Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drafting 9 - Dimensioning
Uploaded by
Honey Grace Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageOriginal Title
DRAFTING 9 - DIMENSIONING
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageDrafting 9 - Dimensioning
Uploaded by
Honey Grace CruzCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
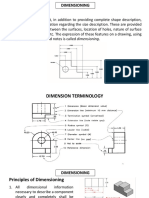
DIMENSIONING
“Dimensioning” in engineering drawings are numerical values indicated graphically in a proper
unit of measurement on engineering drawing with lines, symbols, and notes. These are
indicated on the engineering drawing to define the size characteristics such as length, height,
breadth, diameter, radius, angle, etc. Dimensioning Drawing provides complete shape
description, furnish information regarding the size and description. These are provided through
the distances between the surfaces, location of holes, nature of surface finish, type of material,
etc. You can create dimensions for existing entities by selecting them, or you can create
dimensions by selecting points within a drawing.
Five Basic Types of Dimensioning in Engineering Drawing
1. Linear
2. Angular
3. Radial
4. Diametral
5. Ordinate
Dimension Classification
1. Functional dimension (F) ñ – A dimension that is essential to the function of the part.
2. Non-functional dimension (NF) ñ- A dimension that is not essential to the function of the
part.
3. Auxiliary dimension (AUX) ñ – A dimension given for information purpose only. It is
enclosed in parenthesis and no tolerance applies to it.
Elements of Dimensioning
The elements of dimensioning include the projection line, dimension line, leader line, dimension
line origin indication, its termination, notes, the dimension, etc.
Principles of Dimensioning
1. All dimensional information necessary to describe a component clearly and completely
shall be written directly on a drawing.
2. Each feature shall be dimensioned once only on a drawing, i.e., dimension marked in
one view need not be repeated in another view.
3. Dimension should be placed on the view where the shape is best seen.
4. As far as possible, dimensions should be expressed in one unit only preferably in
millimeters, without showing the unit symbol (mm).
5. As far as possible dimensions should be placed outside the view.
6. Dimensions should be taken from visible outlines rather than from hidden lines.
7. No gap should be left between the feature and the start of the extension line.
8. Crossing of centre lines should be done by a long dash and not a short dash.
Methods of Indicating Dimensions
1. Aligned method- Dimensions should be placed parallel to and above their dimension
lines and preferably at the middle, and clear of the line. Dimensions may be written so
that they can be read from the bottom or from the right side of the drawing.
2. Uni-directional method- Dimensions should be indicated so that they can be read from
the bottom of the drawing only. Non-horizontal dimension lines are interrupted,
preferably in the middle for insertion of the dimension. Horizontal dimensional lines are
not broken to place the dimension.
You might also like
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectAbhishek Raja88% (16)
- AutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing a Floor PlanFrom EverandAutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing a Floor PlanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Technical Drawing GuidelineDocument82 pagesTechnical Drawing GuidelineAyman AlhalfawyNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3From EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- AutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing Dimensions, Elevations and SectionsFrom EverandAutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing Dimensions, Elevations and SectionsNo ratings yet
- CAD & Engineering Drawing Dimensioning GuideDocument13 pagesCAD & Engineering Drawing Dimensioning GuideLaiba Khan100% (1)
- Dimensioning principles and methodsDocument16 pagesDimensioning principles and methodsJustine joy cruzNo ratings yet
- Dimension IngDocument11 pagesDimension IngP.Punit MishraNo ratings yet
- DIMENSIONS AND PROJECTION LINESDocument5 pagesDIMENSIONS AND PROJECTION LINESSulaiman OluwapelumiNo ratings yet
- ME 104 Engineering Drawing Lec Malik Kamran ShakirDocument22 pagesME 104 Engineering Drawing Lec Malik Kamran ShakirMusaab MahmoodNo ratings yet
- TOPIC: How Drawings Are Controlled in Industry in Relevance With Various Quality Systems?Document14 pagesTOPIC: How Drawings Are Controlled in Industry in Relevance With Various Quality Systems?randapaaaNo ratings yet
- CAD & Engineering DrawingDocument51 pagesCAD & Engineering DrawingTravel & tourism100% (1)
- Chapter 03Document46 pagesChapter 03HARRIS RAZZAQNo ratings yet
