Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Chap 8 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Uploaded by
akshayorbgkapapaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Chap 8 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Uploaded by
akshayorbgkapapaCopyright:
Available Formats
Sure Shot Questions
Chapter – 08
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
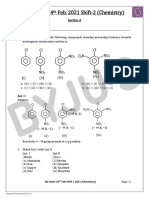
MCQ 4. The reagent which does not react with both,
acetone and benzaldehyde is ________.
1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic
(a) Sodium hydrogensulphite
medium and in the presence of Hg2+ ions as a
(b) Phenyl hydrazine
catalyst. Which of the following products will be
(c) Fehling’s solution
formed on addition of water to but-1-yne under
(d) Grignard reagent
these conditions?
5. Cannizzaro’s reaction is not given by ______.
6.
Structure of ‘A’ and type of isomerism in the above
reaction are respectively
(a) Prop-1-en-2-ol, metamerism
2. The correct order of increasing acidic strength is
(b) Prop-1-en-1-ol, tautomerism
_______.
(c) Prop-2-en-2-ol, geometrical isomerism
(a) Phenol < ethanol < chloroacetic acid < acetic
(d) Prop-1-en-2-ol, tautomerism.
acid
7. Compounds (A) and (C) in the following reactions
(b) Ethanol < phenol < chloroacetic acid < acetic
are
acid
(c) Ethanol < phenol < acetic acid < chloroacetic
acid
(d) Chloroacetic acid < acetic acid < phenol <
(a) Identical
ethanol
(b) Positional isomers
(c) Functional isomers
3. Compound can be prepared by (d) Optical isomers.
reaction of _____. 8. Which is the most suitable reagent for the
(a) Phenol and benzoic acid in the presence of following conversion?
NaOH
(b) Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of
pyridine
(c) Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of
(a) Tollens’ reagent
ZnCl2
(b) Benzoyl peroxide
(d) Phenol and benzaldehyde in the presence of
(c) I2 and NaOH solution
palladium
(d) Sn and NaOH solution
YouTube Channel Arvind Academy link http://bit.ly/2lYvJGF Page 1
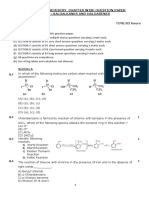
9. Which of the following compounds will give 16. Assertion: The final product in Aldol condensation
butanone on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 is always , -unsaturated carbonyl compound.
solution? Reason: , -unsaturated carbonyl compounds
(a) Butan-1-ol (b) Butan-2-ol
are stabilized due to conjugation.
(c) Both of these (d) None of these
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true
10. In Clemmensen reduction, carbonyl compound is
and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of
treated with ________.
the Assertion (A)
(a) Zinc amalgam + HCl
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true,
(b) Sodium amalgam + HCl
but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation
(c) Zinc amalgam + nitric acid
of the Assertion (A)
(d) Sodium amalgam + HNO3
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is False.
11. Iodoform test is not given by [2020]
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
(a) ethanol (b) ethanal
17. Assertion (A): Reactivity of ketones is more than
(c) pentan-2-one (d) pentan-3-one
aldehydes.
Reason (R): The carbonyl carbon of ketones is less
12. What is the correct IUPAC name of the given
electrophilic as compared to aldehydes.
compound? [2020]
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
statements, and Reason (R) is the correct
explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
(a) 2, 2-Dimethylbutanoic acid statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct
(b) 2-Carboxyl – 2 – methylbutane explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) 2-Ethyl-2-methylpropanoic acid (c) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is
(d) 3-Methylbutanecarboxylic acid incorrect statement.
13. Which one of the following has lowest pKa value? (d) Assertion (A) is incorrect, but Reason (R) is
[2023] correct statement. [2020]
(a) CH3 COOH 18. Assertion (A) : Oxidation of ketones is easier than
(b) O2 N CH 2 COOH aldehydes.
Reason (R): C-C bond of ketones is stronger than
(c) Cl CH 2 COOH
C-H bond of aldehydes.
(d) HCOOH (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
statements, and Reason (R) is the correct
explanation of the Assertion (A).
14. The oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by (b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
chromyl chloride is called statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct
(a) Etard reaction explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Riemer-Tiemann reaction (c) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is
(c) Stephen's reaction wrong statement.
