Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DA Calculus 2 May 2018
Uploaded by
Tran Tuan SangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DA Calculus 2 May 2018
Uploaded by
Tran Tuan SangCopyright:
Available Formats
SOLUTION TO FINAL EXAM
CALCULUS 2, May 31th 2018
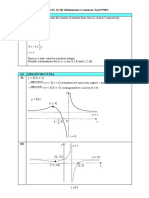
1. (2 points)
a. There are several options for this question. One of those is:
0 6
Area= ( x + 6 − x 2 )dy + (6 − x
2
)dx (0.5)
−2 0
22
= +4 6 (0.5)
3
2
b. Area= 2 x ln x dx (0.5)
1
3
= 2 2ln 2 − (0.5)
4
2. (3 points)
a. Let u = ln x, dv = x 2 dx. (0.25)
3 3 3
x ln x 1 2 x ln x x
x ln x dx = − x dx = − +C
2
(0.75)
3 3 3 9
1 −1
b. (2 + 3x) 3
dx =
6(2 + 3x) 2
(0.5)
1 −1 1 1
(2 + 3x)
0
3
dx = lim
N → 6(2 + 3 N )
2
+ =
12 12
(0.5)
c. I ( x) = e
−1dx
= e− x (0.25)
−x (
e− x xdx + C ) = − x ( − xe− x − e− x + C )
1 1
y ( x) = (0.5)
e e
y(0)=2 implies that C=3. (0.25)
3. (4 points)
(−1)k 22 k +1 −4
k
a. = 2 (0.5)
k =2 3k k =2 3
Số hiệu: BM1/QT-PĐBCL-RĐTV Pages: 2
4
This is a geometric series with r = 1 . Therefore, the series converges and has no
3
sum. (0.5)
23 k + 3 23 k 8
b. Since lim : = 1, (0.5)
k → 5k +1 ( k + 1) 2 5k k 2 5
the given series diverges by Ratio test. (0.5)
c. Use generalized ratio test
ak +1 1
L = lim = | x − 2| (0.25)
k →
ak 3
1
The series converges when | x − 2 | 1 which implies −1 x 5 . (0.25)
3
1
When x = 5 , the series becomes k
k =1
2
, which coverges by p-series Test. (0.25)
(−1) k
When x = −1, the series becomes 2 , which coverges by Alternating series
k =1 k
Test. (0.25)
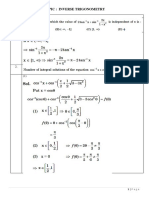
The interval of convergence is −1;5 .
x2
d. f ( x) = = (−3 x) k x 2 = (−3) k x k + 2 (0.5)
1 − (−3 x) k =0 k =0
k+2=102 when k=100. So the coefficient of x102 in this series is (−3)100 . (0.5)
4. (1 point)
( PQ QR ) u = −10, −11,2 1,2, m = 2m − 32 (0.5)
( PQ QR ) u = 0 m = 16 (0.5)
Số hiệu: BM1/QT-PĐBCL-RĐTV Pages: 2
You might also like
- 2021 NYJC JC1 H2MATH (Modified) Common Test SolutionsDocument9 pages2021 NYJC JC1 H2MATH (Modified) Common Test SolutionsGareth WongNo ratings yet
- Comp2024 Btest-11 MathematicsDocument16 pagesComp2024 Btest-11 MathematicsTtttNo ratings yet
- Area calculation and limits evaluationDocument15 pagesArea calculation and limits evaluationWAN SYARAFANA WAN JAFRINo ratings yet
- MAT Paper 2015 SolutionsDocument9 pagesMAT Paper 2015 SolutionsXu SarahNo ratings yet
- Foerign MathematicsDocument37 pagesFoerign MathematicsDivya VatsaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Cl12 Ead Mathematics Solutions To Sample Paper 5Document9 pagesCbse Cl12 Ead Mathematics Solutions To Sample Paper 5sarthakbhardwaj075No ratings yet
- DU KA Special Model Test-02-UniqueSet-0-QuestionEnglish U-02Document7 pagesDU KA Special Model Test-02-UniqueSet-0-QuestionEnglish U-02SakibNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) Solutionsrsarthak227No ratings yet
- MN - T8 - F1A118001 - Muh Asrul Rajab AsriDocument5 pagesMN - T8 - F1A118001 - Muh Asrul Rajab AsriMuh Asrul Rajab AsriNo ratings yet
- GATE Electrical 2015 01 February 07 Forenoon Session Converted 2 1Document75 pagesGATE Electrical 2015 01 February 07 Forenoon Session Converted 2 1Abhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- Tailieuxanh Dap An Calculus 1 Final Test hk2 2019 2020 7797Document5 pagesTailieuxanh Dap An Calculus 1 Final Test hk2 2019 2020 7797Tâm Phạm ThànhNo ratings yet
- NYJC 2017 EOY Exam Paper Solutions 2Document12 pagesNYJC 2017 EOY Exam Paper Solutions 2Low Jia YingNo ratings yet
- GATE Civil 2021 February 10 230PM Converted 1 1Document42 pagesGATE Civil 2021 February 10 230PM Converted 1 1anurag mauryaNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS Previous GateDocument25 pagesMATHEMATICS Previous GateSAGI RATHNA PRASAD me14d210No ratings yet
- April 2023 Math BaremeDocument4 pagesApril 2023 Math BaremeZeinab HijaziNo ratings yet
- Mathematics N4 Test 1Document4 pagesMathematics N4 Test 1MpezaNo ratings yet
- Chap 15 MathDocument13 pagesChap 15 MathKonrad WarrenNo ratings yet
- Other Types of EqtnsDocument2 pagesOther Types of Eqtnssage bristoNo ratings yet
- DP - 11 - FA - 1 - T4 - P1 Differential Calculus MSDocument6 pagesDP - 11 - FA - 1 - T4 - P1 Differential Calculus MSMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class12 Maths Question Paper Solution 2017 Set 1Document13 pagesCBSE Class12 Maths Question Paper Solution 2017 Set 1sumitsagar2405No ratings yet
