Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Muscular System Tutorial Worksheets-1
Uploaded by
Tina HussainiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Muscular System Tutorial Worksheets-1
Uploaded by
Tina HussainiCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy and Physiology Systems 1
1016MSC T1 2023
Module 2 Muscular System
Tutorial Worksheets
Module 2: Muscular system: Topics 2.1, 2.2, 2.3
1
Module 2: Muscular System
2.1: Nature of the muscular system and terminology
Label the connective tissue layers marked on the following diagram.
A Epimysium
B Blood Vessel
A C Perimysium
D Endomysium
E Muscle Fibre
B
C
D
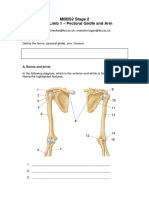
Label the actions occurring at the shoulder joint below.
A B
A ________________________________
Flexion B _______________________________
Extension
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
2
Answer the following questions regarding muscle tissue.
1. Name the connective tissue layer surrounding a bundle of muscle fibres
____________________________________________________________________
Perimysium
2. Identify 3 types of muscle tissue and where you would find them.
a) __________________________________________________________________
Sternocleiodomastoid = Neck
b) __________________________________________________________________
Obicularis Oris = Mouth
c) __________________________________________________________________
Obicularis Oculi = Eye
3. Which muscles work together to perform the same task? _______________________
4. Fixation involves muscles from both compartments acting to ______________ joints.
5. Within opposing pairs of muscles, one muscle called the ______________________
contracts to cause an action, while the other muscle called the __________________
yields or stretches to the action of the agonist.
6. In which part of the body would the following muscles be found?
Orbicularis oculi? ______________________________________________________
Eye
Rectus abdominis? Abdomin
_____________________________________________________
Tibialis anterior? _______________________________________________________
Lower limb
Sternocleidomastoid? Neck
___________________________________________________
Quadriceps femoris? ____________________________________________________
Pelvic Region
7. ______________________
Fixators contract and stabilise intermediate joints to aid the action
of the prime mover.
8. Give an example of a multipennate muscle. __________________________________
Deltoid
9. Give an example of a fusiform muscle. _____________________________________
Bicepts Brachii
10. Describe the appearance of a skeletal muscle cell. ____________________________
Striated, long, cylindrical,
_____________________________________________________________________
multinucleate
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
3
2.2: Muscles of the face, neck, trunk and abdomen.
Answer the following questions.
1. Which muscles elevate the mandible? _________________
Masseter and ____________________
Temporalis
2. Which of these is the prime mover? ___________________________________________
Masseter
3. Sternocleidomastoid is the prime mover for flexion of the head at the atlanto-occipital
joint. If only one sternocleidomastoid contracts, which movements occur?
__________________________________
Ipsilateral Flexion and __________________________________
Contralateral rotation
4. Name 2 facial muscles in which the muscle fascicles have a sphincter arrangement.
________________________________ and ____________________________________
5. Name 2 muscles that act synergistically to help you smile.
________________________________
Obicularis Oculi and ____________________________________
Zygomaticus major
6. Name 3 key muscles that help you to chew food.
1. _____________________________________________________________________
Temporalis
2. _____________________________________________________________________
Masseter
3. _____________________________________________________________________
Buccinator
7. Which of these 3 muscles is the principal muscle of the cheek? _____________________
Buccinator
8. Splenius muscles act as antagonists to sternocleidomastoid in head flexion, but are prime
movers for head extension. What movements are caused by unilateral splenius
contraction? __________________________ and _______________________________
9. What function do the Erector Spinae muscles perform?
________________________________________________________________________
Move the vertebral column
10. Contraction of one Quadratus Lumborum results in which movement(s)?
________________________________________________________________________
11. Unilateral contraction of the abdominal muscles does what?
________________________________________________________________________
12. What type of tissue is the linea alba made of?
________________________________________________________________________
Collagen and elastic fibrous connective tissue
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
4
Label the 3 columns of muscles that form the ‘erector spinae’ muscles.