(d) Cannizzaro's reaction. (d) Assertion (A) is wrong, but Reason (R) is
15. Which of the following tests/ reactions is given by correct statement. [2020]
aldehydes as well as ketones? [2022 – 23] 19. Assertion: Benzoic acid does not give Friedel-Crafts
(a) Fehling's test (b) Tollens' test reaction.
(c) 2,4-DNPtest (d) Cannizzaro reaction Reason: The carboxyl group is deactivating and
gets bonded to Lewis acid AICI3.
Assertion-Reasoning (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
statements, and Reason (R) is the correct
explanation of the Assertion (A).
YouTube Channel Arvind Academy link http://bit.ly/2lYvJGF Page 22
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct
explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is
incorrect statement.
(d) Assertion (A) is incorrect, but Reason (R) is
correct statement. [2021 C]
20. Assertion (A) ; Benzoic acid does not undergo
Friedal-Crafts reaction.
Reason (R) : The carboxyl group is activating and
undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
statements, and Reason (R) is the correct
explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct
explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is
incorrect statement.
(d) Assertion (A) is incorrect, but Reason (R) is
correct statement. [2020]
21. Assertion : Carboxylic acids are more acidic than
phenols.
Reason: Phenols are ortho and pora-directing.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct
statements and reason is correct explanation for
assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct
statements but reason is not correct explanation
for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is
wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is
correct statement. [2020 – 21]
Case study Questions
23. Read the text carefully and answer the
22. Read the text carefully and answer the questions: questions: When an aldehyde with noα - hydrogen
(A), (B) and (C) are three non - cyclic functional reacts with concentrated aqueous NaOH, half the
isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular aldehyde is converted to carboxylic acid salt and other
formula C4H8O. Isomers (A) and (C) give positive half is converted to an alcohol. In other words, half of
Tollens test whereas isomer (B) does not give the reactant is oxidized and other half is reduced. This
Tollen’s test but gives positive iodoform test. reaction is known as Cannizzaro reaction.
Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc.
HCl give the same product (D).
YouTube Channel Arvind Academy link http://bit.ly/2lYvJGF Page 33
Questions
24. Write the reaction involved in the following: Stephen reduction.
25. How do you convert the following:
Toluene to benzoic acid?
26. Do the following conversion in not more than two steps:
Ethyl benzene to benzoic acid
27. Write the equations involved in the following reactions: [Delhi 2017]
(i) Clemmensen reduction
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
28. (a) Write the product in the following reaction:
(b) Give simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Butanal and Butan – 2 – one. [2/5, Al 2017]
29. An organic compound ‘A’ having the molecular formula C3H8O on treatment with Cu at 573K, gives ‘B’. ‘B’ does
not reduce Fehling’s solution but gives a yellow precipitate of the compound ‘C’ with l2/NaOH. Deduce the
structures of A, B and C.
30. (i) Distinguish with a suitable chemical test:
(1) CH3COCH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2CHO
(2) Ethanal and Ethanoic acid
(ii) Write the structure of oxime of acetone.
(iii) Identify A to D.
YouTube Channel Arvind Academy link http://bit.ly/2lYvJGF Page 44
31. Draw the structures of the following:
(i) 𝑝 − 𝑀𝑒𝑡ℎ𝑦𝑙𝑏𝑒𝑛𝑧𝑎𝑙𝑑𝑒ℎ𝑦𝑑𝑒
(ii) 4 − 𝑀𝑒𝑡ℎ𝑦𝑙𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑡 − 3 − 𝑒𝑛 − 2 − 𝑜𝑛𝑒
32. Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻𝑂, 𝐶6 𝐻5 𝐶𝑂𝐶𝐻3 , 𝐻𝐶𝐻𝑂
33. Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products.
34. Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compound :
(i) Propanal and Propanone
(ii) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(iii) Phenol and Benzonic acid
35. How would you bring about the following conversions? Write the complete equation in each case.
(i) Ethanal to 3-hydroxybutanal
(ii) Benzoic acid to m – nitrobenzyl alcohol
(iii) Benzaldehyde to benzophenone
36. Arrange the following in order of property indicated for each set.
(i) 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻𝑂, 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐻3 𝑂𝐶𝐻3 , 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻3(increasing order of boiling points)
(ii) (𝐶𝐻3 )2 𝐶𝐻𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻(𝐵𝑟)𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻(𝐵𝑟)𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻(increasing order of their acid strengths )
(iii) ethanol, propanal, propanone, butanone (increasing order of reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions)
37. A and B are two functional isomers of compound 𝐶3 𝐻6 𝑂. On heating with Na OH and 𝐼2 , isomer A forms yellow
precipitate of iodoform whwereas isomer B does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.
38. An alkene ‘A’ molecular formula (𝐶5 𝐻10 ) on ozonolysis give a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound
‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also reacts with iodine and 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 solution. Compound ‘C’ does not give
Fehling’s test but forms iodoforms. Identify the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ giving suitable explanation and write
the reactions of ozonolysis and iodoform formation from either ‘B’ or ‘C’.
39. Write down functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula 𝐶3 𝐻6 𝑂. Which isomer will react
faster with HCN and why? Explain the mechanism of the reaction also. Will the reaction lead to the completion
YouTube Channel Arvind Academy link http://bit.ly/2lYvJGF Page 55
with the conversion of whole reactant into product at reaction conditions? If a strong acid is added to the
reaction mixture what will be the effect on concentration of the product and why?
40. An organic compound with the molecular formula 𝐶9 𝐻10 𝑂 forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollens’ reagent
and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2- benzenedicarboxylic acid , Identify the
compound.
41. Arrange the following in the decreasing order of their acidic character.
(i) HCOOH, 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐼𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐹3 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐶𝐼3 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻
(ii) 𝐶6 𝐻5 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐹𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝑁𝑂2 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻
(iii) 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐼𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐹𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐶6 𝐻5 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻
42. How would you account for the following:
(i) Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophiles.
(ii) The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than of the correspoinding acids.
(iii) The aldehydes and ketones undergo a number of addition reactions.
43. An organic compound ‘X’ having molecular formula 𝐶4 𝐻8 𝑂 gives orange-red ppt. with 2, 4-DNP reagent. It does
not reduce Tollens’ reagent but gives yellow ppt. of iodoform on heating with 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐼. Compound X on reduction
with 𝐿𝑖𝐴𝐼𝐻4 gives compound ‘Y’ which undergoes dehydration reaction on heating with conc. 𝐻2 𝑆𝑂4 to form but
-2-ene. Identfy the compounds X and Y.
44. Illustrate the following reactions giving a suitable example for each:
(i) Cross aldol condensation (ii)Decarboxylation
45. What is meant by the following terms? Give an example in each case.
(i) Cyanohydrin (ii) Semicarbazone (iii)Hemiacetal
(iv)Ketal (v) 2, 4-DNP derivative.
46. An organic compound ‘A’ with molecular formula 𝐶8 𝐻8 𝑂 gives positive DNP and iodoform test. It does not
reduce Tollens’ or Fehling’s reagent and does not decolourise bromine water also. On oxidation with chromic
acid (𝐻2 𝐶𝑟𝑂4 ), it gives a carboxylic acid (B) with molecular formula 𝐶7 𝐻6 𝑂2 . Deduce the structures of A and B.
47. Predict the products of the following reactions:
48. Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products.
YouTube Channel Arvind Academy link http://bit.ly/2lYvJGF Page 66
49. (a) Account for the following:
(i) 𝐶𝐼 − 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻 is a stronger acid than 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of carbonyl group.
(b) Out of 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝑂 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻3 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝑂 − 𝐶𝐻3 , which gives iodoform test?
50. How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
(i) Propanone to Propene
(ii) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
(iii) Ethanol to 3-Hydrozybutanal
(iv) Benzene to m-Nitracetophenone
(v) Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone
51. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
(i) 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻(𝐵𝑟)𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻 (𝐵𝑟)𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, (𝐶𝐻3 )2 𝐶𝐻𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻, 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻 (acid strength)
(ii) Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrobenzonic acid, 3, 4 – Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4- Methoxybenzoic and (acid strength)
52. Account for the following :
(a) Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel- Crafts reaction.
(b) 𝑝𝐾𝑎 value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid.
