Professional Documents
Culture Documents
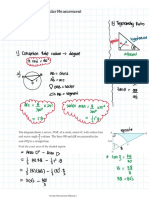
Gradient Tangent Normal
Uploaded by
Tito Bayu ArtomoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gradient Tangent Normal
Uploaded by
Tito Bayu ArtomoCopyright:
Available Formats
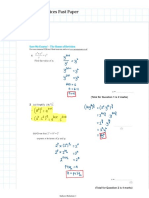
PMT
2. x ( x^2 - 4x + 3) = 0 -> A = 0 and B -> (x-1) (x-3) -> B = 1 C = 3
A = 3(0)^2 - 8(0) + 3 = 3
B = 3(1)^2 - 8 + 3 = -2
C = 3(3)^2 - 24 + 3 - 0
DIFFERENTIATION (Gradient, Tangent & Normal)
1 Find the gradient at the point with x-coordinate 3 on each of the following curves.
3
a y = x3 b y = 4x − x2 c y = 2x2 − 8x + 3 d y= +2
x
3x^2 = 27 4 - 2x = -2 4x - 8 = 4 3/x^2 = 1/3
2 The curve with equation y = x3 − 4x2 + 3x crosses the x-axis at the points A, B and C.
a Find the coordinates of the points A, B and C. 3x^2 - 8x + 3
b Find the gradient of the curve at each of the points A, B and C. A = 0, B = 1 , C = 3
3 For the curve with equation y = 2x2 − 5x + 1,
dy
a find , 4x - 5
dx
dy
b find the value of x for which = 7. 12/4 = 3
dx
4 Find the coordinates of the points on the curve with the equation y = x3 − 8x at which the
gradient of the curve is 4. 4^3 - 8x -> 64 -64 = 0
5 A curve has the equation y = x3 + x2 − 4x + 1. -1.5^3 + -1.5^2 - 4(-1.5) + 1 = -3
a Find the gradient of the curve at the point P (−1, 5).
Given that the gradient at the point Q on the curve is the same as the gradient at the point P,
b find, as exact fractions, the coordinates of the point Q. 3x^2 + 2x -4 = -3 y = 1/3^3 + 1/3^2 -4(1/3) + 1
3x^2 + 2x -1 = 0 y = -5/27
Coordinates = (1/3,-5/27) and (-1,5)
(3x-1) (x+1) => 1/3 , -1 y = -1^3 + -1^2 -4(-1) + 1
y - y1 = m(x - x1)6 Find, in the form y = mx + c, an equation of
y=5
y - 3(2)^2 - 10 + 2 = 7x-14 6x - 5 = 6(2) -5 = 7
a the tangent to the curve y = 3x2 − 5x + 2 at the point on the curve with x-coordinate 2, y = 7x -11
y = 7x -11 3x^2 + 10x = -27 -30 = -57
y - y1 = 1/m(x-x1) b the normal to the curve y = x3 + 5x2 − 12 at the point on the curve with x-coordinate −3. y = 1/57x - 1023/57
y - 3(-3)^2 - 30 -12 = 1/-57(x+3) 3x^2 + 6x - 16 -> 3(2)^2 + 6(2) - 16 = 12
y = 1/57x - 1023/577 A curve has the equation y = x3 + 3x2 − 16x + 2. y +10) = 12x -24
a Find an equation of the tangent to the curve at the point P (2, −10). y = 12x - 34
The tangent to the curve at the point Q is parallel to the tangent at the point P. 3x^2 + 6x - 28 y = 274/3 and -16
b Find the coordinates of the point Q.(14/3,274/3) and (-2,-16) (3x-14)(x+2)
x = 14/3 and -2
8 A curve has the equation y = x2 − 3x + 4. 2x - 3 -> 4 - 3 = 1
y - 2 = -x + 2
a Find an equation of the normal to the curve at the point A (2, 2). y = -x + 4
The normal to the curve at A intersects the curve again at the point B.
b Find the coordinates of the point B. x^2 - 3x + 4 = -x + 4 y = 4 and 2
x^2 -2 = x(x-2) -> x= 0 and 2 (0,4) (2,2)
9 f(x) ≡ x3 + 4x2 − 18.
a Find f ′(x). 3x^2 + 8x
b Show that the tangent to the curve y = f(x) at the point on the curve with x-coordinate −3
passes through the origin.