- TLE-ICT (TechDraft) G10 Q1 W3-4-5 MODULE3 23pagesDocument23 pagesTLE-ICT (TechDraft) G10 Q1 W3-4-5 MODULE3 23pagesWheteng YormaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-BASIC DIMENSIONINGDocument9 pagesUnit 7-BASIC DIMENSIONINGkwangjin1980No ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Syllabus and ConceptsDocument68 pagesEngineering Graphics Syllabus and ConceptsSUSHIL SUSHILNo ratings yet
- Basics of Dimension IngDocument11 pagesBasics of Dimension IngChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document29 pagesLecture 4rishusonkar1526No ratings yet
- Drawing 3 - IsometricDocument2 pagesDrawing 3 - IsometricPirene ZunigaNo ratings yet
- Draftec1 Lo 2.6 Dimensioning A DrawingDocument13 pagesDraftec1 Lo 2.6 Dimensioning A DrawingVon AsiaNo ratings yet
- EdpDocument5 pagesEdpYuuki ChanNo ratings yet
- DimensioningDocument23 pagesDimensioningCassie RomanesNo ratings yet
- PRE-LAB # 11: Object: TheoryDocument8 pagesPRE-LAB # 11: Object: TheoryBaloch MuetNo ratings yet
- Lettering, Lines and DimensioningDocument34 pagesLettering, Lines and DimensioningHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- CPE414 DimensionDocument27 pagesCPE414 DimensionMuhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Chapter B - DimensioningDocument30 pagesChapter B - DimensioningNur Hazirah SadonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Course: An IntroductionDocument13 pagesEngineering Drawing Course: An Introductionvipsdgr8No ratings yet
- Dr. Richard E. Link U.S. Naval Academy Department of Mechanical Engineering 590 Holloway Road Annapolis, MD 21402-5042 All Rights ReservedDocument12 pagesDr. Richard E. Link U.S. Naval Academy Department of Mechanical Engineering 590 Holloway Road Annapolis, MD 21402-5042 All Rights ReservedDaveB2008No ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering Drawing: Usman AbdullahDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Drawing: Usman AbdullahAbrar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Planning Your Engineering DrawingDocument14 pagesPlanning Your Engineering Drawingapi-3707012100% (1)
- Dimensioning Principles and GuidelinesDocument38 pagesDimensioning Principles and Guidelinesemmanuel limaNo ratings yet
- DimensioningDocument44 pagesDimensioningRicky EnsanoNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning: Restricted Use OnlyDocument101 pagesDimensioning: Restricted Use OnlyWael BazziNo ratings yet
- TD DimensioningDocument9 pagesTD DimensioningPatnubay ActecNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing GuideDocument86 pagesEngineering Drawing GuideBhuma Naga PavanNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning: Architectural Visual Communication 1: Graphics 1Document18 pagesDimensioning: Architectural Visual Communication 1: Graphics 1Darryl ReyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dimensioning DrawingsDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Dimensioning DrawingsgurksyNo ratings yet
- Dimention OriginalDocument16 pagesDimention Originalkelvin CollinsNo ratings yet
- 03 EGD Dimensioning TechniquesDocument50 pages03 EGD Dimensioning TechniquesKaran KannojiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lettering and DimensioningDocument37 pagesChapter 2 Lettering and DimensioningKhôi Nguyên Lê100% (1)
- 02 - Lettering and DimensioningDocument36 pages02 - Lettering and Dimensioningakshath.rk2002No ratings yet
- 7 DimentioningDocument98 pages7 DimentioningHaadin ZamanNo ratings yet
- Layout of A Drawing SheetDocument47 pagesLayout of A Drawing SheetAkther MaryNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning: Communicating Part Specifications EffectivelyDocument19 pagesDimensioning: Communicating Part Specifications EffectivelyjfcalaywanNo ratings yet
- Eg Lab RecordDocument57 pagesEg Lab RecordbaradhanNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document12 pagesClass 3amrithakhubaNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument94 pagesDimensioning and TolerancingidontlikeebooksNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning Non-Cylindrical ObjectsDocument2 pagesDimensioning Non-Cylindrical ObjectssujanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 DimensioningDocument14 pagesUnit 3 Dimensioningdaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning Rules and TechniquesDocument36 pagesDimensioning Rules and TechniquesArif Rahman HakimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2pdfDocument44 pagesLecture 2pdfAnthony AbourahalNo ratings yet
- DRAW10W - Sections and DimensionsDocument8 pagesDRAW10W - Sections and DimensionsPaolo GochingcoNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing 8 (Quarter 2 - Week 1)Document4 pagesTechnical Drawing 8 (Quarter 2 - Week 1)cha0% (2)
- Dimensions: Page 1 of 3 Prepared by Nkya JDocument3 pagesDimensions: Page 1 of 3 Prepared by Nkya Jjoseph42No ratings yet
- 11/26/2013 Engineering Drawing & GraphicsDocument20 pages11/26/2013 Engineering Drawing & GraphicsSam ChaduaryNo ratings yet
- Building Construction & Materials-VI: AssignmentDocument20 pagesBuilding Construction & Materials-VI: AssignmentMeenuNo ratings yet
