Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science1 Nanotechnology
Uploaded by
anil suryaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science1 Nanotechnology
Uploaded by
anil suryaCopyright:
Available Formats
TARGET MAINS 2023
BOOKLET-1; S&T-1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Syllabus .......................................................................................................................................... 2
2. Nanotechnology ............................................................................................................................. 2
1) Past Year Mains Questions (since 2013) .................................................................................................... 2
2) Other Practice Questions .......................................................................................................................... 2
3) Introduction ............................................................................................................................................. 3
4) Applications ............................................................................................................................................. 3
5) Future Potential Applications ................................................................................................................... 4
6) Concerns and Limitations ......................................................................................................................... 4
7) Molecular Machines / Nano Machines...................................................................................................... 5
S
8) Example Nano-Materials .......................................................................................................................... 6
IA
A) Schwarzite – New Form of Carbon Created .................................................................................................................. 6
B) Graphene ...................................................................................................................................................................... 7
C) Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) .............................................................................................................................................. 8
P
om
9) Elaborating on some nanotechnology applications ................................................................................... 9
lU
.c
A) Nanotechnology in Textile Sector ................................................................................................................................. 9
il
95 a
B) Nanotechnology in Health Sector ............................................................................................................................... 10
26 ou e
28 gm
C) Some Recent Developments in Nanomedicines (don’t go into details for Mains exams) .......................................... 11
88 hi v
92 t@
D) Nanotechnology in Agriculture Sector ........................................................................................................................ 13
Le
E) Environmental Nanotechnology ................................................................................................................................. 14
10) India and Nano-Technology ................................................................................................................ 15
ab
3. Nuclear Science and Technology ................................................................................................... 17
1) Past Year Mains Questions ..................................................................................................................... 17
2) Basics – What is Nuclear Energy? ............................................................................................................ 17
3) India’s Three-Phase Nuclear Power Program .......................................................................................... 17
4) Thermo Nuclear Reactions (Fusion Reactions) – Progress and India’s contribution ................................. 19
5) Nuclear Energy and Energy Security........................................................................................................ 20
6) Use of Nuclear Radiation tECHNOLOGY FOR PROVIDING BETTER QUALITY OF LIFE ................................. 21
7) Important Scientists and their Contributions: Homi Jehangir Bhabha ..................................................... 24
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658
S
IA
P
om
lU
il.c
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Le ab
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 1 | 26
1. SYLLABUS
1. Science and Technology -
a) Developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
b) Achievements of Indians in science & technology.
c) Indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
2. Awareness in the fields of
a) IT
b) Space
c) Computers
d) Robotics
e) Nanotechnology
f) biotechnology
g) Issues relating to intellectual property rights.
2. NANOTECHNOLOGY
1) PAST YEAR MAINS QUESTIONS (SINCE 2013)
- What do you understand by nanotechnology and how is it helping in health sector? (2020)
- Why is nanotechnology one of the key technologies of the 21st century? Describe the salient features of Indian
Government’s Mission on Nanoscience and Technology and the scope of its application in the development process of
the country (2016)
S
2) OTHER PRACTICE QUESTIONS
IA
a) What is Nanotechnology? Why is it called a general-purpose technology? [10 marks, 150 words]
P
b) “Their unique nano-features may also make them potentially hazardous for human health and environmental safety”
om
Discuss the key concerns associated with nanotechnology. [10 marks, 150 words]
lU
.c
c) What are molecular machines? Discuss the significant role that it may play in various socio-economic sectors. [10
il
95 a
marks, 150 words]
26 ou e
28 gm
d) Discuss the key provisions of the Mission on Nanoscience and Technology [10 marks, 150 words]
88 hi v
92 t@
e) Write a short note on key properties and applications of:
Le
▫ Graphene
▫ Carbon Nano Tube (CNT)
ab
▫ Nanodrums
▫ Schwarzites
f) Suggest some measures to promote nano-technology research in the country. [10 marks, 150 words]
g) “Nano Machines are going to have serious economic, social, environmental and military implications” Elaborate. How
far does Indian Government’s Mission on Nanoscience and Technology prepare India for these implications? [15 marks,
250 words]
h) What is Nano-UREA? How is it going to solve the various problems faced by fertilizer sector in India? [10 marks, 150
words]
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 2 | 26
3) INTRODUCTION
Definition:
a) Nanotechnology is science, engineering, technology, conducted at the nanoscale which is 1 to 100 nanometers.
Nanotechnology and Nanoscience involve the ability to see and to control individual atoms and molecules. In other
words, nanotechnology is the engineering of the functional system at molecular scale.
b) Richard Feynman, the father of nanotechnology, in his 1959 talk described nanotechnology as a field which can
manipulate and control things on the scale of a nanometer. He expected that matter will have surprising properties
at Nano level and thus provide for enormous number of applications
- General Purpose Technology:
4) APPLICATIONS
- Carbon Nanotubes are used in various products ranging from paints and textiles to medical diagnostics tools and
components of future quantum computers because of remarkable properties such as very high elastic strength
alongside low mass density or very high current densities with no heat loss.
- Health
▫ Nanoparticles of silver embedded into fibers have anti-microbial action. It is used in food packaging,
clothing, disinfectants, and household appliances. Bandages are being infused with silver nanoparticles to
heal cuts faster.
▫ Gold Nanoparticles have anti-bacterial properties
▫ Nanomedicines – Diagnosis and Treatment (see details separately)
▫ Water Purification: Special Filters using nanomaterials can remove objects as tiny as viruses from water.
S
- Nanotechnology in Agriculture – Better fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, feeds, better treatment for
IA
domesticated animals.
▫ Nano-Fibre based Agriculture Inputs: For e.g., FIB-SOL provides a five-gram fiber that is soluble in water
P
and can be applied on field using conventional or modern irrigation practices. The product addresses the
om
demand for live bacteria that could rejuvenate the soil. It could also increase the nutrient utilization
lU
.c
efficiency, allowing plants to assimilate nutrients in a better way.
il
95 a
26 ou e
▫ Nano Urea developed by IFFCO (Sep 2022)
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
- Environmental Applications:
Le
▫ Iron nanoparticles can be used to effectively clean-up organic solvents that are polluting the ground water.
The nanoparticles disperse throughout the water and decompose the organic solvents in place.
ab
▫ Adding a little boron to Carbon while creating nanotubes produce solid, spongy, reusable blocks that can
absorb large quantities of oil spilled in water.
▫ Nanotechnology based smart windows have energy saving, easy cleaning, UV controlling and photovoltaic
properties.
▫ Renewable Energy Generation
§ New and Cheap Solar Cells use nanoparticles of Titanium oxide coated with dye molecules to capture
the energy of visible light and convert it into electricity.
§ A novel catalytic nanosheet from of a nickel molybdenum-nitride, a thousand time cheaper than
traditional platinum, is the new model for harvesting hydrogen from water for use as fuel.
- Electronics
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 3 | 26
▫ Graphene is used in transparent electrodes for solar cells, LCD, robust non-volatile atomic switches,
chemical and biological sensors and in spintronic devices.
▫ Semiconducting nanowires are highly versatile optoelectronic components, for a wide variety of
applications such as nano-LEDs and nano-Lasers, solar cells, and biomedical sensors.
- Structural Engineering Applications
▫ Nano-enhanced Cement contained by addition of nanoparticles like nano silica (silica fume),
nanostructured metals, CNTs and carbon nanofibers give stronger, more durable, self-healing, air
purifying, fire resistant, easy to clean quick compacting structure.
▫ Nano-enhanced Construction Ceramics such as floor and wall tiles and sanitary ware have self-cleaning,
anti-bacterial, hygienic, and scratch resistant features.
▫ Nano-enhanced paints can reduce emission of Nitrogen-di-oxide, hydrocarbons, and carbon monoxide in
the atmosphere. It can also make paint scratch proof, easy cleaning, air purifying, UV resistant, water
repellant, flame resistant, and anti-bacterial.
▫ Nanotechnology based smart windows have energy-saving, easy cleaning, UV controlling and
photovoltaic properties.
▫ Fire resistant glasses are produced by addition of fumed silica nanoparticles in glasses.