m = 3(-3)^2 + 8(-3) = 3 it passes
y - (-9) = 3(x-(-3) -> x = 0
y +9 = 9
y=0
Solomon Press
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Worksheet C: IfferentiationDocument2 pagesWorksheet C: IfferentiationKhaleed ChungNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Product Rule - QuestionsDocument1 pageDifferentiation Product Rule - Questionsharry.hbarlowNo ratings yet
- Math Handout Level 3Document46 pagesMath Handout Level 3BayanNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Monthly Test March 2016Document10 pagesAdd Maths Monthly Test March 2016Armadaramor ShiNo ratings yet
- CARTESIAN COORDINATES AND LINEAR EQUATION NotesDocument2 pagesCARTESIAN COORDINATES AND LINEAR EQUATION NotesnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- 3rd Term s1 Further MathematicsDocument21 pages3rd Term s1 Further MathematicsFiffy McCormickNo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument5 pagesAnalytical GeometryNtuthu TshoksNo ratings yet
- Mco Part 2Document5 pagesMco Part 2mica mercadoNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Parabolas in The Real WorldDocument2 pagesQuadratic Equations: Parabolas in The Real WorldMinnow ChangNo ratings yet
- Differentiation - WorksheetDocument2 pagesDifferentiation - WorksheetS PNo ratings yet
- Plynmls 01Document2 pagesPlynmls 01Manas SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths 1b 1st Year Material Notes JR Inter CompressDocument75 pagesMaths 1b 1st Year Material Notes JR Inter CompressVenu PaletiNo ratings yet
- Sin Sin 1 Cos +: X XDX X X DX XDocument2 pagesSin Sin 1 Cos +: X XDX X X DX XAlok RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Faisal YussufNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Functions NoteDocument51 pagesGraphs of Functions NoteJJMBNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics F4 NotesDocument238 pagesBasic Mathematics F4 NotesSylvesterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solutions Solution Manual Introductory Econometrics For FinanceDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Solutions Solution Manual Introductory Econometrics For FinanceNazim Uddin Mahmud50% (2)
- Quadratic factorisation-IGCSE AslevelDocument19 pagesQuadratic factorisation-IGCSE Aslevelmath trainerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3Document4 pagesProblem Set 3Alain LeeNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 1 PDFDocument37 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1 PDFDaniel Danille KristianNo ratings yet
- 1b Important QuestionDocument4 pages1b Important QuestionÇháråñ ÇhèrryNo ratings yet
- Mathematic 1Document6 pagesMathematic 1Alaa Mohammed Hussein Wais علاء محمد حسين ويسNo ratings yet
- Differentiation RevisionDocument4 pagesDifferentiation RevisionMavakise CalvinNo ratings yet
- Finding The Slope of A Line Given An EquationDocument23 pagesFinding The Slope of A Line Given An EquationdaleNo ratings yet
- Algebra Questions: With Answers For Grade 9Document6 pagesAlgebra Questions: With Answers For Grade 9PACITA LESTOJASNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations in 2 Variables Worksheet 8Document2 pagesLinear Equations in 2 Variables Worksheet 8PRATHIKSHANo ratings yet
- Form 4 Add Maths NoteDocument9 pagesForm 4 Add Maths NoteHayati Aini Ahmad100% (1)
- Quadratic EquationsDocument18 pagesQuadratic EquationsErwani KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Peta I Think Fizik t4Document18 pagesPeta I Think Fizik t4Yk TayNo ratings yet
- Background Exercises Answers/SolutionsDocument6 pagesBackground Exercises Answers/SolutionsDung Hanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- MH1811 Tutorial 1 - MC - 2020 - FN - Lmts - SolnDocument11 pagesMH1811 Tutorial 1 - MC - 2020 - FN - Lmts - SolnYachen WuNo ratings yet
- Maths 1b MLM For 1st YearDocument75 pagesMaths 1b MLM For 1st YearAnchula Mounika75% (8)
- Math - 2 - 6oc Tfinal - PartiiDocument92 pagesMath - 2 - 6oc Tfinal - PartiimohamedNo ratings yet
- Home School Sub-Maths NotesDocument36 pagesHome School Sub-Maths NotesbeanoderapperrNo ratings yet
- 25 Pure Maths Resourceful Mock 2016-2Document4 pages25 Pure Maths Resourceful Mock 2016-2BWENGYE NICHOLASNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Question Paper 3Document3 pagesClass 12 Question Paper 3Sohail150788No ratings yet
- Assignment - 3,4,5-1Document4 pagesAssignment - 3,4,5-1Arnob RayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 Graphing Linear Functions by The Point Plotting MethodDocument4 pagesLesson 2.2 Graphing Linear Functions by The Point Plotting MethodAliah GombioNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Math 7 Spcmoi 2021Document10 pagesModule 1 Math 7 Spcmoi 2021Feliculo JaponaNo ratings yet
- The Second Monthly TestDocument3 pagesThe Second Monthly TestJeremy LingNo ratings yet
- Review Exercise 2Document19 pagesReview Exercise 2eventra bangladeshNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument2 pagesPolynomialshello dayNo ratings yet
- Equation of A Circle ProblemsDocument12 pagesEquation of A Circle ProblemsEdward LactamNo ratings yet
- Core Mathematics 1, May 2006: Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument2 pagesCore Mathematics 1, May 2006: Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesPOk TAngNo ratings yet
- Differentiation TechniquesDocument11 pagesDifferentiation TechniquesJessicaNo ratings yet