Spinalis Thoracis
Longissimus
Iliocostalis Lumborum
Label the 4 pairs of abdominal muscles. What is their function as a group?
A External oblique
A B Rectus Abdominis
C Internal Oblique
D B D Transversus Abdominis
C Function
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
5
2.3: Muscles of the upper limb
Match the muscle of the upper limb with its function. eg: 3f
1 Infraspinatus a Scapula adduction 1K
2 Levator scapulae b Elbow flexion (with forearm semipronated) 2d
3 Biceps brachii c Wrist flexion + abduction 3f
4 Rhomboids d Scapula elevation + adduction 4a
5 Pectoralis major e Shoulder abduction + rotator cuff stability 5m
6 Triceps brachii f Elbow flexion + supination 6H
7 Brachioradialis g Shoulder flexion + adduction 7B
8 Flexor carpi radialis h Elbow extension 8
C
9 Supraspinatus i Shoulder extension + adduction + medial rotation 9E
10 Extensor digitorum j Shoulder flexion + abduction + extension 10l
11 Latissimus dorsi k Shoulder lateral rotation + rotator cuff stability 11i
12 Deltoid l Wrist + finger extension 12j
13 Coracobrachialis m Shoulder flexion + adduction + medial rotation 13g
Answer the following questions.
1. Which muscle situated on the anterior thoracic wall acts as a synergist for abduction
of the scapula and is known as the boxer’s muscle? _________________________
Serratus anterior
2. Name 2 muscles of the anterior upper limb compartment that abduct the scapulae.
a) __________________________________________________________________
b) __________________________________________________________________
3. Name 2 muscles of the posterior upper limb compartment that adduct the scapulae.
a) __________________________________________________________________
b) __________________________________________________________________
4. Which actions of the shoulder and elbow are involved in a push-up (starting point
flat on the ground)?
a) __________________________________________________________________
Horizontal adduction (Bringing your arms to the midline of the body)
b) __________________________________________________________________
Elbow extensions (Straightening your arm)
5. Which muscles are involved in performing these actions during the push-up?
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
6
Clinical application:
Tennis elbow
lateral epicondylalgia - lateral elbow pain
tenderness over the lateral epicondyle of
humerus
pain with resisted wrist extension
aggravated by repetitive gripping and
extension activities
common in tennis players, manual workers
http://sporteology.com/top-10-greatest-female-tennis-players-of-all-time/
http://sporteology.com/top-10-greatest-femalhttp://www.bouncephysiobirkdale.com.au/health-tips/tennis-elbow/e-tennis-players-of-all-time/
http://www.dailyherald.com/article/20151006/sports/151009278/
Golfer’s elbow http://www.talarmade.com/topic/85-treatment-for-golfers-elbow.aspx
medial epicondylalgia - medial elbow pain
tenderness over the medial epicondyle of humerus
pain with resisted wrist flexion and repetitive flexion activities
common in golfers, baseball pitchers and climbers
http://www.wildermanphysicaltherapy.com/what-you-need-to-know-about-golfers-elbow-medial-epicondylitis-and-why-you-should-seek-out-a-physical-therapist-first/
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
7
Carpal tunnel
created by
flexor retinaculum anteriorly
carpal bones posteriorly
Carpal tunnel syndrome
narrow passageway in wrist through which flexor
tendons and median nerve pass
inflammation of structures in tunnel place pressure on
median nerve, tendons and blood vessels
pain, weakness and/or numbness in the hand and wrist
caused by:
writing or keyboard typing
gymnastics, cycling, golf, tennis
using screwdrivers or hand tools that vibrate
repetitive heavy lifting
driving
http://blog.prochoice.com.au/ohs/carpal-tunnel-syndrome-are-you-at-risk/ http://www.repetitive-strain.com/ctsindex.html
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
8
Answer the following questions.
