summative TestDocument2 pagesSummative TestMark CabaluNo ratings yet
- 0418 2017 Keshe Foundation Cancer Blueprint Annouceenment 1st Draft LynnDocument95 pages0418 2017 Keshe Foundation Cancer Blueprint Annouceenment 1st Draft LynnbardocgrNo ratings yet
- Amines PDFDocument1 pageAmines PDF최승원No ratings yet
- James P. Hogan - Inherit The Stars PDFDocument127 pagesJames P. Hogan - Inherit The Stars PDFWardion2000100% (1)
- Science CFA - Energy TransferDocument6 pagesScience CFA - Energy TransferHelina AmbayeNo ratings yet