- IITJEE Sample Paper 1Document41 pagesIITJEE Sample Paper 1api-19811512No ratings yet
- TD Extra 2Document1 pageTD Extra 2cbrt53935No ratings yet
- Sigma Notation in 40 CharactersDocument20 pagesSigma Notation in 40 CharactersAzeNo ratings yet
- Sample 2Document12 pagesSample 2exhasbeenslainNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Sample Final QuestionsDocument28 pagesSolutions To Sample Final QuestionscfisicasterNo ratings yet
- Mockb1 p2 AnsDocument8 pagesMockb1 p2 Ans。No ratings yet
- Cal1 TD2 (2023 24)Document2 pagesCal1 TD2 (2023 24)Da VyNo ratings yet
- 2020 Mock Extra 6 Paper 2 Sol EngDocument7 pages2020 Mock Extra 6 Paper 2 Sol EngRonnie ChanNo ratings yet
- X Maths 2023 Sample Paper SolutionsDocument10 pagesX Maths 2023 Sample Paper SolutionsKanchan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 1Document12 pagesChapitre 1boumiasarah4No ratings yet
- Indefinite Integration One Shot - Practice Sheet - JEE Challengers 2023Document7 pagesIndefinite Integration One Shot - Practice Sheet - JEE Challengers 2023ttojo7105No ratings yet
- Math Mains Practice 02Document14 pagesMath Mains Practice 02Share n CashNo ratings yet
- Inverse TrigonometryDocument7 pagesInverse TrigonometryAbhiNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Max Marks 80Document4 pagesClass Xii Max Marks 80kuser6398No ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Thursday, August 26, 2021Document16 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Thursday, August 26, 2021Karishtain NewtonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 3Document40 pagesLecture Note 3Frendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Maths Monthaly Test 2 KV BalliaDocument2 pagesClass Xii Maths Monthaly Test 2 KV Balliasumitsagar2405No ratings yet
- LQ-6A Reviewer FinalDocument3 pagesLQ-6A Reviewer FinalRialyn Mae PaligutanNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Review Sol PDFDocument13 pagesExam 2 Review Sol PDFkanurNo ratings yet
- Master Sheet Limitof Functionby OMSirDocument12 pagesMaster Sheet Limitof Functionby OMSirAditya KapooorNo ratings yet
- s6 Mathematics Internal Mock ExamDocument4 pagess6 Mathematics Internal Mock ExamMugasira CalvinNo ratings yet
- University of Science and Technology Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesUniversity of Science and Technology Exam Questions01 RerollNo ratings yet
- Find the value of P(-1) given remainders when dividing P(xDocument1 pageFind the value of P(-1) given remainders when dividing P(xReevu ThapaNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise SolutionDocument34 pagesRevision Exercise SolutionGabriel FungNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2006 Mathematics Soutions: Time: 2 HoursDocument14 pagesIIT JEE 2006 Mathematics Soutions: Time: 2 HoursSohan PrajapafNo ratings yet
- Last Years de-AUC-DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION & AREA UNDER CURVEDocument21 pagesLast Years de-AUC-DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION & AREA UNDER CURVERaju SinghNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM Set 1 - Ques - Final DraftDocument13 pagesFINAL EXAM Set 1 - Ques - Final DraftMuzzammil ZamriNo ratings yet
- Kvpy SB Solutions PDFDocument34 pagesKvpy SB Solutions PDFSharad SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 620-361 Operations Research Techniques and Algorithms: Assignment 3 SolutionsDocument3 pages620-361 Operations Research Techniques and Algorithms: Assignment 3 SolutionswhhaoNo ratings yet
- Functions and LimitsDocument2 pagesFunctions and LimitsArchie CalimNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Question Paper Solution 2019Document14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Maths Question Paper Solution 2019Ankush BNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Question Paper 2020 Set 1 SolutionDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Maths Question Paper 2020 Set 1 SolutionAbhishek thakurNo ratings yet
- 2006 Mathematics Extension 1 HSC Examination Terry Lee's SolutionDocument4 pages2006 Mathematics Extension 1 HSC Examination Terry Lee's SolutionYe ZhangNo ratings yet
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C3 Paper IDocument3 pages© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C3 Paper I유리No ratings yet