1. In which compartment would you find the wrist extensors?
_____________________________________________________________________
2. Which muscles are involved in shoulder extension?
_____________________________________________________________________
3. Name the common condition caused by overuse of the wrist extensor muscles.
_____________________________________________________________________
4. Where is pain in this condition primarily located?
_____________________________________________________________________
5. Explain the underlying cause for ‘Golfer’s elbow’.
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
6. What is the anatomical name for this condition?
_____________________________________________________________________
7. In which compartment would you find flexor carpi radialis?
_____________________________________________________________________
8. In which compartment would you find the middle deltoid fibres?
_____________________________________________________________________
9. What is the role of extensor indicis and describe where it is located?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
10. What symptoms would someone diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome experience?
Explain why by describing the specific anatomical structures involved and how they
would be affected.
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
9
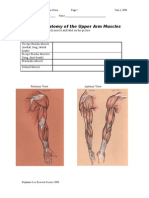
Label as many muscles as you can on the following diagrams.
A. Sternocleidomastoid H. Supraspinatus N. Extensor carpi radialis longus
B. Deltoid I. Infraspinatus O. Extensor carpi radialis brevis
C. Biceps brachii J. Triceps brachii P. Extensor carpi ulnaris x 2
D. Pectoralis major K. Latissimus dorsi Q. Flexor carpi radialis
E. Serratus anterior L. Teres major R. Flexor carpi ulnaris
F. Brachialis M. Teres minor S. Extensor digitorum
G. Brachioradialis x 3 T. Palmaris longus
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
10
Module 2: Muscular system: Topics 2.4, 2.5
2.4: Muscles of the lower limb and selected muscles
Match the muscle of the lower limb with its function. eg:
12f
1 Adductor magnus a Hip adduction 1A
2 Tibialis posterior b Hip abduction + medial rotation 2L
3 Gluteus maximus c Ankle eversion 3K
4 Rectus femoris d Hip flexion + external rotation + abduction 4H
5 Semitendinosus e Hip extension + Knee flexion (medial insertion) 5E
6 Fibularis longus f Toe flexion 6C
7 Sartorius g Hip extension + Knee flexion (lateral insertion) 7D
8 Tibialis anterior h Hip flexion + Knee extension 8M
9 Soleus i Ankle plantarflexion + Knee flexion 9J
10 Biceps femoris j Ankle plantarflexion 10G
11 Gastrocnemius k Hip extension 11J
12 Flexor digitorum longus l Ankle inversion + plantarflexion 12f
13 Gluteus medius m Ankle dorsiflexion + Foot inversion 13B
Name the compartment that each of these muscles of the lower limb is found in?
Anterior Posterior Medial Lateral
1 Adductor magnus Medial
2 Tibialis posterior Posterior
3 Gluteus maximus Posterior
4 Rectus femoris Anterior
5 Semitendinosus Posterior
6 Fibularis longus Lateral
7 Sartorius Anterior
8 Tibialis anterior Anterior
9 Extensor digitorum longus Anterior
10 Biceps femoris Posterior
11 Gastrocnemius Posterior
12 Flexor digitorum longus Posterior
13 Gluteus medius Lateral
14 Soleus Posterior
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
11
Answer the following questions.
1. Describe the 4 muscles, function and location of the Quadriceps group.
Rectus Femoris: knee extension and hip flexion Runs straight down thigh and crosses hip
________________________________________________________________________
joint
________________________________________________________________________
Vastus lateralis: extend leg and stabilizes knee, lateral aspect of thigh
________________________________________________________________________
Vastus medialis: extends leg and stabilizes patella, forms infermedial aspect of thigh
________________________________________________________________________
Vastus intermedius: Extends legs, betweem vastus lateralis and vastus medialis on ant
thigh
2. Which of these muscles is a 2-joint muscle, acting over the hip as well as the knee?
________________________________________________________________________
Rectus femoris: knee extension and hip flexion
3. Name the individual muscles that are collectively termed ‘the hamstrings’ and describe
their function.