- Nanotechnology can promote different forms of insulation solutions like coatings, vacuum insulations glazing
and nanofoams.
- Nano whiskers on clothes create a cushion of air around the fabric so that liquids can’t stain them.
- Cosmetics: Nanoparticles like Zinc oxides and titanium oxides are used in sunscreen and related products. They
provide protection from UVA rays.
5) FUTURE POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS
S
IA
- Advancements like nano-machines will lead to development in the field of nano-medicines, more advanced electronics
circuitry, quantum computing etc.
P
om
lU
.c
6) CONCERNS AND LIMITATIONS
il
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
- Due to their extremely small dimensions, large surface area and high reactivity, they have the potential ability
88 hi v
92 t@
to penetrate living cells quite readily. As a result, their unique nano-features may also make them potentially
Le
hazardous for human health and environmental safety.
ab
- Health
§ Inhaling airborne nanoparticles and nanofibers may lead to a number of pulmonary diseases, e.g., fibrosis.
Some form of carbon nanotubes could be as harmful as asbestos if inhaled in sufficient quantities.
§ Experiments with rats have also shown impact on skin (ageing) and brain.
- Toxicity
ú Lack of investment on nanotoxicology research
- Environmental impact
ú Lack of research on potential harmful impact: Lack of study on Impact of nanomaterial on non-human
species, on ecosystem or the global environment.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 4 | 26
ú e.g. bacteriostatic silver nanoparticles used in socks to reduce foot odor are being released in the wash. These
particles are then flushed into the wastewater stream and may destroy bacteria which are critical component
of natural ecosystem, farms, and wastewater treatment processes.
- More dangerous Weapons
▫ As a general-purpose technology, it will be dual use, meaning it will have many commercial uses and it also
will have military uses - making for more powerful weapons and tools of surveillance.
▫ A technology this powerful could easily be misused. The rapid development cycle and massive manufacturing
capability may lead to an unstable arms race between competing powers.
- Other Concerns
▫ May lead to loss of jobs in traditional farming and manufacturing sector
▫ May bring about crash in certain markets due to lowering of oil and diamonds due to possibility of
developing alternative source of energy that are more efficient and won't require use of fossil fuels. Also,
because people would be able to develop products at molecular level, diamond will lose its significance.
▫ Atomic weapons may become more accessible and more powerful and more destructive.
7) MOLECULAR MACHINES / NANO MACHINES
- Molecular Machine, or nano-machine, is any discrete number of molecular components that produce quasi-
mechanical movements (output) in response to specific stimuli.
- The 2016 Nobel Prize for Chemistry was awarded to ‘Molecular Machine’ trio for the design and synthesis of
molecular machines
ú Details about their contributions
a. Sauvage in 1983 took the first step by linking two ring shaped molecule to form a chain
S
IA
P
om
lU
il.c
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Le ab
b. Stoddart in 1991 developed a rotaxane, a dumbbell-shaped molecular structure that enabled him to build
molecular lift, a molecular muscle and a molecule-based computer chip
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 5 | 26
c. Feringa in 1999 was the first person to develop a molecular motor and in 2011 designed a four-wheeled
nano-car
S
IA
- Significance of those nano-machines
P
- These tiny machines that we can't even see have enormous potential.
om
lU
▫ Medicine and treatment
.c
ú Molecular technology could lead to development of machines that are so small they could be
il
95 a
26 ou e
swallowed or implanted into human bodies with little negative effect.
28 gm
88 hi v
ú They could be used to fight disease in the body, to repair damaged tissues, and even to probe DNA
92 t@
Le
structure.
ú Such precise drug deliver will minimize adverse side-effects.
▫ Smart materials able to adapt to their environment, small sensors that can be controlled remotely, and
ab
drugs that are activated on command
▫ Efficient energy storage devices
8) EXAMPLE NANO-MATERIALS
A) SCHWARZITE – NEW FORM OF CARBON CREATED
- Example Questions
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 6 | 26
▫ What is a Schwarzites? Discuss its future potential applications [10 marks,
150 words]
- Introduction
▫ Schwarzites is a completely new form of carbon that has been created by
scientists recently. It is a negatively curved carbon unlike fullerenes and
graphene which have positive or zero curvature respectively.
- Creation of Schwarzites
▫ Scientists, in Japan and South Korea, while investigating Zeolite-templated
carbons (ZTCs) – crystalline form of silicon di-oxide with carbon structure built into them – accidently created
schwarzites.
▫ Later, scientists at University of California demonstrated that it was possible to create ZTC structures by injecting a
vapor containing carbon into zeolites.
▫ Once inside, the carbon assembles into a graphene-like sheet that lines the walls of the pores in the zeolite. In doing
so, the surface stretches to minimize the area. As schwarzites are topologically minimal surfaces, they tend to
acquire negative curvature. The zeolite is then dissolved to produce pure schwarzites.
- Potential Future Applications (details in class discussion)
▫ Super Capacitors:
▫ Storage of atoms and molecules
▫ Catalyzing Reactions
- Conclusion: Though the applications of schwarzites remains to be seen, the scientists speculate that their unique
electronic, magnetic, and optical properties can make them useful, as super capacitors, battery electrodes and catalysts,
and with their large internal spaces ideal for gas storage and separation.
S
IA
B) GRAPHENE
▫ It is an allotrope of carbon which is a one-atom thick layer of pure carbon.
Carbon atoms are bounded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice.
P
om
lU
▫ How is it produced
il.c
§ By separating a single atom layer film from graphite.
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
Properties: Physical
92 t@
▫
Le
§ 2D – world’s first 2D material
§ Graphene is harder than diamond, more elastic than rubber,
ab
tougher than steel and yet lighter than aluminum.
• In fact, it is 200 times stronger than steel (100 times
stronger than the strongest steel).
§ Thickness: 1 million times thinner than a human hair
§ Stretchable as well as transparent, flexible, and impermeable.
§ It can also act as perfect barrier – not even helium can pass through it
▫ Properties: Thermal, Electrical and Magnetic Properties
▫ Highest electronic conductivity of any material in the world.
▫ Best Heat conductivity of any material in the world
▫ Shows a large and nonlinear diamagnetism
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 7 | 26
- Applications: Graphene’s unique combination of extraordinary properties offer a fascinating material platform for the
development of next-generation technologies in many areas.
▫ Energy Harvesting and Storage: It can be used for better rechargeable batteries; superior capacitors; newer
methods of making solar cells etc. Further, proton transfer in graphene shows promise for artificially mimicking
photosynthesis.
▫ Electronics: Very high electron conductivity allows graphene to be used for low-cost printable electronics, high
performance transistors; thermal management and heat dissipation in nano-electronic devices.
§ The optical properties of graphene can also be controlled by doping and make it well suited for
optoelectronic devices.
▫ Composites and Coatings: Its low mass and low loading requirements make graphene standout as a reinforcing
agent in composites. It can be used for making lubricants with enhanced anti-wearing capabilities; radiation
shielding and lighting strike protection; superhydrophobic coating; transparent, flexible and conductive thin films
etc.
▫ Membranes – It can improve the quality of filters used in desalination or other water purifying instruments.
Graphene oxide is used for the purpose.
§ It can also act as gas barrier for e.g. in food packaging.
§ It can be used for separation of organic solvent with water.
▫ Biomedical Technologies: Very high surface area, electron mobility etc. is paving the way for novel biomedical
technologies. Graphene bioelectronics (transistors and electrode arrays) has become a ground-breaking field
that offers existing opportunities for developing new kinds of biosensors. Key applications include Thermal
ablation of highly resistant cancer cells; Bioelectronics (bionics); Electronic interface to living cells and nerve
tissues; etc.
▫ Sensors: Since every atom of graphene is exposed it is an ideal material for biological, gas and chemical sensors.
It can be used for explosive detection; detecting biomarkers for parkinson’s disease; selective gas sensing; self-
S
healable, multifunctional electronic sensor tattoos; environment monitoring etc.
▫ Wearable technologies
IA
▫ Light weight cars, planes etc.
