Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Philo and pr2 Reviewer 1
Uploaded by
bestboyhaoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Philo and pr2 Reviewer 1
Uploaded by
bestboyhaoCopyright:
Available Formats
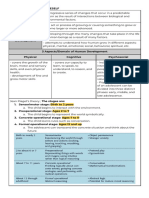
PHILOSOPHY What is Embodied Spirit?
Embodied Spirit -Is an animating core living within each of us. It
is known to be the driving force behind what we
Man- represent the entire human race.
actually think, do and say.
Human- A term used to refer for various
-It is indeed the reflections of our total being by
classifications and species. For a living man,
which our sensations lead to our human feelings,
human is under the classification of Mamalia.
emotions and decision.
Human Being - A term used to separate man
-“embodied spirit”, we normally believed and
from other Human Classifications like animals.
conclude of a spirit becoming flesh.
Person - Refers to an individual who possess
-inseparable union of human body and soul.
self-awareness, selfdetermination, rational mind,
and the capacity to interact with other and with What is Human Person as Embodied Spirit?
himself/herself.
-Self- awareness refers to person having a clear
Personhood - A general term refers to the state perception of oneself, including his or her
of being a person with unique, sacred and ethical thoughts, emotions, identity, and actions.
status within him/herself.
-A human person is able to connect and
Human Nature - A general term refers to the interact with another person, an animal or an
deepest and natural behaviour of a person that inanimate object.
distinguish human from animals
-We are not determined by others. Because we
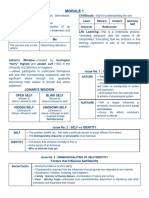
What is Human Person? have interiority; we can direct the course of our
own life.
-Is someone with an exact origin of his/her
classification. -A human person has an inherent value and
importance. This is what we call dignity.
-Is typically with a body which is tangible and
has a three components composed of SOUL, Human Transcendence
MIND and SPIRIT.
-Ability to surpass your limits. This is the
Two kinds to distinguish a human person: definition of Transcendence. You are able to
transcend your limit through your physical and
Cognitive Self (something within and cannot be
mental abilities.
physically seen) is the essential components of a
human persons that deals with THE WHAT OF A Notice Disorder in the Universe
PERSON which includes human persons’ belief,
-The domination of humanity is linked to the
desire, dreams, and intentions.
domination of nature based on the
Physical Self (something can be seen in his/her anthropocentric model. An unfair or unjust
physical appearance) which deals with the utilization of the environment result to ecological
essential features of the human way of life or crisis.
THE WHO OF A PERSON which includes his/her
-Accordingly, humanity needs to develop an
body type, strength and appearances.
"ecological conscience" based on individual
responsibility. Ecologists challenge us to adopt a
lifestyle that involves simple living that honors Aesthetic – Explore the nature and appreciation
the right of all life forms to live, flourish, and of beauty, and taste. The science of beautiful in
create a rich diversity of human and nonhuman various manifestations. Including sublime,
life. cosmic, tragic, pathetic, and ugly.
Pursuing Wisdom and Facing Challenges in PR2
the 21st Cent.
Kinds of Variables and their uses
Scientific Approach – Because the investigation
Variable – Refers to characteristics, or attribute
is systematic. It employs certain procedure.
of an individual or an organization that can be
Natural light of Reason – Philosophy measured or observed and that varies among
investigates things, neither by using on the basis people.
of supernatural revelation, otherwise it becomes
-Any entity that make on different values.
theology.
Anything that vary can be considered as variable.
Study all things – This set the distinction
Independent Variable – Variable that stands
between philosophy and other science.
alone and is not change by the variables you are
-The reason in philo is not one-sided rather it is trying to measure. Probably causes, influence, or
multidimensional or holistic. affects outcome.
First Cause of The Highest Principle: Dependent Variable – Depends on the
independent variable, it is the outcome or result
1.Identity – A thing, idea, or a person, concept,
of the influence of the independent variable. Also
character for that to exist.
called as outcome variable.
2.Non-Contradiction – It is impossible to be and
Intervening Variable – is hypothetical variable
not be at the same time, and at the same respect.
used to explain casual links between variables.
3.Excluded Middle – A thing is either is or Cannot be observed in correlational research. Ex.
either is no; everything must be either be or not Gender, age, income etc. Also known as
be. There is no middle. mediating or moderating variable.
4.Sufficient Reason – Nothing exist without a Experimental Research – Is a quantitative
sufficient reason for its being and existence. research that treats or deals with the object or
subject of the research in a definite or exact
Braches of Philosophy manner and it determines the extent of the affect
or influence of the treatment on the object or
Epistemology – Study the nature of knowledge
subject.
and rationality of beliefs.