- DIMENSIONING GUIDE UNDER 40Document50 pagesDIMENSIONING GUIDE UNDER 40Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Lettering and DimensionsDocument23 pagesLettering and DimensionsMujtaba AbbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 DEMTOL1Document100 pagesChapter7 DEMTOL1Ad Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)No ratings yet
- Technical LetteringDocument11 pagesTechnical LetteringJay Benito100% (1)
- Technical Lettering - Gothic LettersDocument5 pagesTechnical Lettering - Gothic LettersHoney Grace CruzNo ratings yet
- May 20, 2022Document11 pagesMay 20, 2022Honey Grace CruzNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Mechanical Drafting Learning ModuleDocument179 pagesK To 12 Mechanical Drafting Learning ModuleHari Ng Sablay91% (43)
- Text TransitionDocument22 pagesText TransitionHoney Grace CruzNo ratings yet
- Material SymbolsDocument3 pagesMaterial SymbolsHoney Grace CruzNo ratings yet
- On The Spot Postermakingcontest MechanicsDocument1 pageOn The Spot Postermakingcontest MechanicsHoney Grace CruzNo ratings yet
- Lyrics Nursery RhymeDocument2 pagesLyrics Nursery RhymeHoney Grace CruzNo ratings yet
- Activity SheetDocument1 pageActivity SheetHoney Grace CruzNo ratings yet
- Pump Cavitation Caused by Entrained Gas: Plant Safety and EnvironmentDocument4 pagesPump Cavitation Caused by Entrained Gas: Plant Safety and Environmentdanyel87No ratings yet
- Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Column by Steel JacketingDocument5 pagesRetrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Column by Steel JacketingAhsan RafiqNo ratings yet
- A Patient's Guide To Medical Imaging - R. Eisenberg, A. Margulis (Oxford, 2011) WW PDFDocument256 pagesA Patient's Guide To Medical Imaging - R. Eisenberg, A. Margulis (Oxford, 2011) WW PDFraulNo ratings yet
- Air PermeabilityDocument3 pagesAir PermeabilityChuxuan SunNo ratings yet
- Illustrative Example: A Blending Process: An Unsteady-State Mass Balance For The Blending SystemDocument22 pagesIllustrative Example: A Blending Process: An Unsteady-State Mass Balance For The Blending SystemHermes Yesser Pantoja CarhuavilcaNo ratings yet
- Exercise NKNKKKKDocument52 pagesExercise NKNKKKKashu mishra0% (1)
- Coanda Screen Design GuidanceDocument44 pagesCoanda Screen Design GuidanceEstefania Agudelo OrregoNo ratings yet
- UAM Formulas and Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesUAM Formulas and Practice ProblemsCarlos Taroy100% (2)
- Rr311701 Microwave EngineeringDocument8 pagesRr311701 Microwave EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Compact Dual-Band Microstrip Antenna For Universal 2.4 /5.2Ghz Wlan ApplicationsDocument17 pagesCompact Dual-Band Microstrip Antenna For Universal 2.4 /5.2Ghz Wlan Applicationsmahdialii100% (1)
- New Scientist - 13 February 2016 PDFDocument60 pagesNew Scientist - 13 February 2016 PDFEugenio Manuel Fernández AguilarNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument9 pagesOsmosisNadia NovitaNo ratings yet
- F325 01jun11Document24 pagesF325 01jun11lilebtehalzNo ratings yet
- Superposition PrincipleDocument5 pagesSuperposition Principleemmanuel wambuaNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 1 Principles of MomentsDocument2 pagesPhysics Chapter 1 Principles of MomentsMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument566 pagesCalculuscustomerx100% (8)
- Das & Okubo-Lie Groups and Lie Algebras For Physicists PDFDocument358 pagesDas & Okubo-Lie Groups and Lie Algebras For Physicists PDFAlfredo Echegollen Guzmán100% (5)
- Weldox 960 Data SheetDocument2 pagesWeldox 960 Data SheetRui SantosNo ratings yet
- 2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNDocument2 pages2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- EXEC 5S ModuleDocument34 pagesEXEC 5S ModulejaymuscatNo ratings yet
- Trestle foundations-TR-9 RaftDocument15 pagesTrestle foundations-TR-9 RaftSripara KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ANSYS, Inc. Release NotesDocument170 pagesANSYS, Inc. Release NotesDiyaNegiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Application To Manometry PDFDocument15 pagesLecture 4 - Application To Manometry PDFLendo PosaraNo ratings yet
- InstrumentationDocument4 pagesInstrumentationRainneTayNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle Efficiency Increase by The Regenerative Recovery Ofhistorically Rejected Heatrev2 2167 7662 1000155Document10 pagesRankine Cycle Efficiency Increase by The Regenerative Recovery Ofhistorically Rejected Heatrev2 2167 7662 1000155Narendra singh rawatNo ratings yet
- Design and Application of FeederDocument35 pagesDesign and Application of Feederbgn10101977No ratings yet
- Smart Hospital Fault Detection and Alert SystemDocument21 pagesSmart Hospital Fault Detection and Alert SystemPravat SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Bridge Design 25mDocument2 pagesDetailed Bridge Design 25mAnu PathakNo ratings yet