________________________________________________________________________
Biceps Femoris: movement of the hip joint and knee joint
________________________________________________________________________
Semitendinous: Extend at the hip and flex at the knee
________________________________________________________________________
Semimembranosus: Knee flexion, knee internal rotation and hip extension
Hip extension and knee flexion
4. Explain how the functional anatomy of the compartments differ in the lower limb from
the upper limb.
________________________________________________________________________
Upper limb: Anterior compartment muscles are flexors; posterior compartment muscles are
________________________________________________________________________
extensions
________________________________________________________________________
Lower Limb: Anterio compartment muscles are extensors; posterior compartment muscles are
________________________________________________________________________
flexprs. Due to intrauterine development of the lower extremeity consisting of outgrowth
rotation, and regional morphological development of structure (thigh, leg, foot)
5. Name the muscle that is the prime mover for inspiration.
________________________________________________________________________
Diaphragm: Flattens down when breathing
6. Name the 2 muscles that make up the pelvic diaphragm.
________________________________________________________________________
Levator ani and coccygeus
________________________________________________________________________
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
12
Label as many muscles as you can on the following diagrams.
A. Iliacus H. Adductor longus O. Tibialis anterior
B. Psoas major I. Gracilis P. Fibularis longus
C. Tensor fascia latae J. Gluteus maximus Q. Plantaris
D. Sartorius K. Gluteus medius R. Soleus
E. Rectus femoris L. Biceps femoris S. Gastrocnemius
F. Vastus lateralis M. Semitendinosus T. Extensor digitorum longus
G. Vastus medialis N. Semimembranosus U. Pectineus
Gluteus
Medius
Gluteus
Maximum
Adductor Magnus
Bicepts Femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
13
2.5: Physiology of muscle contraction
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
14
Answer the following questions.
1. What causes the striations that characterise skeletal muscle?
________________________________________________________________________
2. Name the functional contractile unit of a muscle cell.
________________________________________________________________________
3. Name the two contractile myofilaments specially arranged in each myofibril.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
4. Which myofilament has a binding site for calcium?
________________________________________________________________________
5. When a muscle fibre contracts the banding pattern changes. Describe this.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
6. List the 3 stages of excitation-contraction coupling prior to the cross-bridge cycle.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
7. What event causes the ‘power stroke’ in the cross-bridge cycle?
________________________________________________________________________
8. What two events are necessary for relaxation of the muscle fibre to occur?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
9. Outline the difference between isotonic and isometric contractions.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
10. Describe the 3 pathways for generating ATP for muscle activity.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
11. Which of these pathways is the fastest?
________________________________________________________________________
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
15
12. Which of these pathways provides the most ATP energy?
________________________________________________________________________
13. Which pathway is predominately used in endurance sports?
________________________________________________________________________
14. Calcium ions bind to which molecule in skeletal muscle cells?
________________________________________________________________________
Label the following diagrams.
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
16
REFLECTION
15. What area do I feel most confident with? Why?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
16. What area needs improvement? How can I make this improvement?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Have you completed your Muscular System checklist?