- 51 QuestionsDocument4 pages51 Questionsyesman69No ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970From EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Normal To Binomial ApproximationDocument2 pagesNormal To Binomial ApproximationTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- APBNDocument7 pagesAPBNTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Congruent & SimilarityDocument3 pagesCongruent & SimilarityTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- 07-07-2023 - Circular MeasurementDocument1 page07-07-2023 - Circular MeasurementTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics 1 ReviewDocument2 pagesPure Mathematics 1 ReviewTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- 9 Narada 03 Probability NotationDocument14 pages9 Narada 03 Probability NotationTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- 9 - Narada - Review Further Probability ANSWER KEYDocument11 pages9 - Narada - Review Further Probability ANSWER KEYTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Y11 Science Math Mid Test ReviewDocument6 pagesY11 Science Math Mid Test ReviewTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- 17-05-2023 - Indices Past PaperDocument3 pages17-05-2023 - Indices Past PaperTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- 02-05-2023 - Further DifferentiationDocument4 pages02-05-2023 - Further DifferentiationTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Increase & Decrease PercentageDocument1 pageIncrease & Decrease PercentageTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- SH - GR 12-WT-AS ScheduleDocument2 pagesSH - GR 12-WT-AS ScheduleTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Try Out UTBKDocument4 pagesPembahasan Try Out UTBKTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- IR2153 Parte6Document1 pageIR2153 Parte6FRANK NIELE DE OLIVEIRANo ratings yet
- Case Study - Suprema CarsDocument5 pagesCase Study - Suprema CarsALFONSO PATRICIO GUERRA CARVAJALNo ratings yet
- Universitas Tidar: Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu PendidikanDocument7 pagesUniversitas Tidar: Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu PendidikanTheresia Calcutaa WilNo ratings yet
- G2 Rust Grades USA PDFDocument2 pagesG2 Rust Grades USA PDFSt3fandragos4306No ratings yet
- Kissoft 15,69,0.4Document10 pagesKissoft 15,69,0.4Daggupati PraveenNo ratings yet
- Mission and VisionDocument5 pagesMission and VisionsanjedNo ratings yet
- Sundar Pichai PDFDocument6 pagesSundar Pichai PDFHimanshi Patle100% (1)
- Alchemy of The HeartDocument7 pagesAlchemy of The HeartAbdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Data MiningDocument28 pagesData MiningGURUPADA PATINo ratings yet
- 02 Object Modeling TechniqueDocument50 pages02 Object Modeling TechniqueMuhammad Romadhon Batukarang EsdNo ratings yet
- SPC FD 00 G00 Part 03 of 12 Division 06 07Document236 pagesSPC FD 00 G00 Part 03 of 12 Division 06 07marco.w.orascomNo ratings yet
- GGG Sri MDocument2 pagesGGG Sri MGiovanni LuigiNo ratings yet
- Math F112Document3 pagesMath F112ritik12041998No ratings yet
- Pubb-0589-L-Rock-mass Hydrojacking Risk Related To Pressurized Water TunnelsDocument10 pagesPubb-0589-L-Rock-mass Hydrojacking Risk Related To Pressurized Water Tunnelsinge ocNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Template No. 1 Teacher'S Report On The Results of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Template No. 1 Teacher'S Report On The Results of The Regional Mid-Year Assessmentkathrine cadalsoNo ratings yet
- Derma Notes 22pages. DR - Vishwa Medical CoachingDocument23 pagesDerma Notes 22pages. DR - Vishwa Medical CoachingΝίκος ΣυρίγοςNo ratings yet
- A.meaning and Scope of Education FinalDocument22 pagesA.meaning and Scope of Education FinalMelody CamcamNo ratings yet
- Coaxial Cable Attenuation ChartDocument6 pagesCoaxial Cable Attenuation ChartNam PhamNo ratings yet
- VRPIN 01843 PsychiatricReportDrivers 1112 WEBDocument2 pagesVRPIN 01843 PsychiatricReportDrivers 1112 WEBeverlord123No ratings yet
- 18-MCE-49 Lab Session 01Document5 pages18-MCE-49 Lab Session 01Waqar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5 - Power System ControlDocument2 pagesTutorial Chapter 5 - Power System ControlsahibNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Australian NovelDocument412 pagesThe Rise of Australian NovelSampath Kumar GummadiNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Manila University: Submitted byDocument5 pagesAteneo de Manila University: Submitted byCuster CoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Template DownloadDocument4 pagesLiterature Review Template Downloadaflsigfek100% (1)
- Federalist Papers 10 51 ExcerptsDocument2 pagesFederalist Papers 10 51 Excerptsapi-292351355No ratings yet
- Victor 2Document30 pagesVictor 2EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Contoh Exposition TextDocument1 pageContoh Exposition TextKristin SeranNo ratings yet
- 25 Middlegame Concepts Every Chess Player Must KnowDocument2 pages25 Middlegame Concepts Every Chess Player Must KnowKasparicoNo ratings yet
- The Palestinian Centipede Illustrated ExcerptsDocument58 pagesThe Palestinian Centipede Illustrated ExcerptsWael HaidarNo ratings yet
- D&D 5.0 Combat Reference Sheet Move Action: Interact With One Object Do Other Simple ActivtiesDocument2 pagesD&D 5.0 Combat Reference Sheet Move Action: Interact With One Object Do Other Simple ActivtiesJason ParsonsNo ratings yet