53. Give chemical tests to distinguish between:
(i) Acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde (ii) Propanone and propanol.
54. (a) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Ethanal is more reactive than acetone towards nucleophilic addition reaction.
(ii) (𝐶𝐻3 )3 𝐶 − 𝐶𝐻𝑂 does not undergo aldol condensation.
(iii) Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than alcohols.
b) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between:
(i) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(ii) Benzaldehyde and Ethanal
55. Predict the products of following reactions
(𝑖)𝐾𝑀𝑛𝑂4 /𝐾𝑂𝐻
(i) 𝐶6 𝐻5 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻3 →
(𝑖)𝑁𝐻3 /∆
(ii) 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻 → ?
For Solutions
Download Arvind Academy App
Click Link: http://bit.ly/2kTWbkj
YouTube Channel Arvind Academy link http://bit.ly/2lYvJGF Page 77
You might also like
- Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument3 pagesAldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acidsonidhruv2206No ratings yet
- 12 AldehydesDocument2 pages12 Aldehydesmystical moonbeamNo ratings yet
- Self Evaluation 1Document3 pagesSelf Evaluation 1Dark HackerNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper Chemistry CBSE Class XII 2023 III-IDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper Chemistry CBSE Class XII 2023 III-IAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 5 12thDocument13 pagesSample Paper 5 12thShreya DubeyNo ratings yet
- Chem NoidaDocument11 pagesChem Noidadithya.a5238No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryrjakrithiNo ratings yet
- 2 12th Chemistry CBSE SET 2Document10 pages2 12th Chemistry CBSE SET 2dsrvdsrv8No ratings yet
- Chemistry HYDocument8 pagesChemistry HYHarini DasNo ratings yet
- Question Chap 9 AminesDocument8 pagesQuestion Chap 9 AminesakshayorbgkapapaNo ratings yet
- Excercise SubjectiveDocument12 pagesExcercise SubjectiveVinod AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Model Paper-3Document2 pagesModel Paper-3mkrishna collegeNo ratings yet
- Assertion Reason Aldehydes KetonesDocument3 pagesAssertion Reason Aldehydes KetonessuryaisonemailNo ratings yet
- SET 2 Question PaperDocument8 pagesSET 2 Question PaperKrityapriya BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Chemset 1 HalfyrlyqpDocument7 pagesChemset 1 HalfyrlyqpDHANWANTH VADIVEL 11348No ratings yet
- XII QP Chemistry2022-2023Document8 pagesXII QP Chemistry2022-2023Akash Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- MCQ Based Paper (Isc Pattern) : Mark: 70 Time 90 MinDocument4 pagesMCQ Based Paper (Isc Pattern) : Mark: 70 Time 90 MinDisha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper Chemistry CBSE Class XII 2023 IDocument6 pagesModel Test Paper Chemistry CBSE Class XII 2023 IAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 28, 2023Document11 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 28, 2023Vikram NeelmegamNo ratings yet
- MCQ Chemistry Practice Qwestions Class 12thDocument8 pagesMCQ Chemistry Practice Qwestions Class 12thMithun ChakladarNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Chemistry Feb 24 Shift 2Document16 pagesJEE Main 2021 Question Paper Chemistry Feb 24 Shift 2B Srinivas.No ratings yet
- XN3lz Std12ChemistryCBSEModel TestQP FinalDocument8 pagesXN3lz Std12ChemistryCBSEModel TestQP FinalPRAKASH .ENo ratings yet
- YCT Amines NEET JEE Questions PracticeDocument60 pagesYCT Amines NEET JEE Questions Practiceitsrudra39No ratings yet
- Jee Main 28with Answer 29 26 Feb 2C 2021 Shift 2Document43 pagesJee Main 28with Answer 29 26 Feb 2C 2021 Shift 2CREATIVE XNo ratings yet
- Chem 12 Term 1Document5 pagesChem 12 Term 1shikhajha9b33No ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 01Document15 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 01milanraj9148No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-31-OctDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-31-Octolivia.benson9331No ratings yet