1016MSC T1 2023 Module 2 Tutorial Workshop Worksheets
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology Lab Manual ReviewDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lab Manual ReviewJustine CarpioNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Lab 2007 Answer SheetDocument5 pagesMuscular System Lab 2007 Answer SheetIsabel Nadia67% (3)
- Shoulder ExamDocument3 pagesShoulder ExamAdriana Valadares TalonNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet 11Document11 pagesReview Sheet 11CarlaReyesAlabanza77% (13)
- Solved Problems in ErgonomicsDocument31 pagesSolved Problems in Ergonomicsrianna rose dela cruz100% (2)
- Bio 137 Lab ManualDocument185 pagesBio 137 Lab ManualReedNo ratings yet
- Prakash Knee Book PDFDocument506 pagesPrakash Knee Book PDFJafild Fild river100% (4)
- Skeletal Muscle Cells and Their Packaging Into Muscles: PerimysiumDocument14 pagesSkeletal Muscle Cells and Their Packaging Into Muscles: PerimysiumMadeleine RayosNo ratings yet
- SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMYDocument7 pagesSKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMYDiana Rose SaludoNo ratings yet
- BBB Month 24 Workout LogDocument8 pagesBBB Month 24 Workout LogGeraldyneNo ratings yet
- Hip mobility and muscle imbalancesDocument13 pagesHip mobility and muscle imbalancesKetsmy Desrosiers100% (1)
- Special TestsDocument10 pagesSpecial TestsAdrian Nasager100% (4)
- Board II Review PDFDocument131 pagesBoard II Review PDFJohnNo ratings yet
- AAP Module 7 SupplementDocument40 pagesAAP Module 7 Supplementmaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- 10 1-2 PE Exam ScriptDocument6 pages10 1-2 PE Exam ScriptRaulNo ratings yet
- MT13 Clinical Anatomy and Physiology For Med Lab Science Laboratory Worksheet - SU - ICLSDocument8 pagesMT13 Clinical Anatomy and Physiology For Med Lab Science Laboratory Worksheet - SU - ICLSGOOKIEBOONo ratings yet
- Prelab 4 Appendicular Skeleton and Joints Winter 2020Document4 pagesPrelab 4 Appendicular Skeleton and Joints Winter 2020Mareline MendietaNo ratings yet
- ATP Muscle Kit Preparation LabDocument11 pagesATP Muscle Kit Preparation Lablaznme2012No ratings yet
- The Muscular System Learning Enhancement Activity LectureDocument6 pagesThe Muscular System Learning Enhancement Activity LectureNathaniel CornistaNo ratings yet
- BI 275 Exam IIDocument8 pagesBI 275 Exam IIAlexandra Lauren EzellNo ratings yet
- Pectoralis Biceps Obliques Rectus Abdominus Deltoid QuadricepsDocument2 pagesPectoralis Biceps Obliques Rectus Abdominus Deltoid QuadricepsAni BayindiryanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 - Anatomical Terms and Organ SystemsDocument7 pagesCH 1 - Anatomical Terms and Organ SystemsmeganNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Gluteal and Thigh Regions: Review Questions For Lsb235 WEEK 4 - 2017Document6 pagesMuscles of The Gluteal and Thigh Regions: Review Questions For Lsb235 WEEK 4 - 2017NathanNo ratings yet
- Chapt10 Study OutlineDocument11 pagesChapt10 Study Outlinekombat13_708353334No ratings yet
- Bio Learn Lab Activities Musculoskeletal Full StudentDocument9 pagesBio Learn Lab Activities Musculoskeletal Full StudentHeydrick GuyoNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction_to_the_KneeDocument73 pages1 Introduction_to_the_Kneeprasherpratik1984No ratings yet
- Q2 at Mapeh6Document4 pagesQ2 at Mapeh6Marhco Tumandao LumanasNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Bones IdentificationDocument5 pagesLower Extremity Bones IdentificationEmmie DaguploNo ratings yet
- LAB11 - MUSCUpperDocument5 pagesLAB11 - MUSCUpperBechris BambiNo ratings yet
- (Template) PE-101-Module-3Document22 pages(Template) PE-101-Module-3Windel TaypinNo ratings yet
- MBBS Stage 2 - Upper Limb 1Document5 pagesMBBS Stage 2 - Upper Limb 1ICNo ratings yet