-Involves experimentation to test impact of the
Metaphysics – Asked questions about the
independent variable to the dependent variable.
essence and existence of being.
Logic – Concerned with reasoning or truth.
Ethics/Axiology – Concerns matter of morality
and value.
Kinds of Research SAMPLING TECHNIQUE
Sampling – Is a systematic process of getting the
sample.
Qualitative Research Quantitative Research
Types of sampling:
Probability Sampling – Where a researcher sets
Experimental Research Non-experimental
a selection of a few criteria and chooses Research
members of population randomly. Everyone has
the opportunity to beResearch
Descriptive chosen/be part.
True-Experimental
Research Types of Probability Sampling:
Comparative
Simple Random Sampling Research
– everyone has equal
Quasi-Experimentalchance to be selected.
Research
-Fishbowl method Correlational Research
-Lottery method
Pre-Experimental
Match-comparative Research
Research Systematic Sampling – Every member of the
population is listed, randomly generating
Quasi-Experimental
Research
numbers, divided in regular intervals.
Time-series Research
Stratified Sampling – It allows to draw more
precise conclusions by ensuring that every
Single-subject Research subgroup is properly represented in the sample.
Cluster Sampling – Dividing the population into
subgroups, but each group should have similar
characteristics to the whole sample. Randomly
select the whole subgroup.
INPUT PROCESS OUTPUT
Non-Probability Sampling – Sampling method
Materials of Preparation ofin which not all the members
Theof the population
the study material, toolshave
and an equal chance to be phenomenon
selected/be part.
Ingredients equipment Types of Non-Probability,Sampling:
or
Equipment Processing the transformati
Evaluations formulated roolpos on
Convenience Sampling – includes the
individuals who happen to be the most
Nutrient analysis
accessible to the researches. Cannot
generalizable results.
Voluntary Response Sampling – Mainly based
on ease of access. People volunteer themselves.
Purposive Sampling – Involves the researchers
using their judgment to select a sample that is
most useful to the purpose of the research.
Snowball Sampling – Can be used to recruit
participants via participants. The number of
people you have access to “snowball” as you get
contact with more people.
You might also like
- Personality 1Document58 pagesPersonality 1nithesh kumar jNo ratings yet
- INTROPSY Reviewer (Book-Based Only) Chapters 1-2Document12 pagesINTROPSY Reviewer (Book-Based Only) Chapters 1-2RAYNE BERNADETTE BALINASNo ratings yet
- Moral Agents Developing Habit As VirtueDocument38 pagesMoral Agents Developing Habit As Virtuerex danielle100% (1)
- Theory and Applications of Ontology Philosophical PerspectivesDocument423 pagesTheory and Applications of Ontology Philosophical PerspectivesAbraham RubínNo ratings yet
- Bodhicittavivarana - Nagarjuna EnglishDocument15 pagesBodhicittavivarana - Nagarjuna EnglishTRAN NGOCNo ratings yet
- Slavoj Zizek - The Parallax View PDFDocument7 pagesSlavoj Zizek - The Parallax View PDFSally OldsNo ratings yet
- Hegel's Conception of God (1896)Document19 pagesHegel's Conception of God (1896)Bilâl ÖğütNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy in Reflexive PerspectiveDocument398 pagesHomeopathy in Reflexive Perspectivealex100% (1)
- Introduction and Psychoanalytic Theory 2Document49 pagesIntroduction and Psychoanalytic Theory 2lishel gonzalesNo ratings yet
- David HumeDocument7 pagesDavid HumePaul Kallan100% (1)
- Zupancic - Realism in PscyhoanalysisDocument16 pagesZupancic - Realism in PscyhoanalysisSchädelstätte100% (1)
- The Place of Bhartrihari in The Kashmirian Shaiva Advaita - Raffaelle TorellaDocument17 pagesThe Place of Bhartrihari in The Kashmirian Shaiva Advaita - Raffaelle TorellaraffaeletorellaNo ratings yet
- CRIM 4 - Professional Conduct and Ethical StandardsDocument27 pagesCRIM 4 - Professional Conduct and Ethical StandardsMar YanNo ratings yet
- Cousins, M. - The Ugly PDFDocument15 pagesCousins, M. - The Ugly PDFelgatomecirNo ratings yet