- Class Xii Chemistry Mcqs and Assertion Reason Questions Feb 24Document43 pagesClass Xii Chemistry Mcqs and Assertion Reason Questions Feb 24Soumya PNo ratings yet
- NEET Chemistry Solved Paper 2022Document7 pagesNEET Chemistry Solved Paper 2022Lol BoiNo ratings yet
- Cblechpl 01Document10 pagesCblechpl 01A4 Broker YTNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 14 Apr Sample Paper 2023 24Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry 14 Apr Sample Paper 2023 24aknishad71385No ratings yet
- MS PB-1 Set A Chem Grade 12 Question Paper - 2022-23Document21 pagesMS PB-1 Set A Chem Grade 12 Question Paper - 2022-23Heroicis FolkNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Full Mock Test 8Document10 pagesJEE Main Full Mock Test 8Aditya SinghNo ratings yet
- SQP1Document10 pagesSQP1The. Daksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Wa0022.Document4 pagesWa0022.michaeldcosta414No ratings yet
- XLLB, Practice Paper - 2Document7 pagesXLLB, Practice Paper - 2rajatNo ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes Sample PaperDocument6 pagesHalo Alkanes Sample PapervasuNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry QPDocument6 pagesXII Chemistry QPSaraswati maharanaNo ratings yet
- ISC 2023 Chemistry Question PaperDocument8 pagesISC 2023 Chemistry Question PaperT rud0No ratings yet
- Chemistry SQP 1Document8 pagesChemistry SQP 1Purnima PandaNo ratings yet
- 6 - QP and MS - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument9 pages6 - QP and MS - Haloalkanes and Haloareneskrish dabhi0% (1)
- Adobe Scan Nov 01, 2023Document5 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 01, 2023dashabhijit761No ratings yet
- Xii PB 2023 Chem QP 16112023Document6 pagesXii PB 2023 Chem QP 16112023Hitesh PerniNo ratings yet
- Class XII - 1259081Document8 pagesClass XII - 1259081Abhinandan VermaNo ratings yet
- CHEM Pre Board-2 BBSR RegionDocument8 pagesCHEM Pre Board-2 BBSR RegionLalitranjan karNo ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry U2 P1 2010Document10 pagesCape Chemistry U2 P1 2010C.No ratings yet
- Holiday Home Work Mid Term 12Document5 pagesHoliday Home Work Mid Term 12Gopala krishnanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry23 24 sp01Document14 pages12 Chemistry23 24 sp01bhattkrrish339No ratings yet
- Question Chap 6 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument9 pagesQuestion Chap 6 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesakshayorbgkapapaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Question Paper Class 12Document7 pagesChemistry Practice Question Paper Class 12tony starkNo ratings yet
- Chemistry XII Pre Board II Paper (2023-2024)Document10 pagesChemistry XII Pre Board II Paper (2023-2024)leothiveshNo ratings yet
- Organic 2Document12 pagesOrganic 2jitesh100kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Pyq Haloalkane and HaloarenesDocument6 pagesPyq Haloalkane and Haloareneskartikdhiman79mznNo ratings yet
- PB 1 Xii Chem Q P 2023 24Document9 pagesPB 1 Xii Chem Q P 2023 24calebanimals123No ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample PaperDocument145 pagesChemistry Sample Paperseemantalukdar4No ratings yet
- Taiyari Board Exam Ke03xii ArrangedDocument3 pagesTaiyari Board Exam Ke03xii ArrangedSHIVANSH SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Bottom of Pyramid - Test # 15 - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesBottom of Pyramid - Test # 15 - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Mumbai ChemDocument8 pagesMumbai ChemvasuNo ratings yet
- Qu - Paper 05Document7 pagesQu - Paper 05Jayshree SinghNo ratings yet
- Gracie Warhurst WarhurstDocument1 pageGracie Warhurst Warhurstapi-439916871No ratings yet
- Vemu Institute of Technology: Department of Computer Science & EngineeringDocument79 pagesVemu Institute of Technology: Department of Computer Science & EngineeringSiva SankarNo ratings yet