P
- Health Risks: Extensively debated
om
lU
▫ Toxicity depends on several factors such as shape, size, purity, post-production processing steps, oxidative state
.c
etc.
il
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
C) CARBON NANOTUBES (CNT)
92 t@
Le
- Intro
▫ Carbon nanotubes are allotropes of carbon with a cylindrical
ab
nanostructure. These cylindrical carbon molecules have unusual
properties, which are valuable for nanotechnology, electronics, optics
and other fields of material science and technology.
- Properties
▫ Strength: One of the most tensile and elastic material discovered yet.
- Wettability
▫ Exhibits a super hydrophobic property
▫ By applying a low voltage as low as 1.3 V, the extreme water repellants surface can be switched into super
hydrophilic.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 8 | 26
Electrical Properties
• CNT are either metallic or semiconducting along the tubular axis.
Thermal Properties
• All nanotubes are expected to be very good thermal conductors along the tube, exhibiting a property known
as "ballistic conduction", but good insulators lateral to the tube axis.
Application
• Current uses and application of nanotubes has mostly been limited to the use of bulk nanotubes, which is a
mass of rather unorganized fragments of nanotubes.
o Used as composite fibers in polymers to improve the mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of the
bulk product
o Tips for atomic force microscope probes
o In tissue engineering, carbon nanotubes can act as scaffolding for bone growth.
Concerns: Toxicity, health risk not clear yet.
9) ELABORATING ON SOME NANOTECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS
A) NANOTECHNOLOGY IN TEXTILE SECTOR
- Example Question
▫ Discuss the various applications of Nanotechnology in textile sector [10 marks, 150 words]
- Introduction:
▫ Nanotechnology is an amazing general-purpose technology that has proven its potential in all the fields, and
the textile sector is not an exception.
S
IA
- Key Applications of Nanotechnology in textile sector
P
om
lU
il.c
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Le ab
▫ How antibacterial properties are obtained: A nano-silver based suspension can be applied on the fabric
surface. Other compounds such as zinc, copper, and their oxides coupled with metal nanoparticles can also
be used as antibacterial agents. Titanium oxide (TiO2) is another strong antimicrobial material that conducts
the phenomenon known as “Photocatalysis”.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 9 | 26
▫ The anti-microbial textiles are most essential in the medical sector, especially in the present deadly
pandemic conditions, for e.g., in curtains, bed covers, face masks, aprons used in the hospitals and
diagnostics center.
▫ It can also serve for best hygiene in sportswear, baby products, sanitary napkins, wound healing
dressings and so on.
▫ Self-cleaning garments using Titanium oxide particles save detergent, water, and electricity simply.
▫ “Wearable sunscreen” are garments using Titanium Oxide nanoparticles which provide protection against
▫ Thermoregulation: Clothings respond to changes in the body temperature and maintain comfort by either
heating or cooling. The Phase Change Material is incorporated into the fabric to fulfill this function.
▫ The Polymeric micro-capsules filled with perfumes/deodorants/insect repellents can be integrated with
fabric for slow release.
▫ Fabric Used in Air Filters: A thin coating of nanofibers on the fabric used in air filters for air conditioners
and automobiles’ exhaust, stops ultrafine particles thereby increasing the efficiency of the filters.
▫ Technical Textiles are used in special applications. For e.g., fireproof and flame retardant fabric is required
in the suit used by firefighters. The high temperature stable materials are combined with thermally
insulating and fireproof materials such as nano-porous silica aerogel for this application. Other examples
of technical textiles include functions like electro-magnetic field shielding, electrical conducting, anti-
static, camouflaging, stealth, water repellency, and so on. The nanomaterials used in these applications
are generally carbon nanotubes, nanoparticles of metals, metal oxides, clay, semiconductors, polymers
etc.
- Way Forward
S
▫ Nanotechnology has a great potential in the textile industry. Functional and smart textiles can play an
important role in the economy of a nation. However, there are limitations in applications due to scientific
IA
complexity and the cost adhered to it.
▫ Therefore, a proper study is necessary to find any toxic effects of handling and wearing the nano
P
materials to eliminate any health risks due to short- or long-term exposure.
om
lU
il.c
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
B) NANOTECHNOLOGY IN HEALTH SECTOR
88 hi v
▫ Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology. It ranges from the medical applications of
92 t@
Le
nanomaterials and biological devices to nanoelectronics biosensors, and even possible future applications of
molecular nanotechnology such as biological machines.
ab
▫ What difficulties nano-medicines will overcome?
▫ Problems with conventional drugs
§ Less soluble conventional medicine, which are not absorbed properly and thus don't impact
the required target
§ Even if drug molecule is soluble, body removes the drug before it has had long enough to provide
a benefit.
§ Conventional drugs could have side effects due to poor delivery at the actual site of disease.
• For e.g. drugs targeting cancer must avoid the healthy tissues and organs or damage can
be caused.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 10 | 26
▫ Nanomedicines therefore can play an important role in ensuring enough of the drugs enter the body,
that the drugs that enters stays in the body for long periods and is targeted specifically in areas that need
treatment.
▫ Medical Applications:
▫ Prevention of disease:
§ Nanoparticles of silver embedded into fibers have anti-microbial action. It is used in food
packaging, clothing, disinfectants, and household appliances. Bandages are being infused with
silver nanoparticles to heal cuts faster.
§ Gold Nanoparticles have anti-bacterial properties
§ Water Purification: Special Filters using nanomaterials can remove objects as tiny as viruses
from water.
▫ Diagnostics: By studying and identifying individual molecules, it is possible to diagnose disease in time
to improve the prognosis for the patient.
▫ Improved Treatment
§ Indian Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST) is developing Magnetic Hyperthermia
mediated cancer therapy - delivery and localization of magnetic material within the targeted
tumour site followed by subsequent application of an alternating Magnetic Field (AMF), thereby
generating heat at the tumour site
§ E.g: Scientist are using gold nanoparticles to target prostate cancer. Here the nanoparticles or
nano shells are made of small payers of Silica glass formed into a sphere and wrapped in a thin
layer of gold. This is made to reach the tumour site and then harnessed to cause the tumorous
tissue to pulse with extreme temperature when light is applied through a laser specifically
designed to excite the particles
S
§ A team of scientists from IISc Bengaluru have developed nano robots to be used in dental
IA
procedure (like root canal therapy).
P
§ With more advancement in Nanomachines – complex surgical procedures would become less
om
lU
intrusive and less complicated
il.c
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Le
C) SOME RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN NANOMEDICINES (DON’T GO INTO DETAILS FOR MAINS EXAMS)
ab
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE VIA VIRTUAL PLATFORM ON “NANOMEDICINE: BIOMOLECULES FOR
HUMAN HEALTH, SMALL MOLECULES: BIG OPPORTUNITIES!” (NBBH-2021) WAS ORGANIZED BY KIRORI
MAL COLLEGE, UNIVERSITY OF DELHI. (OCT 2021)
▫ The Key issues discussed were:
▫ “Vaccine platforms: Delivery and Role of Nanotechnology”. Here emphasis was made on role of formulations of
nanostructures as a vehicle to deliver the vaccine.
▫ Radiation Therapy and Radio-Diagnostics as Nanomedicine – Scientist elaborated on the role of amalgamated
gold nanoparticles and irradiation therapy for effectively treating pancreatic and hepatobiliary tumors.
USING NANOROBOTS FOR DENTAL PROCEDURE (AUG 2021)
- Why in news?
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 11 | 26
ú A team of scientists from IISc Bengaluru have developed nanorobots to be used in dental procedures (like
root canal therapy)
- Background/Need
ú A significant percentage of root canal treatments fail, because the procedure leaves out some bacteria
that are located deep within the dentinal tubules.
- The new method:
ú Scientists have developed Spiral Silica robots measuring 300 nanometers to travel through dentinal
tubules and target bacterias.
ú How do they work:
§ These spiral silica nanobots with a bit of iron embedded in them are not more than 300 nanometers.
They are suspended in water or water like biocompatible medium. There are about a billion
nanorobots in 0.5 ml water. This is almost a trillion times lower than the amount of silica found in a
pint of beer and is effectively harmless for a human body.
§ This is placed in the central canal of the root. Then a rotating magnetic field is applied using a triaxial
Helmholtz coil. The magnetic material embedded in the nanorobot has a magnetic moment that
follows the applied magnetic field. This causes the nanorobot to move – like screws move in wall.