- Nucleus Anabolism Metabolism Histologist Genes: Pharynx Adipose Tissue Trachea Ureter Larynx Pleura Cartilage UrethraDocument6 pagesNucleus Anabolism Metabolism Histologist Genes: Pharynx Adipose Tissue Trachea Ureter Larynx Pleura Cartilage Urethrateemo no JutsuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Physiology WorksheetDocument5 pagesSkeletal Muscle Physiology WorksheetKimberly FerstermannNo ratings yet
- Caraso Mia Jeane - P.E 2 Midterm ExamDocument8 pagesCaraso Mia Jeane - P.E 2 Midterm ExamMìa Jeàne Torres CarasöNo ratings yet
- Human Movement Module 1Document10 pagesHuman Movement Module 1Paula Dimples SantiagoNo ratings yet
- LAB Intro To AnatomyDocument8 pagesLAB Intro To AnatomynanaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2-The Language of MedicineDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 2-The Language of Medicineeddy surielNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga Nursing Packet on Skin, Skeleton and MusclesDocument27 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga Nursing Packet on Skin, Skeleton and MusclesSevilla ErnestdonNo ratings yet
- Dtse Word DocumentDocument2 pagesDtse Word DocumentleestephNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System WorksheetDocument4 pagesSkeletal System Worksheetjezhari talbotNo ratings yet
- General Direction: Answer The Following Question Intelligently. Make Sure To Follow The Instruction, Not Following Directions Will Deemed WrongDocument3 pagesGeneral Direction: Answer The Following Question Intelligently. Make Sure To Follow The Instruction, Not Following Directions Will Deemed WrongDANIEL LANCE NEVADONo ratings yet
- Unit 3 The Skeletal System (4 Hours LEC/6 Hours LAB)Document4 pagesUnit 3 The Skeletal System (4 Hours LEC/6 Hours LAB)Cherry Urmanita BucalingNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular System Open Note TestDocument9 pagesSkeletal and Muscular System Open Note TestDean JezerNo ratings yet
- mock exam 2022Document3 pagesmock exam 2022selene seleneNo ratings yet
- BSC 2085 - WK11 - HO1 - Laura Prado ANSWERSDocument5 pagesBSC 2085 - WK11 - HO1 - Laura Prado ANSWERSxcupcakex122006No ratings yet
- Biology Yr10 t3 2018Document11 pagesBiology Yr10 t3 2018mark smithNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology WorksheetDocument5 pagesAnatomical Terminology WorksheetIzzy Dale Cagas SilangaNo ratings yet
- Unlock SGCh19Document10 pagesUnlock SGCh19Silax100% (1)
- 4 Science6Q2Week1Document25 pages4 Science6Q2Week1Angelique BulanNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment - Axial Skeleton and Associated MusclesDocument5 pagesWritten Assignment - Axial Skeleton and Associated MusclesNadir KhanNo ratings yet
- Muscle Memory Cheat Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesMuscle Memory Cheat Sheet PDFHazel Joan TecsonNo ratings yet
- Know Your Body Type and PostureDocument7 pagesKnow Your Body Type and PostureMerylcyne Bangsao SimsimNo ratings yet
- Taller Bone TissueDocument2 pagesTaller Bone TissueANDREA CATALINA CORTES HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- C9apstudy GuideDocument37 pagesC9apstudy GuidejqtdNo ratings yet
- LIMCHIU, KYLE B. ANAPHY 101 Unit V Module 2Document4 pagesLIMCHIU, KYLE B. ANAPHY 101 Unit V Module 2Kyle LimchiuNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Anatomy Physiology Pathology Exercise TherapyDocument3 pagesPaper 1 Anatomy Physiology Pathology Exercise TherapyRoopendra MauryaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Sample Homework QuestionsDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Sample Homework QuestionsMawuli Wilson ApetiNo ratings yet
- School: San Agustin Elementary School Grade Level: Six Teacher: Jonalvin A. Ke Learning Area: Science Date: August 31, 2018Document7 pagesSchool: San Agustin Elementary School Grade Level: Six Teacher: Jonalvin A. Ke Learning Area: Science Date: August 31, 2018Jonalvin KENo ratings yet