- (Bloomsbury Studies in Philosophy) Andina, Tiziana - Iacobelli, Natalia - The Philosophy of Art - The Question of Definition - From Hegel To Post-Dantian Theories-Bloomsbury Academic (2013)Document209 pages(Bloomsbury Studies in Philosophy) Andina, Tiziana - Iacobelli, Natalia - The Philosophy of Art - The Question of Definition - From Hegel To Post-Dantian Theories-Bloomsbury Academic (2013)Mateus Raynner AndréNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument126 pagesAristotlenda_naumNo ratings yet
- The Gaze: Thomas CumminsDocument3 pagesThe Gaze: Thomas CumminsChoubassi100% (2)
- Idealism PlatoDocument10 pagesIdealism PlatoJuvvilyynGraceMahomat100% (1)
- Phil Losophy YyDocument7 pagesPhil Losophy YyJanna MañozoNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Philo Oral Compre ReviewerDocument24 pagesPart 1 - Philo Oral Compre ReviewerJonathan RacelisNo ratings yet
- Intro To Philo ReviewerDocument4 pagesIntro To Philo ReviewerAntonia Jamila SedigoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document31 pagesLesson 7Mikee GallaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Philo: Philos and Sophia - Love of WisdomDocument11 pagesNotes On Philo: Philos and Sophia - Love of WisdomisseylimboNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Notes Lesson 6Document1 pagePhilosophy Notes Lesson 6arjemmosca08.pvgmaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy 12 ReviewerDocument5 pagesPhilosophy 12 ReviewerJazmin B. LemonerasNo ratings yet
- The Self From The Perspective of Psychology: Lesson 4Document20 pagesThe Self From The Perspective of Psychology: Lesson 4cheche datingaling100% (1)
- Self-AwarenessDocument8 pagesSelf-AwarenessClaire BalatucanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy: What Is A Human Person?Document1 pageIntroduction To Philosophy: What Is A Human Person?Jose GerogalemNo ratings yet
- Pyschological Perspective of The SelfDocument2 pagesPyschological Perspective of The SelfRonjay Allen LacsonNo ratings yet
- Philo ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhilo Reviewerۦۦ ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Social PsychologyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Social Psychologys.oville.kethyrosemeriamNo ratings yet
- Personality (Week 7) ReviewerDocument3 pagesPersonality (Week 7) ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Human Person As An Embodied SpiritDocument18 pagesLesson 3 Human Person As An Embodied SpiritGrace R. OrtegaNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHYDocument5 pagesPHILOSOPHYLadyrose SalazarNo ratings yet
- Sigmund Freud and Psychoanalytic Theory (TOP)Document7 pagesSigmund Freud and Psychoanalytic Theory (TOP)Jaynelle DiamolaNo ratings yet
- Personal Development LESSON 3Document43 pagesPersonal Development LESSON 3Holy Dain Love MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Theories of PERSONALITYDocument38 pagesTheories of PERSONALITYVo BoNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Values EducationDocument6 pagesFoundation of Values EducationDanFernandezNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURALISM. Wundt Is Best Known For Turning The Study Of: Section 1 IntroDocument6 pagesSTRUCTURALISM. Wundt Is Best Known For Turning The Study Of: Section 1 Introjohn FlanneryNo ratings yet
- Personality Written ReportDocument19 pagesPersonality Written ReportangelitoNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter ReviewerDocument17 pages1ST Quarter ReviewerAB12A4-Omaña, Hanna ShaneNo ratings yet
- Human BehaviorDocument200 pagesHuman BehaviorMarjorie Paiton BendoNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self ReviewerDocument17 pagesUnderstanding The Self ReviewerVia Beatris NOLLASNo ratings yet
- Week 4.1 - PsychologyDocument28 pagesWeek 4.1 - PsychologyBeatriz Helaena RasonableNo ratings yet
- Human PersonDocument17 pagesHuman PersonDonnabhelle BernalesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer GSELFDocument22 pagesReviewer GSELFSpace MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Perdev ReviewerDocument8 pagesPerdev ReviewerMeekaNo ratings yet
- G12 Philosophy HandoutDocument11 pagesG12 Philosophy HandoutJoyce Lynel LapitanNo ratings yet
- Wa0022.Document49 pagesWa0022.Saathak AroraNo ratings yet
- Motivation: Is Money The Real Source of Evil?Document8 pagesMotivation: Is Money The Real Source of Evil?rex danielleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EthicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Ethicsoliviadeguzman.beed.passNo ratings yet