- Alternative Network Letter Vol 7 No.1-Apr 1991-EQUATIONSDocument16 pagesAlternative Network Letter Vol 7 No.1-Apr 1991-EQUATIONSEquitable Tourism Options (EQUATIONS)No ratings yet
- User Manual PM3250Document80 pagesUser Manual PM3250otavioalcaldeNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modelling and Design of Electrical DevicesDocument69 pagesNumerical Modelling and Design of Electrical Devicesfabrice mellantNo ratings yet
- Formula:: High Low Method (High - Low) Break-Even PointDocument24 pagesFormula:: High Low Method (High - Low) Break-Even PointRedgie Mark UrsalNo ratings yet
- Эквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Document7 pagesЭквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Алексей ЯмаNo ratings yet
- Research 093502Document8 pagesResearch 093502Chrlszjhon Sales SuguitanNo ratings yet
- 10 Killer Tips For Transcribing Jazz Solos - Jazz AdviceDocument21 pages10 Killer Tips For Transcribing Jazz Solos - Jazz Advicecdmb100% (2)
- Mosharaf HossainDocument2 pagesMosharaf HossainRuhul RajNo ratings yet
- Back Propagation Neural NetworkDocument10 pagesBack Propagation Neural NetworkAhmad Bisyrul HafiNo ratings yet
- BS 7974 2019Document68 pagesBS 7974 2019bcyt00No ratings yet
- Instructions For Preparing Manuscript For Ulunnuha (2019 Template Version) Title (English and Arabic Version)Document4 pagesInstructions For Preparing Manuscript For Ulunnuha (2019 Template Version) Title (English and Arabic Version)Lailatur RahmiNo ratings yet
- Power Curbers, Inc. v. E. D. Etnyre & Co. and A. E. Finley & Associates, Inc., 298 F.2d 484, 4th Cir. (1962)Document18 pagesPower Curbers, Inc. v. E. D. Etnyre & Co. and A. E. Finley & Associates, Inc., 298 F.2d 484, 4th Cir. (1962)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Bacacay South Hris1Document7,327 pagesBacacay South Hris1Lito ObstaculoNo ratings yet
- Agency Canvas Ing PresentationDocument27 pagesAgency Canvas Ing Presentationkhushi jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Math Review CompilationDocument9 pagesMath Review CompilationJessa Laika CastardoNo ratings yet
- Ring and Johnson CounterDocument5 pagesRing and Johnson CounterkrsekarNo ratings yet
- Decision Trees For Management of An Avulsed Permanent ToothDocument2 pagesDecision Trees For Management of An Avulsed Permanent ToothAbhi ThakkarNo ratings yet
- MSC-MEPC.2-Circ.17 - 2019 Guidelines For The Carriage of Blends OfBiofuels and Marpol Annex I Cargoes (Secretariat)Document4 pagesMSC-MEPC.2-Circ.17 - 2019 Guidelines For The Carriage of Blends OfBiofuels and Marpol Annex I Cargoes (Secretariat)DeepakNo ratings yet
- Recruitment SelectionDocument11 pagesRecruitment SelectionMOHAMMED KHAYYUMNo ratings yet
- Product Manual 26086 (Revision E) : EGCP-2 Engine Generator Control PackageDocument152 pagesProduct Manual 26086 (Revision E) : EGCP-2 Engine Generator Control PackageErick KurodaNo ratings yet
- SecuritizationDocument46 pagesSecuritizationHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- RMC 102-2017 HighlightsDocument3 pagesRMC 102-2017 HighlightsmmeeeowwNo ratings yet
- NABARD R&D Seminar FormatDocument7 pagesNABARD R&D Seminar FormatAnupam G. RatheeNo ratings yet
- CORP2165D Lecture 04Document26 pagesCORP2165D Lecture 04kinzi chesterNo ratings yet
- Resume 1Document2 pagesResume 1Aidie HerreraNo ratings yet
- Manual For Tacho Universal Edition 2006: Legal DisclaimerDocument9 pagesManual For Tacho Universal Edition 2006: Legal DisclaimerboirxNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study For Cowboy Cricket Farms Final Report: Prepared For Prospera Business Network Bozeman, MTDocument42 pagesFeasibility Study For Cowboy Cricket Farms Final Report: Prepared For Prospera Business Network Bozeman, MTMyself IreneNo ratings yet
- Dominion Wargame RulesDocument301 pagesDominion Wargame Rules4544juutf100% (4)