Once the bacterial colony is reached, the nanorobots can deploy various antibacterial strategies one
of which is localized heating.
§ These nanorobots can be precisely controlled spatio-temporally and swarms of these robots can be
used to target diseases sites inside teeth to neutralize the harmful biofilms following which they can
be retrieved back to the physician.
ú These scientists have also founded a company, - Theranautilus, which will eventually market this
technology.
S
ú Note:
§ THerannautilus have won the Technology Development Board’s National Award in the Start-up/
IA
Deep-Tech industry category.
§ Technology Development Board is a statutory body established under the Department of Science and
P
Technology under the Technology Development Board Act, 1995 to promote development and
om
lU
commercialization of indigenous technology and adaptation of imported technology for much wider
.c
applications.
il
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
MAGNETIC HYPERTHERMIA-MEDIATED CANCER THERAPY (MHCT)
92 t@
Le
Why in news?
- Efforts of Institute of Nanoscience and Technology (INST) towards developing and improving
Magnetic Hyperthermia-mediated Cancer Therapy (Aug 2020)
ab
About MHCT
- It is a non-invasive cancer treatment technique. It involves the delivery and localization of magnetic
material within the targeted tumour site followed by subsequent application of an alternating
Magnetic Field (AMF), thereby generating heat at the tumour site.
- It can efficiently act against deep-seated inaccessible solid tumors like glioblastoma and is highly
thermo-sensitive towards normal cells with minimal toxicity against healthy counterparts.
- Scientists are working on new material which can make this treatment more efficient.
Efforts by India
- Scientists from Institute of Nanoscience and Technology – an autonomous institute of DST, GoI have
synthesized different magnetic nano-transducers like Stevioside-coated magnetic nanoparticles;
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 12 | 26
citric-acid coated magnetic nanoclusters and Manganese and Zinc doped magnetite nanoparticles
for successful application as magnetic hyperthermia agents for cancer therapy.
Recent Efforts by INST
- INST have synthesized magnetic nanomaterials using a hydrothermal approach. They have also
developed water-stable nanomaterial with a biomolecule as the surfactant to address two of the
main concerns regarding the translation of nanotechnology-based strategies to clinical applications:
ú Biocompatibility of material used
ú Therapeutic response of these nano systems
- The optimization of various parameters like size, shape, and surfactant moieties of nano-heaters by
INST team might contribute towards establishing magnetic hyperthermia as the missing notch for
successful glioblastoma therapy with minimum side-effects to the normal cells.
D) NANOTECHNOLOGY IN AGRICULTURE SECTOR
NANO UREA
Why in news?
▫ Nano Urea fast-tracked for approval despite incomplete trials (Sep 2022)
What is NANO UREA
▫ Nano Urea is a patented and indigenously made liquid that contains nanoparticles of urea, the most
crucial chemical fertilizer for farmers in India. A single half litre bottle of the liquid can compensate for
a 45 kg sack of urea that farmers traditionally rely on.
▫ Fertilizer Minister, Mansukh Mandaviya has claimed that by 2025, India’s domestic urea production as
well as that of nano-Urea would together mean India would be “self-sufficient”, in the manufacture of
Urea and wouldn’t require 90 lakh tonnes that it imported every year and would save the country close
to Rs 40,000 crore.
S
IA
When is Urea used in agriculture and when can it be replaced by Nano Urea?
▫ Urea is used on two occasions – at the time of sowing (or transplantation); and the second is done when
the plant has sprouted a canopy of leaves and is approaching the reproductive phase of plant growth.
P
om
▫ It is to be noted that traditional Urea is still necessary during the initial stage, as basal nitrogen, of crop
lU
development. The nano Urea could be useful once the plant grew after which the product could be
il.c
sprayed on its leaves.
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
How effective is Nano Urea?
92 t@
Le
▫ ICAR studies show that yield is not affected and, in some instances, crop yield increased.
ab
What is the trial issue?
▫ ICAR has given results of field trial based on a year (two seasons) of experiments in its affiliated labs to
Central Fertilizer Committee. Based on this Central Fertilizer Committee approved the use of nano-Urea.
▫ Hindu reported that this was an exception as ICAR normally tests it for 2 years (or three seasons) before
giving go ahead to a new fertilizer.
▫ IFFCO has said that farmer field trials were done over four seasons on 94 crops across 21 states since
2019. Trials were continued during Kharif 2021-22 too in all the agro-climatic regions of India.
Conclusions: Nanotechnology could play a crucial role in promoting sustainable agriculture in India and
nano-urea is an example of that. At the same time, it should be ensured that any new technology based
product is properly evaluated in its efficacy, environmental impact and economic impact on farmers
GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATION OF NANO-BASED AGRI-INPUT AND FOOD PRODUCTS IN INDIA (JULY 2020)
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 13 | 26
- Released by Ministry of Science and Technology
- The guidelines have been prepared jointly by DBT, Ministry of S&T, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer Welfare,
FSSAI, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare through concerted Inter-Ministerial efforts coordinated by DBT.
- These guidelines will help policy makers and regulators to frame effective provisions for future novel nano-
based products in the agri-input and food sectors in India:
- Objectives of the guidelines
ú To promote development of nano-products for agriculture and human consumption
ú To ensure quality and safety of these products
- Guidelines are applicable on:
ú Agri-Input products in the nano-form of finished formulation as well as Active ingredient(s) (AI) of a new
material.
ú Agri-Products in nano-form of finished food formulations, finished feed formulations, finished dairy
formulations, food/feed formulations from marine resources, nano carriers for nutraceuticals delivery etc.
ú They also apply to nanocomposites and sensors made from NMs and those that require direct contact with
crops, food and Feed for data acquisitions.
- Regulations Proposed
ú Nano fertilizers: Safety, Efficacy, Functionality, and other quality data for proposed nano fertilizers should
be conducted under Fertilizer Control Order (FCO), 1985
ú Nano Pesticides: Studies on chemistry, bio efficacy and residues, toxicity, packaging and processing of nano
pesticide products for registration (for manufacture or import) should be conducted as per the regulatory
aspect provisions under Section 9 Specified in the Insecticides Act, 1968.
ú NanoFood: The FDA guidelines and FSS Act, 2006 with additional criteria for inclusion of nanofood may be
S
adopted by FSSAI
IA
ú Nanofeed: Safety, Evaluation, and other quality studies of Nanofeed should be conducted under Cattle
Feed (Regulation and Manufacture and Sale) Order, 2009 with additional criteria for inclusion of Nanofeed
P
may be adopted by FSSAI.
om
lU
.c
Implementation of Standards should be conducted as per Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
il
-
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Le
E) ENVIRONMENTAL NANOTECHNOLOGY
▫ Example Questions
ab
§ What is environmental nanotechnology? Discuss with some practical applications. [10 marks, 150 words]
▫ Introduction
§ Environmental nanotechnology refers to use of nanotech products, processes, and applications to
contribute to environment and climate protection.
§ It may contribute by cleaning the pollutants, reducing the pollutants, making our devices more efficient
and reducing cost of green technologies.
§ Key areas where nano-material researchers are working:
i. Ensuring Potable Drinking Water – Use of Graphene based water filters are expected to increase the
accessibility of clean drinking water in coming future
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 14 | 26
ii. Removing pollutants from water
§ Cleaning up organic chemicals polluting ground water
• Iron nanoparticles can be used to effectively clean-up organic solvents that are polluting
the ground water. The nanoparticles disperse throughout the water and decompose the
organic solvents in place. This method is more effective and costs significantly less than
treatment methods that require the water to be pumped out of ground.
§ Cleaning up of oil spills
• Using photocatalytic cooper tungsten oxide nanoparticles to break down oil into bio-
degradable compounds.
iii. Generating Less pollution during manufacturing of materials
§ E.g. Use of silver nano particles as catalysts can significantly reduce the polluting by products in
the process used to manufacture propylene oxide.
• Propylene oxide is used to produce common materials such as plastics, paint, detergents
and brake fluid.
iv. Producing solar cells that generate electricity at competitive cost
§ E.g. Silicon nanowires embedded in a polymer result in low cost but high efficiency solar cells.
v. Increasing the electricity generated by windmills
§ E.g. use of carbon nanotubes in windmill blades results in stronger and lower weight windmill
blades. This helps in more amount of electricity generated by each windmill.
vi. Reducing cost of fuel cells
§ Changing the spacing of platinum atom in fuel cells increases the catalytic ability of the platinum.