- ETHICS-Module 1-POSTED IN MOODLEDocument4 pagesETHICS-Module 1-POSTED IN MOODLEAcer CamposNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 The Human Person As An Embodied SpiritDocument21 pagesLesson 9 The Human Person As An Embodied SpiritxioteNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document26 pagesWa0000.Signitive ENo ratings yet
- PerdevDocument8 pagesPerdevMeekaNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior PremidfinDocument47 pagesHuman Behavior PremidfinJustin Sim YadanNo ratings yet
- Psychology Unit 1: History and ApproachesDocument6 pagesPsychology Unit 1: History and ApproachesAsper AlshimiNo ratings yet
- Personal Development NotesDocument12 pagesPersonal Development NotesHaru NaechiNo ratings yet
- Self and Personality Refer To The Characteristic Ways in Which We Define Our ExistenceDocument5 pagesSelf and Personality Refer To The Characteristic Ways in Which We Define Our Existencecherryl cruzNo ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument4 pagesUts ReviewerLia Sophia ContrerasNo ratings yet
- L3.Embodied SpiritDocument19 pagesL3.Embodied SpiritJayzl Lastrella CastanedaNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument6 pagesPhilosophyJonel SorianoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Philosophy (1St QTR.)Document7 pagesReviewer - Philosophy (1St QTR.)idk idkNo ratings yet
- Metaphysics Oral ExamDocument7 pagesMetaphysics Oral ExamJohn RagaNo ratings yet
- Uts MidtermsDocument17 pagesUts MidtermsANGEL BUQUIRNo ratings yet
- 4nature of A Human PersonDocument42 pages4nature of A Human Persondaisylabasan33% (3)
- Understanding The SelfDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The SelfGio AmadorNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 EED1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesUNIT 2 EED1 Revieweralexaaluan321No ratings yet
- Dispositional TheoriesDocument7 pagesDispositional TheoriesKent100% (1)
- Ethics - Comes From The Greek Word Ethos Which Can Mean Custom, Habit, Character orDocument2 pagesEthics - Comes From The Greek Word Ethos Which Can Mean Custom, Habit, Character orNail MatodNo ratings yet
- Hantelmann SocioPoliticsexhibitionDocument13 pagesHantelmann SocioPoliticsexhibitionValeriaTellezNiemeyerNo ratings yet
- Bertrand Rusell - The Value of PhilosophyDocument4 pagesBertrand Rusell - The Value of PhilosophyJuanjo Alonso TresguerresNo ratings yet
- DON'T THINK, BUT OBSERVE - Steve de Shazer PDFDocument5 pagesDON'T THINK, BUT OBSERVE - Steve de Shazer PDFguegeNo ratings yet
- The Second Group (Ontology Epistemology Axiology)Document22 pagesThe Second Group (Ontology Epistemology Axiology)Diya FitriNo ratings yet
- Gee 4-Topic 3-Lesson1Document8 pagesGee 4-Topic 3-Lesson1Pitel O'shoppeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Philosophy and Its NatureDocument5 pagesUnit 1 - Philosophy and Its NatureKim ChiNo ratings yet
- Simple Apprehension and The ConceptDocument35 pagesSimple Apprehension and The ConceptBagi RacelisNo ratings yet
- The Self and Its BrainDocument45 pagesThe Self and Its BrainAmelia Negoi100% (1)
- 3.research InsightsDocument19 pages3.research InsightsRomana NakonechnaNo ratings yet
- Why Is Beauty Form? Plotinus' Theory of Beauty in Phenomenological PerspectiveDocument14 pagesWhy Is Beauty Form? Plotinus' Theory of Beauty in Phenomenological PerspectiveJosé SutilNo ratings yet
- On The Meaning of Value - Hilda OakeleyDocument19 pagesOn The Meaning of Value - Hilda OakeleyFabio ViniciusNo ratings yet
- Knowledge As The Unity of The Intellect and The Object of Intellection in Islamic PhilosophyDocument15 pagesKnowledge As The Unity of The Intellect and The Object of Intellection in Islamic PhilosophyAmiraNo ratings yet
- Wallace SamathaDocument14 pagesWallace SamathaMartin SeidenstickerNo ratings yet
- P Kreeft R Tacelli - Life After DeathDocument9 pagesP Kreeft R Tacelli - Life After DeathGeorge OpreaNo ratings yet
- Halpern, B. (1961) - "Myth" and "Ideology" in Modern Usage. History and TheoryDocument22 pagesHalpern, B. (1961) - "Myth" and "Ideology" in Modern Usage. History and TheoryZdravko JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Thinking Against NatureDocument10 pagesThinking Against NatureFredrik MarkgrenNo ratings yet
- What Is MetaphysicsDocument24 pagesWhat Is MetaphysicsDiane EnopiaNo ratings yet