- Jawapan MT Kertas 2 Pahang 2008Document12 pagesJawapan MT Kertas 2 Pahang 2008Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (1)
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1DavidMonteroDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Bothra MecDocument12 pagesBothra MecAnirudha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- I. Absolute Value Functions: Math 150 - Topic 2 Piecewise-Defined FunctionsDocument6 pagesI. Absolute Value Functions: Math 150 - Topic 2 Piecewise-Defined Functionsrohitrgt4uNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Nilesh Vijay SabnisNo ratings yet
- Solving First Order Ordinary Differential Equations Using Least Square Method A Comparative StudyDocument8 pagesSolving First Order Ordinary Differential Equations Using Least Square Method A Comparative StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- FmseDocument5 pagesFmseJacky Boy Endencio AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Projection of PointsDocument36 pagesProjection of PointsUjjWal MahAjanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Module 4 - Bridging Program For Grade 11 EntrantsDocument39 pagesMathematics Module 4 - Bridging Program For Grade 11 EntrantsAnonymous 6gthRenNo ratings yet
- A Unified Approach For Motion and Force Control of Robot Manipulators - The Operational Space Formulation, Oussama KhatibDocument11 pagesA Unified Approach For Motion and Force Control of Robot Manipulators - The Operational Space Formulation, Oussama KhatibtejswrpNo ratings yet
- A1cc EocDocument32 pagesA1cc Eock10924No ratings yet
- PPLATO - Basic Mathematics - Gradients and Directional DerivativesDocument4 pagesPPLATO - Basic Mathematics - Gradients and Directional Derivativesbitconcepts9781No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Specimen NAB AssessmentDocument6 pagesMathematics: Specimen NAB AssessmentJimmyNo ratings yet
- Model Paper 7 emDocument3 pagesModel Paper 7 emReddy GmdNo ratings yet
- Perturbation Methods in Fluid - Mechanics - MiltonVanDykeDocument143 pagesPerturbation Methods in Fluid - Mechanics - MiltonVanDyke700120No ratings yet
- Elements of Linear System TheoryDocument21 pagesElements of Linear System TheorySed Mad TavalNo ratings yet
- Maths (HCF LCM)Document16 pagesMaths (HCF LCM)Saikat Chakraborty100% (1)
- 12 Math CH-5 Exercise 5.1Document50 pages12 Math CH-5 Exercise 5.1jiajia26No ratings yet
- End Sem - Ma 1004 - 2022Document10 pagesEnd Sem - Ma 1004 - 2022AnuragNo ratings yet
- JIM 411 Assignment 1 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesJIM 411 Assignment 1 2019 PDFMohanarajan Mohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Report Group 2 CC06Document11 pagesLinear Algebra Report Group 2 CC06long tranNo ratings yet
- (Maa 3.5) Sin, Cos, Tan On The Unit Circle - Identities - SolutionsDocument6 pages(Maa 3.5) Sin, Cos, Tan On The Unit Circle - Identities - Solutionsrogchen666No ratings yet
- MAST20032 Vector Calculus: Advanced: School of Mathematics and Statistics The University of MelbourneDocument166 pagesMAST20032 Vector Calculus: Advanced: School of Mathematics and Statistics The University of Melbourneclarencet179No ratings yet
- Pre-Algebra - Final Exam - Solutions.practice 1Document8 pagesPre-Algebra - Final Exam - Solutions.practice 1Dream RichNo ratings yet
- New Budget of Work in Mathematics For Grade FiveDocument8 pagesNew Budget of Work in Mathematics For Grade FiveAnonymous yIlaBBQQNo ratings yet
- Revision DPP-3 (Main To Advanced) - PC - EDocument8 pagesRevision DPP-3 (Main To Advanced) - PC - EArpita ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- M1 CifDocument4 pagesM1 Cifdarsind108No ratings yet
- Appendices For Skee2073Document14 pagesAppendices For Skee2073Izlaikha AzizNo ratings yet
- A Unified Theory of Nuclear Reactions 2Document27 pagesA Unified Theory of Nuclear Reactions 2ana1novi1No ratings yet
- Unit A PDFDocument26 pagesUnit A PDFBobby Yaswanth BattulaNo ratings yet
- L01. Review of Mathematical Foundation MatricesDocument26 pagesL01. Review of Mathematical Foundation MatricesCrystal Renz TibayanNo ratings yet
- Bee11303 Engineering Mathematics I Latest Syllabus3 PDFDocument2 pagesBee11303 Engineering Mathematics I Latest Syllabus3 PDF1200736No ratings yet