This allows the fuel cells to function with 80% less platinum, significantly reducing the cost of the
fuel cells.
S
§ Conclusion: Nanotechnology is thus brimming with potential solutions to various environmental and climate
IA
change related issues being faced by India. It’s high time that India’s Mission on Nano Science and Technology is
restructured to include R&D in the field of environment as one of its key goals
P
om
lU
.c
10) INDIA AND NANO-TECHNOLOGY
il
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Mission on Nano Science and Technology (Nano Mission)
Le
- Introduction
ab
a. It is an umbrella program of GoI for overall development in the field of Nanotechnology.
b. It was launched in 2007 with an allocation of Rs 1,000 crore which was further extended during the
12th five-year plan.
c. It is structured in a fashion to achieve synergy between the national research efforts of various
agencies in Nano Science and Technology and launch new programs in a concerted fashion.
d. Department of Science and Technology is the nodal agency for the mission.
- Objectives of the Nano-Mission
a. Basic Research Promotion – funding of basic research by individual scientists or groups of scientists
and creation of centre of excellence for pursuing this research.
b. Infrastructure Development for Nano Science and Technology Research -> development of a chain
of facilities across the country.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 15 | 26
c. Human Resource Development – Providing effective education and training to researchers and
professionals in diversified fields. Launching of M.Sc./M.Tech programmes, create national and
overseas post-doctoral fellowships, chairs in universities etc.
d. International Collaborations – Exploratory visits of scientists, organization of joint workshops,
conferences and joint research projects, facilitate access to sophisticated research facilities abroad,
forge academia-industry partnership.
e. Development of product and processes for national development
§ Especially in areas of national relevance like
Safe Drinking Water
Materials Development
Sensors Development
Drug Delivery
- Achievements of the Mission
a. The mission has resulted into more than 5,000 research papers and some useful products like nano-
hydrogel based eye drops, pesticide removal technology for drinking water, water filters for arsenic
and fluride removal and nano-silver based on anti-microbial textile coating.
b. India has moved from the fourth to the third position in the world in terms of scientific publications
in nanoscience and technology.
- Institute of Nanoscience and Technology (INST): It is an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and
technology, GoI.
- Way Forward:
- Funds
- Human Resource
- Infra – R&D
S
- Industry-Academia collaboration
- University-University Collaboration
IA
P
om
lU
il.c
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Le ab
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 16 | 26
3. NUCLEAR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
1) PAST YEAR MAINS QUESTIONS
1) [2018]: With growing energy needs should India keep on extending its nuclear energy program? Discuss the facts and
fears associated with nuclear energy.
2) [2017]: Give an account of the growth and development of nuclear science and technology in India. What is the
advantage of fast breeder reactor programme in India? (250 words, 15 marks)
2) BASICS – WHAT IS NUCLEAR ENERGY?
- What is nuclear energy?
ú Nuclear energy is the energy in the nucleus of an atom which is released during nuclear fission or fusion
reaction.
ú During these reactions, a small amount of mass is lost and gets converted into energy according to
Einstein’s equation.
§ In nuclear fission, the nucleus of a heavy atom (such as uranium, plutonium or thorium), when
bombarded with low - energy neutrons, can be split apart into lighter nuclei.
§ When this is done tremendous amount of energy is released, if the mass of the original nucleus is
just a little more than the sum of the masses of the individual products.
S
IA
- E.g. of fission reaction
P
om
lU
il.c
95 a
Pu (239, 94) + n (1,0) -> Ba (145, 56) + Sr (92,38) + 2 n(1,0)
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Le
§ E.g. of fusion reaction
ab
ú This is one of the common reactions taking place in sun.
3) INDIA’S THREE-PHASE NUCLEAR POWER PROGRAM
- The three-stage nuclear power production program of India had been conceived by the ‘father of Indian Nuclear
Power Program’ Dr Homi J Bhabha, with the ultimate objective of utilizing the country’s vast reserves of thorium-
232.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 17 | 26
1. The first stage comprises setting up of Heavy Water Reactors/Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors
(PHWRs) and associated fuel cycle facilities.
2. The second stage envisages setting up of Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) backed by reprocessing plants
and plutonium-based fuels fabrication plants. Plutonium is produced by irradiation of U-238.
3. The third stage is based on the thorium-232 -> Uranium 233 Cycle, Uranium-233 is obtained by
irradiation of Thorium.
S
IA
- Progress of the 3 Stages
ú The first stage of Nuclear Power Programme is already in commercial domain. The Nuclear Power
Corporation of India Ltd. (NPCIL), a public sector
P
om
undertaking of DAE, is responsible for the design,
lU
.c
construction, and operation of nuclear reactors. The
il
95 a
company presently operates 22 reactors with a
26 ou e
28 gm
capacity of 6.7 GW. The total operational capacity is
88 hi v
92 t@
expected to go to 22.4 GW by 2031
Le
ú The Second Stage of Nuclear power generation
ab
programme is geared towards setting up the Fast
Breeder Reactors. These reactors produce more fuel
than they consume. The fast breeder program is in
technology demonstration stage.
§ Features of the Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor
(PFBR)
- Fuel: Plutonium Uranium Oxide (PuO2 and UO2)
- Coolant: Liquid Sodium
- Liquid Sodium additional safety requirements
▫ Since sodium explodes if it comes in contact with water and burns when in contacts with air,
additional safety requirements are needed to isolate the coolant from the environment.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 18 | 26
▫ Sodium also absorbs neutron to form Radioactive Na24 isotope.
- Advantages of FBR:
▫ They can ensure upto 60 times as much energy from the original Uranium compared with
normal reactors.
▫ Reduction in radioactive waste.
▫ Safety -> closed fuel cycle would ensure safety
▫ Energy security for India -> India plans third phase of its nuclear energy program on the success
of FBR
ú The Third Stage: of the Nuclear Power Programme is in technology development stage.
- The ongoing development of 300 MWe Advanced Heavy Water Reactor (AHWR) at BARC aims at
developing expertise for thorium utilization and demonstrating advanced safety concepts.
- Thorium-based systems such as AHWR can be set up on commercial scale only after a large capacity
based on fast breeder reactors, is built up.
- Why Thorium based reactors are important for us
i. Abundance: India has the world’s third largest reserve of thorium.
ii. Less Enrichment requirement: Thorium mining produces a single pure isotope, whereas the
mixture of natural uranium isotope must be enriched to function.
iii. Superior Nuclear Properties: Superior physical and nuclear properties
iv. Better Nuclear weapon resistant: Better resistance to nuclear weapon proliferation
§ Weapon grade fissionable material (U-233) is harder to retrieve safely from a thorium
reactor. It contains U-232, a strong source of gamma radiation that makes it difficult to
work with. Further, its daughter product, thallium-208, is equally difficult to handle and
easy to detect.
v. Reduced plutonium and actinide production
S
vi. They have miniscule long lived radioactive waste.
IA
4) THERMO NUCLEAR REACTIONS (FUSION REACTIONS) – PROGRESS AND INDIA’S
CONTRIBUTION
P
om
lU
.c
ú Fusion reactions are also called Thermonuclear reactions
il
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
ú What is the need of extremely high temperature -> to overcome the electrical repulsive force
88 hi v
92 t@
Le
ú So far, fusion devices that show a net energy gain have not been demonstrated in lab
ú USA’s Attempt: An experiment at the U.S. National Ignition Facility (NIF), within the Livermore National
ab
Laboratory, Livermore, California, comes close to a successful fusion reaction in lab producing energy (Aug 2021)
§ The new experiment in USA, comes close to demonstrating a net energy gain in fusion reaction in lab. In
this lab, using laser beams, tiny pellets of deuterium and tritium (heavier isotopes of hydrogen) have been
fused to form helium and release energy that very nearly matches the amount of energy input using the
laser.