- Science6 ST1 Q2Document4 pagesScience6 ST1 Q2Meriam LuatNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-01 at 2.49.43 PMDocument25 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-01 at 2.49.43 PMShamsheera SaleemNo ratings yet
- CPT Exam Prep WorkbookDocument63 pagesCPT Exam Prep WorkbookAmethyst Carey100% (1)
- SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 6- 2nd quarter 1st summativeDocument10 pagesSUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 6- 2nd quarter 1st summativeJohn Cyrel MondejarNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet Grade 5 For Ut1Document5 pagesRevision Sheet Grade 5 For Ut1Sudeep BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Notes Part 2 kd12Document4 pagesMuscular System Notes Part 2 kd12AparrisakpNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 1: (Activity Sheet)Document3 pagesPhysical Education 1: (Activity Sheet)kukoypedro100% (1)
- Post-op shoulder rehab protocolDocument3 pagesPost-op shoulder rehab protocolUpender YadavNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of cephalic and breech presentationsDocument2 pagesBiomechanics of cephalic and breech presentationsMed PoxNo ratings yet
- Exercise Programme PDFDocument25 pagesExercise Programme PDFskhumbuzomadunaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Nuerologic, Musculoskeletal and Peripheral Vascular System RubricsDocument4 pagesAssessing The Nuerologic, Musculoskeletal and Peripheral Vascular System RubricsSamantha ZacharyNo ratings yet
- 6 Day Female Training Program PDFDocument1 page6 Day Female Training Program PDFSmyle KatariaNo ratings yet
- Gluteal RegionDocument30 pagesGluteal Regiondivyam20084780No ratings yet
- Ultrasound Guided Interventional Procedures In.4Document13 pagesUltrasound Guided Interventional Procedures In.4andrew herringNo ratings yet
- Hip BoneDocument3 pagesHip BonecrossNo ratings yet
- Module 3-Anatomy and Physiology (Abegail Relunia - Bsed3-C Science) )Document3 pagesModule 3-Anatomy and Physiology (Abegail Relunia - Bsed3-C Science) )Abegail ReluniaNo ratings yet
- Exercises for mastectomy recovery in two stagesDocument14 pagesExercises for mastectomy recovery in two stagespoongodi cNo ratings yet
- Hip Arthroscopy Recovery ExercisesDocument5 pagesHip Arthroscopy Recovery ExercisesbekchievagNo ratings yet
- Shoulder ArthrosDocument11 pagesShoulder ArthrosLaineyNo ratings yet
- THERA EX - RANGE OF MOTION LaboratoryDocument3 pagesTHERA EX - RANGE OF MOTION LaboratoryMarili Camille CoquiaNo ratings yet
- Muscles QuestionsDocument3 pagesMuscles QuestionsIRADUKUNDA Marie SolangeNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Posterior Stabilizing VS Cruciate Retaining Prosthesis in Total Knee ReplacementDocument15 pagesComparative Study of Posterior Stabilizing VS Cruciate Retaining Prosthesis in Total Knee ReplacementIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Arce 2013Document11 pagesArce 2013Fillipe AgraNo ratings yet
- Push Pull Legs Jeff NippardDocument48 pagesPush Pull Legs Jeff Nippardtyronereese318No ratings yet
- Manual - SamboDocument218 pagesManual - SamboNihilist100% (2)
- Obturator Nerve CompressionDocument136 pagesObturator Nerve CompressionShahriar SakibNo ratings yet
- Radial Nerve InjuryDocument5 pagesRadial Nerve InjuryMuhammad RezaNo ratings yet
- It Enter Between Separates: Flexor RetinaculumDocument20 pagesIt Enter Between Separates: Flexor RetinaculumInsyirah JohariNo ratings yet
- Frozen Shoulder Home ExercisesDocument5 pagesFrozen Shoulder Home ExercisesJörgen PuisNo ratings yet
- The hip joint muscles and movementsDocument7 pagesThe hip joint muscles and movementsKrissy WilhelmsenNo ratings yet
- Strain and Counterstrain Cervical and Thoracic Tender Points GuideDocument99 pagesStrain and Counterstrain Cervical and Thoracic Tender Points GuideD.O. dobirdNo ratings yet