§ The NIF has been able to achieve this after a decade of efforts. Now, the experiment has produced a yield
that almost equals the laser energy input. To be functional, a reactor has to produce an output that is at
least tens of times the input energy.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 19 | 26
ú In Aug 2022, NIF reported that they have reached another milestone in fusion research; they produced a plasma
in which self-heating locally surpass not only the external heating but also all loss mechanism, satisfying the so-
called Lawson criterion for fusion ignition.
ú Advantages of Nuclear Fusion:
§ Raw material easily available
§ Nuclear Fusion is a clean and green route to produce energy, as it doesn’t involve any remnant waste
products.
§ Long term energy security
ú About International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER)
§ India is also participating in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER).
§ Prime Minister Narendra Modi while participating in the ITER Assembly said the ITER is a perfect example
of the age-old Indian belief – Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam - the entire world is working together for the
betterment of mankind and that India stands proud with its fair share of contributions to the cooling water,
cryogenic and cry-distribution systems, auxiliary heating devices using RF and beam technologies etc.
5) NUCLEAR ENERGY AND ENERGY SECURITY
- Introduction:
ú Energy security means consistent availability of sufficient energy in various forms at affordable prices. When
a country moves ahead on the path of development, it is necessary to utilize every energy resource available
S
in the country.
IA
ú Currently, nuclear energy makes up about 3% of India’s energy sources
P
om
- Advantages of Nuclear Energy:
lU
a) Least carbon footprint (lesser than renewable energy)
.c
il
- The threat of climate change and environmental pollution are likely to constraint the use of fossil fuels
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
b) Cost of nuclear power
88 hi v
- The cost of nuclear power plants is pretty competitive to other fossil versions
92 t@
Le
c) Quantity of waste generated is also very less
d) Potential of self sufficiency
ab
- India has huge reserves of thorium which if properly utilized will reduce the dependency of India on
foreign country
e) Depleting fossil fuels and import dependency: India is currently drawing around 63% of its total energy from
thermal sources. A significant part of this is imported.
f) Limitations of Renewable Energy
- Renewable energy are subject to vagaries of weather; they are land intensive; dependence on import
technology; energy storage handicaps;
- Renewable energy is inevitable and nuclear option should be retained as insurance.
- Limitations
a) Safety concerns in light of recent disasters
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 20 | 26
b) Nuclear waste disposal is a big concern
• India still doesn't have a credible waste disposal policy.
c) Potential of developing nuclear weapons
d) Security concerns
• Nuclear power plants can be favorite targets for terrorist organizations. If this happens it may cause
irreversible damage to people living in the region and the ecosystem.
e) India is dependent on other countries both for raw material and technology
• Our future potentially depends on third stage of nuclear program.
f) Ecological concerns
• Nuclear plants are generally set near the coast as it requires a lot of water.
• It is going to put pressure on coastline as India's western coastline is home to fragile ecology of western
Ghats.
g) Long gestation period
• Till now only more than 20 plants are operational. There are long gestation periods which increases the
cost of plants significantly.
h) More safeguards -> more costly
• Post Fukushima disaster, the cost of per unit energy has gone up. This has led to concerns regarding the
cost viability of nuclear power plants.
- Way Forward
§ As we know that India's total energy demand is expected to cross 800 GW by 2032, it is very important to utilize
all possible options available and nuclear energy is one of the most important of those options.
§ We need to develop a fledging domestic nuclear industry which will reduce our dependence as well as help us in
reducing the gestation period of the plants.
§ In light of the limitation’s association with nuclear energy, stress should be laid on cautious development, safety
precautions in operation and disposal of wastes. But development of nuclear energy can't be stonewalled in the
light of such concerns.
S
6) USE OF NUCLEAR RADIATION TECHNOLOGY FOR PROVIDING BETTER QUALITY OF LIFE
IA
1) Introduction
P
om
lU
- Even before the use in nuclear bombs and nuclear energy, radiations were used in therapeutic and palliative
.c
for cancer cure in the early part of the 20th century.
il
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
- In the subsequent decades, nuclear fission made possible the harnessing of nuclear energy for electricity
88 hi v
92 t@
production.
Le
- However, the peaceful uses of the atom have developed several other large-scale applications in agriculture,
ab
medicines and industrial sectors.
2) Important fields in which radiation technology is being used
1. Health: Care to Cure
- Healthcare has grown into one of the most important peaceful uses of nuclear energy.
- Nuclear Medicine - Diagnosis
▫ Nuclear medicine is a medical speciality that uses trace amounts of radioactive substances
(called radio - pharmaceuticals) in the diagnosis and treatment of wide range of diseases and
conditions in a safe and painless way.
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 21 | 26
▫ Radio pharmaceuticals can be administered by injection, inhalation, or orally and selectively
localized and retained at sites of diseases. And thus, allow an image to be obtained of the loci
using gamma scintigraphy or to deliver cytotoxic dose of radiation to specific disease sites
without adversely affecting the surrounding normal tissues.
▫ They help in identification of abnormalities in organ function even in early stages of a disease.
- Radiation Therapy
▫ A treatment that involve use of high-energy radiation either by using special machines or from
radioactive substance. The aim is to impart specific amount of radiation at tumors or parts of
the body to destroy the malignant cells.
1. External Beam Radiation Therapy / teletherapy
§ Radiation is delivered by using a machine outside the body.
§ A machine, either a 60Co-teletherapy unit or linear accelerator is used
§ It can be used to treat Breast Cancer, Bowel Cancer, Head and Neck Cancer and
Lung Cancer.
§ Bhabatron is a teletherapy machine developed by BARC and has been installed in
50 cancer hospitals.
• It is cheaper than any imported telecobalt machine.
2. Internal Radiation Therapy or brachytherapy
S
§ Radioactive material is placed in the body near cancer cells.
IA
§ It makes it possible to treat a cancer with a larger dose of radiation that can’t be
given with external beam radiation therapy.
P
om
§ Tiny titanium encapsulated Iodine-125 seeds have been developed by BARC and
lU
.c
have provided an avenue to treat eye cancer.
il
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
2. Food Security (1. Nuclear Agriculture 2. Food Preservation)
Le
• Use of ionizing radiation based technologies provide safe hygienic and economically viable
solutions to address issue of agricultural productivity
ab
1. Nuclear Agriculture
- Ionizing radiation is being used by BARC to induce mutation in plant breeding, and around
50 varieties of different crops have been released to Indian farmers for commercial
cultivation in the country.
▫ e.g. groundnuts, mungbean, blackgram, pigeon pea, cowpea, mustard etc.
- Advantages
▫ Higher yield
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 22 | 26
▫ Earliness
▫ Large seed size
▫ Resistance to biotic and abiotic stress
2. Food Preservation - Produce and Preserve
§ Almost 30% of the food produced in India is lost due to spoilage because of pest attack,
contamination and moulds infestation. These are encountered both during harvesting as well
as post-harvest handling storage of the edible and cash crops.
§ Limitation of using pesticides
• Health hazards
• Disturbance to ecology
• Development of resistance in pest
§ Radiation Processing can provide a viable, effective, and eco-friendly alternative to chemical
fumigants and microbial decontamination, as the latter affect human health and
environment adversely.
§ There is an utmost need to adopt and integrate the irradiated foods into the country's supply
chains and promote the widespread use of this technology to ensure food safety and
security.
S
§ Advantages of using radiation processing
IA
• Disinfestation of insects, pests in cereals, pulses and grain.
Microbial decontamination (hygienization) of dry species etc. for preservation/shelf
P
•
om
life extension by applying pre-determined radiation doses.
lU
il.c
• Increasing the exportability of Indian food produce.
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
• Elimination of parasites and pathogens of public health importance in food
92 t@
Le
• Delay in ripening and senescence in fruits and vegetables
ab
• Inhibition of sprouting in tubers, bulbs and rhizomes
§ Radiation in no ways make production radioactive.
• Radiation therapy has been approved by WHO, IAEA, WTO, FSSAI etc.
Thus, as of Aug 2021, 26 Radiation Therapy plants are operational in the country.
3. Energy Security - Nuclear is Clean and Green – already discussion
4. Societal Application
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 23 | 26
1. Sludge Hygenisation - from waste to wealth -> reduces spread of disease; protects environment;
increased manufacture of manure etc.
5. Hydrogel - Healing the wound
§ The process was developed by BARC scientists and technologically has been transferred for
commercial purpose.
§ Hydrogel is a thin transparent sheet of gel and is an excellent medical tool particularly useful for
burn and injury dressings.
§ Production
§ It is prepared by cross linking molecules of hydrophilic polymers like PVA either chemically
or by Gamma/Electron beam irradiation.
§ A 3D network of gel like structure is formed which holds large quantities of water. Gamma
Irradiation achieves gel formation and sterilization in one step.
6. Water Resources
1. Isotope Hydrology techniques
§ Isotope hydrology techniques enable accurate tracing of measurement of the extent of new
and renewable underground water resources at various locations.
§ The data obtained is used towards resource planning and sustainable management of water
resources.
S
2. Measuring contaminants in water
IA
§ BARC has developed low cost and user-friendly kits for measurement of contaminants in
P
water.
om
lU
il.c
95 a
7. Industrial Applications
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
1. Radiation Sterilization of Medical Products
Le
2. Radiography
ab
§ Radioisotopes which emit gamma rays are more portable than x-ray machines, and may give
higher-energy radiation, which can be used to check welds of new gas and oil pipeline
systems, with the radioactive source being placed inside the pipe and the film outside the
weld.
§ Radiography can also be used to gauge the thickness and density of materials or locate
components that are not visible to other means.
7) IMPORTANT SCIENTISTS AND THEIR CONTRIBUTIONS: HOMI JEHANGIR BHABHA
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 24 | 26
- He is an Indian born nuclear physicist who made important contributions to quantum theory and cosmic
radiations.
- For his contributions in Nuclear Science and Technology in India, he is also known as the “Father of India’s Nuclear
Science Program”.
▫ He returned to India from England in 1939 to join Indian Institute of Science, where he founded the
Cosmic Ray Research Unit.
▫ He understood the importance of atomic energy and wrote a letter to Prime Minister Nehru for
promotion of the field. He established a Nuclear Research Centre in Trombay in 1954 which later came
to be known as Bhabha Atomic Research Centre.
▫ With the help of J.R.D. Tata, he played an instrumental role in the establishment of the Tata Institute of
Fundamental Research in Mumbai.
▫ He headed India’s nuclear program till his death in 1966.
For his contributions, he was awarded Adams Prize (in 1942) and Padma Bhushan (1954). He was also nominated
for Nobel Prize for Physics in 1951 and 1953-56.
S
IA
P
om
lU
il.c
95 a
26 ou e
28 gm
88 hi v
92 t@
Le ab
Shop No 6, Old Rajinder Nagar New Delhi 110060| www.levelupias.com|+91-8826486658 , +91-8826496658 P a g e 25 | 26
You might also like
- Future Opportunities in Catalytic and Separation TechnologyFrom EverandFuture Opportunities in Catalytic and Separation TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Target Mains 2021 Current Affairs Program Booklet-16 Science and Technology-1 Nanotechnology, Nuclear ScienceDocument26 pagesTarget Mains 2021 Current Affairs Program Booklet-16 Science and Technology-1 Nanotechnology, Nuclear ScienceNikhil Reddy AndruNo ratings yet
- Science2 RoboticsDocument7 pagesScience2 Roboticsanil suryaNo ratings yet
- Science6 HandoutDocument126 pagesScience6 Handoutanil suryaNo ratings yet
- Traffic Flow On NetworksDocument257 pagesTraffic Flow On Networksruss007100% (3)
- Nanotechnology Innovations For The Construction IndustryDocument47 pagesNanotechnology Innovations For The Construction Industryedmagdaluyo4662No ratings yet
- A Review On Why Researchers Apply External Magnetic Field On NanofluidsDocument8 pagesA Review On Why Researchers Apply External Magnetic Field On NanofluidsabdullaalakourNo ratings yet
- Nanotecnología en Tiempos ActualesDocument9 pagesNanotecnología en Tiempos ActualesHass GraceNo ratings yet
- Course Code: BEI03 Course Name: Introduction To Sustainable EngineeringDocument4 pagesCourse Code: BEI03 Course Name: Introduction To Sustainable EngineeringJohnNo ratings yet
- Te 1536 WebDocument870 pagesTe 1536 WeblarisszaNo ratings yet
- Report 255Document139 pagesReport 255Felipe López GarduzaNo ratings yet
- Ruaumoko Theory Manual: ResearchDocument117 pagesRuaumoko Theory Manual: ResearchCarlosRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fatima Adamu Silver Nanoparticle ReportDocument39 pagesFatima Adamu Silver Nanoparticle Reportsassy5046No ratings yet
- Aluminium Oxide Nanoparticles 2013 PDFDocument48 pagesAluminium Oxide Nanoparticles 2013 PDFDeepak Jo BenelliluvrNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument11 pages1 PB PDFSantiago HernándezNo ratings yet
- Occupational Intakes P2 For ConsultationDocument231 pagesOccupational Intakes P2 For ConsultationwurihandayaniNo ratings yet
- J Cosrev 2018 11 002Document21 pagesJ Cosrev 2018 11 002vedddaaaahNo ratings yet
- Sustainability in the Construction Industry كك- Ortiz - 2009Document12 pagesSustainability in the Construction Industry كك- Ortiz - 2009M7md YehyaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Geotechnical Properties of LateriticDocument87 pagesInvestigation of The Geotechnical Properties of LateriticaruamanatariaNo ratings yet
- Vigilancia Tecnologica: Programa Ingenieria IndustrialDocument11 pagesVigilancia Tecnologica: Programa Ingenieria IndustrialAndrés MalvaNo ratings yet
- Robotic ArmDocument19 pagesRobotic ArmAlthaf MkNo ratings yet
- Life-Cycle Assessment of Pavements 2Document88 pagesLife-Cycle Assessment of Pavements 2Valentina Rojas PercyNo ratings yet
- ICME-UNEP Tailings Management Case StudiesDocument66 pagesICME-UNEP Tailings Management Case Studiesabozman123No ratings yet
- Synthesis and Screening of Bimetallic Three-Way CatalystsDocument77 pagesSynthesis and Screening of Bimetallic Three-Way CatalystsNguyen Vu LeNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine BladeDocument10 pagesWind Turbine Bladeahalawat90No ratings yet
- Neuclonic SafetyDocument118 pagesNeuclonic SafetyRajesh DwivediNo ratings yet
- Economía Circular en La Industria de La Construcción-1Document17 pagesEconomía Circular en La Industria de La Construcción-1Diana Soledad Paliza ChinoNo ratings yet
- NZDE Course DescriptorsDocument197 pagesNZDE Course DescriptorsNajif IsmailNo ratings yet
- IFC Tunnels - Requirements Analysis ReportDocument176 pagesIFC Tunnels - Requirements Analysis ReportJohn TreffNo ratings yet
- DR 140 TDocument43 pagesDR 140 TAndrei MarinasNo ratings yet
- For Public Comment: Draft Malaysian StandardDocument25 pagesFor Public Comment: Draft Malaysian StandardAriffin NgahNo ratings yet
- Pta Desalinizadora Nuclear Te - 1326 - WebDocument175 pagesPta Desalinizadora Nuclear Te - 1326 - WebIsmar AdrianNo ratings yet
- Trends and Frontiers of MEMS: Wen H. KoDocument6 pagesTrends and Frontiers of MEMS: Wen H. KoOm PrakashNo ratings yet
- IEGC Review Expert Group Report 2020 PDFDocument291 pagesIEGC Review Expert Group Report 2020 PDFRavi Sankar ChittavarjulaNo ratings yet
- 859917Document156 pages859917Étoile FilanteNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Oxide Nanoparticles As Efficient Catalysts in OxidationDocument30 pagesTransition Metal Oxide Nanoparticles As Efficient Catalysts in Oxidationdoctorji1925No ratings yet
- PSAT Documentation 2011Document484 pagesPSAT Documentation 2011MARpreparadoresNo ratings yet
- 2018 Ibc Seaoc Structural Seismic Design Manual Volume 2 Examplespdf CompressDocument385 pages2018 Ibc Seaoc Structural Seismic Design Manual Volume 2 Examplespdf Compressvkch saipavan100% (3)
- Thin Solid Films: Joon Seok Park, Wan-Joo Maeng, Hyun-Suk Kim, Jin-Seong ParkDocument15 pagesThin Solid Films: Joon Seok Park, Wan-Joo Maeng, Hyun-Suk Kim, Jin-Seong ParkRajesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 18ITME598 Final ReportDocument33 pages18ITME598 Final Reportsachini weesingheNo ratings yet
- Thesis Ebe 2017 Wills James AlexanderDocument218 pagesThesis Ebe 2017 Wills James AlexanderAhmed M. AssalNo ratings yet
- Seminar 3Document40 pagesSeminar 3akashdeep khicharNo ratings yet
- Improving Techniques and Practices On The Geotechnical Centrifuge. Including Literature ReviewDocument103 pagesImproving Techniques and Practices On The Geotechnical Centrifuge. Including Literature ReviewJonny SimonsNo ratings yet
- Review of Functional Titanium Oxides PDFDocument20 pagesReview of Functional Titanium Oxides PDFEverlinFerreiraNo ratings yet
- Radiotracer Technology As Applied To Industry: IAEA-TECDOC-1262Document104 pagesRadiotracer Technology As Applied To Industry: IAEA-TECDOC-1262Samira MimountNo ratings yet
- Suspension For Electrathon VehicleDocument55 pagesSuspension For Electrathon VehicleJulius RojoNo ratings yet
- 1 - On The Sustainability of Machining ProcessesDocument15 pages1 - On The Sustainability of Machining ProcessesJonatas Rangel dos SantosNo ratings yet
- REY Hugo R2A 2016-2017Document71 pagesREY Hugo R2A 2016-2017Miguel EgidoNo ratings yet
- Te 1142 PRNDocument202 pagesTe 1142 PRNCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Hkw&Laiozqu Osq Fy, JHFR Lafgrk: HKKJRH EkudDocument108 pagesHkw&Laiozqu Osq Fy, JHFR Lafgrk: HKKJRH EkudJishna K JNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Aerospace Industry 12.42.21 PMDocument28 pagesNanotechnology in Aerospace Industry 12.42.21 PMAkshay HegdeNo ratings yet
- A Review of Essential Standards and Patent Landscapes F 2016 Advanced EngineDocument22 pagesA Review of Essential Standards and Patent Landscapes F 2016 Advanced Enginerrm77No ratings yet
- Operational Improvement of Nissan's Parts WarehouseDocument56 pagesOperational Improvement of Nissan's Parts WarehousedeguNo ratings yet
- Teske 2016 Global Outlook 2016 PDFDocument114 pagesTeske 2016 Global Outlook 2016 PDFaabbNo ratings yet
- Nanotechology - Seminar Report - U20143030041Document21 pagesNanotechology - Seminar Report - U20143030041ChristianNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsDocument9 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviewssiddiqa batoolNo ratings yet
- 人工智能和机器学习对科学、技术和科学任务的推进带来的机遇和挑战Document66 pages人工智能和机器学习对科学、技术和科学任务的推进带来的机遇和挑战meiwanlanjunNo ratings yet
- A Review On Quality Factor Enhanced On-Chip Microwave PlanarDocument7 pagesA Review On Quality Factor Enhanced On-Chip Microwave PlanarpramodinibidharNo ratings yet
- Flow Induced Vibration - 1992Document25 pagesFlow Induced Vibration - 1992prafullp1962No ratings yet
- Kong 010505482Document197 pagesKong 010505482Srinivas VCENo ratings yet
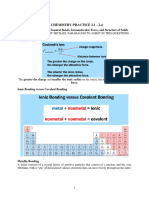
- Ap Chemistry Practice 2.1-2.4Document7 pagesAp Chemistry Practice 2.1-2.4alialhammaditt1No ratings yet
- Solid-State and Particle Size Control of Pharmaceutical Cocrystals UsingDocument24 pagesSolid-State and Particle Size Control of Pharmaceutical Cocrystals UsingRedevilz Sufizm PujionoNo ratings yet
- Structural Properties and Surface Characteristics of Alumina PowdersDocument10 pagesStructural Properties and Surface Characteristics of Alumina PowdersHenrry EscolásticoNo ratings yet
- Packaging of Dairy Products: B. Tech. (Dairy Technology) DT-9 ResourcesDocument6 pagesPackaging of Dairy Products: B. Tech. (Dairy Technology) DT-9 ResourcesAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Egirdir IRON TrialDocument40 pagesEgirdir IRON Trialhany wanasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility Plastic Material Chart For PA66, PEEK, PPS, PVDF and POMDocument9 pagesChemical Compatibility Plastic Material Chart For PA66, PEEK, PPS, PVDF and POMDeepak patilNo ratings yet
- SC5a Ionic-Bonding-Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesSC5a Ionic-Bonding-Worksheet AnswersSri THIRUGNANA SAMBANDAMNo ratings yet
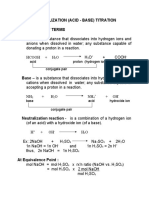
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument13 pagesAcid-Base TitrationSham WawNo ratings yet
- Marathon: Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageMarathon: Technical Data SheetTamerTamerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 6.4 - 6.9Document4 pagesChemistry Notes 6.4 - 6.9Grace LeeNo ratings yet
- Anions, Although Few Cases of Cations Acting As: B + H BHDocument38 pagesAnions, Although Few Cases of Cations Acting As: B + H BHArei DizonNo ratings yet
- Reaction Coupled SeparationDocument75 pagesReaction Coupled SeparationAnushka DashputraNo ratings yet
- Geo Textile A Tremendous Invention of GeDocument7 pagesGeo Textile A Tremendous Invention of GexpreimentNo ratings yet
- Intratec PortfolioDocument279 pagesIntratec Portfolioagarwalashwin32No ratings yet
- PTG Chapter 1 Asal ChemistryDocument14 pagesPTG Chapter 1 Asal ChemistryKai GeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MYP 3 Section 3Document15 pagesChemistry MYP 3 Section 3Hadeel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Soil Science Lab Exercise 1Document3 pagesSoil Science Lab Exercise 1qgalauraNo ratings yet
- Brochure Oilfield Corrosion Inhibitors Global enDocument5 pagesBrochure Oilfield Corrosion Inhibitors Global enpedroNo ratings yet
- Ee 51e Quiz # 03Document2 pagesEe 51e Quiz # 03Niño John JaymeNo ratings yet
- Basic Cooling Water Management IIDocument32 pagesBasic Cooling Water Management IIDiaa GobranNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Pre-Board 2023Document3 pagesChemistry Pre-Board 2023Muhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Transpoxy Primer 1.16Document3 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Transpoxy Primer 1.16Sachin NambiarNo ratings yet
- Double-Perovskite Anode Materials Sr2MMoO6 (M Co, Ni) For Solid Oxide Fuel CellsDocument8 pagesDouble-Perovskite Anode Materials Sr2MMoO6 (M Co, Ni) For Solid Oxide Fuel CellssinytellsNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 NotesDocument10 pagesTopic 5 NotesRaviNo ratings yet
- Articol Stabilitate (2020) LCGC - Namerica - June2020Document60 pagesArticol Stabilitate (2020) LCGC - Namerica - June2020dnarcisroNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Size Enlargement (Agglomeration) : Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument20 pagesChapter Three: Size Enlargement (Agglomeration) : Chemical Engineering DepartmentYohannes EndaleNo ratings yet
- Provocative Opinion: Arrhenius StudentsDocument2 pagesProvocative Opinion: Arrhenius StudentsAitor PastorNo ratings yet
- TDS + Superfloc A-100 HMW SERIES +kemira English + O&M + PS D0012 + 05.12.2013Document2 pagesTDS + Superfloc A-100 HMW SERIES +kemira English + O&M + PS D0012 + 05.12.2013Metalurgista SosNo ratings yet
- A New Synthetic Method For The Preparation of 5-Deazaflavins and 5-Deaza-10-OxaflavinsDocument2 pagesA New Synthetic Method For The Preparation of 5-Deazaflavins and 5-Deaza-10-OxaflavinsThéoNo ratings yet
- Coatings (E) FinalDocument8 pagesCoatings (E) FinalGhita-Mehedintu GheorgheNo ratings yet